径向基函数插值(2)一维数据的插值
假设我们有N组数据(xi,yi),,,,,,,,这时我们根据径向基函数我们的目的主要是找到径向基函数中的位置参数的值,
我们要用这些已知数据的值用最小二乘法得到这些参数。。
现在我们用一般的方法matlb自带的插值函数进行新值得计算:
x = 0:1.25:10;
y = sin(x);
xi = 0:.1:10;
%Matlab
yi = interp1(x,y,xi);
subplot(2,1,1); plot(x,y,'o',xi,yi, xi, sin(xi),'r'); title('Interpolation using Matlab function interp1');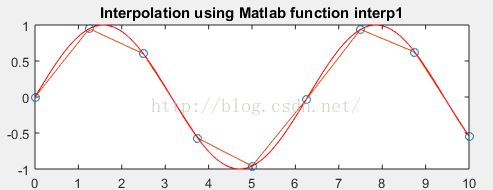
现在我们用径向基函数的方法进行插值
1、
x = 0:1.25:10;
y = sin(x);
xi = 0:.1:10; 2、设定调用函数的参数
% 1D Interpolation
%**************************************************************************
x = 0:1.25:10;
y = sin(x);
xi = 0:.1:10;
%Matlab
yi = interp1(x,y,xi);
subplot(2,1,1); plot(x,y,'o',xi,yi, xi, sin(xi),'r'); title('Interpolation using Matlab function interp1');
%%
%RBF
%op=rbfcreate(x, y,'RBFFunction', 'thinplate'); rbfcheck(op);
%op=rbfcreate(x, y,'RBFFunction', 'linear'); rbfcheck(op);
%op=rbfcreate(x, y,'RBFFunction', 'cubic'); rbfcheck(op);
%op=rbfcreate(x, y,'RBFFunction', 'gaussian'); rbfcheck(op);
op=rbfcreate(x, y,'RBFFunction', 'multiquadric', 'RBFConstant', 2); rbfcheck(op);
op=rbfcreate(x, y); rbfcheck(op);
%op=rbfcreate(x, y,'RBFFunction', 'gaussian');
%op=rbfcreate(x, y);
fi = rbfinterp(xi, op);
subplot(2,1,2); plot(x, y,'o', xi, fi,xi, sin(xi),'r'); title('RBF interpolation');
求解径向基函数的系数过程function options = rbfcreate(x, y, varargin)
%RBFCREATE Creates an RBF interpolation
% OPTIONS = RBFSET(X, Y, 'NAME1',VALUE1,'NAME2',VALUE2,...) creates an
% radial base function interpolation
%
% RBFCREATE with no input arguments displays all property names and their
% possible values.
%
%RBFCREATE PROPERTIES
%
%
% Alex Chirokov, [email protected]
% 16 Feb 2006
tic;
% Print out possible values of properties.
if (nargin == 0) & (nargout == 0)
fprintf(' x: [ dim by n matrix of coordinates for the nodes ]\n');
fprintf(' y: [ 1 by n vector of values at nodes ]\n');
fprintf(' RBFFunction: [ gaussian | thinplate | cubic | multiquadrics | {linear} ]\n');
fprintf(' RBFConstant: [ positive scalar ]\n');
fprintf(' RBFSmooth: [ positive scalar {0} ]\n');
fprintf(' Stats: [ on | {off} ]\n');
fprintf('\n');
return;
end
Names = [
'RBFFunction '
'RBFConstant '
'RBFSmooth '
'Stats '
];
[m,n] = size(Names);
names = lower(Names);
options = [];
for j = 1:m
options.(deblank(Names(j,:))) = [];
end
%**************************************************************************
%Check input arrays
%**************************************************************************
[nXDim nXCount]=size(x);
[nYDim nYCount]=size(y);
if (nXCount~=nYCount)
error(sprintf('x and y should have the same number of rows'));
end;
if (nYDim~=1)
error(sprintf('y should be n by 1 vector'));
end;
options.('x') = x;
options.('y') = y;
%**************************************************************************
%Default values
%**************************************************************************
options.('RBFFunction') = 'linear';
options.('RBFConstant') = (prod(max(x')-min(x'))/nXCount)^(1/nXDim); %approx. average distance between the nodes
options.('RBFSmooth') = 0;
options.('Stats') = 'off';
%**************************************************************************
% Argument parsing code: similar to ODESET.m
%**************************************************************************
i = 1;
% A finite state machine to parse name-value pairs.
if rem(nargin-2,2) ~= 0
error('Arguments must occur in name-value pairs.');
end
expectval = 0; % start expecting a name, not a value
while i <= nargin-2
arg = varargin{i};
if ~expectval
if ~isstr(arg)
error(sprintf('Expected argument %d to be a string property name.', i));
end
lowArg = lower(arg);
j = strmatch(lowArg,names);
if isempty(j) % if no matches
error(sprintf('Unrecognized property name ''%s''.', arg));
elseif length(j) > 1 % if more than one match
% Check for any exact matches (in case any names are subsets of others)
k = strmatch(lowArg,names,'exact');
if length(k) == 1
j = k;
else
msg = sprintf('Ambiguous property name ''%s'' ', arg);
msg = [msg '(' deblank(Names(j(1),:))];
for k = j(2:length(j))'
msg = [msg ', ' deblank(Names(k,:))];
end
msg = sprintf('%s).', msg);
error(msg);
end
end
expectval = 1; % we expect a value next
else
options.(deblank(Names(j,:))) = arg;
expectval = 0;
end
i = i + 1;
end
if expectval
error(sprintf('Expected value for property ''%s''.', arg));
end
%**************************************************************************
% Creating RBF Interpolatin
%**************************************************************************
%选择所用基函数的形式 这五种函数 高斯 线性 立方 薄板 多项式
switch lower(options.('RBFFunction'))
case 'linear'
options.('rbfphi') = @rbfphi_linear; %线性
case 'cubic'
options.('rbfphi') = @rbfphi_cubic;%立方
case 'multiquadric'
options.('rbfphi') = @rbfphi_multiquadrics;%多项式
case 'thinplate'
options.('rbfphi') = @rbfphi_thinplate;%薄板
case 'gaussian'
options.('rbfphi') = @rbfphi_gaussian;%高斯型
otherwise
options.('rbfphi') = @rbfphi_linear;
end
phi = options.('rbfphi');
% 调用函数,求解出数据集使用调用||x-xi||函数的值
A=rbfAssemble(x, phi, options.('RBFConstant'), options.('RBFSmooth'));
b=[y'; zeros(nXDim+1, 1)]; %这是数据集对应的输出值Y
%inverse
rbfcoeff=A\b; %这是径向基函数对应的参数系数
%SVD
% [U,S,V] = svd(A);
%
% for i=1:1:nXCount+1
% if (S(i,i)>0) S(i,i)=1/S(i,i); end;
% end;
% rbfcoeff = V*S'*U*b;
options.('rbfcoeff') = rbfcoeff;
if (strcmp(options.('Stats'),'on'))
fprintf('%d point RBF interpolation was created in %e sec\n', length(y), toc);
fprintf('\n');
end;
function [A]=rbfAssemble(x, phi, const, smooth)
%x 为已知的数据集
%phi 表示调用的是哪个基函数形式
%const 表示高斯形式时的方差
%smooth 偏移量 一般为0
[dim n]=size(x); %得到数据集的维数
A=zeros(n,n); %初始化有数据集带入基函数中得到的值
for i=1:n
for j=1:i
r=norm(x(:,i)-x(:,j)); %每个数据跟其他数据之间的距离
temp=feval(phi,r, const); %带入相应的基函数中得到的值,存储到A中,用于求解系数
A(i,j)=temp;
A(j,i)=temp;
end
A(i,i) = A(i,i) - smooth;
end
% Polynomial part
P=[ones(n,1) x'];
A = [ A P
P' zeros(dim+1,dim+1)];
%**************************************************************************
% Radial Base Functions
%**************************************************************************
%五种基函数的表达式
function u=rbfphi_linear(r, const)
u=r;
function u=rbfphi_cubic(r, const)
u=r.*r.*r;
function u=rbfphi_gaussian(r, const)
u=exp(-0.5*r.*r/(const*const));
function u=rbfphi_multiquadrics(r, const)
u=sqrt(1+r.*r/(const*const));
function u=rbfphi_thinplate(r, const)
u=r.*r.*log(r+1);已知新的插入值,和上一个函数得到的径向基函数的参数,进行计算,得到新插入值的解
function [f] = rbfinterp(x, options)
%x 为插值的数据
%options 径向基函数的参数设定
tic;
phi = options.('rbfphi'); %调用的基函数形式
rbfconst = options.('RBFConstant');%基函数的方差设置
nodes = options.('x'); %已知的数据集x
rbfcoeff = (options.('rbfcoeff'))';%求得的径向基函数的系数
[dim n] = size(nodes);
[dimPoints nPoints] = size(x);
if (dim~=dimPoints)
error(sprintf('x should have the same number of rows as an array used to create RBF interpolation'));
end;
f = zeros(1, nPoints);
r = zeros(1, n);
for i=1:1:nPoints
s=0;
r = (x(:,i)*ones(1,n)) - nodes; %新数据点到已知每个数据点的距离
r = sqrt(sum(r.*r, 1));
% for j=1:n
% r(j) = norm(x(:,i) - nodes(:,j));
% end
s = rbfcoeff(n+1) + sum(rbfcoeff(1:n).*feval(phi, r, rbfconst));
for k=1:dim
s=s+rbfcoeff(k+n+1)*x(k,i); % linear part
end
f(i) = s;
end;
if (strcmp(options.('Stats'),'on'))
fprintf('Interpolation at %d points was computed in %e sec\n', length(f), toc);
end;