基于Android搭建tensorflow lite,实现官网的Demo以及运行自定义tensorflow模型(二)
基于上一篇在android studio 中已经布置好的环境进行开发。
这篇文章是基于手写识别的例子,在tensorflow中搭建一个简单的BP神经网络,在实现手写数字的识别,然后把这个网络生成文件,在android的tensorflow lite中运行。
一 在tensorflow 中生成tflite文件
我的python是3.6,tensorflow配置的是1.8.0,然后直接上代码。
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("mnist",one_hot=True)
# 定义批次大小
batch_size = 100
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples
# 定义placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[1,784],name='input_x')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[1,10],name='output_y')
# 定义 测试
x_test = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='input_test_x')
y_test = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='input_test_y')
# 创建一个简单的神经网络
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]),name="W")
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,10]),name="b")
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W)+b)
# 创建损失函数
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.02).minimize(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction)))
# 名称转换
def canonical_name(x):
return x.name.split(":")[0]
# 计算准确率
test_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x_test,W)+b)
accuarcy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_test,1),tf.argmax(test_prediction,1)),tf.float32))
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
out = tf.identity(prediction, name="output")
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(10):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
for index in range(len(batch_xs)):
xs = batch_xs[index].reshape(1,784)
ys = batch_ys[index].reshape(1,10)
sess.run(train, feed_dict={x: xs, y: ys})
acc = sess.run(accuarcy,feed_dict={x_test:mnist.test.images,y_test:mnist.test.labels})
print("over"+str(acc))
frozen_tensors = [out]
out_tensors = [out]
frozen_graphdef = tf.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, sess.graph_def, list(map(canonical_name, frozen_tensors)))
tflite_model = tf.contrib.lite.toco_convert(frozen_graphdef, [x], out_tensors)
open("writer_model.tflite", "wb").write(tflite_model)运行之后就可以生文件,writer_model.tflite.
二 创建自己的分类器
在上一篇搭建好平台之后,最重要的是模型的输入和输出,模型的输入函数。
private ByteBuffer convertBitmapToByteBuffer(Bitmap bitmap) {
// 获取图片的宽度
int width = bitmap.getWidth();
// 获取图片的高度
int height = bitmap.getHeight();
// 传入模型数据必须是ByteBuffer格式的,所以说必须把数据转入到
ByteBuffer tempData = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(width * height * 4);
// 数组排列用nativeOrder
tempData.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
// 获取图片的像素值
int[] pixels = getPicturePixel(bitmap);
for (int i = 0; i < pixels.length; i++) {
byte[] bytes = float2byte((float)(pixels[i]));
for (int k = 0; k < bytes.length; k++) {
tempData.put(bytes[k]);
}
}
return tempData;
}直接上完整的分类器代码
package com.fangt.classifer;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.AssetFileDescriptor;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import org.tensorflow.lite.Interpreter;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class WriterIdentify {
// 运行生成的文件,形成分类器
private Interpreter tflite;
// 输出的结构
private float[][] labelProbArray = null;
public static WriterIdentify newInstance(Context context) {
WriterIdentify writerIdentify = new WriterIdentify(context);
return writerIdentify;
}
private WriterIdentify(Context context) {
try {
tflite = new Interpreter(loadModelFile(context));
} catch (Exception e) {
}
labelProbArray = new float[1][10];
}
public void run(Bitmap bitmap) {
tflite.run(convertBitmapToByteBuffer(bitmap), labelProbArray);
//convertBitmapToByteBuffer(bitmap,width,height);
}
// 返回输出的结果
public int getResult() {
int[] resultDict = new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
for (int i = 0; i < labelProbArray[0].length; i++) {
if (labelProbArray[0][i] == 1.0f) {
return resultDict[i];
}
}
return -1;
}
private ByteBuffer convertBitmapToByteBuffer(Bitmap bitmap) {
int width = bitmap.getWidth();
int height = bitmap.getHeight();
ByteBuffer tempData = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(width * height * 4);
// 数组排列用nativeOrder
tempData.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
int[] pixels = getPicturePixel(bitmap);
for (int i = 0; i < pixels.length; i++) {
byte[] bytes = float2byte((float)(pixels[i]));
for (int k = 0; k < bytes.length; k++) {
tempData.put(bytes[k]);
}
}
return tempData;
}
// 读取图片像素
private int[] getPicturePixel(Bitmap bitmap) {
int width = bitmap.getWidth();
int height = bitmap.getHeight();
// 保存所有的像素的数组,图片宽×高
int[] pixels = new int[width * height];
bitmap.getPixels(pixels, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height);
String str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < pixels.length; i++) {
pixels[i] = pixels[i] & 0x000000ff;
}
return pixels;
}
// 把float转bytes字节
private byte[] float2byte(float f) {
// 把float转换为byte[]
int fbit = Float.floatToIntBits(f);
byte[] b = new byte[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
b[i] = (byte) (fbit >> (24 - i * 8));
}
// 翻转数组
int len = b.length;
// 建立一个与源数组元素类型相同的数组
byte[] dest = new byte[len];
// 为了防止修改源数组,将源数组拷贝一份副本
System.arraycopy(b, 0, dest, 0, len);
byte temp;
// 将顺位第i个与倒数第i个交换
for (int i = 0; i < len / 2; ++i) {
temp = dest[i];
dest[i] = dest[len - i - 1];
dest[len - i - 1] = temp;
}
return dest;
}
// 获取文件
private MappedByteBuffer loadModelFile(Context context) throws IOException {
AssetFileDescriptor fileDescriptor = context.getAssets().openFd(getModelPath());
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(fileDescriptor.getFileDescriptor());
FileChannel fileChannel = inputStream.getChannel();
long startOffset = fileDescriptor.getStartOffset();
long declaredLength = fileDescriptor.getDeclaredLength();
return fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, startOffset, declaredLength);
}
private String getModelPath() {
return "writer_model.tflite";
}
}
三 读取MNIST数据集中的数据
由于我们测试数据,就需要把图片从MNIST中提取出来,这里写了一个小工具,先从MNIST官网下载文件。
http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/
下载之后解压,运行下下面的小工具就可以了。
import numpy as np
import struct
from PIL import Image
import os
data_file = 'MNIST_data/train-images.idx3-ubyte' # 需要修改的路径
# It's 47040016B, but we should set to 47040000B
data_file_size = 47040016
data_file_size = str(data_file_size - 16) + 'B'
data_buf = open(data_file, 'rb').read()
magic, numImages, numRows, numColumns = struct.unpack_from(
'>IIII', data_buf, 0)
datas = struct.unpack_from(
'>' + data_file_size, data_buf, struct.calcsize('>IIII'))
datas = np.array(datas).astype(np.uint8).reshape(
numImages, 1, numRows, numColumns)
datas_root = 'images/' # 需要修改的路径
for ii in range(100):
print(ii)
img = Image.fromarray(datas[ii, 0, 0:28, 0:28])
file_name = datas_root + 'mnist_' + str(ii) + '.png'
img.save(file_name)四 在android中运行自定的分类器
先需要把图片导入到文件中
先创建XML文件,页面布局
之后是后台文件,也就是调用分类器。
package com.fangt.fragment;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.example.android.tflitecamerademo.R;
import com.fangt.classifer.WriterIdentify;
public class WriterFragment extends Fragment implements View.OnClickListener {
private Button btnStart;
private Button btnChange;
private TextView tvContent;
private ImageView ivNumber;
private Context context;
// 图片数据
private int[] imageIds;
private static int currentImageIds;
public WriterFragment() {
}
// TODO: Rename and change types and number of parameters
public static WriterFragment newInstance(String param1, String param2) {
WriterFragment fragment = new WriterFragment();
return fragment;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_writer, container, false);
context = view.getContext();
init(view);
return view;
}
private void init(View view) {
btnStart = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.btnStart);
tvContent = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tvContent);
ivNumber = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.ivNumber);
btnChange = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.btnChange);
btnStart.setOnClickListener(this);
btnChange.setOnClickListener(this);
imageIds = new int[]{R.drawable.mnist_0,R.drawable.mnist_1,R.drawable.mnist_2,
R.drawable.mnist_3,R.drawable.mnist_4,R.drawable.mnist_5,
R.drawable.mnist_6,R.drawable.mnist_7,R.drawable.mnist_8,
R.drawable.mnist_9,R.drawable.mnist_10,R.drawable.mnist_11,
R.drawable.mnist_12};
currentImageIds = 0;
ivNumber.setImageResource(imageIds[currentImageIds]);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.btnStart:
WriterIdentify writerIdentify = WriterIdentify.newInstance(context);
BitmapFactory.Options bfoOptions = new BitmapFactory.Options();
bfoOptions.inScaled = false;
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), imageIds[currentImageIds],bfoOptions);
writerIdentify.run(bitmap);
tvContent.setText("Result:" + writerIdentify.getResult());
break;
case R.id.btnChange:
currentImageIds = (++currentImageIds) % imageIds.length;
ivNumber.setImageResource(imageIds[currentImageIds]);
break;
}
}
}
到这里基本内容就完成了。
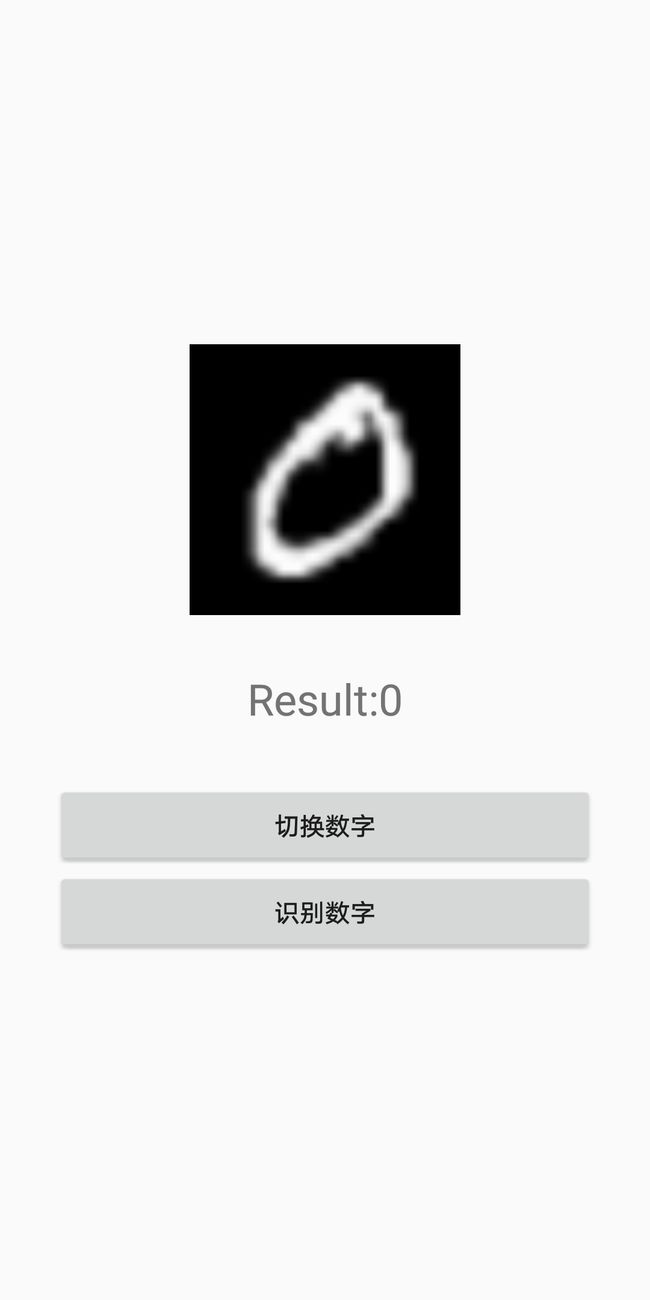
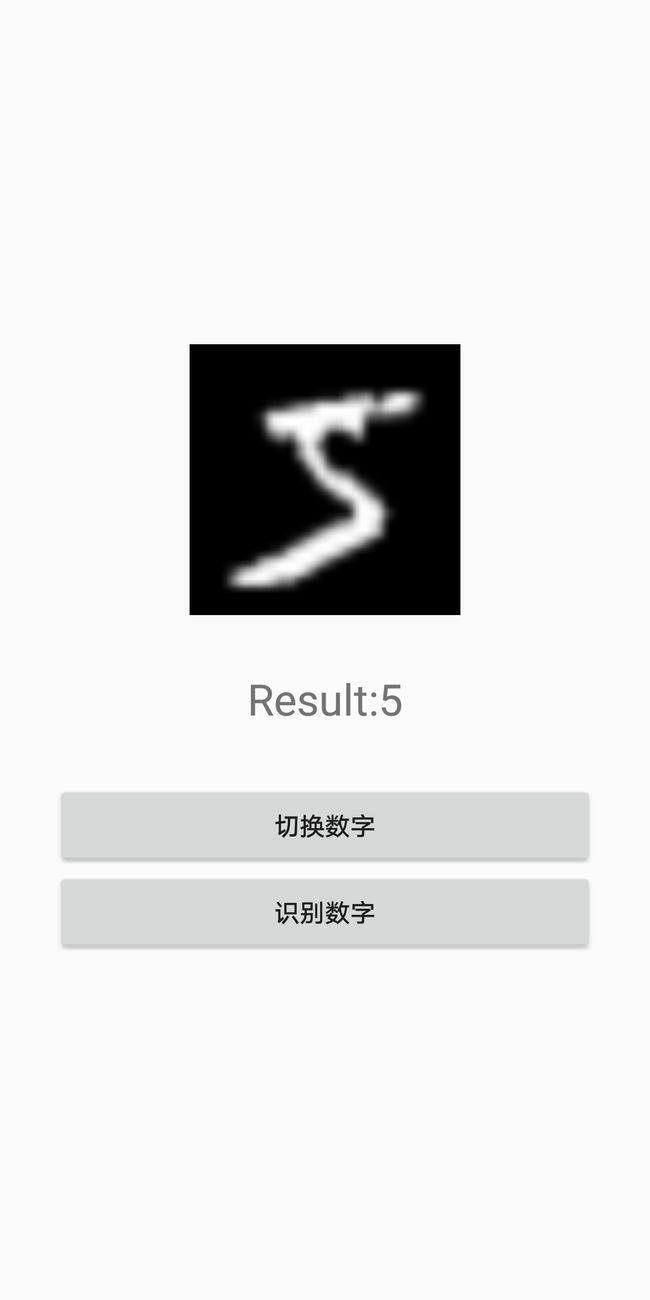
下面展示几张效果图:
对5进行分类
到这就结束了,喜欢的可以关注一下,有什么问题可以给我私信。谢谢。
我把APP上传到CSDN下载,地址
https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_22765745/10443505