第1章 ansible软件介绍
1.1 ansible软件介绍
l ansible是一个基于Python开发的自动化运维工具!(saltstack) python语言是运维人员必会的语言!
l 其功能实现基于SSH远程连接服务!
l ansible可以实现批量系统配置、批量软件部署、批量文件拷贝、批量运行命令等功能
1.2 ansible软件相关参考链接信息
http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/intro_installation.html
http://www.ansible.com.cn/
http://docs.ansible.com/modules_by_category.html
http://www.ansible.cn/docs/
1.3 ansible软件特点说明
1. 不需要单独安装客户端(no agents),基于系统自带的sshd服务,sshd就相当于ansible的客户端。
2. 不需要服务端(no servers)。
3. 需要依靠大量的模块实现批量管理。
4. 配置文件/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg,不用配置
第2章 ansible软件部署
2.1 确保可以免秘钥登录被管理端(详细信息查看以前的文档)
yum install -y sshpass
[root@m01 scripts]# vim fenfa.sh 1 #!/bin/bash 2 3 # create key pair 4 \rm /root/.ssh/id_rsa* -f 5 ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa -P "" &>/dev/null 6 7 # fenfa 8 for ip in 7 8 31 41 9 do 10 echo =====================172.16.1.$ip fenfa info========================== 11 sshpass -p123456 ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub "172.16.1.$ip -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no" 12 echo =====================172.16.1.$ip fenfa end=========================== 13 echo "" 14 done |
[root@m01 scripts]# sh fenfa.sh =====================172.16.1.7 fenfa info========================== Warning: Permanently added '172.16.1.7' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '172.16.1.7 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no'", and check in:
.ssh/authorized_keys
to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
=====================172.16.1.7 fenfa end===========================
=====================172.16.1.8 fenfa info========================== Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '172.16.1.8 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no'", and check in:
.ssh/authorized_keys
to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting. =====================172.16.1.8 fenfa end===========================
=====================172.16.1.31 fenfa info========================== Warning: Permanently added '172.16.1.31' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '172.16.1.31 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no'", and check in:
.ssh/authorized_keys
to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
=====================172.16.1.31 fenfa end===========================
=====================172.16.1.41 fenfa info========================== Warning: Permanently added '172.16.1.41' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '172.16.1.41 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no'", and check in:
.ssh/authorized_keys
to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
=====================172.16.1.41 fenfa end=========================== |
[root@m01 scripts]# ssh 172.16.1.31 hostname nfs01 |
2.2 安装软件
2.2.1 管理端主机
安装ansible软件: yum install -y ansible
2.2.2 被管理主机
yum install libselinux-python -y --- 如果selinux关闭的,可以不安装(建议安装)
至此:ansible软件在centos系统上安装完毕
2.2.3 ansible软件配置
[root@m01 scripts]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts ----定义ansible可管理的主机 [wuhuang] 172.16.1.7 172.16.1.8 172.16.1.31 172.16.1.41 |
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m command -a "uptime" ----查看wuhuang主机组的负载信息 172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 14:24:06 up 4:31, 2 users, load average: 0.08, 0.02, 0.01
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 14:24:06 up 4:37, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 14:24:06 up 4:32, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 14:24:06 up 4:30, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00 |
参数说明: wuhuang -----主机组 -m -----指定模块参数(command为默认模块,不写也可以) command -----模块名称 -a -----指定利用模块执行的动作参数,-a后面的是要执行的命令 uptime -----批量执行的命令 |
2.2.4 利用ansible基于口令方式管理
[root@m01 scripts]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts [wuhuang] 172.16.1.7 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456 172.16.1.8 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456 172.16.1.31 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456 172.16.1.41 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456 |
说明:后面的用户和密码项是非必须的,在配置key认证的情况下,不使用密码也可以直接操作 。
未使用key的,也可以在ansible通过 -k参数在操作前询问手动输入密码。
2.2.5 ansible以交互方式输入密码登录
[root@m01 scripts]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts [wuhuang] 172.16.1.7 172.16.1.8 172.16.1.31 ansible_ssh_user=root 172.16.1.41 |
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible 172.16.1.31 -m ping -k SSH password: 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "ping": "pong" } |
说明:以交互方式,输入密码信息进行远程管理 |
小结:ansible软件命令常用参数
-k --ask-pass:以交互方式输入密码,进行远程管理
-a :指定应用模块的相应参数信息
-m :指定应该什么模块(默认为command模块)
进行ansible软件批量管理:
l 熟悉ansible命令参数语法(重要!!!!)
l 指定管理主机的方法
Ø 1)指定单台主机地址信息
Ø 2)指定主机组信息
Ø 3)管理全部主机(all)
第3章 ansible模块总结
3.1 预备姿势
3.1.1 ansible输出详细信息方法
ansible mount -m setup -vvvv --- 主要用于排查ansible批量管理错误
3.1.2 ansible系统命令帮助文档查看方法:
ansible-doc -l --- 列出所有可用的模块信息,
ansible-doc -s cron --- 查看指定模块的参数信息
3.1.3 ansible软件颜色信息:
绿色: 表示查看信息,对远程主机未做改动的命令
红色: 批量管理产生错误信息
×××: 对远程主机做了相应改动
粉色: 对操作提出建议或忠告
3.2 第一个模块:command模块实践
官方链接:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/command_module.html
3.2.1 实例
批量显示远程主机的网卡信息
ansible wuhuang -m command -a "ifconfig"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m command -a "ifconfig" |
批量切换到远程主机的/tmp目录下,创建hosts01这个文件
ansible wuhuang -m command -a "chdir=/tmp touch hosts01"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m command -a "chdir=/tmp touch hosts01" [WARNING]: Consider using file module with state=touch rather than running touch
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> |
[root@web01 tmp]# ll total 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 3 15:31 hosts01 |
批量判断远程主机/tmp下有没有hosts这个文件,如果有就skip,没有就执行后面的命令
ansible wuhuang -m command -a "creates=/tmp/hosts01 touch hosts01"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m command -a "creates=/tmp/hosts01 touch hosts01" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> skipped, since /tmp/hosts01 exists
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> skipped, since /tmp/hosts01 exists
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> skipped, since /tmp/hosts01 exists
172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> skipped, since /tmp/hosts01 exists |
批量判断远程主机/tmp下有没有hosts01这个文件,如果有就执行后面的命令, 没有就skip
ansible wuhuang -m command -a "removes=/tmp/hosts01 touch /tmp/123.txt"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m command -a "removes=/tmp/hosts01 touch /tmp/123.txt" [WARNING]: Consider using file module with state=touch rather than running touch
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> |
[root@web01 tmp]# ll total 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 3 15:50 123.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 3 15:31 hosts01 |
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m command -a "ls -l" 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> total 40 -rw-------. 1 root root 1220 Jan 18 21:29 anaconda-ks.cfg -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 21736 Jan 18 21:29 install.log -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5890 Jan 18 21:25 install.log.syslog
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> total 48 -rw-------. 1 root root 1220 Jan 18 21:29 anaconda-ks.cfg -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 21736 Jan 18 21:29 install.log -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5890 Jan 18 21:25 install.log.syslog -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6 Jan 31 15:35 max_queued_events~ -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6 Jan 31 15:38 max_queued_eventz~
172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> total 40 -rw-------. 1 root root 1220 Jan 18 21:29 anaconda-ks.cfg -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 21736 Jan 18 21:29 install.log -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5890 Jan 18 21:25 install.log.syslog
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> total 40 -rw-------. 1 root root 1220 Jan 18 21:29 anaconda-ks.cfg -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 21736 Jan 18 21:29 install.log -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5890 Jan 18 21:25 install.log.syslog |
3.2.2 总结
说明:command模块为默认模块,可以省略不用输入
chdir --- 在执行命令之前,通过cd命令进入到指定目录中
creates --- 定义一个文件是否存在,如果不存在,则运行相应命令;如果存在跳过此步骤
removes --- 定义一个文件是否存在,如果存在运行相应命令;如果不存在跳过此步骤
free_form(默认参数) --- 可以输入任何系统命令信息,但是不包含一些特殊环境变量信息和特殊
符号信息"<", ">", "|", ";" and "&" (默认必须要存在的参数)
3.3 第二个模块:ping模块实践
官方链接:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/ping_module.html
ansible wuhuang -m ping
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m ping 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "ping": "pong" } 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "ping": "pong" } 172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "ping": "pong" } 172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "ping": "pong" } |
说明: 返回pong,说明可以登录SSH连接,这里ping不是测试网络连通性的,用于验证能否登录SSH连接,在查 看是否满足python的支持, 属于system模块 |
3.4 第三个模块:copy模块实践(将数据推送远程主机)
官方链接:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/copy_module.html
3.4.1 copy参数src
将本机/etc/sysconfig/iptables文件复制到远程主机的/tmp目录下(如果/tmp下已有同名文件,则会被覆盖)
ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/sysconfig/iptables dest=/tmp"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/sysconfig/iptables dest=/tmp" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "checksum": "b0abfab2d50ce1648e54b9cb7d2fcddcb2089852", "dest": "/tmp/iptables", "gid": 0, "group": "root", "md5sum": "5ee09def44bd598f82e3717df846e2fc", "mode": "0644", "owner": "root", "size": 476, "src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1517648150.54-133195812780831/source", "state": "file", "uid": 0 } …… |
如果远程主机没有dir目录,那么会创建wuhuang_dir目录
ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/wuhuang_dir/"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/wuhuang_dir/" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "checksum": "74e3f808eb07d3f8193b8fbe91877db4bc5930fd", "dest": "/tmp/wuhuang_dir/hosts", "gid": 0, "group": "root", "md5sum": "757d257f69f5040eaed85c14229dc86e", "mode": "0644", "owner": "root", "size": 372, "src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1517648947.23-279635150878284/source", "state": "file", "uid": 0 } …… |
传输文件时,如果上级目录不存在,则不会创建,传输就无法成功
ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/1/2/3/4/"
传输目录时,如果远程主机目录不存在,传输时可以创建多层目录;
如果传输的是目录本身及下面内容,后面不要加/(类似与rsync);
如果传输的是目录下面的内容,后面必须加/
ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/tmp dest=/tmp/1/2/3/4"
批量操作远程主机,对他们本机上的文件进行本地操作,设置为true时(默认为flase),不支持递归复制
ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "remote_src=true src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/1/2/"
3.4.2 copy参数backup=yes
分发文件时,如果与远程主机下iptables文件内容不一致,那么会备份源文件为"iptables.5714...以时间戳命名",再修改iptables源文件的内容
不输入默认backup=no,就是不备份,会覆盖源文件
ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/sysconfig/iptables dest=/tmp backup=yes"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/sysconfig/iptables dest=/tmp backup=yes" 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "checksum": "b0abfab2d50ce1648e54b9cb7d2fcddcb2089852", "gid": 0, "group": "root", "mode": "0644", "owner": "root", "path": "/tmp/iptables", "size": 476, "state": "file", "uid": 0 } …… |
3.4.3 copy参数mode、owner、group
改变文件的权限为0600,所有者和属组为wuhuang
ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp owner=wuhuang group=wuhuang mode=600"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp owner=wuhuang group=wuhuang mode=600" 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "checksum": "74e3f808eb07d3f8193b8fbe91877db4bc5930fd", "gid": 502, "group": "wuhuang", "mode": "0600", "owner": "wuhuang", "path": "/tmp/hosts", "size": 372, "state": "file", "uid": 502 } …… |
3.4.4 copy参数force
默认为forec=yes,如果和远程主机信息不一致,会覆盖
如果force=no,那么远程主机同名文件不会做改变
ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/sysconfig/iptables dest=/tmp force=no"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=/etc/sysconfig/iptables dest=/tmp force=no" 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "dest": "/tmp", "src": "/etc/sysconfig/iptables" } 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "dest": "/tmp", "src": "/etc/sysconfig/iptables" } 172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "dest": "/tmp", "src": "/etc/sysconfig/iptables" } 172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "dest": "/tmp", "src": "/etc/sysconfig/iptables" } |
3.4.5 copy参数content
写入信息到/tmp/ alex.txt中会把源内容覆盖掉,谨慎操作,只能添加少量的信息,添加多量的,可以用template模块
ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "content='alex.python' dest=/tmp/alex.txt"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "content='alex.python' dest=/tmp/alex.txt" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "checksum": "f017f4745821dc0d2ad6ca28d813f448d2454279", "dest": "/tmp/alex.txt", "gid": 0, "group": "root", "md5sum": "c3c6844b44a0436fe2c9d0a4a4232b27", "mode": "0644", "owner": "root", "size": 11, "src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1517648848.56-260572564303392/source", "state": "file", "uid": 0 } …… |
总结:
如果远程主机没有相应的目录,可以通过copy模块传输数据时进行创建,并且可以创建多级目录
Ø src --- 本地路径文件复制到远程服务器;可以是绝对路径也可以是相对路径
如果路径是一个目录,将会递归复制。
在这种情况下,如果路径以“/”结束,只将在该目录的内容复制到目的地
否则,如果它不以“/”结束,目录和目录下所有内容都会被复制
以上这种复制方式类似于rsync
Ø dest --- 文件应该被拷贝到的远程绝对路径信息。如果src是一个目录,dest也必须是目录
(默认必须要存在的)
Ø owner --- 定义所拥有文件/目录的所属用户名称,类似交由chown命令进行处理
Ø group --- 定义所拥有文件/目录的所属用户组名称,类似交由chown命令进行处理
Ø mode --- 定义文件或目录的权限信息;就像使用/usr/bin/chmod 设定八进制数(如0644)
取消掉前导零可能会有意想不到的结果。
作为1,8版本,可以指定为符号模式(如 u+rwx or u=rw,g=r,o=r)
Ø backup --- 创建备份文件包含时间戳信息,以便能够还原回原文件,在某种情况原文件被覆盖 错误时。
Ø force --- 默认为yes,当远程文件内容和源文件内容不同时,将覆盖目标文件
如果为no,文件将只被传输,在目标主机不存在此文件时
别名:thirsty
Ø content --- 当使用代替src参数时,将文件的内容直接设置为指定值。远端创建有指定内容文 件,这是只是简单值,对于任何复杂或者有格式化的内容,请切换到template模块
Ø remote_src --- 如果为 False,将搜索源信息在本地/管理及机器上
如果为True,将到远程/目标主机的机器上搜索
默认为false,目前remote_src不支持递归拷贝
3.5 第四个模块:shell模块实践(执行命令在节点上)
3.5.1 通过shell执行命令
[root@m01 tmp]# ansible wuhuang -m shell -a "uptime;df -h" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 18:01:51 up 8:15, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00 Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda3 20G 1.5G 17G 9% / tmpfs 238M 0 238M 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 190M 40M 141M 22% /boot
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 18:01:51 up 8:09, 2 users, load average: 0.08, 0.02, 0.01 Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda3 20G 1.5G 17G 9% / tmpfs 238M 0 238M 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 190M 40M 141M 22% /boot
172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 18:01:52 up 8:08, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00 Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda3 20G 1.6G 17G 9% / tmpfs 238M 0 238M 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 190M 40M 141M 22% /boot 172.16.1.31:/data 20G 1.5G 17G 9% /data
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 18:01:52 up 8:07, 3 users, load average: 0.08, 0.02, 0.01 Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda3 20G 1.6G 17G 9% / tmpfs 238M 0 238M 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 190M 40M 141M 22% /boot 172.16.1.31:/data 20G 1.5G 17G 9% /data |
说明:支持特殊符号,-a里面可接多个名,用分号分割 |
3.5.2 用shell执行一个脚本
说明:shell模块运行脚本,需要将脚本推送到远程主机中,需要授权脚本文件为执行权限
1)推送脚本并授权
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m copy -a "src=./test.sh dest=/tmp mode=+x" |
2)运行脚本
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m shell -a "/tmp/test.sh" 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> backup
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> nfs01
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> web02
172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> web01 |
3.6 第五个模块:script模块实践(将本地脚本中的信息,在远程主机上执行)
ansible wuhuang -m script -a "/server/scripts/test.sh"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m script -a "/server/scripts/test.sh" 172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "rc": 0, "stderr": "Shared connection to 172.16.1.7 closed.\r\n", "stdout": "web01\r\n", "stdout_lines": [ "web01" ] } 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "rc": 0, "stderr": "Shared connection to 172.16.1.31 closed.\r\n", "stdout": "nfs01\r\n", "stdout_lines": [ "nfs01" ] } …… |
3.7 第六个模块:yum模块实践
通过yum模块安装nmap软件
ansible wuhuang -m yum -a "name=nmap state=installed"
3.8 第七个模块:service模块实践
ansible wuhuang -m service -a "name=crond state=stopped enabled=yes"
说明:此处的name是服务名,表示将crond停止,并且取消开机自启动。
3.9 第八个模块:file模块实践
作用: 修改文件或目录属性信息,可用于创建文件或目录,也可以用mode、owner、group定义文件或目录的权限信息
3.9.1 path参数 :指定路径,是dest,name的别名,作用一样
ansible wuhuang -m file "path=/tmp/ state=directory mode=0644"
3.9.2 state参数
ansible wuhuang -m file -a "dest=/server/scripts/test.sh mode=0644" ---将test.sh权限改为0644
ansible wuhuang -m file -a "dest=/tmp/wuhuang_01dir/ state=directory" ---创建目录为wuhuang_01dir
ansible wuhuang -m file -a "dest=/tmp/wuhuang_01file state=touch" ---创建文件为wuhuang_01file
ansible wuhuang -m file -a "dest=/tmp/wuhuang_01file state=absent" ---删除文件wuhuang_01file
ansible wuhuang -m file -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/hosts state=link" ---创建链接文件
3.9.3 总结
Ø owner --- 定义所拥有文件/目录的所属用户名称,类似交由chown命令进行处理
Ø group --- 定义所拥有文件/目录的所属用户组名称,类似交由chown命令进行处理
Ø mode --- 定义文件或目录的权限信息;就像使用/usr/bin/chmod 设定八进制数(如0644)
取消掉前导零可能会有意想不到的结果。
作为1,8版本,可以指定为符号模式(如 u+rwx or u=rw,g=r,o=r)
Ø path --- 文件路径管理:(别名方式:dest,name)
Ø src --- 要链接的文件路径(只能应用 state=link),接受绝对、相对以及不存在的路径
相对路径不能扩展
Ø state --- 如果指定参数为directory
所有不存在的子目录将会被创建,并且从1.7开始支持设置目录权限
--- 如果指定参数为file
如果文件不存在将不能被创建,如果想创建可以参考copy和template模块
--- 如果指定参数为link,符号链接将被创建或更改。
--- 如果指定参数为hard,便会创建出硬链接
--- 如果指定参数为absent
目录将被递归删除以及文件,而链接将被取消链接。
请注意,定义文件不存在不会失败,只是输出没有发生任何改变的结果
--- 如果指定参数为touch
如果路径不存在将创建一个空文件,如果文件或目录存在将接收更新的文件访问和修改
时间(类似于“touch”从命令行工作的方式)。
3.10 cron模块实践(定时任务模块)
3.10.1 常用参数
* * * * * /bin/sh /server/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null
分 时 日 月 周 定时任务要完成什么工作
l minute --- 定义分钟信息
l hour --- 定义小时信息
l day --- 定义日期信息
l month --- 定义月份信息
l weekday --- 定义周几信息
l job --- 定义定时任务要做什么事
l name --- 对定时任务信息加上备注,从而避免创建多个重复的定时任务(根据定时任务备份判断
是否生成一个新的定时任务)
l state --- 若设置为present,表示创建定时任务(默认配置)
若设置为absent,表示删除指定定时任务
只能管理自己创建的定时任务,本来有的管理不了
l disabled --- 将定时任务信息,进行临时关闭(添加注释)
3.10.2 实例
创建定时任务
ansible wuhuang -m cron -a "minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null'"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m cron -a "minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null'" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "envs": [], "jobs": [ "None" ] } 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "envs": [], "jobs": [ "None" ] } …… |
[root@web01 tmp]# crontab -l #tongbu date */5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com >/dev/null 2>&1 #Ansible: None 0 0 * * * /bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null |
ansible wuhuang -m cron -a "name='backup server02' minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null'"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m cron -a "name='backup server02' minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null'" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "envs": [], "jobs": [ "backup server02" ] } 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "envs": [], "jobs": [ "backup server02" ] } …… |
[root@web01 tmp]# crontab -l #tongbu date */5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com >/dev/null 2>&1 #Ansible: backup server02 0 0 * * * /bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null |
注释掉定时任务,反之取消注释
ansible wuhuang -m cron -a "name='backup server' minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null' disabled=yes"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m cron -a "name='backup server' minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null' disabled=yes" 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "envs": [], "jobs": [ "backup server02", "backup server" ] } 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "envs": [], "jobs": [ "backup server02", "backup server" ] } …… |
[root@web01 tmp]# crontab -l #tongbu date */5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com >/dev/null 2>&1 #Ansible: backup server02 0 0 * * * /bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null #Ansible: backup server #0 0 * * * /bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null |
删除定时任务
ansible wuhuang -m cron -a "name='backup server02' minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null' state=absent"
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m cron -a "name='backup server02' minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /servser/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null' state=absent" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "envs": [], "jobs": [] } 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "envs": [], "jobs": [] }
…… |
[root@web01 tmp]# crontab -l #tongbu date */5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com >/dev/null 2>&1 已经没有backup server02这一条 |
3.11 第十个模块:mount模块实践
mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/data /mnt
l fstype --- 指定挂载时的文件系统类型
l opts --- 在挂载时,指定挂载参数信息
l path --- 指定挂载点路径信息
l src --- 指定将什么目录或设备进行挂载
l state --- 如果为state=mounted,在fstab文件中的设备将被激活挂载或适当配置,如果指定
mounted的挂载挂载点不存在,会创建
--- 如果为state=unmounted,设备将被卸载并不会改变fstab文件信息
--- absent和present只处理fstab,但将不影响目前的挂载,如果指定mounted和挂载点不存在,挂载点将被创建,类似的,指定absent将移除挂载点目录
ansible mount -m mount -a "state=mounted fstype=nfs src='172.16.1.31:/data/' path=/mnt/"
3.12 第十一个模块:debug调试模块实践
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible wuhuang -m debug 172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "msg": "Hello world!" } 172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "msg": "Hello world!" } 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "msg": "Hello world!" } 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "msg": "Hello world!" } |
说明:此模块在执行过程中打印语句,对于调试变量或表达式非常有用,而不一定会停止播放。与“When:”指令一起调试非常有用。 |
3.13 第十二个模块:setup模块实践
ansible wuhuang -m setup
显示远程主机的所有信息(后面加-v显示详细信息),提取IP、或架构信息等,X86来判断主机架构,
装合适的软件
ansible georhe -m setup -v
主要用于解决一些错误:如远程主机hang住了,ansible会输出少量信息(最多-vvvv)
第4章 ansible剧本编写
4.1 ansible剧本编写规则说明
4.1.1 语法格式
ansible剧本格式:遵循yaml语法格式(类似python脚本编写格式)
rsync配置文件格式:ini语法格式
sersync配置文件格式:xml语法格式(标签格式)
4.1.2 pyYAML语法规则
规则一:缩进
yaml使用一个固定的缩进风格表示数据层结构关系,Saltstack需要每个缩进级别由两个空格组成。一定不能使用tab键
规则二:冒号
CMD="echo"
yaml:
mykey:
每个冒号后面一定要有一个空格(以冒号结尾不需要空格,表示文件路径的模版可以不需要空格)
规则三:短横线
想要表示列表项,使用一个短横杠加一个空格。多个项使用同样的缩进级别作为同一个列表的一部分
核心规则:有效的利用空格进行剧本的编写,剧本编写是不支持tab的
4.2 ansible-playbook编写格式
4.2.1 剧本编写内容扩展
1. 剧本的开头
- hosts: all <- all表示所有主机,可以写某个主机组; -(空格)hosts:(空格)all task: <- 剧本所要干的事情; (空格)(空格)task: - command: echo hello oldboy linux. (空格)(空格)空格)(空格)-(空格)模块名称:(空格)模块中对应的功能 |
2. 剧本任务定义名称
- hosts: all <- all表示所有主机,可以写某个主机组; -(空格)hosts:(空格)all task: <- 剧本所要干的事情; (空格)(空格)task: - command: echo hello oldboy linux. (空格)(空格)空格)(空格)-(空格)模块名称:(空格)模块中对应的功能 |
3. 剧本任务编写定时任务
# ansible all -m cron -a "name='restart network' minute=00 hour=00 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov >/dev/null 2>&1'" |
剧本内容 - hosts: all tasks: - name: restart-network cron: name='restart network' minute=00 hour=00 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov >/dev/null 2>&1' |
# ansible-playbook -C /etc/ansible/network-restart.yml -vvvx 说明:测试剧本命令后面可以跟多个-v进行调试检查 |
4. 剧本任务编写多个任务
- hosts: all tasks: - name: restart-network cron: name='restart network' minute=00 hour=00 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov >/dev/null 2>&1' - name: sync time cron: name='sync time' minute=*/5 job="/usr/sbin/ntpdate pool.ntp.com >/dev/null 2>&1" |
5. 剧本任务编写多个主机
- hosts: 172.16.1.7 tasks: - name: restart-network cron: name='restart network' minute=00 hour=00 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov >/dev/null 2>&1' - name: sync time cron: name='sync time' minute=*/5 job="/usr/sbin/ntpdate pool.ntp.com >/dev/null 2>&1" - hosts: 172.16.1.31 tasks: - name: show ip addr to file shell: echo $(hostname -i) >> /tmp/ip.txt |
4.2.2 创建部署rsyn服务剧本
第一步:编写剧本
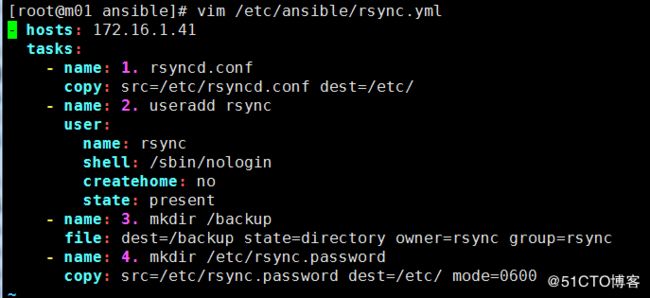
[root@m01 ansible]# cat /etc/ansible/rsync.yml - hosts: 172.16.1.41 <- 处理指定服务器(all <- 处理所有服务器) tasks: <- 剧本所要干的事情 - name: 1. rsyncd.conf 第一步:将配置文件复制的rsync服务器 copy: src=/etc/rsyncd.conf dest=/etc/ - name: 2. useradd rsync 第二步:创建备份目录管理用户 user: name: rsync shell: /sbin/nologin createhome: no state: present - name: 3. mkdir /backup 第三步:创建备份目录 file: dest=/backup state=directory owner=rsync group=rsync - name: 4. mkdir /etc/rsync.password 第四步:创建认证用户密码文件 copy: src=/etc/rsync.password dest=/etc/ mode=0600 - name: 5. rsync --daemon 第五步:启动 shell: rsync --daemon - name: 6. kaiji zidong run 第六步:开机自启动 shell: echo "rsync --daemon" >>/etc/rc.local |
第二步:将对应文件放到剧本指定位置
[root@m01 ~]# ll /etc/rsync.password /etc/rsyncd.conf -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 451 Feb 4 11:47 /etc/rsyncd.conf -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 17 Feb 4 11:53 /etc/rsync.password |
第三步:对剧本进行语法检查
[root@m01 ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check /etc/ansible/rsync.yml
playbook: /etc/ansible/rsync.yml |
第四步:测试剧本
[root@m01 ansible]# ansible-playbook -C /etc/ansible/rsync.yml -vvv |
说明:测试剧本命令后面可以跟多个-v进行调试检查 |
第五步:执行剧本
[root@m01 ansible]# ansible-playbook /etc/ansible/rsync.yml
PLAY [172.16.1.41] *********************************************************************************************************** TASK [Gathering Facts] ******************************************************************************************************* ok: [172.16.1.41] TASK [1. rsyncd.conf] ******************************************************************************************************** ok: [172.16.1.41] TASK [2. useradd rsync] ****************************************************************************************************** ok: [172.16.1.41] TASK [3. mkdir /backup] ****************************************************************************************************** ok: [172.16.1.41] TASK [4. mkdir /etc/rsync.password] ****************************************************************************************** ok: [172.16.1.41] TASK [5. rsync --daemon] ***************************************************************************************************** changed: [172.16.1.41] TASK [6. kaiji zidong run] *************************************************************************************************** changed: [172.16.1.41] PLAY RECAP ******************************************************************************************************************* 172.16.1.41 : ok=7 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 |