关于iOS GYDataCenter本地数据库解决方案的那些事儿--上卷
之前提到到前端处理数据线程的解决方案,这里有需要到数据的本地存储,数据持久最好的方式首选数据库。那现在在我们的面前的有两种选择,一种是apple的coredata,另外一种就是采用FMDB。我的主观反应是,我首推的是FMDB,FMDB的灵活性能更强,适用于多种场景,在数据处理上,可以通过选择不同的SQL语句,达到更好的效果。在FMDB的基础上,还有一个更便利的框架--GYDataCenter。
这里就从一个比较完整的数据模型的创建来讲解着一个解决方案。
这个解决方案大体上分为:数据模型(数据表),数据操作(逻辑运算)和数据迁移,其实就是数据的增删查改,对于不是很了解的SQL语句的开发者来说,这个在方便不过了,在下面的内容里面也穿插讲解一下MD5和基础用户存储的一些解决方案。
主要内容:
1.用户的概念
2.如何创建一个数据库和库表
3.如何进行增删查改
本文主要讲解1 、 2两个点。
1.用户的概念
#import
@interface QYJUserInfo : NSObject
{
NSString *_id;
}
/**
* 账号
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *username;
/**
* 密码
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *password;
/**
* 邮箱
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *email;
/**
* 删除标识,未删:0,已删:1
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *deleted;
/**
* 用户ID
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *userID;
/**
* 中文名
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *cname;
/**
* 联系手机号码
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *phone;
/**
* 用户类型
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *type;
/**
* 英文名
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *ename;
/**
* 创建时间
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *created_dt;
/**
* 更新时间
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *updated_dt;
/**
* 基础方法
*/
/*
@method toModelWithDictionary:
@abstrac 字典转模型,用户类型一般只处理一个
@discussion 字典转模型
@param dict (NSDictionary *)
@result QYJUserInfo 对象
*/
+ (instancetype)toModelWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dict;
/*
@method toDictionary
@abstrac 转字典
@discussion 转字典
@param No param
@result NSDictionary
*/
- (NSDictionary *)toDictionary;
/*
@method getMD5
@abstrac 将对象的值和属性名转成字符串MD5
@discussion 将对象的值和属性名转成字符串MD5
@param No param
@result NSString
*/
- (NSString *)getMD5;
/*
@method saveObjectToLocal
@abstrac 保存对象到本地
@discussion 保存对象到本地
@param No param
@result BOOL 保存结果
*/
- (BOOL)saveObjectToLocal;
/*
@method localUserInfo:
@abstrac 查询本地用户信息,一般做自动登录的用户只允许有一个
@discussion 查询本地用户信息
@param No param
@result QYJUserInfo对象
*/
+ (instancetype)localUserInfo;
/*
@method deleteUserInfo:
@abstrac 删除本地存储的用户数据,在用户点击出按钮的时候调用
@discussion 删除本地存储的用户数据,在用户点击出按钮的时候调用
@param No param
@result No return
*/
+ (void)deleteUserInfo;
/*
@method compare:
@abstrac 比较大小
@discussion 比较大小
@param QYJUserInfo对象
@result NSOrderedAscending = -1L, NSOrderedSame, NSOrderedDescending
*/
- (NSComparisonResult)compare:(QYJUserInfo *)otherObject;
@end
在.m的文件中我们要去实现我们声明的文件。
#import "QYJUserInfo.h"
//runtime 需要引用的头文件
#import
#import "NSString+MD5.h"
// 保存的Key
static NSString *const localSaveKey = @"com.userInfo.qyj";
@implementation QYJUserInfo
@synthesize userID = _id;
#pragma mark - NSCopying
- (id)copyWithZone:(NSZone *)zone {
Class modelClass = [self class];
QYJUserInfo *object = [[modelClass alloc] init];
NSArray *propertyName = [modelClass getPropertyNames];
NSLog(@"%@", propertyName);
for (NSString *property in propertyName) {
[object setValue:[self valueForKey:property] forKey:property];
}
return object;
}
+ (NSArray *)getPropertyNames {
NSMutableArray *names = @[].mutableCopy;
u_int count;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList(self, &count);
for (int i=0; i #import "AppDelegate.h"
#import "QYJUserInfo.h"
@interface AppDelegate ()
@end
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
NSDictionary *userInfoDict = @{
@"username" : @"123456789",
@"password" : @"*******",
@"email" : @"[email protected]",
@"deleted" : @"0",
@"id" : @"666",
@"cname" : @"狗剩",
@"phone" : @"182xxxx3233",
@"type" : @"M",
@"ename" : @"Tom",
@"created_dt": @"2011-02-03",
@"updated_dt": @"2017-02-08"
};
QYJUserInfo *object = [QYJUserInfo toModelWithDictionary:userInfoDict];
NSLog(@"%@", object);
[object saveObjectToLocal];
return YES;
}
- (NSString *)description {
NSArray *propertyNames = [[self class] getPropertyNames];
NSString *result = nil;
for (NSString *propertyName in propertyNames) {
NSString *temp = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@:%@\n", propertyName, [self valueForKey:propertyName]];
if (!result) {
result = temp;
} else {
result = [result stringByAppendingString:temp];
}
}
return result;
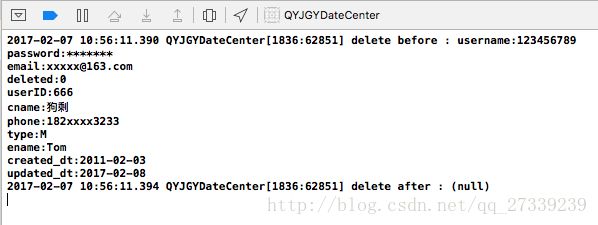
} 运行结果:
修改AppDelegate的代码:
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
QYJUserInfo *object1 = [QYJUserInfo localUserInfo];
NSLog(@"delete before : %@", object1);
//删除本地的档案
[QYJUserInfo deleteUserInfo];
//在获取一次本地的档案,查看是否可以获取
QYJUserInfo *object2 = [QYJUserInfo localUserInfo];
NSLog(@"delete after : %@", object2);
return YES;
}用户数据存储就完成了。
2.如何创建一个数据库
首先,我们要知道,GYDataCenter(下面简称GY)这个框架创建表的时候,不需要我们去写创建语句,也不用像FMDB那样,每次增删查改的时候都要读取数据。只要调用相关的该表的SQL语句,框架内部就可以自动创建。
GYDataCenter的github地址:https://github.com/Zepo/GYDataCenter
开始创建一个本地的数据库,建库的方法有很多,可以用一些数据库工具创建一个空的数据库,放到工程里面,也可以用代码去创建。这里通过讲解一个简单的场景去学习如何使用数据库。
我们要做的事情很简单,就是读取手机通讯录的数据,然后转化成相应的数据保存到我们的数据库中,这里我们先写一个通讯录的表。GYDataCenter只是一层封装,不包括FMDB,这里我们要从github上面把FMDB下载下来,导入到工程里面,同时依赖需要的静态库——libsqlite3.0.tbd。编译,无报错,GYDataCenter和FMDB就可以使用了。
创建一个继承于GYModelObject这类的通讯录类,继承GYModelObject之后就可以使用GY的一下数据库的相关方法。
#import "GYModelObject.h"
@interface QYJContactsInfo : GYModelObject
/**
* 主键
*/
@property (assign, nonatomic, readonly) NSInteger primaryKeyId;
/**
* 联系人姓名
*/
@property (strong, nonatomic, readonly) NSString *name;
/**
* 顾客姓名首字母
*/
@property (strong, nonatomic, readonly) NSString *nameFirstLetter;
/**
* 顾客姓名拼音
*/
@property (strong, nonatomic, readonly) NSString *namePinyin;
/**
* 电话号码
*/
@property (strong, nonatomic, readonly) NSString *phoneNum;
- (NSDictionary *)toDictionary;
@end
#import "QYJContactsInfo.h"
#import
#define PrimaryKeyId @"primaryKeyId"
@implementation QYJContactsInfo
+ (NSString *)dbName {
//需要将表存放的数据库
return @"thisIsDatabaseName";
}
+ (NSString *)tableName {
//数据存放的表名字
return @"thisIsTableName";
}
+ (NSString *)primaryKey {
//主键的字段名
return PrimaryKeyId;
}
+ (NSArray *)persistentProperties {
//这里是返回你的属性名,顺序和@interface中声明的是一样的
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
static NSArray *properties = nil;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
properties = @[
@"primaryKeyId",
@"name",
@"nameFirstLetter",
@"namePinyin",
@"phoneNum",
];
});
return properties;
}
- (BOOL)isEqual:(id)object {
if (![object isKindOfClass:[self class]]) return NO;
NSDictionary *selfDict = [self toDictionary];
NSDictionary *tempDcit = [(QYJContactsInfo *)object toDictionary];
return [selfDict isEqualToDictionary:tempDcit];
}
- (NSString *)description {
NSArray *propertyNames = [[self class] getPropertyNames];
NSString *result = nil;
for (NSString *propertyName in propertyNames) {
NSString *temp = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@:%@\n", propertyName, [self valueForKey:propertyName]];
if (!result) {
result = temp;
} else {
result = [result stringByAppendingString:temp];
}
}
return result;
}
- (NSDictionary *)toDictionary {
NSMutableDictionary *dict = @{}.mutableCopy;
NSArray *propertyName = [[self class] getPropertyNames];
for (NSString *property in propertyName) {
id value = [self valueForKey:property];
//这里字典不能传入一个nil的对象,这里就加一个判断
if ([property isEqualToString:PrimaryKeyId]) {
//自增的ID,自动填写,无需自己手动编号,一般于业务无关,这里转字典的时候,根据实际需求修改
continue;
}
[dict setValue:value ? value : @"" forKey:property];
}
return dict;
}
+ (NSArray *)getPropertyNames {
NSMutableArray *names = @[].mutableCopy;
u_int count;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList(self, &count);
for (int i=0; i + (NSString *)dbName;
+ (NSString *)tableName;
+ (NSString *)primaryKey;
+ (NSArray *)persistentProperties;
这三个方法必须实现,这里关系到数据表的创建和使用。一个数据表的创建方式大体就是这样子了,除上述4个方法开发者根据业务的需求去增加的。接下来就是去获取我们通讯录,联系人的数据了。这里要注意一下权限的问题,在iOS 10中,通讯录权限必须要在.plist文件里面去声明注册,否则在iOS10以上的机子上会出现闪出。
.plist文件里面添加
这里是注册权限,
iOS 9以后有一个新的获取通讯录联系人的API,这里不做深入探讨,有兴趣的可以自己查看API文档或者去看其他大神的技术分享博客。
//iOS 9之前
#import
//iOS 9以后
#import
#import "QYJContactsInfoManager.h"
//iOS 9之前
#import
//iOS 9以后
#import
@implementation QYJContactsInfoManager
+ (NSMutableArray *)addressBookiOSNineBefore {
//新建一个通讯录类
__block ABAddressBookRef addressBooks = nil;
//addressBooks = ABAddressBookCreateWithOptions(NULL, NULL);
if (ABAddressBookGetAuthorizationStatus() == kABAuthorizationStatusNotDetermined) {
ABAddressBookRequestAccessWithCompletion(addressBooks, ^(bool granted, CFErrorRef error){
CFErrorRef *error1 = NULL;
addressBooks = ABAddressBookCreateWithOptions(NULL, error1);
});
}
else if (ABAddressBookGetAuthorizationStatus() == kABAuthorizationStatusAuthorized){
CFErrorRef *error = NULL;
addressBooks = ABAddressBookCreateWithOptions(NULL, error);
}
else {
return [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
}
//获取通讯录权限
dispatch_semaphore_t sema = dispatch_semaphore_create(0);
ABAddressBookRequestAccessWithCompletion(addressBooks, ^(bool granted, CFErrorRef error){dispatch_semaphore_signal(sema);
});
dispatch_semaphore_wait(sema, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
//获取通讯录中的所有人
CFArrayRef allPeople = ABAddressBookCopyArrayOfAllPeople(addressBooks);
//通讯录中人数
CFIndex nPeople = ABAddressBookGetPersonCount(addressBooks);
NSMutableArray *addressBookTemp = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
//循环,获取每个人的个人信息
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < nPeople; i++)
{
//获取个人
ABRecordRef person = CFArrayGetValueAtIndex(allPeople, i);
//获取个人名字
CFTypeRef abName = ABRecordCopyValue(person, kABPersonFirstNameProperty);
CFTypeRef abLastName = ABRecordCopyValue(person, kABPersonLastNameProperty);
// CFTypeRef adBirthDay = ABRecordCopyValue(person, kABPersonBirthdayProperty);
CFStringRef abFullName = ABRecordCopyCompositeName(person);
NSString *nameString = (__bridge NSString *)abName;
NSString *lastNameString = (__bridge NSString *)abLastName;
// NSString *birthDay = (__bridge NSString *)adBirthDay;
NSString *tel ;
if ((__bridge id)abFullName != nil) {
nameString = (__bridge NSString *)abFullName;
} else {
if ((__bridge id)abLastName != nil)
{
nameString = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@", nameString, lastNameString];
}
nameString = @"";
}
ABPropertyID multiProperties[] = {
kABPersonPhoneProperty,
kABPersonEmailProperty
};
NSInteger multiPropertiesTotal = sizeof(multiProperties) / sizeof(ABPropertyID);
for (NSInteger j = 0; j < multiPropertiesTotal; j++) {
ABPropertyID property = multiProperties[j];
ABMultiValueRef valuesRef = ABRecordCopyValue(person, property);
NSInteger valuesCount = 0;
if (valuesRef != nil) valuesCount = ABMultiValueGetCount(valuesRef);
if (valuesCount == 0) {
CFRelease(valuesRef);
continue;
}
for (NSInteger k = 0; k < valuesCount; k++) {
CFTypeRef value = ABMultiValueCopyValueAtIndex(valuesRef, k);
tel = (__bridge NSString*)value;
NSMutableDictionary * pinyinDic = [[NSMutableDictionary alloc]init];
if (nameString != nil && tel != nil) {
if (nameString.length == 0) {
nameString = tel;
}
[pinyinDic setObject:nameString forKey:@"name"];
[pinyinDic setObject:tel forKey:@"phoneNum"];
} else{
continue;
}
[addressBookTemp addObject:pinyinDic];
CFRelease(value);
}
CFRelease(valuesRef);
}
}
return addressBookTemp;
}
@end
在AppDelegate中调用相关的API,
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
//获取联系人
NSMutableArray *contacts = [QYJContactsInfoManager addressBookiOSNineBefore];
//打印路径,方便查看
NSLog(@"%@, %@", contacts, NSHomeDirectory());
for (NSDictionary *dict in contacts) {
//用一个字典去生成对象
QYJContactsInfo *contactsInfo = [QYJContactsInfo objectWithDictionary:dict];
//保存到数据库中
[contactsInfo save];
}
return YES;
}
运行结果:

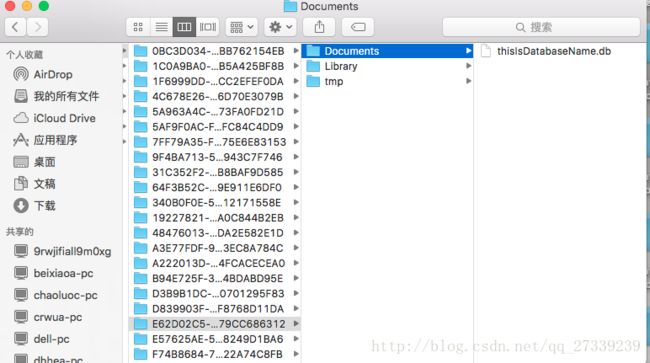
调用 save方法就开始保存到数据库里面,只要调用了数据库,这里就会自动去生成数据库和数据表。
如果使用真机调试可以用同步助手或者itune去查看数据库,这里是用模拟器,使用SQLite Professional来打开数据库。
数据库里面的内容:
数据库和数据表的创建就是这样了,下一篇博客详细的数据操作。