Android-传感器-计步
参考文章:http://www.jianshu.com/p/5d57f7fd84fa
本文对原文计步项目进行了精简,移除了进程服务和计时、守护进程、数据库保存等等,方便扩展功能。
本文源码:https://github.com/lioilwin/StepOrient
Android4.4以上版本,有些手机有计步传感器可以直接使用,
而有些手机没有,但有加速度传感器,也可以实现计步功能(需要计算加速度波峰波谷来判断人走一步)!
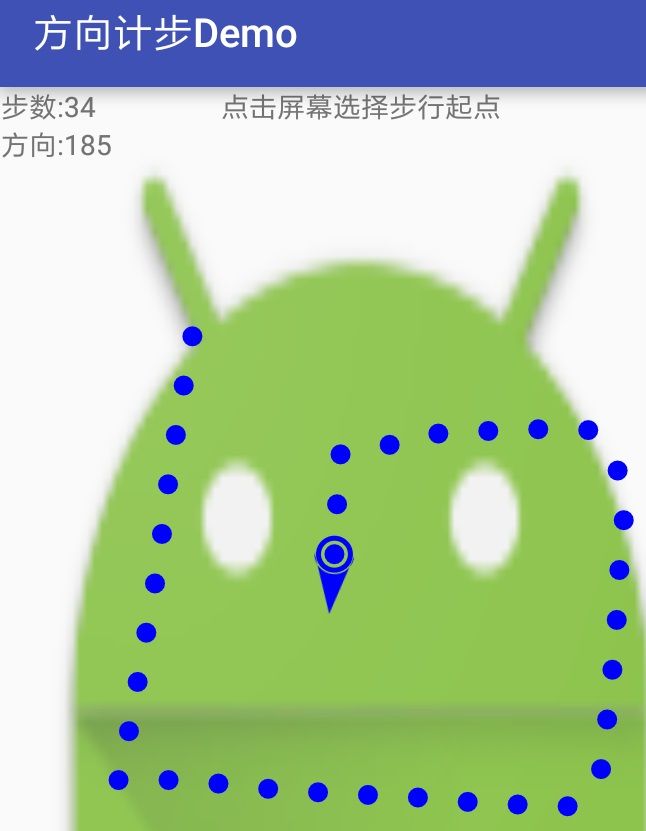
一.调用
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements StepSensorBase.StepCallBack{
.........
@Override
public void Step(int stepNum) {
// 计步回调
stepText.setText("步数:" + stepNum);
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
stepText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.step_text);
// 开启计步监听, 分为加速度传感器、或计步传感器
stepSensor = new StepSensorPedometer(this, this);
if (!stepSensor.registerStep()) {
Toast.makeText(this, "计步传传感器不可用!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
stepSensor = new StepSensorAcceleration(this, this);
if (!stepSensor.registerStep()) {
Toast.makeText(this, "加速度传感器不可用!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
.......
}
/**
* 计步传感器抽象类,子类分为加速度传感器、或计步传感器
*/
public abstract class StepSensorBase implements SensorEventListener {
private Context context;
protected StepCallBack stepCallBack;
protected SensorManager sensorManager;
protected static int CURRENT_SETP = 0;
protected boolean isAvailable = false;
public StepSensorBase(Context context, StepCallBack stepCallBack) {
this.context = context;
this.stepCallBack = stepCallBack;
}
public interface StepCallBack {
/**
* 计步回调
*/
void Step(int stepNum);
}
/**
* 开启计步
*/
public boolean registerStep() {
if (sensorManager != null) {
sensorManager.unregisterListener(this);
sensorManager = null;
}
sensorManager = SensorUtil.getInstance().getSensorManager(context);
registerStepListener();
return isAvailable;
}
/**
* 注册计步监听器
*/
protected abstract void registerStepListener();
/**
* 注销计步监听器
*/
public abstract void unregisterStep();
}
二.直接使用计步传感器实现计步
/**
* 计步传感器
*/
public class StepSensorPedometer extends StepSensorBase {
private final String TAG = "StepSensorPedometer";
private int lastStep = -1;
private int liveStep = 0;
private int increment = 0;
private int sensorMode = 0; // 计步传感器类型
public StepSensorPedometer(Context context, StepCallBack stepCallBack) {
super(context, stepCallBack);
}
@Override
protected void registerStepListener() {
Sensor detectorSensor = sensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_STEP_DETECTOR);
Sensor countSensor = sensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_STEP_COUNTER);
if (sensorManager.registerListener(this, detectorSensor, SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_GAME)) {
isAvailable = true;
sensorMode = 0;
Log.i(TAG, "计步传感器Detector可用!");
} else if (sensorManager.registerListener(this, countSensor, SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_GAME)) {
isAvailable = true;
sensorMode = 1;
Log.i(TAG, "计步传感器Counter可用!");
} else {
isAvailable = false;
Log.i(TAG, "计步传感器不可用!");
}
}
@Override
public void unregisterStep() {
sensorManager.unregisterListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
liveStep = (int) event.values[0];
if (sensorMode == 0) {
Log.i(TAG, "Detector步数:"+liveStep);
StepSensorBase.CURRENT_SETP += liveStep;
} else if (sensorMode == 1) {
Log.i(TAG, "Counter步数:"+liveStep);
StepSensorBase.CURRENT_SETP = liveStep;
}
stepCallBack.Step(StepSensorBase.CURRENT_SETP);
}
@Override
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int accuracy) {
}
}
三.使用加速度传感器实现计步
/**
* 加速度传感器
*/
public class StepSensorAcceleration extends StepSensorBase {
private final String TAG = "StepSensorAcceleration";
//存放三轴数据
final int valueNum = 5;
//用于存放计算阈值的波峰波谷差值
float[] tempValue = new float[valueNum];
int tempCount = 0;
//是否上升的标志位
boolean isDirectionUp = false;
//持续上升次数
int continueUpCount = 0;
//上一点的持续上升的次数,为了记录波峰的上升次数
int continueUpFormerCount = 0;
//上一点的状态,上升还是下降
boolean lastStatus = false;
//波峰值
float peakOfWave = 0;
//波谷值
float valleyOfWave = 0;
//此次波峰的时间
long timeOfThisPeak = 0;
//上次波峰的时间
long timeOfLastPeak = 0;
//当前的时间
long timeOfNow = 0;
//当前传感器的值
float gravityNew = 0;
//上次传感器的值
float gravityOld = 0;
//动态阈值需要动态的数据,这个值用于这些动态数据的阈值
final float initialValue = (float) 1.7;
//初始阈值
float ThreadValue = (float) 2.0;
//初始范围
float minValue = 11f;
float maxValue = 19.6f;
/**
* 0-准备计时 1-计时中 2-正常计步中
*/
private int CountTimeState = 0;
public static int TEMP_STEP = 0;
private int lastStep = -1;
//用x、y、z轴三个维度算出的平均值
public static float average = 0;
private Timer timer;
// 倒计时3.5秒,3.5秒内不会显示计步,用于屏蔽细微波动
private long duration = 3500;
private TimeCount time;
public StepSensorAcceleration(Context context, StepCallBack stepCallBack) {
super(context, stepCallBack);
}
@Override
protected void registerStepListener() {
// 注册加速度传感器
isAvailable = sensorManager.registerListener(this, sensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_GAME);
if (isAvailable) {
Log.i(TAG, "加速度传感器可用!");
} else {
Log.i(TAG, "加速度传感器不可用!");
}
}
@Override
public void unregisterStep() {
sensorManager.unregisterListener(this);
}
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor arg0, int arg1) {
}
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
Sensor sensor = event.sensor;
synchronized (this) {
if (sensor.getType() == Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER) {
calc_step(event);
}
}
}
synchronized private void calc_step(SensorEvent event) {
average = (float) Math.sqrt(Math.pow(event.values[0], 2)
+ Math.pow(event.values[1], 2) + Math.pow(event.values[2], 2));
detectorNewStep(average);
}
/*
* 检测步子,并开始计步
* 1.传入sersor中的数据
* 2.如果检测到了波峰,并且符合时间差以及阈值的条件,则判定为1步
* 3.符合时间差条件,波峰波谷差值大于initialValue,则将该差值纳入阈值的计算中
* */
public void detectorNewStep(float values) {
if (gravityOld == 0) {
gravityOld = values;
} else {
if (DetectorPeak(values, gravityOld)) {
timeOfLastPeak = timeOfThisPeak;
timeOfNow = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (timeOfNow - timeOfLastPeak >= 200
&& (peakOfWave - valleyOfWave >= ThreadValue) && (timeOfNow - timeOfLastPeak) <= 2000) {
timeOfThisPeak = timeOfNow;
//更新界面的处理,不涉及到算法
preStep();
}
if (timeOfNow - timeOfLastPeak >= 200
&& (peakOfWave - valleyOfWave >= initialValue)) {
timeOfThisPeak = timeOfNow;
ThreadValue = Peak_Valley_Thread(peakOfWave - valleyOfWave);
}
}
}
gravityOld = values;
}
private void preStep() {
// if (CountTimeState == 0) {
// // 开启计时器
// time = new TimeCount(duration, 700);
// time.start();
// CountTimeState = 1;
// Log.v(TAG, "开启计时器");
// } else if (CountTimeState == 1) {
// TEMP_STEP++;
// Log.v(TAG, "计步中 TEMP_STEP:" + TEMP_STEP);
// } else if (CountTimeState == 2) {
StepSensorBase.CURRENT_SETP++;
// if (stepCallBack != null) {
stepCallBack.Step(StepSensorBase.CURRENT_SETP);
// }
// }
}
/*
* 检测波峰
* 以下四个条件判断为波峰:
* 1.目前点为下降的趋势:isDirectionUp为false
* 2.之前的点为上升的趋势:lastStatus为true
* 3.到波峰为止,持续上升大于等于2次
* 4.波峰值大于1.2g,小于2g
* 记录波谷值
* 1.观察波形图,可以发现在出现步子的地方,波谷的下一个就是波峰,有比较明显的特征以及差值
* 2.所以要记录每次的波谷值,为了和下次的波峰做对比
* */
public boolean DetectorPeak(float newValue, float oldValue) {
lastStatus = isDirectionUp;
if (newValue >= oldValue) {
isDirectionUp = true;
continueUpCount++;
} else {
continueUpFormerCount = continueUpCount;
continueUpCount = 0;
isDirectionUp = false;
}
// Log.v(TAG, "oldValue:" + oldValue);
if (!isDirectionUp && lastStatus
&& (continueUpFormerCount >= 2 && (oldValue >= minValue && oldValue < maxValue))) {
peakOfWave = oldValue;
return true;
} else if (!lastStatus && isDirectionUp) {
valleyOfWave = oldValue;
return false;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/*
* 阈值的计算
* 1.通过波峰波谷的差值计算阈值
* 2.记录4个值,存入tempValue[]数组中
* 3.在将数组传入函数averageValue中计算阈值
* */
public float Peak_Valley_Thread(float value) {
float tempThread = ThreadValue;
if (tempCount < valueNum) {
tempValue[tempCount] = value;
tempCount++;
} else {
tempThread = averageValue(tempValue, valueNum);
for (int i = 1; i < valueNum; i++) {
tempValue[i - 1] = tempValue[i];
}
tempValue[valueNum - 1] = value;
}
return tempThread;
}
/*
* 梯度化阈值
* 1.计算数组的均值
* 2.通过均值将阈值梯度化在一个范围里
* */
public float averageValue(float value[], int n) {
float ave = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ave += value[i];
}
ave = ave / valueNum;
if (ave >= 8) {
// Log.v(TAG, "超过8");
ave = (float) 4.3;
} else if (ave >= 7 && ave < 8) {
// Log.v(TAG, "7-8");
ave = (float) 3.3;
} else if (ave >= 4 && ave < 7) {
// Log.v(TAG, "4-7");
ave = (float) 2.3;
} else if (ave >= 3 && ave < 4) {
// Log.v(TAG, "3-4");
ave = (float) 2.0;
} else {
// Log.v(TAG, "else");
ave = (float) 1.7;
}
return ave;
}
class TimeCount extends CountDownTimer {
public TimeCount(long millisInFuture, long countDownInterval) {
super(millisInFuture, countDownInterval);
}
@Override
public void onFinish() {
// 如果计时器正常结束,则开始计步
time.cancel();
StepSensorBase.CURRENT_SETP += TEMP_STEP;
lastStep = -1;
Log.v(TAG, "计时正常结束");
timer = new Timer(true);
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
public void run() {
if (lastStep == StepSensorBase.CURRENT_SETP) {
timer.cancel();
CountTimeState = 0;
lastStep = -1;
TEMP_STEP = 0;
Log.v(TAG, "停止计步:" + StepSensorBase.CURRENT_SETP);
} else {
lastStep = StepSensorBase.CURRENT_SETP;
}
}
};
timer.schedule(task, 0, 2000);
CountTimeState = 2;
}
@Override
public void onTick(long millisUntilFinished) {
if (lastStep == TEMP_STEP) {
Log.v(TAG, "onTick 计时停止:" + TEMP_STEP);
time.cancel();
CountTimeState = 0;
lastStep = -1;
TEMP_STEP = 0;
} else {
lastStep = TEMP_STEP;
}
}
}
}
简书: http://www.jianshu.com/p/6b05b1b8603e
CSDN博客: http://blog.csdn.net/qq_32115439/article/details/61619644
GitHub博客:http://lioil.win/2017/03/12/Android-Step.html
Coding博客:http://c.lioil.win/2017/03/12/Android-Step.html