Springboot系列之二十三(2):Spring boot集成mongodb使用MongoRepository完成CURD和复杂查询
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39214304/article/details/84791953
Spring Data简介
Spring Data 是spring的组件之一,主要目的是为了让开发者再工作中能更加轻松的完成CURD,简化代码应该是所有框架的目的吧。今天介绍的Spring-data-mongodb只是其中的一个模块而已,Spring团队的强大不言而喻,有兴趣的请移步官网查看更多模块。
Spring-Data
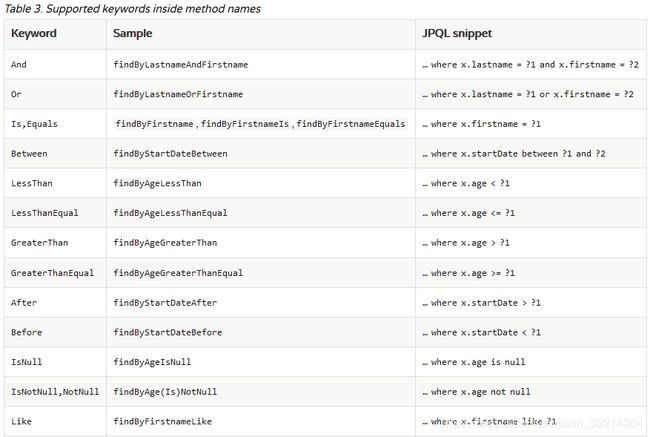
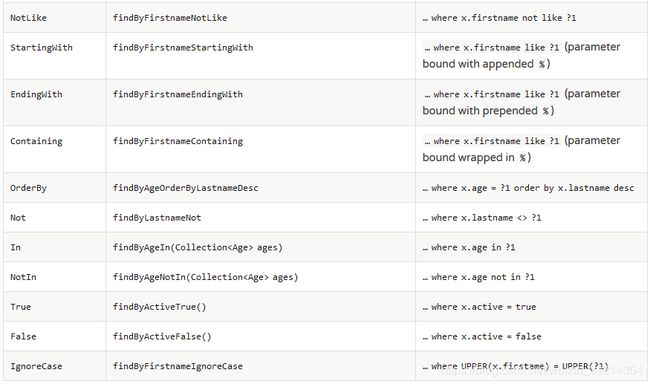
Spring Data Jpa 方法定义规范
网上的博文关于这部分大同小异,这里只贴部分内容,详细规则可以参考官方文档。这些方法只是在特定情况下才用的到,比如MongoRepository不能完成的工作,但是在本人实际工作中MongoRepository已经覆盖了9成以上的需求,如果你感觉有什么需求它完成不了,很有可能是没有找对方法。
Spring-Data-Jpa
MongoRepository实战操作
spring.data.mongodb.host=localhost
spring.data.mongodb.port=27017
spring.data.mongodb.database=testmongodb
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 分别新建实体类User/Repository接口UserRespository/控制器UserController
public class User {
private String id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private int age;
private long createTime;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public long getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(long createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
package com.ppw.mongoexample.repository;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
import com.ppw.mongoexample.model.User;
public interface UserRepository extends MongoRepository<User, String>{
public Page<User> findByUserNameLike(String userName, Pageable pageable);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
package com.ppw.mongoexample.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Example;
import org.springframework.data.domain.ExampleMatcher;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort.Order;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort.Direction;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import com.ppw.mongoexample.model.User;
import com.ppw.mongoexample.repository.UserRepository;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/v1/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
@PostMapping(consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public User createUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
/**
* 根据id查询
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value="/{id}")
public User readUserById(@PathVariable(“id”) String id){
return userRepository.findOne(id);
}
/**
* 根据一个或者多个属性查询单个结果
* @param name
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value="/name/{name}")
public User readUserByName(@PathVariable(“name”) String name){
User user = new User();
user.setUserName(name);
ExampleMatcher matcher = ExampleMatcher.matching().withIgnorePaths(“age”,“createTime”);
Example<User> example = Example.of(user, matcher);
return userRepository.findOne(example);
}
/**
* 根据一个或者多个属性分页查询
* @param pageNumber
* @param pageSize
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = “/page/{pageNumber}/pagesize/{pageSize}/name/{name}”)
public Page<User> readUsersByPage(@PathVariable(“pageNumber”) int pageNumber,
@PathVariable(“pageSize”) int pageSize,@PathVariable(“name”) String name) {
User user = new User();
user.setUserName(name);
ExampleMatcher matcher = ExampleMatcher.matching().withIgnorePaths(“age”,“createTime”);
Example<User> example = Example.of(user, matcher);
if (pageNumber < 1) {
pageNumber = 1;
} else if (pageSize == 0) {
pageSize = 20;
}
PageRequest pageable = new PageRequest(pageNumber - 1, pageSize);
return userRepository.findAll(example, pageable);
}
/**
* 根据用户年龄升序排序
* @return
*/
@GetMapping
public List<User> readUsers(){
Order order = new Order(Direction.ASC,"age");
Sort sort = new Sort(order);
return userRepository.findAll(sort);
}
/**
* 模糊查询带分页
* @param pageNumber
* @param pageSize
* @param keyWords
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = “/page/{pageNumber}/pagesize/{pageSize}/keyword/{keyWords}”)
public Page<User> readUsersByKeywords(@PathVariable(“pageNumber”) int pageNumber,
@PathVariable(“pageSize”) int pageSize,@PathVariable(“keyWords”) String keyWords) {
if (keyWords null) {
keyWords = “”;
}
if (pageNumber < 1) {
pageNumber = 1;
} else if (pageSize 0) {
pageSize = 20;
}
PageRequest pageable = new PageRequest(pageNumber - 1, pageSize);
return userRepository.findByUserNameLike(keyWords, pageable);
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
@DeleteMapping(value="/{id}")
public void removeUser(@PathVariable(“id”) String id) {
userRepository.delete(id);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
Postman测试部分接口结果如下图所示
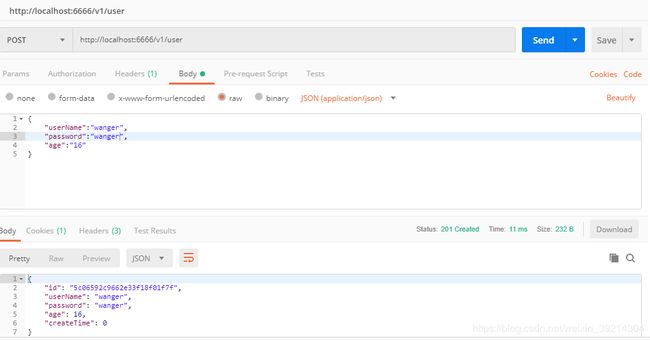
1.新建用户
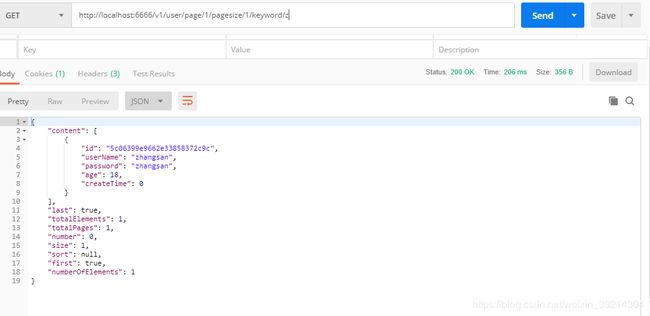
 2.根据用户名模糊查询并分页
2.根据用户名模糊查询并分页
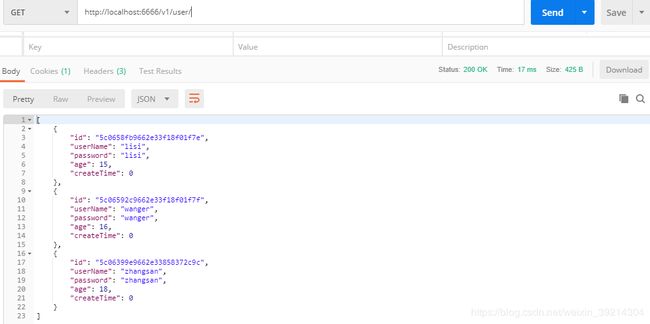
 3.根据年龄升序排序
3.根据年龄升序排序
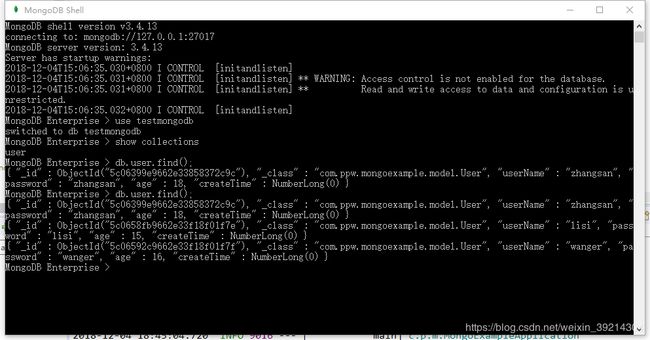
Mongodb截图如下
注意事项
在使用MongoRepository的过程中,非模糊查询多配合使用Example/ExampleMatcher来完成工作,MongoRepository已经非常强大,常用功能如排序,分页都已实现,当然还有很多方法文中没有提到感兴趣的可以深入了解一下。如果MongoRepository能实现,尽量不要做冗余的工作,如果非要自定义方法才能实现,一定要符合Spring-Data的规则来定义方法名。这里有一个小坑需要注意一下,如果实体类中包含有基本数据类型的属性,那么在使用repository.find(Example)时,需要把这些属性忽略掉,因为基本数据类型在新建对象时会有默认值,这时如果你按照别的属性查找数据时,这些属性也会附带到条件里。比如上文代码中有一个根据用户名查找用户的方法,此时你期望的是在查询过程中只有用户名起作用,那么这时候就要加上下面的代码。如果不加,则条件中会多出age=0&createTime=0,查出的结果有误。