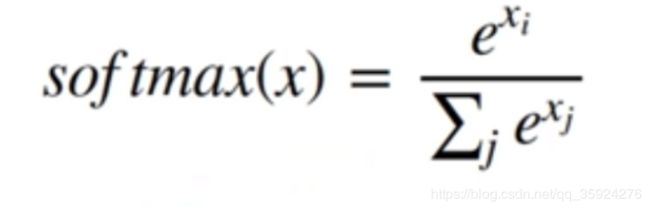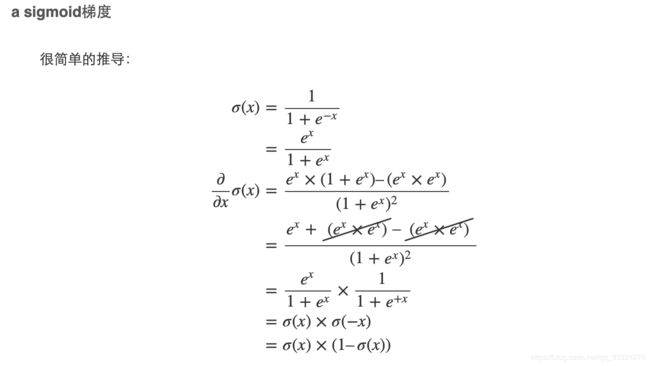斯坦福cs224n assignment1
有些来自于http://www.hankcs.com/nlp/ 讲解更精简,有很多学习资料
第一部分关于Softmax
第一个问题 a 是关于公式推导,验证 softmax函数的常数不变性
第二部分 b 是实现代码 要求既能处理向量,也能处理矩阵(视作多个不相干的行向量集合)。
根据公式可能一开始会想当然的写(我一开始是这样以为的///)
import numpy as np
def softmax(x):
"""Compute the softmax of vector x."""
exp_x = np.exp(x)
softmax_x = exp_x / np.sum(exp_x)
return softmax_x但实际上,遇到较大的数值向量时就有问题了。
这是由numpy中的浮点型数值范围限制所导致的。当输入一个较大的数值时,sofmax函数将会超出限制,导致出错。
上面证明了softmax函数的常数不变性,所以 运用这个性质。一般在实际运用中,通常设定c = - max(x)。
以下是基于矩阵和基于vector的实现
矩阵(行为样本,列为标签)
import numpy as np
def softmax(x):
orig_shape = x.shape
if len(x.shape) > 1:
# Matrix 矩阵形式
### YOUR CODE HERE
#找出最大值
x -= np.max(x, axis=1, keepdims=True) #(行方向 axis=1, 维度保持不变)
x = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x),axis=1) #归一化,将其变成概率
### END YOUR CODE
else:
# Vector
### YOUR CODE HERE
x_max = np.max(x, axis= 0 ,keepdims=True)
x = x - x_max
x = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x),axis=0)
### END YOUR CODE
assert x.shape == orig_shape
return x
from q1_softmax import softmax
# return 20 if softmax(测试值) == 正确值 else 0
def test_softmax_basic():
"""
Some simple tests to get you started.
Warning: these are not exhaustive.
"""
print ("Running basic tests...")
test1 = softmax(np.array([1,2]))
print (test1)
ans1 = np.array([0.26894142, 0.73105858])
assert np.allclose(test1, ans1, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-06)
test2 = softmax(np.array([[1001,1002],[3,4]]))
print (test2)
ans2 = np.array([
[0.26894142, 0.73105858],
[0.26894142, 0.73105858]])
assert np.allclose(test2, ans2, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-06)
test3 = softmax(np.array([[-1001,-1002]]))
print (test3)
ans3 = np.array([0.73105858, 0.26894142])
assert np.allclose(test3, ans3, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-06)
print ("You should be able to verify these results by hand!\n")
def test_softmax():
"""
Use this space to test your softmax implementation by running:
python q1_softmax.py
This function will not be called by the autograder, nor will
your tests be graded.
"""
print ("Running your tests...")
### YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError
### END YOUR CODE
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_softmax_basic()
# test_softmax()
另一段也是一样的结果
import numpy as np
def softmax(x):
"""Compute the softmax function for each row of the input x.
It is crucial that this function is optimized for speed because
it will be used frequently in later code. You might find numpy
functions np.exp, np.sum, np.reshape, np.max, and numpy
broadcasting useful for this task.
Numpy broadcasting documentation:
http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/user/basics.broadcasting.html
You should also make sure that your code works for a single
D-dimensional vector (treat the vector as a single row) and
for N x D matrices. This may be useful for testing later. Also,
make sure that the dimensions of the output match the input.
You must implement the optimization in problem 1(a) of the
written assignment!
Arguments:
x -- A D dimensional vector or N x D dimensional numpy matrix.
Return:
x -- You are allowed to modify x in-place
"""
orig_shape = x.shape
if len(x.shape) > 1:
# Matrix 矩阵形式
### YOUR CODE HERE
exp_minmax = lambda x: np.exp(x - np.max(x))
denom = lambda x: 1.0 / np.sum(x)
x = np.apply_along_axis(exp_minmax, 1, x)
denominator = np.apply_along_axis(denom, 1, x)
if len(denominator.shape) == 1:
denominator = denominator.reshape((denominator.shape[0], 1))
x = x * denominator
### END YOUR CODE
else:
# Vector
### YOUR CODE HERE
x_max = np.max(x)
x = x - x_max
numerator = np.exp(x)
denominator = 1.0 / np.sum(numerator)
x = numerator.dot(denominator)
### END YOUR CODE
assert x.shape == orig_shape
return x
from q1_softmax import softmax
# return 20 if softmax(测试值) == 正确值 else 0
def test_softmax_basic():
"""
Some simple tests to get you started.
Warning: these are not exhaustive.
"""
print ("Running basic tests...")
test1 = softmax(np.array([1,2]))
print (test1)
ans1 = np.array([0.26894142, 0.73105858])
assert np.allclose(test1, ans1, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-06)
test2 = softmax(np.array([[1001,1002],[3,4]]))
print (test2)
ans2 = np.array([
[0.26894142, 0.73105858],
[0.26894142, 0.73105858]])
assert np.allclose(test2, ans2, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-06)
test3 = softmax(np.array([[-1001,-1002]]))
print (test3)
ans3 = np.array([0.73105858, 0.26894142])
assert np.allclose(test3, ans3, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-06)
print ("You should be able to verify these results by hand!\n")
def test_softmax():
"""
Use this space to test your softmax implementation by running:
python q1_softmax.py
This function will not be called by the autograder, nor will
your tests be graded.
"""
print ("Running your tests...")
### YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError
### END YOUR CODE
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_softmax_basic()
# test_softmax()
softmax小结
1.指数变换去负数,突出特征
2.归一化变为概率的近似
3.利用常数不变防溢出
4.每个维度代表的含义
5. axis = 0/1
第二部分 神经网络基础
第一个问题 sigmod函数求导
第二个问题 用softmax 函数实现一个交叉绱损失函数的梯度求导
实现sigmod函数
#!/usr/bin/env python
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(x):
"""
Compute the sigmoid function for the input here.
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array.
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
### YOUR CODE HERE
s = 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
### END YOUR CODE
return s
def sigmoid_grad(s):
"""
Compute the gradient for the sigmoid function here. Note that
for this implementation, the input s should be the sigmoid
function value of your original input x.
Arguments:
s -- A scalar or numpy array.
Return:
ds -- Your computed gradient.
"""
### YOUR CODE HERE
ds = s * (1 - s)
### END YOUR CODE
return ds