spring自动扫描包详解
配置文件
前面的例子我们都是使用XML的bean定义来配置组件。在一个稍大的项目中,通常会有上百个组件,如果这些组件采用XML的bean定义来配置,显然会增加配置文件的体积,查找及维护起来也不太方便。
Spring2.5为我们引入了组件自动扫描机制,它可以在类路径底下寻找标注了@Component、@Service、@Controller、@Repository注解的类,并把这些类纳入进Spring容器中管理。
它的作用和在XML文件中使用bean节点配置组件是一样的。要使用自动扫描机制,我们需要打开以下配置信息:
其中
在xml配置了这个标签后,spring可以自动去扫描base-pack下面或者子包下面的java文件,如果扫描到有@Component @Controller@Service等这些注解的类,则把这些类注册为bean
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
另外
1.
2.
在说明这两个子标签前,先说一下
Use-default-filter此时为true那么会对base-package包或者子包下的所有的进行java类进行扫描,并把匹配的java类注册成bean。
可以发现这种扫描的粒度有点太大,如果你只想扫描指定包下面的Controller,该怎么办?此时子标签
与如下的这个等同
这样就会只扫描base-package指定下的有@Controller下的java类,并注册成bean
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
但是因为use-dafault-filter在上面并没有指定,默认就为true,所以当把上面的配置改成如下所示的时候,就会产生与你期望相悖的结果(注意base-package包值得变化)
此时,spring不仅扫描了@Controller,还扫描了指定包所在的子包service包下注解@Service的java类
此时指定的include-filter没有起到作用,只要把use-default-filter设置成false就可以了。这样就可以避免在base-packeage配置多个包名这种不是很优雅的方法来解决这个问题了。
另外在我参与的项目中可以发现在base-package指定的包中有的子包是不含有注解了,所以不用扫描,此时可以指定
综合以上说明
Use-dafault-filters=”false”的情况下:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注解
@Service用于标注业务层组件、 @Controller用于标注控制层组件(如Struts2中的action)、@Repository用于标注数据访问组件,即DAO组件。而@Component泛指组件,当组件不好归类的时候,我们可以使用这个注解进行标注。
本文是建立在@Autowire注解与自动装配的案例基础上的。我们首先将Spring的配置文件改为:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
一个实例
然后使用@Service注解标注PersonServiceBean类,如下:
@Service
public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService {
private PersonDao personDao;
public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) {
this.personDao = personDao;
}
@Override
public void save() {
personDao.add();
}
}使用@Repository注解标注PersonDaoBean类,如下:
@Repository
public class PersonDaoBean implements PersonDao {
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("执行PersonDaoBean中的add()方法");
}
}最后,我们修改SpringTest类的代码为:
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void instanceSpring() {
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
PersonService personService = (PersonService) ctx.getBean("personServiceBean");
PersonDao personDao = (PersonDao) ctx.getBean("personDaoBean");
System.out.println(personService);
System.out.println(personDao);
ctx.close();
}
}测试instanceSpring()方法,可看到Eclipse控制台打印: 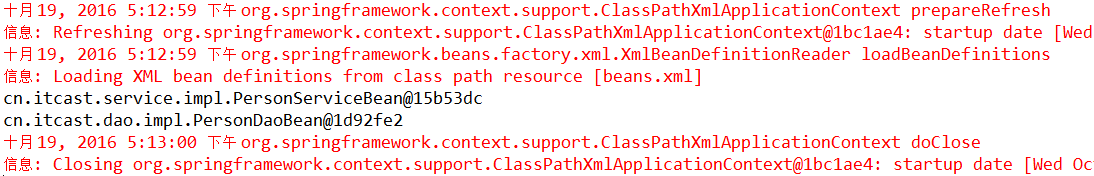
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
如果我们想使用按指定名称获取,可将PersonServiceBean类的代码修改为:
@Service("personService")
public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService {
private PersonDao personDao;
public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) {
this.personDao = personDao;
}
@Override
public void save() {
personDao.add();
}
}这样,SpringTest类的代码应改为:
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void instanceSpring() {
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
PersonService personService = (PersonService) ctx.getBean("personService");
System.out.println(personService);
ctx.close();
}
}测试instanceSpring()方法,可看到Eclipse控制台打印: 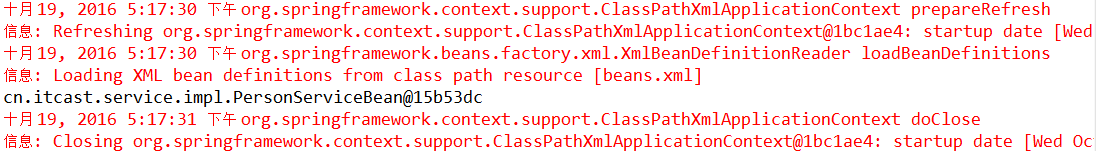
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
我们前面学过Spring管理的bean的作用域,我们就能知道以上Spring管理的两个bean的作用域默认是singleton。当然了,我们也可以更改Spring管理的bean的作用域,如将PersonServiceBean类的代码改为:
@Service("personService") @Scope("prototype")
public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService {
private PersonDao personDao;
public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) {
this.personDao = personDao;
}
@Override
public void save() {
personDao.add();
}
}意味着Spring管理的PersonServiceBean这个bean的作用域变成prototype了,这时我们将SpringTest类的代码修改为:
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void instanceSpring() {
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
PersonService personService1 = (PersonService) ctx.getBean("personService");
PersonService personService2 = (PersonService) ctx.getBean("personService");
System.out.println(personService1 == personService2);
ctx.close();
}
}测试instanceSpring()方法,可看到Eclipse控制台打印: 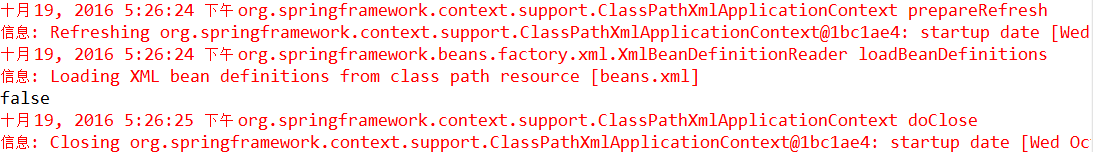
prototype作用域本来就意味着每次从Spring容器获取bean都是新的对象嘛。
有关bean作用域的详解:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36098284/article/details/80665708
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
若是通过在classpath路径下自动扫描方这种式把组件纳入Spring容器中管理,如何指定bean的初始化方法和销毁方法呢?这时我们就需要用到两个注解:@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy。为了试验,我们将PersonServiceBean类的代码修改为:
@Service("personService")
public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService {
private PersonDao personDao;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("初始化资源");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("销毁、关闭资源");
}
public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) {
this.personDao = personDao;
}
@Override
public void save() {
personDao.add();
}
}接下来还要将SpringTest类的代码修改为:
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void instanceSpring() {
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
PersonService personService = (PersonService) ctx.getBean("personService");
ctx.close();
}
}这样,测试instanceSpring()方法,Eclipse控制台会打印: 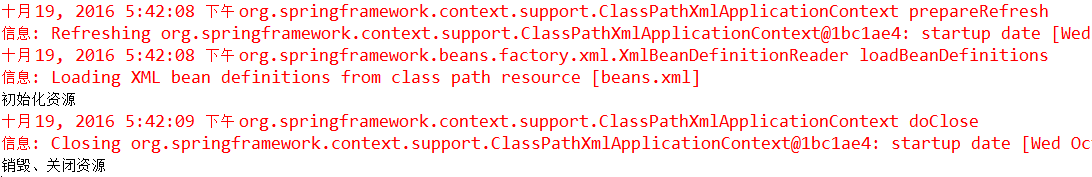
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
如要查看源码,可点击让Spring自动扫描和管理Bean进行下载。
本文参考:https://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/52861403
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/chunqiuwei/article/details/16115135