tensorflow 机器学习 波士顿房价预测 笔记
机器学习Machine Learning
机器学习(Machine Learning, ML)是一门多领域交叉学科,涉及概率论、统计学、逼近论、凸分析、算法复杂度理论等多门学科。专门研究计算机怎样模拟或实现人类的学习行为,以获取新的知识或技能,重新组织已有的知识结构使之不断改善自身的性能。
它是人工智能的核心,是使计算机具有智能的根本途径,其应用遍及人工智能的各个领域,它主要使用归纳、综合而不是演绎。
我学习的机器学习问题两种:
1.分类问题
2.线性回归问题
波士顿房价预测属于线性回归问题
学习了吴恩达老师的机器学习
波士顿房价预测
一、安装tensorflow
安装很简单,如果你的网络流程的话,最好可以科学上网
官方安装简单
使用 Python 的 pip 软件包管理器安装 TensorFlow
没有安装pip的需要先安装pip
windows安装
pip install --upgrade tensorflow
验证安装效果:
python -c "import tensorflow as tf; tf.enable_eager_execution(); print(tf.reduce_sum(tf.random_normal([1000, 1000])))"
有结果输出没报错,就是安装成功了
二、开始写波士顿房价预测例子代码
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
# 数据路径 现在直接放在项目目录下,方便用
train_path = ["csv/train_data.csv", "csv/train_labels.csv"]
test_path = ["csv/test_data.csv", "csv/test_labels.csv"]
# 数据读取 直接用numpy提供的loadtxt函数进行读取csv格式的数据
# loadtxt函数的参数(路径, 读取csv数据的分隔符, 读取的csv的列数, 读取的格式)
train_data = np.loadtxt(train_path[0],delimiter=',',usecols=np.arange(0,13),encoding='UTF-8-sig')
train_labels = np.loadtxt(train_path[1],delimiter=',',usecols=(0),encoding='UTF-8-sig')
test_data = np.loadtxt(test_path[0],delimiter=',',usecols=np.arange(0,13),encoding='UTF-8-sig')
test_labels = np.loadtxt(test_path[1],delimiter=',',usecols=(0),encoding='UTF-8-sig')
# boston_housing = keras.datasets.boston_housing
# (train_data, train_labels), (test_data, test_labels) = boston_housing.load_data()
# Shuffle the training set
order = np.argsort(np.random.random(train_labels.shape))
train_data = train_data[order]
train_labels = train_labels[order]
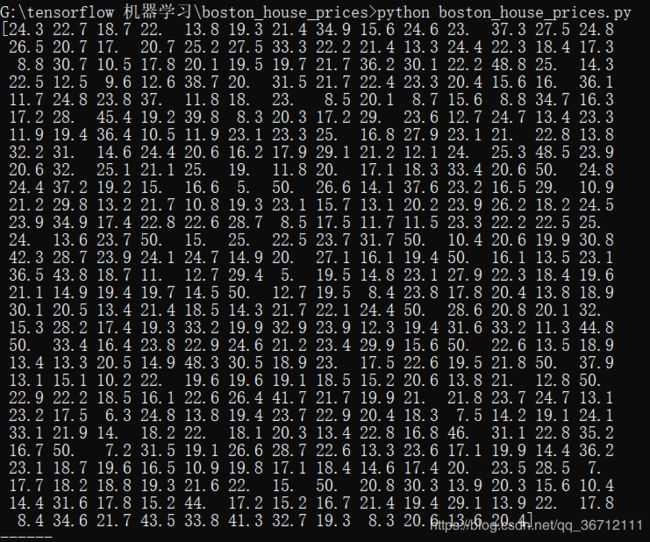
print(train_labels)
print('------')
print(train_data[0])
print(type(train_data))
print(len(train_data))
# print(train_labels)
# 没有id这个attribute
# print("Training set: {}".format(train_data.id)) # 404 examples, 13 features
print("Training set: {}".format(train_data.shape)) # 404 examples, 13 features
print("Testing set: {}".format(test_data.shape)) # 102 examples, 13 features
print(train_data[0]) # Display sample features, notice the different scales
import pandas as pd
column_names = ['CRIM', 'ZN', 'INDUS', 'CHAS', 'NOX', 'RM', 'AGE', 'DIS', 'RAD',
'TAX', 'PTRATIO', 'B', 'LSTAT']
df = pd.DataFrame(train_data, columns=column_names)
df.head()
print(df.head())
print(train_labels[0:10]) # Display first 10 entries
# Test data is *not* used when calculating the mean and std
mean = train_data.mean(axis=0)
std = train_data.std(axis=0)
train_data = (train_data - mean) / std
test_data = (test_data - mean) / std
print(train_data[0]) # First training sample, normalized
def build_model():
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(64, activation=tf.nn.relu,
input_shape=(train_data.shape[1],)),
keras.layers.Dense(64, activation=tf.nn.relu),
keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(0.001)
model.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['mae'])
return model
model = build_model()
model.summary()
# Display training progress by printing a single dot for each completed epoch
class PrintDot(keras.callbacks.Callback):
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs):
if epoch % 100 == 0: print('')
print('.', end='')
EPOCHS = 200
# Store training stats
history = model.fit(train_data, train_labels, epochs=EPOCHS,
validation_split=0.2, verbose=0,
callbacks=[PrintDot()])
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_history(history):
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Mean Abs Error [1000$]')
plt.plot(history.epoch, np.array(history.history['mean_absolute_error']),
label='Train Loss')
plt.plot(history.epoch, np.array(history.history['val_mean_absolute_error']),
label = 'Val loss')
plt.legend()
plt.ylim([0, 5])
plt.show()
plot_history(history)
model = build_model()
# The patience parameter is the amount of epochs to check for improvement
early_stop = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=20)
history = model.fit(train_data, train_labels, epochs=EPOCHS,
validation_split=0.2, verbose=0,
callbacks=[early_stop, PrintDot()])
plot_history(history)
[loss, mae] = model.evaluate(test_data, test_labels, verbose=0)
print("Testing set Mean Abs Error: ${:7.2f}".format(mae * 1000))
test_predictions = model.predict(test_data).flatten()
plt.scatter(test_labels, test_predictions)
plt.xlabel('True Values [1000$]')
plt.ylabel('Predictions [1000$]')
plt.axis('equal')
plt.xlim(plt.xlim())
plt.ylim(plt.ylim())
_ = plt.plot([-100, 100], [-100, 100])
plt.show()
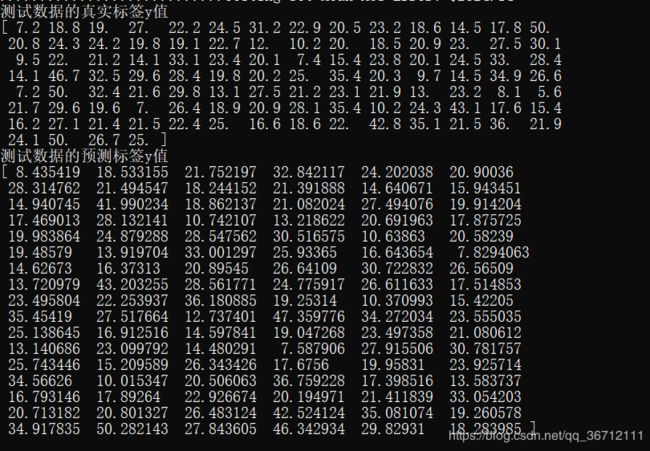
print("测试数据的真实标签y值")
print(test_labels)
print("测试数据的预测标签y值")
print(test_predictions)
test_predictions
np.savetxt('csv/test_predictions.csv', test_predictions, delimiter = ',')
error = test_predictions - test_labels
plt.hist(error, bins = 50)
plt.xlabel("Prediction Error [1000$]")
_ = plt.ylabel("Count")
plt.show()
三、运行结果
tensorflow简称tf
1.数据查看
2. tf构建好的神经网络模型

3.跑出来的结果,Train 预测的标签值,Val实际的标签值

4.跑的第二次

5.回归方程,和预测出来的值,拟合度不错