postman工具的json和XML请求格式以及数据接收和转换
程序员新手,第一次写博客,自己的工作记录和学习笔记,如有不当之处,欢迎指正。
在接口开发工程中,我们会经常使用postman模拟数据请求,用来调试或测试代码,其中经常遇到类似于数据格式转换问题,下面是我个人对自己已解决问题的总结.
直接上图:
1.json使用对象格式请求:
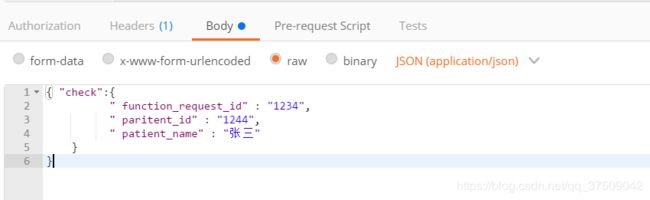
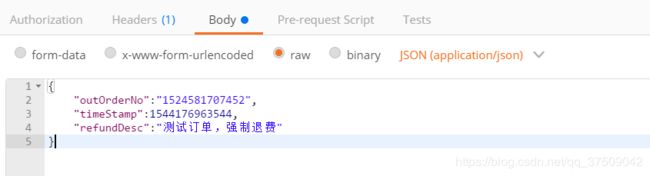
2.json直接传参数请求:
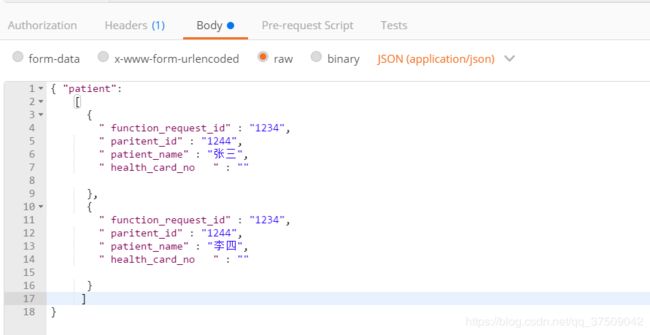
3.json对象数组
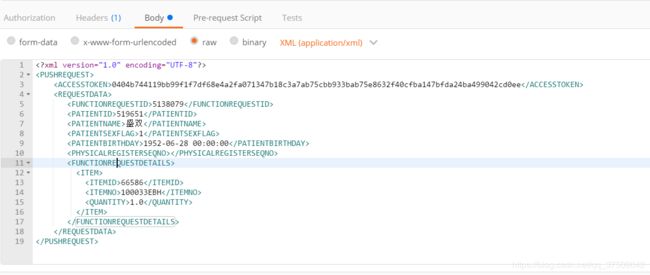
4.xml请求格式
json/xml格式的数据接收和处理:
数据接收方式有很多种,下面罗列一下我用过的方式:
1.使用HttpServletRequest 接收,将接收到的数据转为String,然后再做相应的处理。
接收数据代码 json/xml 格式请求均适用。
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/add",produces = {"text/plain;charset=UTF-8"})
public Object check(HttpServletRequest request) {
String respData="";
String mapStr = HttpDataUtil.getReqData(request);
logger.info(mapStr);
String code = checkService.applyCheck(mapStr);
try {
respData = HttpDataUtil.buildPushResponse(code,"000000".equals(code) ? "接收成功":"内部异常",null);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return respData;
}
json/xml 格式的请求的数据处理
xml格式的处理。
@Override
public String applyCheck(String xmlStr) {
String result = "000500";
try {
//将String转为map
Map<String, Object> map = XmlJsonUtil.xml2map(xmlStr, true);
//直接获取map里面的对象
Map<String, Object> pushRequest = (Map<String, Object>) map.get("PUSHREQUEST");
Map<String, Object> requestData = (Map<String, Object>) pushRequest.get("REQUESTDATA");
Map<String, Object> functionRequestDetails = (Map<String, Object>) requestData.get("FUNCTIONREQUESTDETAILS");
//map转bean
Check check = (Check) MapUtil.transMap2Bean2(requestData, Check.class);
result = checkRequest(check);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("异常信息:" + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
return result;
}
return result;
}
json格式的处理
@Override
public String checkFromSelect(String jsonStr) {
String result = "000500";
try {
//string 转map
Map<String, Object> map = XmlJsonUtil.json2Map(jsonStr);
//这里可以直接获取到check对象
Map<String, Object> objectMap =(Map<String, Object>) map.get("check");
//如果是对象数组,这边获取到的是数组,可以使用for循环取到object再转换
/* ArrayList list =(Map) map.get("check");
for (Check check : list ) {
Map objectmap = (Map)list;
Check check = (Check) MapUtil.transMap2Bean2(objectmap, Check.class);
}*/
//map转bean
Check check = (Check) MapUtil.transMap2Bean2(objectMap, Check.class);
result = checkRequest(check);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("异常信息:" + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
return result;
}
return result;
}
还有一些用过的接收数据方式:
1)使用 @RequestBody注解接收
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/getPatient")
public RespDataModel getPatientInfo(@RequestBody Map patientMap,HttpSession session) {
try{
Patient patient = appPatientService.getPatientByNo((String)patientMap.get("health_card_no"));
session.setAttribute("patientInfo",patient);
if(patient == null){
return RespData.setData(RespData.ERROR, "查询无数据", null);
}
return RespData.setData(RespData.OK, "查询成功", patient);
}catch (Exception e) {
return RespData.setData(RespData.ERROR, "查询异常", null);
}
}
2)使用 @RequestParam注解和HttpServletRequest 接收
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/formUpload")
public RespDataModel formUpload(
@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile[] files,
@RequestParam("account_id") int accountId,HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Map<String, Object> retData = new HashMap<String, Object>();
String path = request.getSession().getServletContext()
.getRealPath("/image/appImg");
Img img =new Img();
img.setCreate_user(Long.parseLong(String.valueOf(accountId)));
if (appImgService.uploadImgList(files, img, path,"/image/appImg")) {
return RespData.setData(RespData.OK, "上传成功", retData);
} else {
return RespData.setData(RespData.ERROR, "上传失败", retData);
}
}