Mybatis之SqlSessionFactoryBean源码初步解析(三)mapper的动态代理
见鬼,这个csdn 有bug 吧, 粘贴复制然后卡死,gg归零了解一下
sql的动态代理(反推)
我跟着第二篇后面继续写,在第二篇的时候我们提到了knowMappers代码如下:
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
当我看到MapperProxyFactory的时候我看到了proxy这个单词就知道是一个动态代理。我们点进去看
Mapper接口(每个mapper的interface)的代理类
public MapperProxyFactory(Class mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class getMapperInterface() {
return this.mapperInterface;
}
public Map getMethodCache() {
return this.methodCache;
}
//这里就是对于mapper接口中所有的方法进行动态代理,代理对象是mapperProxy (这里的mapperInterface就是代表**某一个**mapper接口)
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{this.mapperInterface}, mapperProxy);
}
//代理对象就是在这里生成的
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, this.mapperInterface, this.methodCache);
return this.newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
MapperProxy 类中的invoke方法做了什么
如果方法的类型是Object 就直接掉用接口方法(不知道这边是什么意思,到时候补充)
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
if (this.isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return this.invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable var5) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var5);
}
MapperMethod mapperMethod = this.cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args);
}
进入cachedMapperMethod 方法中
查看缓存中是否存在,存在直接取出来用 。
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
//若存在则直接调用
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
//不存在则去生成语句去
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
若不存在则会new MapperMethod 就会调到构造方法里面去(第一次启动都是不存在的)
sqlCommand 里面会获取configuartion里面的MapperStatement 这里面封装了解析的xml (ps :博主写过的一个解析xml语句的地址)
根据mapperStatement 来确定返回值类型以及查询类型等等比如如果returnType=List,那么就会执行executeForMany 。
public MapperMethod(Class mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
在executeForMany最终执行的是sqlsession.方法
sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds)
sqlsession是一个接口我们最终需要掉哪个实现类呢?先看下面的解析 【1】
动态代理在哪里调用的
我们上面看了动态代理是怎么执行的。但是只有调用newInstance()这个方法才能注册动态代理。这个方法我们crtl+shift+g
1)发现是MapperRegistry调用的
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
2)而MapperRegistry的getMapper方法是由Configuration的 getMapper 方法调用的
3)Configuration 中的getMapper方法是由 ?
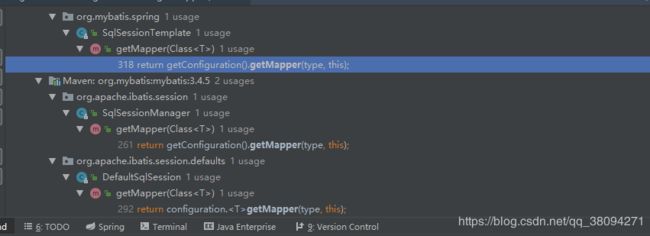
这里按快捷键会发现 有三个类里面调用了 这个方法。于是我们不清楚是哪个类调用的了,但是我发现这三个类都实现了sqlSession的接口
然而sqlSession的getMapper 方法是由MapperFactoryBean 的getObject()实现的,
MapperFactoryBean 实现的接口与继承的类
public class MapperFactoryBean extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean
FactoryBean 接口必须实现的两个方法 一个是getObject(),另外一个是getObjectType();当实现这个接口的类实例化的时候会自动的调用。
SqlSessionDaoSupport 这个类我们点进去看
private SqlSession sqlSession;
private boolean externalSqlSession;
public void setSqlSessionFactory(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
if (!this.externalSqlSession) {
this.sqlSession = new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
public void setSqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSessionTemplate;
this.externalSqlSession = true;
}
找半天才发现, 这个this.sqlSession = new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
于是得出个结论,MapperFactoryBean 中的sqlSession 是sqlSessionTemplate类型,所以第三步,Configuartion 是由sqlSessionTemplate调用的。
4)sqlSessionTemplate是由MapperFactoryBean调用的
由此我们再回到**[1]**标记位的问题,那么调用sqlsession的方法就会调用sqlsessionTemplate的方法,点进去后
我们看到了sqlSessionProxy这个东西,是哪里初始化的呢?
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
return this.sqlSessionProxy. selectList(statement, parameter, rowBounds);
}
是在SqlSessionTemplate的构造方法中初始化的, newProxyInstance一看就是做了动态代理。
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
所以当sqlSession的方法被调用的时候就会走到SqlSessionInterceptor,这个继承了InvokeHandle类,将调用invoke方法;
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(
SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
invoke里面第一句就是getSession()
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Creating a new SqlSession");
}
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
暂时不知道为什么 这个sessionFactory是DefaultSessionFactory.但是debug进去就是。。。
先不管他继续往下走
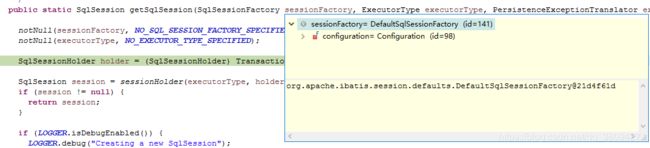
session为null,走sessionFactory.openSession();
这边会走到openSessionFromDataSource方法
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);这句代码就是加载过滤器
点进去有如下代码 ,
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
interceptorChain意思是拦截器链,将所有的拦截器遍历如下:
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
笔者自己写了个拦截器:
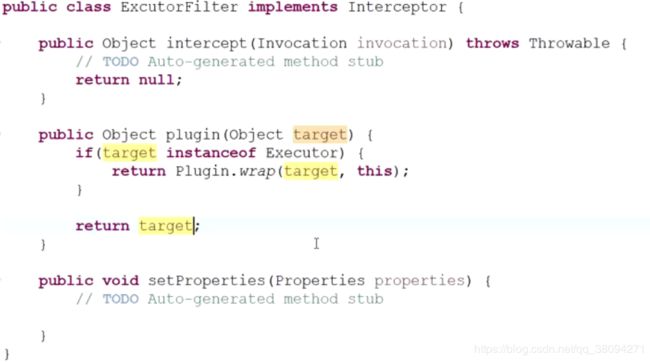
先判断是不是Executor类型的 我们传进来的是simpleExecutor所以是的,然后调用warp 方法;
warp 实际上就是让每个类对各个定义的Signature数组做动态代理(不早了 这边细一点的话, 以后写)
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
Map> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class type = target.getClass();
Class[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}