Python 井字棋
用python写井字棋小游戏井字棋简介:井字棋又称三子棋,英文名为Tic Tac Toe。具体玩法为在一个3x3的棋盘上,一个玩家用X做棋子,另一个玩家用O做棋子,谁先在棋盘上的一行、一列或对角线上画满三个棋子,即可获胜,如果棋盘下满无人胜出,即为平局。
井字棋在与电脑对战时涉及到了简单的人工智能,人工智能分为四个等级:
巅峰级——已经实现了无法超越的最优能力
超越人类级——比所有人类的能力都要强
强人类级——比大多数人类的能力要强
弱人类级——比大多数人类的能力要弱
而在井字棋下的人工智能可以达到巅峰级—————人类永远无法战胜电脑。这是游戏本身性质所导致,同龄人之间下井字棋,多下几把后便很难出现胜方,只要掌握了其中的套路,认真一下,就不再会输了。
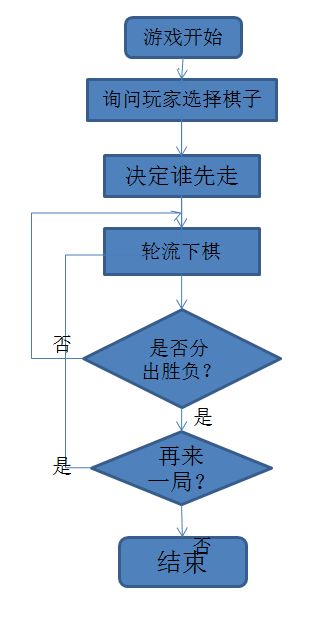
这是游戏设计的流程图,源代码也是按照这个思路来的。
关于落子问题
由于只能采用键盘输入,所以需要对棋盘进行坐标表示。有两种方式,一种是用横竖坐标来表示,这种方法常见于围棋和五子棋中。井字棋是一种简单的棋盘游戏,只有9个棋子位,所以用另一种更简单的表示方法,即直接用1-9个9个数字来表示位置,其索引顺序与键盘上的数字键排列一致,下棋时看着数字键下,较为简便。
计算机的算法--寻找最佳落子位置
首先简单的将棋盘划分为三个部分——中心(1),角(4),边(4)。中心虽然只有一个但却不是最重要的,三个部分落子的优先顺序依次为:角、中心、边。这是关于井字棋最有算法的相关文章链接,请自行查阅,http://www.guokr.com/article/4754/
因此,井字棋的AI算法计算最佳落子位置的顺序如下:
- 直接落子获胜
- 阻止玩家获胜
- 在角上落子
- 在中心落子
- 在边上落子
程序源代码
# Tic Tac Toe
import random
def drawBoard(board):
# 打印棋盘
# "board"是长度为10的列表,为了方便输入,忽略第一个元素board[0]
print('\n\n\n\n')
print('\t\t\t┌─┬─┬─┐')
print('\t\t\t│'+board[7]+' │'+board[8]+' │'+board[9]+' │')
print('\t\t\t├─┼─┼─┤')
print('\t\t\t│'+board[4]+' │'+board[5]+' │'+board[6]+' │')
print('\t\t\t├─┼─┼─┤')
print('\t\t\t│'+board[1]+' │'+board[2]+' │'+board[3]+' │')
print('\t\t\t└─┴─┴─┘')
def inputPlayerLetter():
# 让玩家选择棋子
# 返回一个列表,第一个是玩家的棋子,第二个是电脑的
letter = ''
while not (letter == 'X' or letter == 'O'):
print('Do you want to be X or O?')
letter = input().upper()
if letter == 'X':
return ['X', 'O']
else:
return ['O', 'X']
def whoGoesFirst():
# 随机产生谁先走
if random.randint(0, 1) == 0:
return 'computer'
else:
return 'player'
def playAgain():
# 再玩一次?输入yes或y返回True
print('Do you want to play again? (yes or no)')
return input().lower().startswith('y')
def makeMove(board, letter, move):
#落子
board[move] = letter
def isWinner(bo, le):
# 判断所给的棋子是否获胜
# 参数为棋盘上的棋子(列表)和棋子符号
# 以下是所有可能胜利的情况,共8种
return ((bo[7] == le and bo[8] == le and bo[9] == le) or
(bo[4] == le and bo[5] == le and bo[6] == le) or
(bo[1] == le and bo[2] == le and bo[3] == le) or
(bo[7] == le and bo[4] == le and bo[1] == le) or
(bo[8] == le and bo[5] == le and bo[2] == le) or
(bo[9] == le and bo[6] == le and bo[3] == le) or
(bo[7] == le and bo[5] == le and bo[3] == le) or
(bo[9] == le and bo[5] == le and bo[1] == le))
def getBoardCopy(board):
# 复制一份棋盘,供电脑落子时使用
dupeBoard = []
for i in board:
dupeBoard.append(i)
return dupeBoard
def isSpaceFree(board, move):
# 判断这个位置是否有子,没子返回True
return board[move] == ' '
def getPlayerMove(board):
# 玩家落子
move = ' '
while move not in '1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9'.split() or not isSpaceFree(board, int(move)):
print('What is your next move? (1-9)')
move = input()
return int(move)
def chooseRandomMoveFromList(board, movesList):
# 随机返回一个可以落子的坐标
# 如果没有所给的movesList中没有可以落子的,返回None
possibleMoves = []
for i in movesList:
if isSpaceFree(board, i):
possibleMoves.append(i)
if len(possibleMoves) != 0:
return random.choice(possibleMoves)
else:
return None
def getComputerMove(board, computerLetter):
# 确定电脑的落子位置
if computerLetter == 'X':
playerLetter = 'O'
else:
playerLetter = 'X'
# Tic Tac Toe AI核心算法:
# 首先判断电脑方能否通过一次落子直接获得游戏胜利
for i in range(1, 10):
copy = getBoardCopy(board)
if isSpaceFree(copy, i):
makeMove(copy, computerLetter, i)
if isWinner(copy, computerLetter):
return i
# 判断玩家下一次落子能否获得胜利,如果能,给它堵上
for i in range(1, 10):
copy = getBoardCopy(board)
if isSpaceFree(copy, i):
makeMove(copy, playerLetter, i)
if isWinner(copy, playerLetter):
return i
# 如果角上能落子的话,在角上落子
move = chooseRandomMoveFromList(board, [1, 3, 7, 9])
if move != None:
return move
# 如果能在中心落子的话,在中心落子
if isSpaceFree(board, 5):
return 5
# 在边上落子
return chooseRandomMoveFromList(board, [2, 4, 6, 8])
def isBoardFull(board):
# 如果棋盘满了,返回True
for i in range(1, 10):
if isSpaceFree(board, i):
return False
return True
print('Welcome to Tic Tac Toe!')
while True:
# 更新棋盘
theBoard = [' '] * 10
playerLetter, computerLetter = inputPlayerLetter()
turn = whoGoesFirst()
print('The ' + turn + ' will go first.')
gameIsPlaying = True
while gameIsPlaying:
if turn == 'player':
# 玩家回合
drawBoard(theBoard)
move = getPlayerMove(theBoard)
makeMove(theBoard, playerLetter, move)
if isWinner(theBoard, playerLetter):
drawBoard(theBoard)
print('Hooray! You have won the game!')
gameIsPlaying = False
else:
if isBoardFull(theBoard):
drawBoard(theBoard)
print('The game is a tie!')
break
else:
turn = 'computer'
else:
# 电脑回合
move = getComputerMove(theBoard, computerLetter)
makeMove(theBoard, computerLetter, move)
if isWinner(theBoard, computerLetter):
drawBoard(theBoard)
print('The computer has beaten you! You lose.')
gameIsPlaying = False
else:
if isBoardFull(theBoard):
drawBoard(theBoard)
print('The game is a tie!')
break
else:
turn = 'player'
if not playAgain():
break