(python)多线程
线程指的是一条流水线的工作过程。进程根本就不是一个执行单位,其实是一个资源单位。
一个进程内必须带一个线程,因为线程才是执行单位。
在传统的操作系统中,每一个进程有一个资源空间,而默认就有一个控制线程.线程是一条流水线工作过程,而一条流水线必须在一个车间内.一个车间的工作过程,就相当于一个进程,车间负责把资源整合到一起,让这些资源给多条流水线使用.
所以,进程是只是用来开辟资源空间,线程是cpu上的执行单位.
多线程的概念就是在一个进程内有多个线程,多个线程共享该进程的空间资源.
进程vs线程
1、同一进程内的线程们共享该进程内资源,不同进程内的线程资源肯定是隔离的.
2、创建线程的开销比创建进程的开销小的多.
开启线程的两种方式:
方式一:
from threading import Thread
def task(name):
print('%s is running' %name)
if __name__=='__main__':
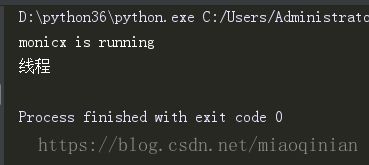
t=Thread(target=task,args=('monicx',))
t.start()
print('主线程')运行结果:
如果用进程启这一段代码的话:
from multiprocessing import Process
def task(name):
print('%s is running' %name)
if __name__=='__main__':
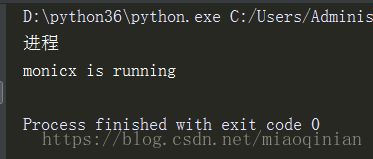
t=Process(target=task,args=('monicx',))
t.start()
print('进程')
结果就是这样:
我们可以看出开启一个线程的速度比启一个进程快的多的多.
看下面一段代码:
from threading import Thread
x=1000
def task(name):
global x
x=0
print('%s is running' %name)
if __name__=='__main__':
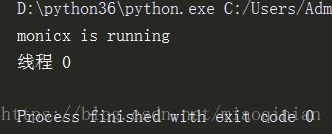
t=Thread(target=task,args=('monicx',))
t.start()
print('线程',x)运行结果:
证明线程是共享进程里面的资源.
方式二:
from threading import Thread
import time
class MyThread(Thread):
def run(self):
print('%s is running ' %self.name)
time.sleep(3)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t=MyThread()
t.start()
print('线程')运行结果:
线程的其它用法:
is_alive():判断某线程是否还活着
active_count():统计一个进程内所有线程数量。
enumerate():列表的形式得到进程里每个线程的信息。
current_thread():定位当前线程
from threading import Thread,current_thread,active_count,enumerate
import time
def task():
print('%s is running' %current_thread().name)
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t1= Thread(target=task,name='第一个线程')
t2=Thread(target=task)
t3=Thread(target=task)
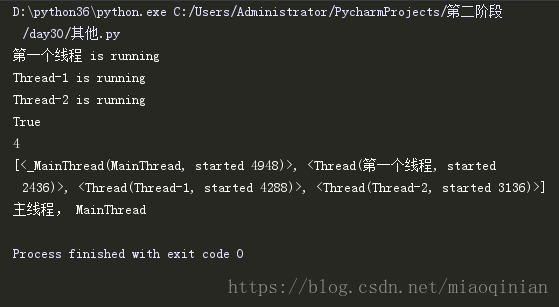
t1.start()
t2.start()
t3.start()
print(t1.is_alive())
print(active_count())
print(enumerate())
print('主线程,',current_thread().name)运行结果:
守护线程:
import time
from threading import Thread
def foo():
print('我是守护线程的东东')
time.sleep(1)
print('我也是守护线程的东东')
def bar():
print('我是子线程的西西')
time.sleep(3)
print('我还是子线程的西西')
if __name__=='__main__':
t1=Thread(target=foo)
t2=Thread(target=bar)
t1.daemon=True
t1.start()
t2.start()
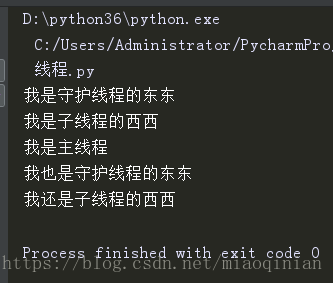
print('我是主线程')运行结果:
但如果延长守护线程的运行时间,从1秒改成5秒:
运行的结果就变为:
主进程代码运行完,守护进程就挂了.但从上面的结果发现:主线程中有一或多条子线程在运行.守护线程要等主线程中的其它子线程都运行完了,才会挂掉.
线程锁:
我们来开100个线程。每开一次线程的时候,让统计数x减1,在执行减的过程中,我们让线程休息0.1秒。
import time
from threading import Thread
x=100
def task():
global x
temp=x
time.sleep(0.1)
x=temp-1
if __name__ == '__main__':
start=time.time()
t_1=[]
for i in range(100):
t=Thread(target=task)
t_1.append(t)
t.start()
for t in t_1:
t.join()
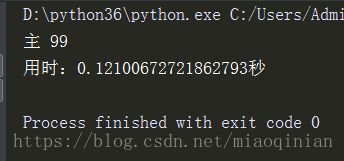
print('主',x)
print('用时:%s秒'%(time.time()-start))运行结果:
可以发现,运行的结果不是我们相要的结果.因为线程开启的速度非常的快。0.1秒的时间内够所有的线程启动起来,拿到的x都是100,所以运行结果x不为0为99。
线程同步能够保证多个线程安全访问竞争资源,最简单的同步机制是引入互斥锁。互斥锁为资源引入一个状态:锁定/非锁定。某个线程要更改共享数据时,先将其锁定,此时资源的状态为“锁定”,其他线程不能更改;直到该线程释放资源,将资源的状态变成“非锁定”,其他的线程才能再次锁定该资源。互斥锁保证了每次只有一个线程进行写入操作,从而保证了多线程情况下数据的正确性。
import time
from threading import Thread,Lock
mutex=Lock()
x=100
def task():
global x
mutex.acquire()
temp=x
time.sleep(0.1)
x=temp-1
mutex.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
start=time.time()
t_1=[]
for i in range(100):
t=Thread(target=task)
t_1.append(t)
t.start()
for t in t_1:
t.join()
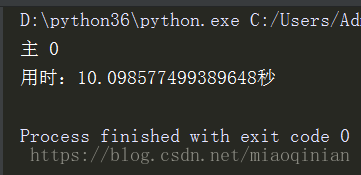
print('主',x)
print('用时:%s秒'%(time.time()-start))运行结果:
从运行时间上看,它牺牲了效率,换取了数据的安全(准确)。
线程死锁:
我们自己来写一个下面的死锁
from threading import Thread,Lock
import time
mutexA=Lock()
mutexB=Lock()
class MyThread(Thread):
def run(self):
self.f1()
self.f2()
def f1(self):
mutexA.acquire()
print('%s 拿到了A锁' %self.name)
mutexB.acquire()
print('%s 拿到了B锁' % self.name)
mutexB.release()
mutexA.release()
def f2(self):
mutexB.acquire()
print('%s 拿到了B锁' %self.name )
time.sleep(0.1)
mutexA.acquire()
print('%s 拿到了A锁' % self.name)
mutexA.release()
mutexB.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(5):
t=MyThread()
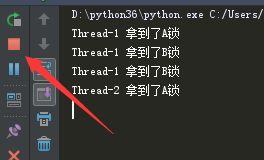
t.start()无论怎么运行,结果都是如下,卡在了Thread-2 拿到了A锁:
为了解决这个问题,我们可以用上递归锁
递归锁:
RLock内部维护着一个Lock和一个counter变量,counter记录了acquire的次数,从而使得资源可以被多次require。直到一个线程所有的acquire都被release,其他的线程才能获得资源。还是以上面的例子为例,如果使用RLock代替Lock,则不会发生死锁:from threading import Thread,RLock
import time
mutexB=mutexA=RLock()
class MyThread(Thread):
def run(self):
self.f1()
self.f2()
def f1(self):
mutexA.acquire()
print('%s 拿到了A锁' %self.name)
mutexB.acquire()
print('%s 拿到了B锁' % self.name)
mutexB.release()
mutexA.release()
def f2(self):
mutexB.acquire()
print('%s 拿到了B锁' %self.name )
time.sleep(0.1)
mutexA.acquire()
print('%s 拿到了A锁' % self.name)
mutexA.release()
mutexB.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(5):
t=MyThread()
用上递归锁,无论怎么执行都不会产生死锁的现象.运行结果:
信号量(Sempahore):
信号量,是一个变量,控制着对公共资源或者临界区的访问。信号量维护着一个计数器,指定可同时访问资源或者进入临界区的线程数。 每次有一个线程获得信号量时,计数器-1。若计数器为0,其他线程就停止访问信号量,直到另一个线程释放信号量。每当调用acquire()时,内置计数器-1 每当调用release()时,内置计数器+1。
下面我们用信号量来模拟10个人上4个蹲位的wc。
from threading import Thread,Semaphore,current_thread
import time,random
sm=Semaphore(4)
def go_wc():
sm.acquire()
print('%s 上wc ing'%current_thread().getName())
time.sleep(random.randint(1,3))
sm.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(10):
t=Thread(target=go_wc)
t.start()
运行结果:
关于线程了解更多,可看下面它的源码:
class Thread:
"""A class that represents a thread of control.
This class can be safely subclassed in a limited fashion. There are two ways
to specify the activity: by passing a callable object to the constructor, or
by overriding the run() method in a subclass.
"""
_initialized = False
# Need to store a reference to sys.exc_info for printing
# out exceptions when a thread tries to use a global var. during interp.
# shutdown and thus raises an exception about trying to perform some
# operation on/with a NoneType
_exc_info = _sys.exc_info
# Keep sys.exc_clear too to clear the exception just before
# allowing .join() to return.
#XXX __exc_clear = _sys.exc_clear
def __init__(self, group=None, target=None, name=None,
args=(), kwargs=None, *, daemon=None):
"""This constructor should always be called with keyword arguments. Arguments are:
*group* should be None; reserved for future extension when a ThreadGroup
class is implemented.
*target* is the callable object to be invoked by the run()
method. Defaults to None, meaning nothing is called.
*name* is the thread name. By default, a unique name is constructed of
the form "Thread-N" where N is a small decimal number.
*args* is the argument tuple for the target invocation. Defaults to ().
*kwargs* is a dictionary of keyword arguments for the target
invocation. Defaults to {}.
If a subclass overrides the constructor, it must make sure to invoke
the base class constructor (Thread.__init__()) before doing anything
else to the thread.
"""
assert group is None, "group argument must be None for now"
if kwargs is None:
kwargs = {}
self._target = target
self._name = str(name or _newname())
self._args = args
self._kwargs = kwargs
if daemon is not None:
self._daemonic = daemon
else:
self._daemonic = current_thread().daemon
self._ident = None
self._tstate_lock = None
self._started = Event()
self._is_stopped = False
self._initialized = True
# sys.stderr is not stored in the class like
# sys.exc_info since it can be changed between instances
self._stderr = _sys.stderr
# For debugging and _after_fork()
_dangling.add(self)
def _reset_internal_locks(self, is_alive):
# private! Called by _after_fork() to reset our internal locks as
# they may be in an invalid state leading to a deadlock or crash.
self._started._reset_internal_locks()
if is_alive:
self._set_tstate_lock()
else:
# The thread isn't alive after fork: it doesn't have a tstate
# anymore.
self._is_stopped = True
self._tstate_lock = None
def __repr__(self):
assert self._initialized, "Thread.__init__() was not called"
status = "initial"
if self._started.is_set():
status = "started"
self.is_alive() # easy way to get ._is_stopped set when appropriate
if self._is_stopped:
status = "stopped"
if self._daemonic:
status += " daemon"
if self._ident is not None:
status += " %s" % self._ident
return "<%s(%s, %s)>" % (self.__class__.__name__, self._name, status)
def start(self):
"""Start the thread's activity.
It must be called at most once per thread object. It arranges for the
object's run() method to be invoked in a separate thread of control.
This method will raise a RuntimeError if called more than once on the
same thread object.
"""
if not self._initialized:
raise RuntimeError("thread.__init__() not called")
if self._started.is_set():
raise RuntimeError("threads can only be started once")
with _active_limbo_lock:
_limbo[self] = self
try:
_start_new_thread(self._bootstrap, ())
except Exception:
with _active_limbo_lock:
del _limbo[self]
raise
self._started.wait()
def run(self):
"""Method representing the thread's activity.
You may override this method in a subclass. The standard run() method
invokes the callable object passed to the object's constructor as the
target argument, if any, with sequential and keyword arguments taken
from the args and kwargs arguments, respectively.
"""
try:
if self._target:
self._target(*self._args, **self._kwargs)
finally:
# Avoid a refcycle if the thread is running a function with
# an argument that has a member that points to the thread.
del self._target, self._args, self._kwargs
def _bootstrap(self):
# Wrapper around the real bootstrap code that ignores
# exceptions during interpreter cleanup. Those typically
# happen when a daemon thread wakes up at an unfortunate
# moment, finds the world around it destroyed, and raises some
# random exception *** while trying to report the exception in
# _bootstrap_inner() below ***. Those random exceptions
# don't help anybody, and they confuse users, so we suppress
# them. We suppress them only when it appears that the world
# indeed has already been destroyed, so that exceptions in
# _bootstrap_inner() during normal business hours are properly
# reported. Also, we only suppress them for daemonic threads;
# if a non-daemonic encounters this, something else is wrong.
try:
self._bootstrap_inner()
except:
if self._daemonic and _sys is None:
return
raise
def _set_ident(self):
self._ident = get_ident()
def _set_tstate_lock(self):
"""
Set a lock object which will be released by the interpreter when
the underlying thread state (see pystate.h) gets deleted.
"""
self._tstate_lock = _set_sentinel()
self._tstate_lock.acquire()
def _bootstrap_inner(self):
try:
self._set_ident()
self._set_tstate_lock()
self._started.set()
with _active_limbo_lock:
_active[self._ident] = self
del _limbo[self]
if _trace_hook:
_sys.settrace(_trace_hook)
if _profile_hook:
_sys.setprofile(_profile_hook)
try:
self.run()
except SystemExit:
pass
except:
# If sys.stderr is no more (most likely from interpreter
# shutdown) use self._stderr. Otherwise still use sys (as in
# _sys) in case sys.stderr was redefined since the creation of
# self.
if _sys and _sys.stderr is not None:
print("Exception in thread %s:\n%s" %
(self.name, _format_exc()), file=_sys.stderr)
elif self._stderr is not None:
# Do the best job possible w/o a huge amt. of code to
# approximate a traceback (code ideas from
# Lib/traceback.py)
exc_type, exc_value, exc_tb = self._exc_info()
try:
print((
"Exception in thread " + self.name +
" (most likely raised during interpreter shutdown):"), file=self._stderr)
print((
"Traceback (most recent call last):"), file=self._stderr)
while exc_tb:
print((
' File "%s", line %s, in %s' %
(exc_tb.tb_frame.f_code.co_filename,
exc_tb.tb_lineno,
exc_tb.tb_frame.f_code.co_name)), file=self._stderr)
exc_tb = exc_tb.tb_next
print(("%s: %s" % (exc_type, exc_value)), file=self._stderr)
# Make sure that exc_tb gets deleted since it is a memory
# hog; deleting everything else is just for thoroughness
finally:
del exc_type, exc_value, exc_tb
finally:
# Prevent a race in
# test_threading.test_no_refcycle_through_target when
# the exception keeps the target alive past when we
# assert that it's dead.
#XXX self._exc_clear()
pass
finally:
with _active_limbo_lock:
try:
# We don't call self._delete() because it also
# grabs _active_limbo_lock.
del _active[get_ident()]
except:
pass
def _stop(self):
# After calling ._stop(), .is_alive() returns False and .join() returns
# immediately. ._tstate_lock must be released before calling ._stop().
#
# Normal case: C code at the end of the thread's life
# (release_sentinel in _threadmodule.c) releases ._tstate_lock, and
# that's detected by our ._wait_for_tstate_lock(), called by .join()
# and .is_alive(). Any number of threads _may_ call ._stop()
# simultaneously (for example, if multiple threads are blocked in
# .join() calls), and they're not serialized. That's harmless -
# they'll just make redundant rebindings of ._is_stopped and
# ._tstate_lock. Obscure: we rebind ._tstate_lock last so that the
# "assert self._is_stopped" in ._wait_for_tstate_lock() always works
# (the assert is executed only if ._tstate_lock is None).
#
# Special case: _main_thread releases ._tstate_lock via this
# module's _shutdown() function.
lock = self._tstate_lock
if lock is not None:
assert not lock.locked()
self._is_stopped = True
self._tstate_lock = None
def _delete(self):
"Remove current thread from the dict of currently running threads."
# Notes about running with _dummy_thread:
#
# Must take care to not raise an exception if _dummy_thread is being
# used (and thus this module is being used as an instance of
# dummy_threading). _dummy_thread.get_ident() always returns -1 since
# there is only one thread if _dummy_thread is being used. Thus
# len(_active) is always <= 1 here, and any Thread instance created
# overwrites the (if any) thread currently registered in _active.
#
# An instance of _MainThread is always created by 'threading'. This
# gets overwritten the instant an instance of Thread is created; both
# threads return -1 from _dummy_thread.get_ident() and thus have the
# same key in the dict. So when the _MainThread instance created by
# 'threading' tries to clean itself up when atexit calls this method
# it gets a KeyError if another Thread instance was created.
#
# This all means that KeyError from trying to delete something from
# _active if dummy_threading is being used is a red herring. But
# since it isn't if dummy_threading is *not* being used then don't
# hide the exception.
try:
with _active_limbo_lock:
del _active[get_ident()]
# There must not be any python code between the previous line
# and after the lock is released. Otherwise a tracing function
# could try to acquire the lock again in the same thread, (in
# current_thread()), and would block.
except KeyError:
if 'dummy_threading' not in _sys.modules:
raise
def join(self, timeout=None):
"""Wait until the thread terminates.
This blocks the calling thread until the thread whose join() method is
called terminates -- either normally or through an unhandled exception
or until the optional timeout occurs.
When the timeout argument is present and not None, it should be a
floating point number specifying a timeout for the operation in seconds
(or fractions thereof). As join() always returns None, you must call
isAlive() after join() to decide whether a timeout happened -- if the
thread is still alive, the join() call timed out.
When the timeout argument is not present or None, the operation will
block until the thread terminates.
A thread can be join()ed many times.
join() raises a RuntimeError if an attempt is made to join the current
thread as that would cause a deadlock. It is also an error to join() a
thread before it has been started and attempts to do so raises the same
exception.
"""
if not self._initialized:
raise RuntimeError("Thread.__init__() not called")
if not self._started.is_set():
raise RuntimeError("cannot join thread before it is started")
if self is current_thread():
raise RuntimeError("cannot join current thread")
if timeout is None:
self._wait_for_tstate_lock()
else:
# the behavior of a negative timeout isn't documented, but
# historically .join(timeout=x) for x<0 has acted as if timeout=0
self._wait_for_tstate_lock(timeout=max(timeout, 0))
def _wait_for_tstate_lock(self, block=True, timeout=-1):
# Issue #18808: wait for the thread state to be gone.
# At the end of the thread's life, after all knowledge of the thread
# is removed from C data structures, C code releases our _tstate_lock.
# This method passes its arguments to _tstate_lock.acquire().
# If the lock is acquired, the C code is done, and self._stop() is
# called. That sets ._is_stopped to True, and ._tstate_lock to None.
lock = self._tstate_lock
if lock is None: # already determined that the C code is done
assert self._is_stopped
elif lock.acquire(block, timeout):
lock.release()
self._stop()
@property
def name(self):
"""A string used for identification purposes only.
It has no semantics. Multiple threads may be given the same name. The
initial name is set by the constructor.
"""
assert self._initialized, "Thread.__init__() not called"
return self._name
@name.setter
def name(self, name):
assert self._initialized, "Thread.__init__() not called"
self._name = str(name)
@property
def ident(self):
"""Thread identifier of this thread or None if it has not been started.
This is a nonzero integer. See the thread.get_ident() function. Thread
identifiers may be recycled when a thread exits and another thread is
created. The identifier is available even after the thread has exited.
"""
assert self._initialized, "Thread.__init__() not called"
return self._ident
def is_alive(self):
"""Return whether the thread is alive.
This method returns True just before the run() method starts until just
after the run() method terminates. The module function enumerate()
returns a list of all alive threads.
"""
assert self._initialized, "Thread.__init__() not called"
if self._is_stopped or not self._started.is_set():
return False
self._wait_for_tstate_lock(False)
return not self._is_stopped
isAlive = is_alive
@property
def daemon(self):
"""A boolean value indicating whether this thread is a daemon thread.
This must be set before start() is called, otherwise RuntimeError is
raised. Its initial value is inherited from the creating thread; the
main thread is not a daemon thread and therefore all threads created in
the main thread default to daemon = False.
The entire Python program exits when no alive non-daemon threads are
left.
"""
assert self._initialized, "Thread.__init__() not called"
return self._daemonic
@daemon.setter
def daemon(self, daemonic):
if not self._initialized:
raise RuntimeError("Thread.__init__() not called")
if self._started.is_set():
raise RuntimeError("cannot set daemon status of active thread")
self._daemonic = daemonic
def isDaemon(self):
return self.daemon
def setDaemon(self, daemonic):
self.daemon = daemonic
def getName(self):
return self.name
def setName(self, name):
self.name = name
# The timer class was contributed by Itamar Shtull-Trauring