前言
iOS里的UI控件其实没有几个,界面基本就是围绕那么几个控件灵活展开,最难的应属UICollectionView了,因为它的可定制化程度最高,最灵活,值得我们去研究一番
目录
- ** UICollectionView的基本使用**
- ** 自定义布局整体思路**
- 实现瀑布流
- ** 每页多个Cell的水平滚动布局**
- 实现CoverFlow效果
- 轮转卡片
- 模仿今日头条实现Cell重排
- iOS9用系统属性实现Cell重排
- iOS10后UICollectionView的优化与预加载
1.UICollectionView的基本使用
- 创建UICollectionFlowLayout对象
- 根据flowlayout创建UICollectionView的对象
- 注册cell或头尾部视图
- 遵守协议
创建UICollectionFlowLayout对象
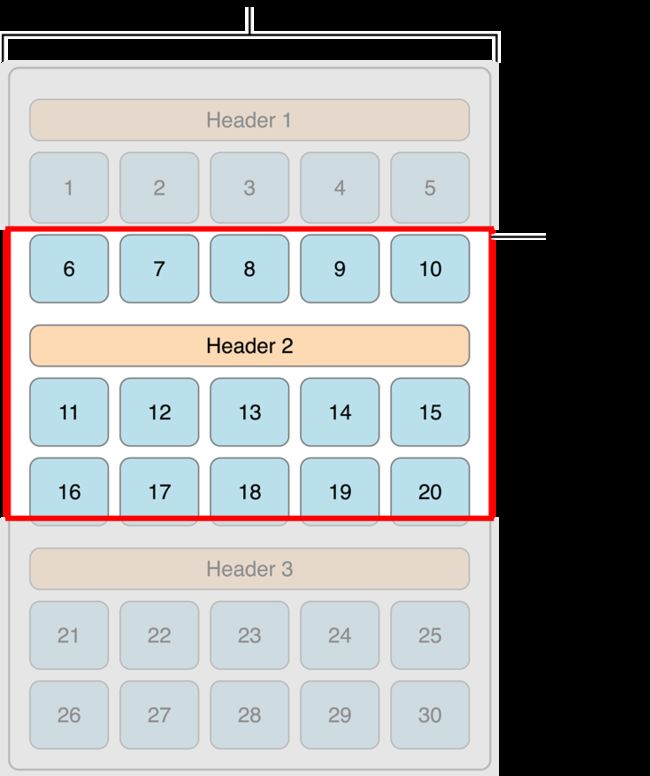
itemSizecell的大小scrollDirection滚动方向minimumInteritemSpacing与滚动方向相反的两个item之间最小距离,默认为10,它会根据你设定的这个值加上item的大小,来查看能一行最多能放多少个item,再把确定的item铺满总行,左右不留间隙,每个item之间的距离可能会比这个值大-
minimumLineSpacing滚动方向上item的间距,如果你的是水平滚动,留心水平间距别误设为minimumInteritemSpacing,笔者就上过这样的当,默认为10,在有规律的item之间严格按照设定的距离来,但是在无规律的item之间,就是每行item的最小距离,如下图绿色箭头所示
-
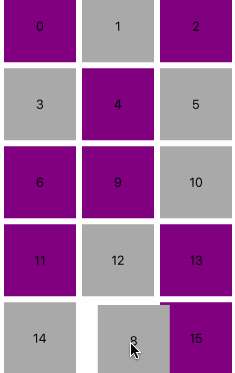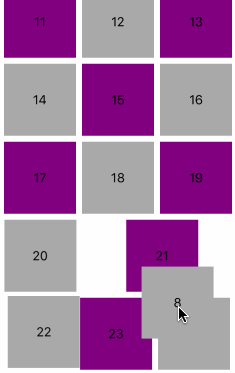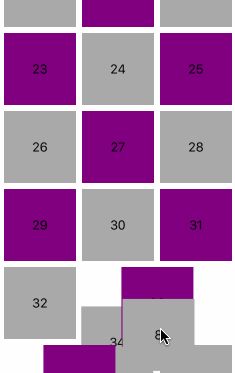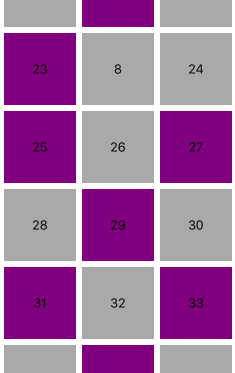
sectionInset每组的内切距,默认都为0,item会根据它来铺满总行,如下图所示
headerReferenceSizefooterReferenceSize每组的头部视图和尾部视图的大小sectionHeadersPinToVisibleBoundssectionHeadersPinToVisibleBoundsiOS 9.0 以后新特性,滚动时,每组的头部视图或尾部视图是否固定在头部或者尾部如果你的layout对象属性不是固定的,你需要实现
UICollectionViewDelegateFlowLayout协议里相应属性的数据源方法
let layout = UICollectionViewFlowLayout()
let margin: CGFloat = 8
let itemW = (view.bounds.width - margin * 4) / 3
let itemH = itemW
// 每个item的大小
layout.itemSize = CGSize(width: itemW, height: itemH)
// 最小行间距
layout.minimumLineSpacing = margin
// 最小item之间的距离
layout.minimumInteritemSpacing = margin
// 每组item的边缘切距
layout.sectionInset = UIEdgeInsetsMake(0, margin, 0, margin)
// 滚动方向
layout.scrollDirection = .vertical
// 创建collection
let collectionView = UICollectionView(frame: view.bounds, collectionViewLayout: layout)
// 遵守协议
collectionView.delegate = self
collectionView.dataSource = sel
注册cell和头尾部视图
- 使用
registerClass:forCellWithReuseIdentifier:或者registerNib:forCellWithReuseIdentifier:注册cell - 使用
registerClass:forSupplementaryViewOfKind:withReuseIdentifier:或者registerNib:forSupplementaryViewOfKind:withReuseIdentifier:注册头尾部视图,kind类型有UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader和UICollectionElementKindSectionFooter - 自定义头尾部视图必须继承
UICollectionReusableView,其实UICollectionViewCell也是继承自它
// 注册cell
collectionView.register(BaseCollectionViewCell.self, forCellWithReuseIdentifier: baseCellID)
// 注册头尾部视图,它们必须继承自UICollectionReuseView
collectionView.register(UINib(nibName: "BaseHeaderAndFooterCollectionReusableView", bundle: nil), forSupplementaryViewOfKind: UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader, withReuseIdentifier: baseReuseHeaderID)
collectionView.register(UINib(nibName: "BaseHeaderAndFooterCollectionReusableView", bundle: nil), forSupplementaryViewOfKind: UICollectionElementKindSectionFooter, withReuseIdentifier: baseReuseFooterID)
遵循数据源协议
-
numberOfSections(in:)方法里 返回组数 -
collectionView(_:numberOfItemsInSection)返回每组个数 -
collectionView(_:cellForItemAt:)和collectionView(_:viewForSupplementaryElementOfKind:at:)编辑你的cell和头尾部视图
func numberOfSections(in collectionView: UICollectionView) -> Int {
return 3
}
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, numberOfItemsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return 10 + section * 3
}
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, cellForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UICollectionViewCell {
let cell = collectionView.dequeueReusableCell(withReuseIdentifier: baseCellID, for: indexPath) as! BaseCollectionViewCell
cell.cellIndex = indexPath.item
return cell
}
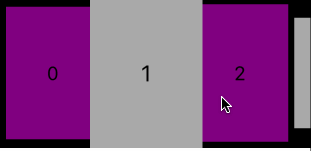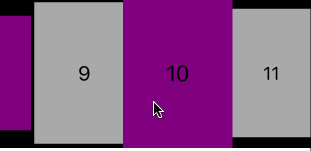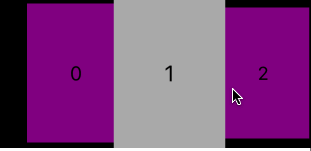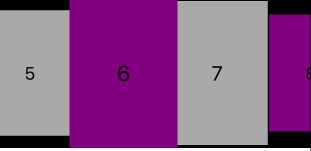
// 头尾部的数据源协议
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, viewForSupplementaryElementOfKind kind: String, at indexPath: IndexPath) -> UICollectionReusableView {
if kind == UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader {
let header = collectionView.dequeueReusableSupplementaryView(ofKind: UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader, withReuseIdentifier: baseReuseHeaderID, for: indexPath) as! BaseHeaderAndFooterCollectionReusableView
header.backgroundColor = .purple
header.textLabel.text = "第 \(indexPath.section) 组的头部"
return header
}
let footer = collectionView.dequeueReusableSupplementaryView(ofKind: UICollectionElementKindSectionFooter, withReuseIdentifier: baseReuseFooterID, for: indexPath) as! BaseHeaderAndFooterCollectionReusableView
footer.textLabel.text = "第 \(indexPath.section) 组的尾部"
footer.backgroundColor = .lightGray
return footer
}
最后效果:
2.自定义布局整体思路
让类继承
UICollectionViewLayout或者UICollectionViewFlowLayout在
prepare()方法里准备你需要布局的信息,这个方法会在第一次布局和reloadData()以及invalidateLayout()时会调用,对于那些不会随视图滚动而改变的布局的对象,都应该在这里计算好,进行缓存在
collectionViewContentSize里返回collectionView的contentSize如果布局随着范围改变而实时改变,在
shouldInvalidateLayout(forBoundsChange:)函数里返回true-
layoutAttributesForElements(in:)里返回布局数组,如果你的布局对象都已经缓存好了,也应该只返回跟layAttributes.frame跟Rect相交的这个区间内的对象数组,如下图所示
对于那些随滚动而改变的item,应该在这里进行重新计算, 记住,千万不要在这方法里调用UICollectionView的visibleCells方法,因为这个范围内所有的cell还没确定; 如果想调整滚动的位置,例如让距离中心最近的
cell居中,在targetContentOffset(forProposedContentOffset:withScrollingVelocity:)方法里进行调整什么情况下需要自定义
UICollectionAttributes对象,首先问UICollectionViewcell为什么不跟UITableViewCell一样,直接就把布局搞定,非要多出一个UICollectionViewLayout对象,因为它更复杂灵活,自定义程度高,那UICollectionViewcell是怎么获取布局对象 的, 通过apply(_:)这个方法来获取布局UICollectionAttributes对象,再根据它来布局,但UICollectionAttributes的属性不多,例如我们想要一个锚点、一种颜色等它都是没有的,如果你需要用到这些额外属性传递给cell布局,就需要自定义布局对象;怎么自定义
UICollectionAttributes布局对象,首先在类里面添加你自定义的属性,由于布局时会拷贝对象,需要遵守NSCoping协议,实现copy(with:)方法,UICollectionReusableView(Cell也是它的子类)需要实现apply(_:)方法,在iOS7之后,它会判断你的布局对象是否改变,来决定是否调用apply(_:)方法,如果你的自定义UICollectionAttributes里只有自定义的属性改变,而其它属性没有改变,它会视为你这个对象没有改变,你需要重写isEqual方法,来判断对象是否改变对于
layoutAttributesForItem(at:)方法,它是不会主动调用的,只是让我们在布局方法prepare() 和layoutAttributesForElements(in:)里主动调用它来获得layoutAttributes对象,但我们一般通过UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes(forCellWith:)方法自己创建
3.实现瀑布流
瀑布流是每个item宽度相同,高度不同的一种的布局, 自定义一个继承UICollectionViewFlowLayout的类,效果图如下
定义基本属性
var cols = 4 // 列数
/// 布局frame数组
fileprivate lazy var layoutAttributeArray: [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes] = []
/// 每列的高度的数组
fileprivate lazy var yArray: [CGFloat] = Array(repeating: self.sectionInset.top, count: self.cols)
/// 最大高度
fileprivate var maxHeight: CGFloat = 0
在prepare()方法里添加我们需要的布局属性,并计算出ContentSize的最大高度,重点是怎么把每列的高度存起来,接着最小的一列继续排列
/// 重写Prepare方法,准备我们要缓存的布局对象
override func prepare() {
super.prepare()
let itemW = (collectionView!.bounds.width - sectionInset.left - sectionInset.right - minimumInteritemSpacing * CGFloat(cols - 1)) / CGFloat(cols)
let itemCount = collectionView!.numberOfItems(inSection: 0)
// 最小高度的那一个的索引
var minHeightIndex = 0
// 从 layoutAttributeArray.count 开始,避免重复加载
for j in layoutAttributeArray.count ..< itemCount {
let indexPath = IndexPath(item: j, section: 0)
let attr = UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes(forCellWith: indexPath)
// item高度,从代理中获取
let itemH = delegate?.waterFlowLayout(self, itemHeightAt: indexPath)
// 找出最小高度的那一列
let value = yArray.min()
minHeightIndex = yArray.index(of: value!)!
var itemY = yArray[minHeightIndex]
// 大于第一行的高度才相加
if j >= cols {
itemY += minimumInteritemSpacing
}
let itemX = sectionInset.left + (itemW + minimumInteritemSpacing) * CGFloat(minHeightIndex)
attr.frame = CGRect(x: itemX, y: itemY, width: itemW, height: CGFloat(itemH!))
layoutAttributeArray.append(attr)
// 重新设置最小列高度
yArray[minHeightIndex] = attr.frame.maxY
}
maxHeight = yArray.max()! + sectionInset.bottom
}
- 返回collectionViewContentSize的大小,记住这里宽度不能设置为0,如果设置为0,在layoutAttributesForElements(in:)不能正确的返回大小
override var collectionViewContentSize: CGSize {
return CGSize(width: collectionView!.bounds.width, height: maxHeight)
}
- 在layoutAttributesForElements返回布局对象数组
override func layoutAttributesForElements(in rect: CGRect) -> [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes]? {
// 找出相交的那些,别全部返回
return layoutAttributeArray.filter { $0.frame.intersects(rect)}
}
4.每页多个Cell的水平方向滚动布局
如果每页的item很多,而且是水平方向滚动,item是一列一列的排,这给我们很不好的感觉,因为我们习惯是一行一行看的,原效果图如下
我们需要改成按水平方向排列的效果:
实现方法跟瀑布流基本类似,首先定义基本属性
var cols = 4 // 列数,默认为4
var line = 4 // 行数,默认为4
/// contentSize的最大宽度
fileprivate var maxWidth: CGFloat = 0
/// 布局frame数组
fileprivate lazy var layoutAttributeArray: [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes] = []
在prepare()方法里添加我们需要的布局属性,并计算出ContentSize的最大宽度,重点就是怎么把位置给算出来
/// 重写Prepare方法,准备我们要缓存的布局对象
override func prepare() {
super.prepare()
// 每个item的宽度
let itemW = (collectionView!.bounds.width - sectionInset.left - sectionInset.right - minimumInteritemSpacing * CGFloat(cols - 1)) / CGFloat(cols)
// 每个item的高度
let itemH = (collectionView!.bounds.height - sectionInset.top - sectionInset.bottom - minimumLineSpacing * CGFloat(line - 1)) / CGFloat(line)
// 求出对应的组数
let sections = collectionView?.numberOfSections
// 每个item所在组的 前面总的页数
var prePageCount: Int = 0
for i in 0..- 返回collectionViewContentSize的大小
override var collectionViewContentSize: CGSize {
return CGSize(width: maxWidth, height: 0)
}
- 在layoutAttributesForElements返回布局对象数组
override func layoutAttributesForElements(in rect: CGRect) -> [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes]? {
// 找出相交的那些,别全部返回
return layoutAttributeArray.filter { $0.frame.intersects(rect)}
}
5.实现CoverFlow效果
CoverFlow是一种很酷的封面浏览效果,item的大小随着滑动而缩放,滑动结束时,距中最近的一个item局中显示,效果图如下
- 因为item大小随范围变化而实时变化,在prepare()方法里计算缓存已经无用,需要在layoutAttributesForElements(in:)里亲自计算来返回布局对象数组
override func layoutAttributesForElements(in rect: CGRect) -> [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes]? {
// 获取这个范围的布局数组
let attributes = super.layoutAttributesForElements(in: rect)
// 找到中心点
let centerX = collectionView!.contentOffset.x + collectionView!.bounds.width / 2
// 每个点根据距离中心点距离进行缩放
attributes!.forEach({ (attr) in
let pad = abs(centerX - attr.center.x)
let scale = 1.8 - pad / collectionView!.bounds.width
attr.transform = CGAffineTransform(scaleX: scale, y: scale)
})
return attributes
}
- 让滚动停止时,距中心最近item居中显示
/// 重写滚动时停下的位置
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - proposedContentOffset: 将要停止的点
/// - velocity: 滚动速度
/// - Returns: 滚动停止的点
override func targetContentOffset(forProposedContentOffset proposedContentOffset: CGPoint, withScrollingVelocity velocity: CGPoint) -> CGPoint {
var targetPoint = proposedContentOffset
// 中心点
let centerX = proposedContentOffset.x + collectionView!.bounds.width
// 获取这个范围的布局数组
let attributes = self.layoutAttributesForElements(in: CGRect(x: proposedContentOffset.x, y: proposedContentOffset.y, width: collectionView!.bounds.width, height: collectionView!.bounds.height))
// 需要移动的最小距离
var moveDistance: CGFloat = CGFloat(MAXFLOAT)
// 遍历数组找出最小距离
attributes!.forEach { (attr) in
if abs(attr.center.x - centerX) < abs(moveDistance) {
moveDistance = attr.center.x - centerX
}
}
// 只有在ContentSize范围内,才进行移动
if targetPoint.x > 0 && targetPoint.x < collectionViewContentSize.width - collectionView!.bounds.width {
targetPoint.x += moveDistance
}
return targetPoint
}
- Bounds变化时,应该重新布局
override func shouldInvalidateLayout(forBoundsChange newBounds: CGRect) -> Bool {
return true
}
- 返回collectionViewContentSize的大小
override var collectionViewContentSize: CGSize {
return CGSize(width:sectionInset.left + sectionInset.right + (CGFloat(collectionView!.numberOfItems(inSection: 0)) * (itemSize.width + minimumLineSpacing)) - minimumLineSpacing, height: 0)
}
- 为了让中间的cell不被拦住,我们需要把它放到最前面,在控制器中实现这些方法
/// 把中间的cell带到最前面
fileprivate func bringMiddleCellToFront() {
let pointX = (collectionView.contentOffset.x + collectionView.bounds.width / 2)
let point = CGPoint(x: pointX, y: collectionView.bounds.height / 2)
// 找到中心点的indexPath
let indexPath = collectionView.indexPathForItem(at: point)
if let letIndexPath = indexPath {
let cell = collectionView.cellForItem(at: letIndexPath)
guard let letCell = cell else {
return
}
// 把cell放到最前面
collectionView.bringSubview(toFront: letCell)
}
}
/// 第一次显示需要主动调用把中间的cell的放在最前面
override func viewDidLayoutSubviews() {
super.viewDidLayoutSubviews()
bringMiddleCellToFront()
}
/// 滚动时,每次调用这方法
func scrollViewDidScroll(_ scrollView: UIScrollView) {
bringMiddleCellToFront()
}
6.实现轮转卡片效果
在轮转卡片中,我们需要用到自定义UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes的自定义类,来改变cell的锚点和positon, 从而改变cell的旋转角度
- 首先自定义
UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes类,添加锚点属性,一定要遵守NSCoping协议, 因为不只自定义属性锚点实时改变,还有自带的transform属性改变,可以不重写isEqual方法
/// 主要为了存储 anchorPoint,好在cell的apply(_:)方法中使用来旋转cell,因为UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes没有这个属性
class CircularCollectionViewLayoutAttributes: UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes {
var anchorPoint = CGPoint(x: 0.5, y: 0.5)
/// 需要实现这个方法,collection View 实时布局时,会copy参数,确保自身的参数被copy
override func copy(with zone: NSZone? = nil) -> Any {
let copiedAttributes: CircularCollectionViewLayoutAttributes = super.copy(with: zone) as! CircularCollectionViewLayoutAttributes
copiedAttributes.anchorPoint = anchorPoint
return copiedAttributes
}
}
在自定义UICollectionViewLayout对象中,自定义属性
有n个item, 我们就设ContentSize的宽度为 item * n
每个item的相对于上一个item的偏移角度我们自定义一个为 anglePerItem
当偏移量为 0时,第一个item处于正中间,偏移角度为0,当collectionView的偏移量最大时,最后一个item处于正中间,偏移角度为0
/// 每个item的大小
let itemSize = CGSize(width: 133, height: 173)
/// 属性数组
var attributesList: [CircularCollectionViewLayoutAttributes] = []
/// 设置半径,需要重新设置布局
var radius: CGFloat = 500 {
didSet {
invalidateLayout()
}
}
/// 每两个item 之间的角度,任意值
var anglePerItem: CGFloat {
return atan(itemSize.width / radius) // atan反正切
}
/// 当collectionView滑到极端时,第 0个item的角度 (第0个开始是 0 度, 当滑到极端时, 最后一个是 0 度)
var angleAtextreme: CGFloat {
return collectionView!.numberOfItems(inSection: 0) > 0 ? -CGFloat(collectionView!.numberOfItems(inSection: 0) - 1) * anglePerItem : 0
}
/// 滑动时,第0个item的角度
var angle: CGFloat {
return angleAtextreme * collectionView!.contentOffset.x / (collectionViewContentSize.width - collectionView!.bounds.width)
}
- 重写prepare()方法,求出相对应的属性数组attributesList
override func prepare() {
super.prepare()
// 整体布局是将每个item设置在屏幕中心,然后旋转 anglePerItem * i 度
let centerX = collectionView!.contentOffset.x + collectionView!.bounds.width / 2.0
// 锚点的y值,多增加了raidus的值
let anchorPointY = ((itemSize.height / 2.0) + radius) / itemSize.height
/// 不要计算所有的item,只计算在屏幕中的item,theta最大倾斜
let theta = atan2(collectionView!.bounds.width / 2, radius + (itemSize.height / 2.0) - collectionView!.bounds.height / 2)
var startIndex = 0
var endIndex = collectionView!.numberOfItems(inSection: 0) - 1
// 开始位置
if angle < -theta {
startIndex = Int(floor((-theta - angle) / anglePerItem))
}
// 结束为止
endIndex = min(endIndex, Int(ceil((theta - angle) / anglePerItem)))
if endIndex < startIndex {
endIndex = 0
startIndex = 0
}
// startIndex...endIndex
attributesList = (startIndex...endIndex).map({ (i) -> CircularCollectionViewLayoutAttributes in
let attributes = CircularCollectionViewLayoutAttributes(forCellWith: IndexPath(item: i, section: 0))
attributes.size = self.itemSize
// 设置居中
attributes.center = CGPoint(x: centerX, y: collectionView!.bounds.midY)
// 设置偏移角度
attributes.transform = CGAffineTransform(rotationAngle: self.angle + anglePerItem * CGFloat(i))
// 锚点,我们自定义的属性
attributes.anchorPoint = CGPoint(x: 0.5, y: anchorPointY)
return attributes
})
}
- 在
layoutAttributesForElements(in:)返回布局数组
// 返回布局数组
override func layoutAttributesForElements(in rect: CGRect) -> [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes]? {
return attributesList
}
- 让滚动停止时,距中心最近item居中显示
/// 重写滚动时停下的位置
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - proposedContentOffset: 将要停止的点
/// - velocity: 滚动速度
/// - Returns: 滚动停止的点
override func targetContentOffset(forProposedContentOffset proposedContentOffset: CGPoint, withScrollingVelocity velocity: CGPoint) -> CGPoint {
var finalContentOffset = proposedContentOffset
// 每单位偏移量对应的偏移角度
let factor = -angleAtextreme / (collectionViewContentSize.width - collectionView!.bounds.width)
let proposedAngle = proposedContentOffset.x * factor
// 大约偏移了多少个
let ratio = proposedAngle / anglePerItem
var multiplier: CGFloat
// 往左滑动,让multiplier成为整个
if velocity.x > 0 {
multiplier = ceil(ratio)
} else if (velocity.x < 0) { // 往右滑动
multiplier = floor(ratio)
} else {
multiplier = round(ratio)
}
finalContentOffset.x = multiplier * anglePerItem / factor
return finalContentOffset
}
- Bounds变化时,应该重新布局
override func shouldInvalidateLayout(forBoundsChange newBounds: CGRect) -> Bool {
return true
}
- 返回collectionViewContentSize的大小,为item * n
override var collectionViewContentSize: CGSize {
return CGSize(width: CGFloat(collectionView!.numberOfItems(inSection: 0)) * itemSize.width, height: collectionView!.bounds.height)
}
- 在我们自定的cell中重写
apply(_:)方法,拿到layoutAttribute中的锚点进行布局
override func apply(_ layoutAttributes: UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes) {
super.apply(layoutAttributes)
let circularlayoutAttributes = layoutAttributes as! CircularCollectionViewLayoutAttributes
layer.anchorPoint = circularlayoutAttributes.anchorPoint
layer.position.y = layer.position.y + (circularlayoutAttributes.anchorPoint.y - 0.5) * bounds.height
}
7. 模仿今日头条实现Cell重排
移动cell在照片排版和新闻类的APP中比较常见,主要用到的是moveItem(at indexPath: IndexPath, to newIndexPath: IndexPath)这个方法进行交换,主要思路
给collectionView添加长按和拖拽手势,拖拽手势主要是点击进入编辑状态后,可拖拽cell直接进行交换,因为拖拽手势不比长按手势需要按一段时间才开始,反应很快,快速滑动时,有很多问题,需要留意
根据手势的三种状态对cell进行操作,手势开始时对cell进行截图,并隐藏开始cell, 手势移动时,让截图跟着移动,当到达别的cell上时,进行交换,手势结束时,移除截图,并让隐藏的开始cell显示
点击cell,移动它进行添加删除
主要效果图如下:
- 给collectionView添加手势
/// collectionView的pan手势
func panGestureRecognized(_ sender: UIPanGestureRecognizer) {
guard self.isEdit else { return }
handleGesture(sender)
}
/// collectionView的长按手势
func longPressGestureRecognized(_ sender: UILongPressGestureRecognizer) {
handleGesture(sender)
}
func handleGesture(_ sender: UIGestureRecognizer) {
let senderState = sender.state
// 手指在collectionView中的位置
fingerLocation = sender.location(in: collectionView)
// 手指按住位置对应的indexPath,可能为nil
relocatedIndexPath = collectionView?.indexPathForItem(at: fingerLocation)
switch senderState {
case .began:
// 根据relocatedIndexPath,找出cell,隐藏它,并截图
case .changed:
// 根据fingerLocation,移动cell,如果到达其它cell上,交换两个cell
case .ended:
// 移除截图,并让开始cell,显示
didEndDraging()
}
/// 拖动结束,显示cell,并移除截图
func didEndDraging() {
...
UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.2, animations: {
self.snapshot!.center = cell!.center
// 隐藏截图
self.snapshot!.alpha = 0
self.snapshot!.transform = .identity
cell?.alpha = 1
}) { (_) in
self.snapshot!.removeFromSuperview()
self.snapshot = nil
self.originalIndexPath = nil
self.relocatedIndexPath = nil
}
}
- 因为结束手势后,隐藏截图的动画时间设置了0.2秒,在动画还没结束时,可能又开启了另一个拖拽手势,我们需要给拖拽手势设置代理,并决定是否启用它
func gestureRecognizerShouldBegin(_ gestureRecognizer: UIGestureRecognizer) -> Bool {
let sender = gestureRecognizer as! UIPanGestureRecognizer
let trnslationPoint = sender.translation(in: collectionView)
// 结束动画有时间,扫的手势很容易出问题,需要保证 snapshot == nil,才让它开始,
// pan手势结束和开始可能会特别快,需要格外留心,
// 为了保证pan手势不影响collectionView的竖直滑动,竖直方向偏移不让它开始
if abs(trnslationPoint.x) > 0.2 && snapshot == nil {
return true
}
return false
}
具体详情参见示例代码
8. iOS9使用系统自带属性进行重排
在iOS9 之后,苹果给collectionView推出了几个方法
beginInteractiveMovementForItem(at:)
updateInteractiveMovementTargetPosition(_ :)
endInteractiveMovement()
cancelInteractiveMovement()
四个方法分别为开始交互、更新交互位置、结束交互、取消交互,跟上面的一样给collectionView添加手势,在手势的三种状态里面,分别调用上面相应的四种方法,实现系统的collectionView(_:moveItemAt:to:)方法,更新数据源,实现效果如下
func handleLongGesture(_ gesture: UILongPressGestureRecognizer) {
switch(gesture.state) {
case .began:
guard let selectedIndexPath = self.collectionView.indexPathForItem(at: gesture.location(in: self.collectionView)) else {
break
}
// 开始交互
collectionView.beginInteractiveMovementForItem(at: selectedIndexPath)
case .changed:
// 更新位置
collectionView.updateInteractiveMovementTargetPosition(gesture.location(in: gesture.view!))
case .ended:
// 结束交互
collectionView.endInteractiveMovement()
default:
// 默认取消交互
collectionView.cancelInteractiveMovement()
}
}
/// 更新我们自己的数据源
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, moveItemAt sourceIndexPath: IndexPath, to destinationIndexPath: IndexPath) {
let number = dataNumbers.remove(at: sourceIndexPath.item)
dataNumbers.insert(number, at: destinationIndexPath.item)
}
它的使用很简单,如果控制器是
UICollectionViewController,不需要我们调用交互方法,就可以实现拖拽cell了,只需要在collectionView(_:moveItemAt:to:)方法里,更新数据源,如果我们想关闭拖拽功能,设置installsStandardGestureForInteractiveMovement为false就行了拖拽时,当cell触及到屏幕边缘时它会自动滚动,在iOS10中,如果设置了属性collectionveiw的isPagingEnabled属性为true,拖拽到屏幕边缘时会翻页滚动,苹果的设计是需要拖到边缘稍微停留一会儿才翻页,而不翻页滚动的只需要cell触碰到边缘就会马上移动
iOS10后UICollectionView的优化与预加载
为了使UICollectionView的滑动更流畅,官方进行了一些优化,首先得明白cell的加载顺序是什么样的,是先调用collectionView(_:cellForItemAt:)数据源方法,再调用collectionView(_:willDisplay:forItemAt:)显示cell,cell消失调用collectionView(_:didEndDisplaying:forItemAt:)方法
在iOS9以前,只到了屏幕边缘才调用
cellForItemAt方法,调用完之后马上就会调用willDisplay, 但在iOS10中,willDisplay这方法还是跟以前一样,只在cell马上进入屏幕的时候才调用, 而cellForItemAt却提前了,它会在距离屏幕边缘还有一段距离的时候就调用,这样保证了我们有更多的时间去加载我们的资源cell的生命周期延长,滑出屏幕之后,它会保留一段时间,如果cell快速滑动时,却突然向相反方向快速滑动,这时它不会调用
cellForItemAt方法,而是直接调用willDisplay方法,如果是在cellForItemAt方法里动态改变cell属性,就需要留意了,可能会出现问题,因为这个方法根本不会调用,如果还是想在这方法里改变cell, 跟iOS9一样,可以设置collectionView的isPrefetchingEnabled为false如果collectionView每行有多列cell,在iOS9会整行整行的加载,而到了iOS10它会一个一个的加载,保证了流畅性
提供了预加载方法,
collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, prefetchItemsAt indexPaths: [IndexPath]),在这里提前加载图片资源,注意这些资源一定要是异步加载,仔细观察了下,屏幕有多个cell,它就多加载多少个cell, 但是我发现cellForItemAt方法居然在滑动时也提前加载了这么多个cell,唯一不同的是实现了这些代理方法,我们会在第一次没有滑动显示时,collectionView(_:prefetchItemsAt:)会提前加载屏幕这么多的cell,而cellForItemAt只加载屏幕上显示的cell,不会多加载屏幕以外的cell取消预加载方法
collectionView(_:cancelPrefetchingForItemsAt:),它只在快速滑动还没停下来时,突然往相反方向快速滑动调用,当它调用时,程序也基本不会走cellForItemAt方法,直接走willDisplaycell方法显示cell
实现预加载,效果图如下:
- 遵守协议
collectionView?.prefetchDataSource = self - 实现预加载数据源协议
// 预加载,每次都会领先基本一页的数据
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, prefetchItemsAt indexPaths: [IndexPath]) {
let urls = indexPaths.flatMap {
URL(string: dataArray[$0.item])
}
// 开始下载
ImagePrefetcher(urls: urls).start()
}
// 取消预加载,会在快速滑动还没停下来时,突然往相反方向快速滑动调用,当它调用, 程序也基本不会走cellForItemAt 方法, 直接走 willDisplaycell方法
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, cancelPrefetchingForItemsAt indexPaths: [IndexPath]) {
let urls = indexPaths.flatMap {
URL(string: dataArray[$0.item])
}
// 取消下载
ImagePrefetcher(urls: urls).stop()
}
结语
断断续续花了不少时间终于写完了,但觉得挺值得的,感觉最深的就是这控件太灵活了
Demo地址