一、环境搭建(Ubuntu)
Ubuntu 18.04.2 自带Python3
安装所需要的全部环境:
sudo apt install curl python-pip python3-pip
sudo pip3 install --index-url https://pypi.douban.com/simple --upgrade --ignore-installed tensorflow Keras matplotlib PyQt5 lxml
二、快速开始
下载程序:https://github.com/qqwweee/keras-yolo3
生成.h5:
参考readme文件
下载权重文件:wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
复制到keras-yolo3-master根目录下。
转换为h5文件:python3 convert.py yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights model_data/yolo.h5
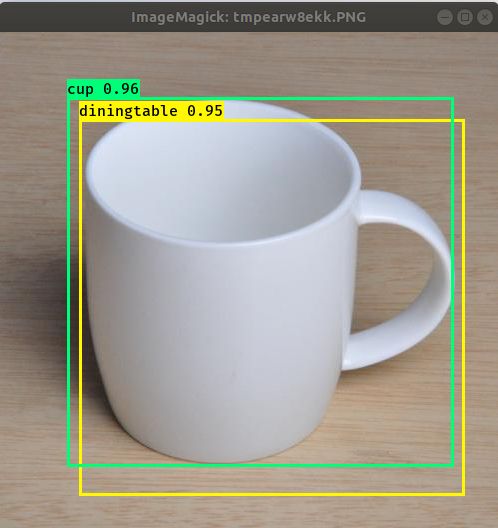
最后在keras-yolo3-master根目录下执行:python3 yolo_video.py --image
等待运行,当程序出现 inout image filename: 的时候,输入一张图片的路径与名称即可得到识别结果。
三、训练自己的模型
如果不想使用官方的权重而用自己的模型,可以先训练。
1、首先,收集一些素材,我收集了100张上衣的图片作为素材,有可能的话最好多收集一些。将素材都放在一个单独的文件夹里,并且不要在里头放其他无关的文件,路径确保是英文。
2、然后将他们按数字顺序命名,可以写一个脚本帮助完成这个工作。
@echo off
SETLOCAL ENABLEDELAYEDEXPANSION
set /A num=0
FOR /F "tokens=*" %%i in ('dir /A-D /B /OD /TC') do (
IF NOT "%%i"=="%~n0%~x0" (
set /A num+=1
if !num! LSS 10 (
ren "%%i" 0000!num!%%~xi
) ELSE (
if !num! LSS 100 (
ren "%%i" 000!num!%%~xi
) ELSE (
if !num! LSS 1000 (
ren "%%i" 00!num!%%~xi
) ELSE (
if !num! LSS 10000 ren "%%i" 0!num!%%~xi
)
)
)
)
)
ENDLOCAL
exit
将以上内容复制到一个txt里并改后缀为.bat,放在素材所在的文件夹里,运行即可。
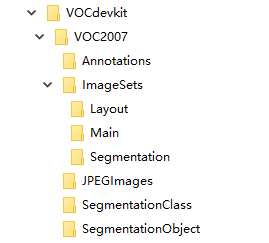
同时,准备一个文件夹结构,树形图如下,请务必保持一致,否则部分脚本无法正常运行(当然也可以手动改脚本):
将素材图片全部放在JPEGImages下。
3、打标
打标使用的是LabelImg程序。 参考: LabelImg
安装:
pip3 install PyQt5 -i https://pypi.douban.com/simple
pip3 install lxml
git clone https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg.git
github上LabelImg资源很慢,提供一个度盘地址:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1OsmM3bhzTtuY6oNZ-Q4Kdg
提取码:qzvd
在labelimg目录下:
pyrcc5 -o resources.py resources.qrc
python3 labelImg.py
即可运行Labelimg。
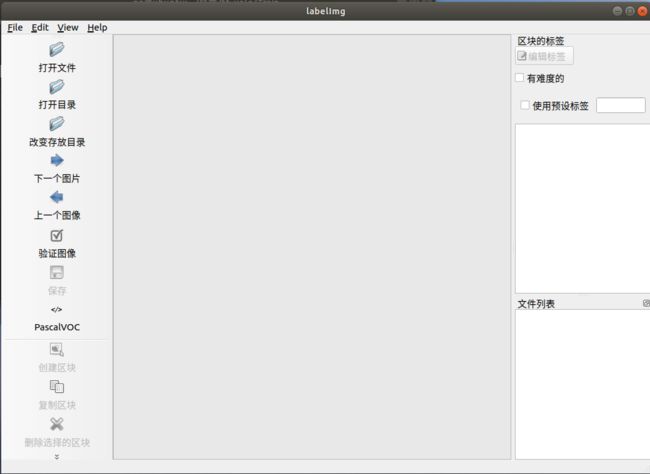
使用方法很简单,选择“改变存放目录”,打开要保存标记文件的目录,也就是/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations。
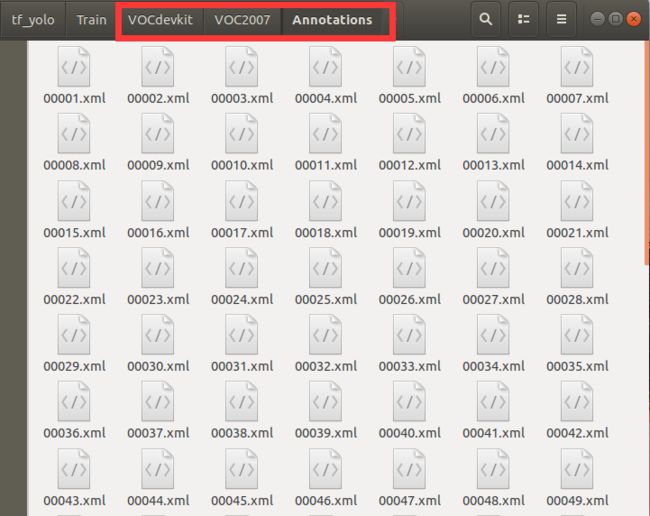
点击“打开目录”,打开素材的目录。PascalVOC选项不变。当打开图片后,选择右侧“使用预设标签”,输入一个自定义的标签。接着选择程序左侧的“创建区块”,将需要学习的部分框选出来,最后点击保存,就完成了对这张图片的打标,点击下一个图片,重复以上操作直到打标完所有的图片。最后可以看到Annotations文件夹里是大量xml文件。
4、准备训练材料
首先明确几点前提条件。
1、VOCdevkit文件夹目录结构正确创建
2、所有图片都已经被正确命名并存放在JPEGImages下
3、所有xml文件都已经被正确命名并存放在Annotations下
4、所有xml文件内容都是正确的
编辑一个脚本test.py,放在VOC2007目录下,内容如下:
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0.4
train_percent = 0.6
xmlfilepath = 'Annotations'
txtsavepath = 'ImageSets\Main'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets/Main/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('ImageSets/Main/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('ImageSets/Main/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftest.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftrain.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
执行,会在ImageSets/Main下生成四个文件,里面是随机分配的训练和测试文件名。
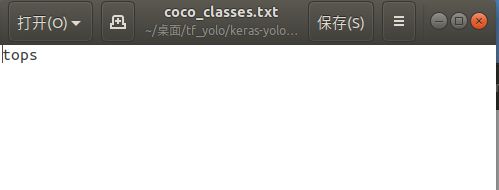
接着将keras-yolo3-master文件夹里的voc_annotation.py复制到VOCdevkit同一目录下,修改内容,将classes=[""]内的内容改为自己定义的标签。运行。
会在目录下生成三个 2007_开头的文件,内容是根据xml文件生成的 含有样本与标记的清单:
每一行的内容解释如下:
图片位置 [第一个标记框的坐标,标签序号] [第二个标记框的坐标,标签序号] [第三个标记框的坐标,标签序号] [......]
将这三个文件放在keras-yolo3-master文件夹根目录下。
四、开始训练
在keras-yolo3-master文件夹下创建logs/000目录,用于输出训练好的模型。
在keras-yolo3-master文件夹下创建一个train_my_model.py,内容如下:
"""
Retrain the YOLO model for your own dataset.
"""
import numpy as np
import keras.backend as K
from keras.layers import Input, Lambda
from keras.models import Model
from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint, EarlyStopping
from yolo3.model import preprocess_true_boxes, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body, yolo_loss
from yolo3.utils import get_random_data
def _main():
annotation_path = '2007_train.txt'
log_dir = 'logs/000/'
classes_path = 'model_data/voc_classes.txt'
anchors_path = 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'
class_names = get_classes(classes_path)
anchors = get_anchors(anchors_path)
input_shape = (416,416) # multiple of 32, hw
model = create_model(input_shape, anchors, len(class_names) )
train(model, annotation_path, input_shape, anchors, len(class_names), log_dir=log_dir)
def train(model, annotation_path, input_shape, anchors, num_classes, log_dir='logs/'):
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss={
'yolo_loss': lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred})
logging = TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir)
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(log_dir + "ep{epoch:03d}-loss{loss:.3f}-val_loss{val_loss:.3f}.h5",
monitor='val_loss', save_weights_only=True, save_best_only=True, period=1)
batch_size = 10
val_split = 0.1
with open(annotation_path) as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(lines)
num_val = int(len(lines)*val_split)
num_train = len(lines) - num_val
print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
model.fit_generator(data_generator_wrap(lines[:num_train], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//batch_size),
validation_data=data_generator_wrap(lines[num_train:], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
validation_steps=max(1, num_val//batch_size),
epochs=500,
initial_epoch=0)
model.save_weights(log_dir + 'trained_weights.h5')
def get_classes(classes_path):
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
def get_anchors(anchors_path):
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
def create_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes, load_pretrained=False, freeze_body=False,
weights_path='model_data/yolo_weights.h5'):
K.clear_session() # get a new session
image_input = Input(shape=(None, None, 3))
h, w = input_shape
num_anchors = len(anchors)
y_true = [Input(shape=(h//{0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l], w//{0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l], \
num_anchors//3, num_classes+5)) for l in range(3)]
model_body = yolo_body(image_input, num_anchors//3, num_classes)
print('Create YOLOv3 model with {} anchors and {} classes.'.format(num_anchors, num_classes))
if load_pretrained:
model_body.load_weights(weights_path, by_name=True, skip_mismatch=True)
print('Load weights {}.'.format(weights_path))
if freeze_body:
# Do not freeze 3 output layers.
num = len(model_body.layers)-7
for i in range(num): model_body.layers[i].trainable = False
print('Freeze the first {} layers of total {} layers.'.format(num, len(model_body.layers)))
model_loss = Lambda(yolo_loss, output_shape=(1,), name='yolo_loss',
arguments={'anchors': anchors, 'num_classes': num_classes, 'ignore_thresh': 0.5})(
[*model_body.output, *y_true])
model = Model([model_body.input, *y_true], model_loss)
return model
def data_generator(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
n = len(annotation_lines)
np.random.shuffle(annotation_lines)
i = 0
while True:
image_data = []
box_data = []
for b in range(batch_size):
i %= n
image, box = get_random_data(annotation_lines[i], input_shape, random=True)
image_data.append(image)
box_data.append(box)
i += 1
image_data = np.array(image_data)
box_data = np.array(box_data)
y_true = preprocess_true_boxes(box_data, input_shape, anchors, num_classes)
yield [image_data, *y_true], np.zeros(batch_size)
def data_generator_wrap(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
n = len(annotation_lines)
if n==0 or batch_size<=0: return None
return data_generator(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes)
if __name__ == '__main__':
_main()
然后运行train_my_model.py即可开始训练。训练出结果后在logs/000/文件夹下可以找到。