0x00 文中用到的工具
Frida
jadx-gui 一个强大的android反编译工具
genymotion模拟器
Python2.7以及frida-python库
radare2 反汇编器
pycharm
0x01 hook示例的安装与分析
Frida官网给我们了一个ctf的示例,就以此为例子,开始学习frida在android逆向的使用。
rps.apk 下载地址查看原帖(点击左下角阅读原文查看)
安装
使用genymotion等类似android模拟器安装好打开,发现这是一个石头剪刀布的游戏应用,简单的玩了一下,没什么特别的,直接分析代码吧,看看到底想干什么。
源代码分析
使用jadx-gui反编译,发现app没有加壳和混淆,当然一来就加壳和混淆的话对我们就太不友好了,接下分析就简单了,直接看java代码。当然也可以使用androidkiller,jeb等其他强大的反编译工具。
在MainActivity中找到OnCreate()方法,可以看到只是简单的声明了button控件以及对应的监听器。
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
this.P = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
this.S = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button3);
this.r = (Button) findViewById(R.id.buttonR);
this.P.setOnClickListener(this);
this.r.setOnClickListener(this);
this.S.setOnClickListener(this);
this.flag = 0;
}
继续查看button的onclick方法,可以看出cpu是通过随机数组出的,其判断输赢的方法在 this.showMessageTask 中。
public void onClick(View v) {
if (this.flag != 1) {
this.flag = 1;
((TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView3)).setText("");
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView);
TextView tv2 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView2);
this.m = 0;
this.n = new Random().nextInt(3); //随机数0,1,2
tv2.setText(new String[]{"CPU: Paper", "CPU: Rock", "CPU: Scissors"}[this.n]); //随机出石头,剪刀,布
if (v == this.P) {
tv.setText("YOU: Paper");
this.m = 0;
}
if (v == this.r) {
tv.setText("YOU: Rock");
this.m = 1;
}
if (v == this.S) {
tv.setText("YOU: Scissors");
this.m = 2;
}
this.handler.postDelayed(this.showMessageTask, 1000);//输赢判断方法
}
}
跟进分析showMessageTask,可以看到如果赢了mainActivity.cnt会+1,但是一旦输了cnt就会置0,而获取flag的要求是我们得获胜1000次,...... :(
private final Runnable showMessageTask = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
TextView tv3 = (TextView) MainActivity.this.findViewById(R.id.textView3);
MainActivity mainActivity;
//我方:布 CPU:石头 or 我方:石头 CUP:剪刀 ,则为赢
if (MainActivity.this.n - MainActivity.this.m == 1) {
mainActivity = MainActivity.this;
mainActivity.cnt++;
tv3.setText("WIN! +" + String.valueOf(MainActivity.this.cnt));
//反过来当然是输咯
} else if (MainActivity.this.m - MainActivity.this.n == 1) {
MainActivity.this.cnt = 0;
tv3.setText("LOSE +0");
//一样则打平
} else if (MainActivity.this.m == MainActivity.this.n) {
tv3.setText("DRAW +" + String.valueOf(MainActivity.this.cnt));
//我布 cup:剪刀
} else if (MainActivity.this.m < MainActivity.this.n) {
MainActivity.this.cnt = 0;
tv3.setText("LOSE +0");
} else {
mainActivity = MainActivity.this;
mainActivity.cnt++;
tv3.setText("WIN! +" + String.valueOf(MainActivity.this.cnt));
}
//获胜1000次则能够获取flag
if (1000 == MainActivity.this.cnt) {
tv3.setText("SECCON{" + String.valueOf((MainActivity.this.cnt + MainActivity.this.calc()) * 107) + "}");
}
MainActivity.this.flag = 0;
}
};
简单分析一下获取flag需要的条件,总结有3个办法:
分析calc()方法能算出答案,但这个方法在so中,得分析汇编代码才行,当然可以尝试使用ida pro,F5查看C代码分析,前提是算法不难。
获取calc函数的返回值,从而计算答案。
还有一个方法就是,直接将MainActivity.this.cnt的值构造成1000。
接下来就用frida,使用后两种思路来解这个简单的示例。但在这之前得先了解Frida自带的Messages机制,了解frida怎么从通过一个python脚本发送和接收message消息是一个提升理解frida的好方法。
0x02 frida自带的Messages机制与进程交互
先来看看一个Messages的模板,这里用到的语言分别是python和javascript,他们之间的关系是python作为载体,javascript作为在android中真正执行代码。
import frida, sys
//hook代码,采用javascript编写
jscode = """
//javascript代码,重点
"""
//自定义回调函数
def on_message(message, data):
if message['type'] == 'send':
print("[*] {0}".format(message['payload']))
else:
print(message)
#重点的4行代码
process = frida.get_usb_device().attach('应用完整包名')
script = process.create_script(jscode)
script.on('message', on_message)
script.load()
sys.stdin.read()
当然如果是对此简单的使用,只需要编写jscode,以及填写你要hook的应用完整包名就行了,不过如果单纯只会用可能在以后会被模板限制,所以一探究竟还是很有必要。
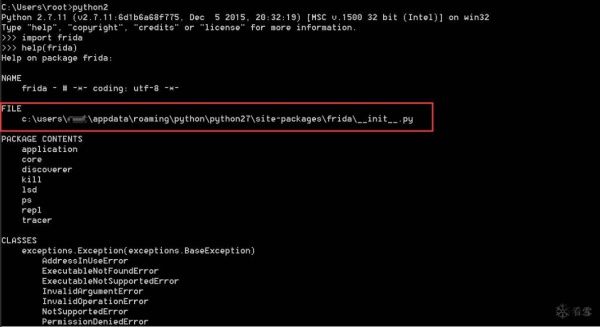
可以在cmd中,使用python终端的help()函数找到frida库的源代码的绝对路径。
接下来就来具体看看这几句代码做了什么事情。
process = frida.get_usb_device().attach('应用完整包名')
script = process.create_script(jscode)
script.on('message', on_message)
script.load()
sys.stdin.read()
首先使用了 frida.get_usb_device(),返回了一个 _get_device 函数,跟进_get_device 方法。
def get_usb_device(timeout = 0):
return _get_device(lambda device: device.type == 'tether', timeout)
在 _get_device 中,通过 get_device_manager() 实例化 DeviceManager 类,并调用该类中的 enumerate_devices() 方法。
def _get_device(predicate, timeout):
mgr = get_device_manager() //获取设备管理
def find_matching_device(): //寻找匹配设备
usb_devices = [device for device in mgr.enumerate_devices() if predicate(device)]
if len(usb_devices) > 0:
return usb_devices[0]
else:
return None
device = find_matching_device()
...省略
get_device_manager()代码
def get_device_manager():
global _device_manager
if _device_manager is None:
from . import core
_device_manager = core.DeviceManager(_frida.DeviceManager())
return _device_manager
DeviceManager中enumerate_devices()方法,可以看到 enumerate_devices() 方法实际上是返回了一个Device()类的实例化对象List。
class DeviceManager(object):
def __init__(self, impl):
self._impl = impl
def __repr__(self):
return repr(self._impl)
//返回了一个Device()类的实例化。
def enumerate_devices(self):
return [Device(device) for device in self._impl.enumerate_devices()]
def add_remote_device(self, host):
return Device(self._impl.add_remote_device(host))
def remove_remote_device(self, host):
self._impl.remove_remote_device(host)
def get_device(self, device_id):
devices = self._impl.enumerate_devices()
if device_id is None:
return Device(devices[0])
for device in devices:
if device.id == device_id:
return Device(device)
raise _frida.InvalidArgumentError("unable to find device with id %s" % device_id)
def on(self, signal, callback):
self._impl.on(signal, callback)
def off(self, signal, callback):
self._impl.off(signal, callback)
继续跟进Device类中的,就找到了attach()方法。在attach方法这是设置断点,看看传入的数据。
接下来提供的“应用完整名”是通过self._pid_of()函数去找到对应的进程号pid,然后将pid后通过Session类初始化。到此第一句代码过程就算是明白了,最终得到的是一个对应进程号pid的Session实例化对象process。
class Device(object):
def __init__(self, device):
self.id = device.id
self.name = device.name
self.icon = device.icon
self.type = device.type
self._impl = device
def __repr__(self):
return repr(self._impl)
...节省空间删除部分方法,详细内容可自行查看源码
def kill(self, target):
self._impl.kill(self._pid_of(target))
//返回了一个Session的实例化对象
def attach(self, target):
return Session(self._impl.attach(self._pid_of(target)))
def inject_library_file(self, target, path, entrypoint, data):
return self._impl.inject_library_file(self._pid_of(target), path, entrypoint, data)
def inject_library_blob(self, target, blob, entrypoint, data):
return self._impl.inject_library_blob(self._pid_of(target), blob, entrypoint, data)
def on(self, signal, callback):
self._impl.on(signal, callback)
def off(self, signal, callback):
self._impl.off(signal, callback)
def _pid_of(self, target):
if isinstance(target, numbers.Number):
return target
else:
return self.get_process(target).pid
第二句,紧接着 process.create_script(jscode),可以看到它返回一个Script类的实例化,参数不确定。
def create_script(self, *args, **kwargs):
return Script(self._impl.create_script(*args, **kwargs))
跟进Script类,可以找到on()方法,在on方法中可以设置自定义回调函数。
class Script(object):
def __init__(self, impl):
self.exports = ScriptExports(self)
self._impl = impl
self._on_message_callbacks = []
self._log_handler = self._on_log
self._pending = {}
self._next_request_id = 1
self._cond = threading.Condition()
impl.on('destroyed', self._on_destroyed)
impl.on('message', self._on_message)
...节省空间删除部分类方法,详细内容可自行查看源码
def load(self):
self._impl.load()
//设置自定义回调函数
def on(self, signal, callback):
if signal == 'message':
self._on_message_callbacks.append(callback)
else:
self._impl.on(signal, callback)
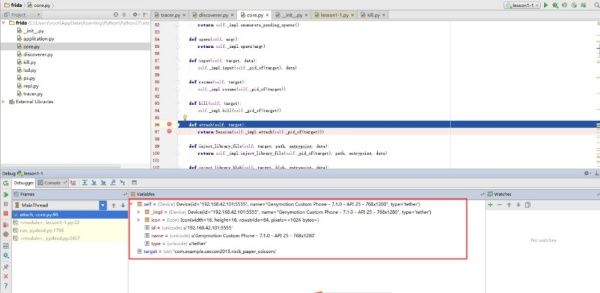
在IDE中可以看到_on_message_callbacks中存放的on_message函数地址。
接下来调用load()方法,在服务端就启动javascript脚本了,至于在frida-server服务端怎么执行的,可逆向研究一下frida-server,它才是真正的核心。
0x03 Javascript代码构造与执行
现在就来使用frida实现刚刚试想的方法。
方法一:获取calc()返回值
第一种思路就是直接获取calc的返回值,从native函数定义上知道它的返回值是int类型,当然直接获取calc函数的返回值是解出问题最简单的方法。
public native int calc();
那怎么获取calc()函数的返回值呢,这个函数在MainActivity类中,直接引用该类下的calc()方法,不就ok了吗,原理是这样,下面就来构造一下Javascript代码。
//Java.Perform 开始执行JavaScript脚本。
Java.perform(function () {
//定义变量MainActivity,Java.use指定要使用的类
var MainActivity = Java.use('com.example.seccon2015.rock_paper_scissors.MainActivity');
//hook该类下的onCreate方法,重新实现它
MainActivity.onCreate.implementation = function () {
send("Hook Start...");
//调用calc()方法,获取返回值
var returnValue = this.calc();
send("Return:"+returnValue);
var result = (1000+returnValue)*107;
//解出答案
send("Flag:"+"SECCON{"+result.toString()+"}");
}
});
JavaScript代码就是这样,如果不是很理解,学习一下JavaScript基础即可,下面看看完整的python脚本。
import frida, sys
def on_message(message, data):
if message['type'] == 'send':
print("[*] {0}".format(message['payload']))
else:
print(message)
jscode = """
Java.perform(function () {
var MainActivity = Java.use('com.example.seccon2015.rock_paper_scissors.MainActivity');
MainActivity.onCreate.implementation = function () {
send("Hook Start...");
var returnValue = this.calc();
send("Return:"+returnValue);
var result = (1000+returnValue)*107;
send("Flag:"+"SECCON{"+result.toString()+"}");
}
});
"""
process = frida.get_usb_device().attach('com.example.seccon2015.rock_paper_scissors')
script = process.create_script(jscode)
script.on('message', on_message)
script.load()
sys.stdin.read()
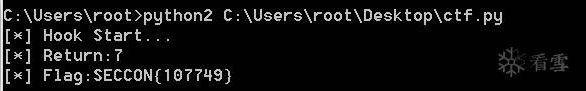
接下来运行一下,看看能否成功。
步骤如下:
启动模拟器,使用adb push将对应架构的frida-server文件push到模拟器中
/data/local/tmp目录下。
adb shell 进入/data/local/tmp目录,启动frida-server。
开启端口转发
adb forward tcp:27043 tcp:27043
adb forward tcp:27042 tcp:27042
启动应用后,在命令行等执行python脚本。
因为hook的是应用的onCreate方法,执行python脚本的前提是应用首先启动,这样才能attach到该应用,所以还得返回模拟器桌面重新启动应用,这样它才会执行hook的onCreate()方法,结果如下。
方法二:修改cnt的值为1000
第二种思路也比较简单,我们需要修改cnt的值,但如果直接修改cnt的初始值为1000的话,在游戏中可能存在不确定因素,比如输了会置0,赢了cnt值就变成1001了,所以还得控制一下输赢,而输赢的条件是电脑出什么,所以最终hook的方法就在onClick中。
从onClick()中可以知道,控制输赢的在于修改this.n 和 this.m的值,再来看看源代码。
public void onClick(View v) {
if (this.flag != 1) {
this.flag = 1;
((TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView3)).setText("");
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView);
TextView tv2 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView2);
this.m = 0;
//控制电脑出拳
this.n = new Random().nextInt(3);
tv2.setText(new String[]{"CPU: Paper", "CPU: Rock", "CPU: Scissors"}[this.n]);
if (v == this.P) {
tv.setText("YOU: Paper");
this.m = 0;
}
if (v == this.r) {
tv.setText("YOU: Rock");
this.m = 1;
}
if (v == this.S) {
tv.setText("YOU: Scissors");
this.m = 2;
}
this.handler.postDelayed(this.showMessageTask, 1000);
}
来看JavaScript代码怎么写吧
Java.perform(function () {
var MainActivity = Java.use('com.example.seccon2015.rock_paper_scissors.MainActivity');
//hook onClick方法,此处要注意的是onClick方法是传递了一个View参数v
MainActivity.onClick.implementation = function (v) {
send("Hook Start...");
//调用onClick,模拟点击事件
this.onClick(v);
//修改参数
this.n.value = 0;
this.m.value = 2;
this.cnt.value = 999;
send("Success!")
}
});
完整python代码
import frida, sys
def on_message(message, data):
if message['type'] == 'send':
print("[*] {0}".format(message['payload']))
else:
print(message)
jscode = """
Java.perform(function () {
var MainActivity = Java.use('com.example.seccon2015.rock_paper_scissors.MainActivity');
MainActivity.onClick.implementation = function (v) {
send("Hook Start...");
this.onClick(v);
this.n.value = 0;
this.m.value = 2;
this.cnt.value = 999;
send("Success!")
}
});
"""
process = frida.get_usb_device().attach('com.example.seccon2015.rock_paper_scissors')
script = process.create_script(jscode)
script.on('message', on_message)
script.load()
sys.stdin.read()
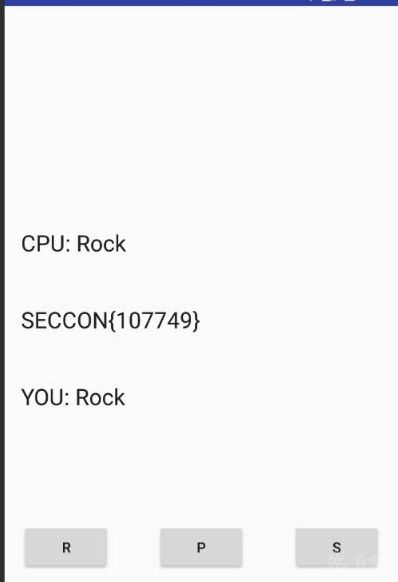
执行python脚本,任意点击按钮,答案就出来了。
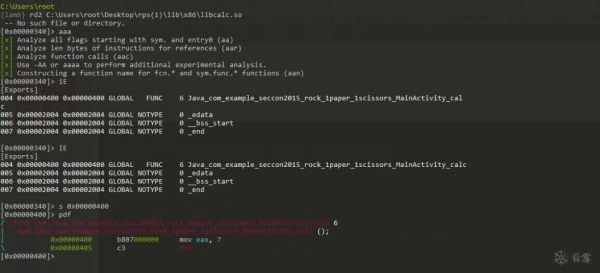
当然,如果so中的calc()函数算法不难的前提,直接使用ida pro或者radare2分析汇编代码也是可以的。这里给出用radare2反汇编出来的代码。可以看到,calc()函数就单纯的返回了int值7。
0x04 总结
一般分析流程
1. 反编译apk,分析代码寻找hook点。
2. 编写js代码,调用类的方法或者替换。
3. 在python中执行即可。
下面一篇会更详细介绍frida的使用。
来源:[原创]初识Frida--Android逆向之Java层hook (一)
本文由看雪论坛 ghostmazeW 原创
转载请注明来自看雪社区