一、时间状语从句
(一)when, while, as
1. 从属连词 when 既可引导一个持续性动作, 也可引导一个短暂性动作; 可用于主句动作和从句动作同时发生, 也可用于从句动作先于主句动作发生。
When I lived there, I used to go to the seashore on Sundays.
我住在那里时, 星期天常到海滨去。
When the film ended, the people went back.
电影一结束, 看电影的人便回去了。
当when 引导的时间状语从句为系表结构, 而且其主语和主句的主语一致, 其表语又是一个名词时, 就可以用由as 引导的省略结构来代替 when 引导的从句。
As a young man( = When he was a young man), he was fond of hunting.
他年轻时喜欢打猎。
2. 从属连词 while 引导的动作必须是持续性的, 侧重主句动作和从句动作相对比。
Please don't talk so loud while others are working.
别人在工作时请别那么大声谈话。
3. 从属连词as 可表示从句和主句的两个动作交替进行或同时完成, 可译为“一边……, 一边……”或“随着……”。
He hurried home, looking behind as he went.
他匆匆忙忙回家去, 一边走一边回头望。
As time goes on, it's getting warmer and warmer.
随着时间的推移, 天气变得越来越暖和了。
4. 如果主句表示的是短暂性动作, 而从句用延续性动词的进行时态表示在一段时间内正在进行的动作, 此时when, while与as 可互换使用。
When/While/As I was walking down the street, I came across an old friend of mine.
当我沿大街行走时, 碰巧遇到了我的一个老朋友。
题组训练 用when, while, as 填空
① When/While/As I was waiting at the bus stop, I noticed a police car in front of the store.
② When John arrived, I was cooking lunch.
③ As he grew older, he lost interest in everything except gardening.
(二)as soon as, immediately, directly, the moment, the minute, the instant 和once(一……就……)这些从属连词引导的从句都表示从句的动作一发生, 主句的动作随即发生, 常译为“一……就……”。
The moment I heard the voice, I knew my father was coming.
一听到那个声音, 我就知道父亲快来了。
The boy burst into tears immediately he saw his mother.
那个男孩一见到他妈妈便放声大哭。
注意: no sooner...than...; hardly/scarcely...when...也可表示“一……就……”, 这一结构的时态搭配为: no sooner 与 hardly/scarcely 所在的主句的谓语动词应用过去完成时, 而 than 与when引导的从句的谓语动词应用一般过去时。此外, 当把 no sooner 和 hardly/scarcely 提到句首时, 其所在的主句应用倒装语序。
I had hardly got home when it began to rain.
Hardly had I got home when it began to rain.
我一到家天就下起雨来。
We had no sooner arrived at the station than the train left.
No sooner had we arrived at the station than the train left.
我们一到车站, 火车就离站了。
题组训练 单句填空
④He had no sooner finished his speech than the students started cheering.
⑤You will be successful in the interview once/if you have confidence.
⑥Just use this room for the time being, and we'll offer you a larger one as soon as it becomes available.
(三)till, until 和not...until
1. 肯定句: 主句的谓语动词必须是延续性动词, 主句、从句都为肯定式, 意为“某动作一直延续到某时间点才停止”。
He remained there until/till she arrived.
他在那儿一直待到她来。
You may stay here until/till the rain stops.
你可以在这里待到雨停。
2. 否定句: 主句的谓语动词必须是非延续性动词, 从句为肯定式, 意为“某动作直到某时间才开始”。
He won't go to bed till/until she returns.
直到她回来他才会去睡。
3. till 不可以置于句首, 而until 可以。
Until you told me I had no idea of it.
直到你告诉我, 我才知道此事。
4. not until...句型的强调和倒装用法。
直到你告诉我, 我才知道这件事。
It was not until you told me that I had any idea of it.(强调句型)
Not until you told me did I have any idea of it.(not until 置于句首, 主句要部分倒装)
题组训练 同义句转换
I didn't leave until she came back.
⑦ Not until she came back did I leave.
⑧ It was not until she came back that I left .
(四)before 和since
1. 若表达“还未……就……; 不到……就……; ……才……; 还没来得及……就……”时, 需用连词before。
We had sailed four days and four nights before we saw land.
我们航行了四天四夜才看到陆地。
We hadn't run a mile before he felt tired.
我们跑了还不到一英里他就感到累了。
Before I could get in a word, he had measured me.
我还没来得及插话, 他就给我量好了尺寸。
2. before 从句中谓语不用否定式。
Before they reached the station, the train had gone.
他们到火车站前(他们还没到火车站), 火车就已开走了。
3.“It will be/was + 一段时间 + before...” 常翻译成: ……才; ……就。
It was half a year before I came back.
半年后我才回来。
It won't be long before we meet again.
过不了多长时间我们就会再见面了。
4. since 从句的谓语动词一般是非延续性动词, 主句的谓语动词是延续性的或者是反复发生的动作。since 从句的时态若是一般过去时, 主句中的时态常是现在完成时或现在完成进行时。
I have written home four times since I came here.
自从我来到这儿, 我已经给家里写过四封信了。
She has been working in this factory since she left school.
她离开学校以后就一直在这个工厂工作。
5. 在“It is + 一段时间 + since 从句” 句型中, since 引导的从句的谓语动词若是延续性动词, 常理解为某一状态的终止; 若是终止性动词, 则理解为某一动作的开始。
It is three years since the war broke out.(终止性动词)
自战争爆发以来已有三年了。
It is three years since I smoked( = since I stopped smoking).(延续性动词)
我不吸烟已有三年了。
如果译成“我吸烟已有三年了”, 应为: It is three years since I began to smoke.(终止性动词)
题组训练 英译汉
⑨It is three years since she was in our class.
她离开我们班已有三年了。
⑩It is three years since he lived here.
他不在这儿住已有三年了。
单句填空
[11]As is reported, it is 100 years since Qinghua University was founded.
[12]Because of the heavy traffic, it was already time for lunch break when she got to her office.
[13] (2013 陕西, 18)I have heard a lot of good things about you since I came back from abroad.
(五)every time, each time, next time, the last time, any time 等名词短语用来引导时间状语从句, 表示“ 每当……; 每次……; 下次……”等。
Every/Each time I was in trouble, he would come to help me out.
每当我处于困境, 他就会来帮助我。
Next time you come, do remember to bring your son here.
下次你来这里的时候, 一定记着把你儿子带来。
The last time she saw James, he was lying in bed.
上次她看见詹姆斯的时候, 他正躺在床上。
二、地点状语从句
引导地点状语从句的从属连词where, wherever 指具体地点时, 从句可用于主句之前或之后; 表示抽象条件的含义时, 从句需放在主句之前。
We should go where the Party needs us most.
我们应到党最需要我们的地方去。
You are free to go wherever you like.
你愿意去哪里就去哪里。
Where there is a will, there is a way.
有志者, 事竟成。
Where there is smoke, there is fire.
无火不生烟。/无风不起浪。
题组训练 单句填空
[14]After the war, a new school building was put up where there had once been a theatre.
[15]I have kept the portrait where I can see it every day, as it always reminds me of my university days in London.
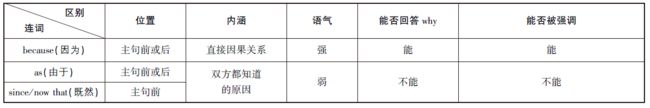
三、原因状语从句
1. 引导原因状语从句的从属连词主要有: because, as, since, now that。每个连词的含义不尽相同。
I was absent from the meeting because I was ill.
因为我病了, 所以我开会缺席了。
As it is raining, we shall not go to the park.
由于在下雨, 我们不去公园了。
Now that/Since everybody is here, let's begin our meeting.
既然大家都在这里, 我们开始开会吧。
2. 此外, when, seeing that, considering that 也可以表示原因, 意为: 既然; 考虑到。
It was foolish of you to take a taxi when you could walk there in five minutes.
既然你步行5 分钟能到那里, 却打的, 真够愚蠢的。
题组训练 单句填空
[16] Now that my head had cleared, my brain was also beginning to work much better.
四、目的状语从句
引导目的状语从句的从属连词有: so that, in order that, in case 等。
1. in order that, so that
两个连词都意为“以便……; 为了……”, 它们引导的状语从句中常用情态动词。in order that 比so that 正式, 引导的状语从句可置于主句之前或之后, 而so that 引导的从句只能置于主句之后。
I'll speak slowly so that you can understand me.
我会慢慢说, 以便你能明白我的意思。
In order that we might see the sunrise, we started for the peak early. 为了能看到日出, 我们很早就出发去了山顶。
2. for fear that 与in case
引导目的状语从句时, for fear that 表示“害怕、担心”某事会发生; in case 表示“以防(万一)”出现某种情况。
Mary didn't want to get out of bed for fear that she might wake her baby(up).玛丽不想起床, 担心吵醒她的宝宝。
Take your raincoat in case it rains. 带上雨衣以防下雨。
题组训练 单句填空
[17] ( 2013 北京, 30 ) I took my driving license with me on holiday, in case I wanted to hire a car.
[18] She finally ran away for fear that her parents would scold her.
五、结果状语从句
1. 引导结果状语从句的从属连词有: so that, so...that..., such...that...。在非正式语体中, 由 so...that..., such...that...引导的句子中的 that 可以省略, 注意其结构:
so + 形容词/副词 + that 从句
so + 形容词 + a/an + 可数名词单数形式 + that 从句
so + many/much/few/little(少) + 名词 + that 从句
such + a/an + 形容词 + 可数名词单数形式 + that 从句
such + 形容词 + 可数名词复数形式/不可数名词 + that 从句
such + a lot of/lots of + 名词 + that 从句
Mike is such an honest worker that we all believe in him.
=Mike is so honest a worker that we all believe in him.
迈克是一个如此诚实的工人, 以至于我们都信任他。
It is such fine weather that we all want to go to the park.
天气如此晴朗, 以至于我们都想去公园。
He earned so little money that he couldn't support his family.
他挣这么少的钱, 以至于养不起家。
注意:
(1)为了强调形容词和副词, 当so 或such 置于句首时, 主句要用倒装语序。
So clever a student was he that he was able to work out all the difficult questions.
他是如此聪明的一个学生, 以至于能够解出所有难题。
(2)当so 或such 所在的主句主语与结果状语从句中的主语一致时, 还可简化为: so/such...as to...。
He was so clever a student that he was able to work out all the difficult questions.→
He was so clever a student as to be able to work out all the difficult questions.
题组训练 用so 或such 填空
[19] It is not surprising that such little worms eat so little grain.
[20] Can you believe that in such a rich country there should be so many poor people?
[21]He is so smart a boy that I like him very much.
2. 除结果状语从句外, too...to...( 太…… 而不能……), enough to...(达到某种程度可以……) 等不定式结构同样可以表示结果。
他起床太晚了, 没有赶上那班公共汽车。
He didn't get up early enough to catch the bus.
=He got up too late to catch the bus.
题组训练 同义句转换
He is so young that he can't join the army.
[22]He is not old enough to join the army.
[23]He is too young to join the army.
[24]He is so young as not to join the army.
3. such...that...引导的状语从句与such...as...引导的定语从句的区别。
首先观察两个句子:
①He is such a clever boy as everyone likes.
他是一个人人都喜爱的聪明孩子。
②He is such a clever boy that everyone likes him.
他是一个如此聪明的孩子, 以至于人人都喜欢他。
第①个句子中everyone likes 成分残缺, 缺少宾语, 故可判断该句为定语从句;
第②句中everyone likes him 结构完整, 不缺任何成分, 故可判断为状语从句。
题组训练 用as, that 填空
[25]Such advice as he was given proved almost worthless.
[26] It was such a boring speech that I fell asleep.
六、条件状语从句
引导条件状语从句的从属连词有: if, unless( = if...not 如果不; 除非……否则……), so/as long as(只要), in case(如果), on condition that ( 条件是), suppose/supposing ( that) ( 假设), providing/provided that(如果)等。
You'll fail the exam unless you study hard ( = if you don't study hard).除非你努力学习, 否则你考试会不及格。
As long as you don't lose heart, you will succeed.
你只要不灰心就会成功。
Suppose/Supposing (that)they refuse us, who else can we turn to for help?
假如他们拒绝了我们, 我们还能求助于谁?
In case there is a fire, what will we do first?
如果发生火灾, 我们首先做什么?
题组训练 单句填空
[27] Unless our manager objects to Tom's joining the club, we shall accept him as a member.
[28]You may use the room as you like as/so long as you clean it up afterwards.
七、方式状语从句
引导方式状语从句的从属连词有: as, as if, as though 等。方式状语从句应放在主句之后。其中as if 或as though 引导的从句一般用虚拟语气, 但如果从句中所陈述的情况很可能实现, 也可用陈述语气。
Do as you are told, or you'll be fired.
叫你做什么你就做什么, 否则你会被解雇。
The old lady treats the boy as if he were her own son.(虚拟语气)这位老太太对待这个男孩就像他是她自己的儿子似的。
I feel as if I have a fever.(陈述语气)
我感觉我好像发烧了。
题组训练 单句填空
[29]Leave the table as it is.
[30]Jack wasn't saying anything but the teacher smiled at him as if he had done something very clever.
八、让步状语从句
1. although/though( 尽管, 虽然), even though/even if( 即使, 尽管)引导的让步状语从句。
although 与though 两者意思相同, 一般可互换, 都可以与yet, still 或nevertheless 连用, 但不能和but 连用。
He is unhappy, though/although he has a lot of money.
虽然他很有钱, 但他并不幸福。
Although/Though it was raining hard, yet they went on playing football.
虽然雨下得很大, 但他们还是继续踢足球。
Even though/Even if it is raining, we'll go there.(陈述语气)
尽管下着雨, 我们也要去那里。
Even if I were busy, I would go.(虚拟语气)
即使忙, 我也要去。
注意: though 还可用作副词, 意为“可是, 然而”, 置于句末。如:
He said he would come; he didn't, though.
他说他会来, 可是没有来。
2. whether...or...(不管……还是……); 疑问词 + -ever 与no matter + 疑问词(不管……; 无论……)。
Whether you believe it or not, it is true.
不管你相信与否, 那都是真的。
Whatever( = No matter what) you say, he won't believe you.
无论你说什么, 他都不会相信你。
Whoever you are( = No matter who you are), you must obey the rules. 无论你是谁, 你都要遵守规则。
注意: whoever, whatever, whomever, whichever 还可以引导名词性从句。
You can take whatever you like.(宾语从句)
你喜欢什么就可以拿什么。
3. when, while 也可作从属连词表让步, while 常用在句首, when 常用在句中, 相当于although。
Suddenly, she stopped when she ought to have continued.
尽管她应该继续下去, 她却突然停住了。
While I admit that there are problems, I don't agree that they cannot be solved.
尽管我承认有问题存在, 但我不同意说这些问题不能解决。
4. as 或though 引导让步状语从句时倒装的情况( 详见“特殊句式”专题)
题组训练 单句填空
[31]It was a nice meal, though a little expensive.
[32] While/Although/Though all of them are strong candidates, only one will be chosen for the post.