前言
开心一刻
一只被二哈带偏了的柴犬,我只想弄死隔壁的二哈
what:是什么
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口很简单,只包含一个方法
/** * 通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor,我们自定义修改应用程序上下文中的bean定义 * * 应用上下文能够在所有的bean定义中自动检测出BeanFactoryPostProcessor bean, * 并在任何其他bean创建之前应用这些BeanFactoryPostProcessor bean * * BeanFactoryPostProcessor对自定义配置文件非常有用,可以覆盖应用上下文已经配置了的bean属性 * * PropertyResourceConfigurer就是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的典型应用 * 将xml文件中的占位符替换成properties文件中相应的key对应的value */ @FunctionalInterface public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor { /** * 在应用上下文完成了标准的初始化之后,修改其内部的bean工厂 * 将加载所有bean定义,但尚未实例化任何bean. * 我们可以覆盖或添加bean定义中的属性,甚至是提前初始化bean */ void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; }
推荐大家直接去读它的源码注释,说的更详细、更好理解
简单来说,BeanFactoryPostProcessor是spring对外提供的接口,用来拓展spring,能够在spring容器加载了所有bean的信息信息之后、bean实例化之前执行,修改bean的定义属性;有人可能会问,这有什么用?大家还记得spring配置文件中的占位符吗? 我们会在spring配置中配置PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer(继承PropertyResourceConfigurer)bean来处理占位符, 举个例子大家就有印象了
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
classpath:mysqldb.properties class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
mysqldb.properties
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.100:3306/mybatis jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root
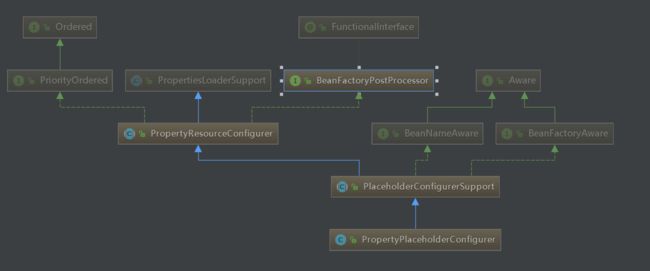
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer类的继承关系图
how:怎么用
怎么用,这个问题比较简单,我们实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,然后将将其注册到spring容器即可,在spring启动过程中,在常规bean实例化之前,会执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法(里面有我们想要的逻辑),完成我们想要的操作;
重点应该是:用来干什么
上述占位符的例子是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的应用之一,但这是spring提供的BeanFactoryPostProcessor拓展,不是我们自定义的;实际工作中,自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor的情况确实少,反正至少我是用的非常少的,但我还是有使用印象的,那就是对敏感信息的解密处理;上述数据库的连接配置中,用户名和密码都是明文配置的,这就存在泄漏风险,还有redis的连接配置、shiro的加密算法、rabbitmq的连接配置等等,凡是涉及到敏感信息的,都需要进行加密处理,信息安全非常重要
配置的时候以密文配置,在真正用到之前在spring容器中进行解密,然后用解密后的信息进行真正的操作,下面我就举个简单的例子,用BeanFactoryPostProcessor来完整敏感信息的解密
加解密工具类:DecryptUtil.java
package com.lee.app.util; import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils; import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder; import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder; import javax.crypto.Cipher; import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator; import java.security.Key; import java.security.SecureRandom; public class DecryptUtil { private static final String CHARSET = "utf-8"; private static final String ALGORITHM = "AES"; private static final String RANDOM_ALGORITHM = "SHA1PRNG"; public static String aesEncrypt(String content, String key) { if (content == null || key == null) { return null; } Key secretKey = getKey(key); try { Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey); byte[] p = content.getBytes(CHARSET); byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(p); BASE64Encoder encoder = new BASE64Encoder(); String encoded = encoder.encode(result); return encoded; } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public static String aesDecrypt(String content, String key) { Key secretKey = getKey(key); try { Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey); BASE64Decoder decoder = new BASE64Decoder(); byte[] c = decoder.decodeBuffer(content); byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(c); String plainText = new String(result, CHARSET); return plainText; } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } private static Key getKey(String key) { if (StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) { key = "hello!@#$world";// 默认key } try { SecureRandom secureRandom = SecureRandom.getInstance(RANDOM_ALGORITHM); secureRandom.setSeed(key.getBytes()); KeyGenerator generator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM); generator.init(secureRandom); return generator.generateKey(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // key可以随意取,DecryptConfig中decryptKey与此相同即可 String newUserName= aesEncrypt("root", "hello!@#$world"); // QL34YffNntJi1OWG7zGqVw== System.out.println(newUserName); String originUserName = aesDecrypt(newUserName, "hello!@#$world"); System.out.println(originUserName); String newPassword = aesEncrypt("123456", "hello!@#$world"); // zfF/EU6k4YtzTnKVZ6xddw== System.out.println(newPassword); String orignPassword = aesDecrypt(newPassword, "hello!@#$world"); System.out.println(orignPassword); } }
配置文件:application.yml
server: servlet: context-path: /app port: 8888 spring: #连接池配置 datasource: type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource druid: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 #Enc[:解密标志前缀,]:解密后缀标志,中间内容是需要解密的内容 username: Enc[QL34YffNntJi1OWG7zGqVw==] password: Enc[zfF/EU6k4YtzTnKVZ6xddw==] initial-size: 1 #连接池初始大小 max-active: 20 #连接池中最大的活跃连接数 min-idle: 1 #连接池中最小的活跃连接数 max-wait: 60000 #配置获取连接等待超时的时间 pool-prepared-statements: true #打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小 max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20 validation-query: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL validation-query-timeout: 30000 test-on-borrow: false #是否在获得连接后检测其可用性 test-on-return: false #是否在连接放回连接池后检测其可用性 test-while-idle: true #是否在连接空闲一段时间后检测其可用性 #mybatis配置 mybatis: type-aliases-package: com.lee.app.entity #config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml # pagehelper配置 pagehelper: helperDialect: mysql #分页合理化,pageNum<=0则查询第一页的记录;pageNum大于总页数,则查询最后一页的记录 reasonable: true supportMethodsArguments: true params: count=countSql decrypt: prefix: "Enc[" suffix: "]" key: "hello!@#$world"
工程中解密:DecryptConfig.java
package com.lee.app.config; import com.lee.app.util.DecryptUtil; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.boot.env.OriginTrackedMapPropertySource; import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware; import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.core.env.MutablePropertySources; import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import java.util.stream.StreamSupport; /** * 敏感信息的解密 */ @Component public class DecryptConfig implements EnvironmentAware, BeanFactoryPostProcessor { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DecryptConfig.class); private ConfigurableEnvironment environment; private String decryptPrefix = "Enc["; // 解密前缀标志 默认值 private String decryptSuffix = "]"; // 解密后缀标志 默认值 private String decryptKey = "hello!@#$world"; // 解密可以 默认值 @Override public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) { this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment; } @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { LOGGER.info("敏感信息解密开始....."); MutablePropertySources propSources = environment.getPropertySources(); StreamSupport.stream(propSources.spliterator(), false) .filter(ps -> ps instanceof OriginTrackedMapPropertySource) .collect(Collectors.toList()) .forEach(ps -> convertPropertySource((PropertySource) ps)); LOGGER.info("敏感信息解密完成....."); } /** * 解密相关属性 * @param ps */ private void convertPropertySource(PropertySource ps) { LinkedHashMap source = ps.getSource(); setDecryptProperties(source); source.forEach((k,v) -> { String value = String.valueOf(v); if (!value.startsWith(decryptPrefix) || !value.endsWith(decryptSuffix)) { return; } String cipherText = value.replace(decryptPrefix, "").replace(decryptSuffix, ""); String clearText = DecryptUtil.aesDecrypt(cipherText, decryptKey); source.put(k, clearText); }); } /** * 设置解密属性 * @param source */ private void setDecryptProperties(LinkedHashMap source) { decryptPrefix = source.get("decrypt.prefix") == null ? decryptPrefix : String.valueOf(source.get("decrypt.prefix")); decryptSuffix = source.get("decrypt.suffix") == null ? decryptSuffix : String.valueOf(source.get("decrypt.suffix")); decryptKey = source.get("decrypt.key") == null ? decryptKey : String.valueOf(source.get("decrypt.key")); } }
主要就是3个文件,DecryptUtil对明文进行加密处理后,得到的值配置到application.yml中,然后工程启动的时候,DecryptConfig会对密文进行解密,明文信息存到了spring容器,后续操作都是在spring容器的明文上进行的,所以与我们平时的不加密的结果一致,但是却对敏感信息进行了保护;工程测试结果如下:
完整工程地址:spring-boot-BeanFactoryPostProcessor
有兴趣的可以去看下jasypt-spring-boot的源码,你会发现他的原理是一样的,也是基于BeanFactoryPostProcessor的拓展
why:为什么能这么用
为什么DecryptConfig实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,将DecryptConfig注册到spring之后,DecryptConfig的postProcessBeanFactory方法就会执行?事出必有因,肯定是spring启动过程中会调用DecryptConfig实例的postProcessBeanFactory方法,具体我们来看看源码,我们从AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法开始
不得不说,spring的命名、注释确实写得好,很明显我们从refresh中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法开始,大家可以仔细看下PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,先按PriorityOrdered、Ordered、普通(没有实现PriorityOrdered和Ordered接口)的顺序调用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,然后再按先按PriorityOrdered、Ordered、普通的顺序调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor,这个顺序还是值得大家注意下的,如果我们自定义的多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor有顺序之分,而我们又没有指定其执行顺序,那么可能出现的不是我们想要的结果
这里可能会有会有人有这样的的疑问:bean定义(BeanDefinition)是在什么时候加载到spring容器的,如何保证BeanFactoryPostProcessor实例起作用之前,所有的bean定义都已经加载到了spring容器
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,在springboot的createApplicationContext阶段注册到spring容器的,也就是说在spring的refresh之前就有了ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实例;ConfigurationClassPostProcessor被应用的时候(调用其postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法),会加载全部的bean定义(包括我们自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor实例:DecryptConfig)到spring容器,bean的加载详情可查看:springboot2.0.3源码篇 - 自动配置的实现,是你想象中的那样吗,那么在应用BeanFactoryPostProcessor实例之前,所有的bean定义就已经加载到spring容器了,BeanFactoryPostProcessor实例也就能修改bean定义了
至此,BeanFactoryPostProcessor的机制我们就清楚了,为什么能这么用这个问题也就明了了
总结
1、BeanFactoryPostProcessor是beanFactory的后置处理器接口,通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor,我们可以自定义spring容器中的bean定义,BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义信息之后、bean实例化之前执行;
2、BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的bean会被spring自动检测,在常规bean实例化之前被spring调用;
3、BeanFactoryPostProcessor的常用场景包括spring中占位符的处理、我们自定义的敏感信息的解密处理,当然不局限与此;
其实只要我们明白了BeanFactoryPostProcessor的生效时机,哪些场景适用BeanFactoryPostProcessor也就很清楚了