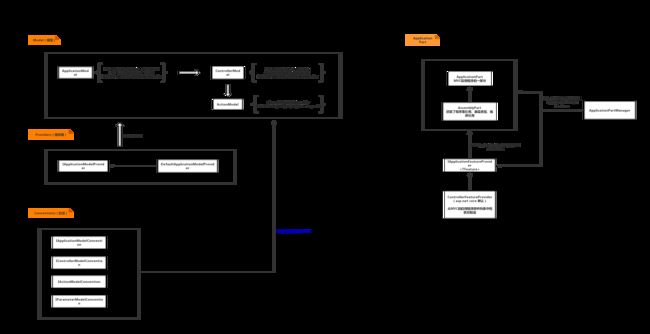
一、前言
参照前篇《4. abp中的asp.net core模块剖析》,首先放张图,这也是asp.net core框架上MVC模块的扩展点
二、abp的mvc对象
AbpAspNetCoreMvcOptions类
从这个类的名称来看,这个是abp框架里面的asp.net core配置mvc选项类,是abp对asp.net core mvc的封装。源码如下:
public class AbpAspNetCoreMvcOptions
{
public ConventionalControllerOptions ConventionalControllers { get; }
public AbpAspNetCoreMvcOptions()
{
ConventionalControllers = new ConventionalControllerOptions();
}
}这个类只有一个默认构造函数,用于实例化一个名为ConventionalControllerOptions的类,从名称来看(得益于变量和类的命名规范化)这是Controller的规约配置。
ConventionalControllerOptions类
该类源码如下:
public class ConventionalControllerOptions
{
public ConventionalControllerSettingList ConventionalControllerSettings { get; }
public List FormBodyBindingIgnoredTypes { get; }
public ConventionalControllerOptions()
{
ConventionalControllerSettings = new ConventionalControllerSettingList();
FormBodyBindingIgnoredTypes = new List
{
typeof(IFormFile)
};
}
public ConventionalControllerOptions Create(Assembly assembly, [CanBeNull] Action optionsAction = null)
{
var setting = new ConventionalControllerSetting(assembly, ModuleApiDescriptionModel.DefaultRootPath);
optionsAction?.Invoke(setting);
setting.Initialize();
ConventionalControllerSettings.Add(setting);
return this;
}
} 在这里要提下asp.net core的options模式,一般XXXOptions类都会在默认的构造函数中实例化一些对象,Options类的作用就是将一个POCO类注册到服务容器中,使得我们可以在控制器的构造函数中通过IOptions 获取到TOptions类的实例。
这个类只有一个Create方法,返回当前TOptions类的实例,当然,在这个方法中构造了规约控制器的配置(ConventionalControllerSetting) 。在这个Create方法中,首先实例化一个ConventionalControllerSetting类,参数就是传过来的规约控制器所在的程序集以及url路由中默认的根目录(app)。接下来再调用委托,参数就是前面实例化的ConventionalControllerSetting,然后就是实例化(Initialize)操作,检索规约控制器集合。
ConventionalControllerSetting类
这个规约控制器的配置如下:
public class ConventionalControllerSetting
{
[NotNull]
public Assembly Assembly { get; }
[NotNull]
public HashSet ControllerTypes { get; } //TODO: Internal?
[NotNull]
public string RootPath
{
get => _rootPath;
set
{
Check.NotNull(value, nameof(value));
_rootPath = value;
}
}
private string _rootPath;
[CanBeNull]
public Action ControllerModelConfigurer { get; set; }
[CanBeNull]
public Func UrlControllerNameNormalizer { get; set; }
[CanBeNull]
public Func UrlActionNameNormalizer { get; set; }
public Action ApiVersionConfigurer { get; set; }
public ConventionalControllerSetting([NotNull] Assembly assembly, [NotNull] string rootPath)
{
Assembly = assembly;
RootPath = rootPath;
ControllerTypes = new HashSet();
ApiVersions = new List();
}
public void Initialize()
{
var types = Assembly.GetTypes()
.Where(IsRemoteService)
.WhereIf(TypePredicate != null, TypePredicate);
foreach (var type in types)
{
ControllerTypes.Add(type);
}
}
private static bool IsRemoteService(Type type)
{
if (!type.IsPublic || type.IsAbstract || type.IsGenericType)
{
return false;
}
var remoteServiceAttr = ReflectionHelper.GetSingleAttributeOrDefault(type);
if (remoteServiceAttr != null && !remoteServiceAttr.IsEnabledFor(type))
{
return false;
}
if (typeof(IRemoteService).IsAssignableFrom(type))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
} 在这个类中有几个重要的成员变量,首先是Assembly,这个是规约控制器所在的程序集,abp通过这个程序集去检索规约控制器;第二个就是ControllerTypes,它用于存储规约控制器类型,而这些类型就是从Assembly程序集中检索出来的;最后就是RootPath,它表示默认的根目录,在abp中是"app"。接下来就是两个方法了,首先是IsRemoteService,顾名思义就是检索RemoteService,从代码来看,主要就是检索RemoteAttribute和继承自IRemoteService接口的类,为什么要根据这两个来检索呢?很简单,看看IAppService的定义:
public interface IApplicationService :
IRemoteService
{
}再来看看Initialize方法:
public void Initialize()
{
var types = Assembly.GetTypes()
.Where(IsRemoteService)
.WhereIf(TypePredicate != null, TypePredicate);
foreach (var type in types)
{
ControllerTypes.Add(type);
}
}它正是通过调用IsRemoteService方法来检索规约控制器,然后添加到ControllerTypes中的。
三、abp中的应用模型规约
在最上面的aspnetcore mvc扩展图中,规约模块(Convention)可以调换掉mvc框架的默认应用模型(Model),从而自定义的控制器等。abp中封装了这么一个规约类,源码如下:
public class AbpServiceConvention : IAbpServiceConvention, ITransientDependency
{
private readonly AbpAspNetCoreMvcOptions _options;
public AbpServiceConvention(IOptions options)
{
_options = options.Value;
}
public void Apply(ApplicationModel application)
{
ApplyForControllers(application);
}
protected virtual void ApplyForControllers(ApplicationModel application)
{
foreach (var controller in application.Controllers)
{
var controllerType = controller.ControllerType.AsType();
var configuration = GetControllerSettingOrNull(controllerType);
//TODO: We can remove different behaviour for ImplementsRemoteServiceInterface. If there is a configuration, then it should be applied!
//TODO: But also consider ConventionalControllerSetting.IsRemoteService method too..!
if (ImplementsRemoteServiceInterface(controllerType))
{
controller.ControllerName = controller.ControllerName.RemovePostFix(ApplicationService.CommonPostfixes);
configuration?.ControllerModelConfigurer?.Invoke(controller);
ConfigureRemoteService(controller, configuration);
}
else
{
var remoteServiceAttr = ReflectionHelper.GetSingleAttributeOrDefault(controllerType.GetTypeInfo());
if (remoteServiceAttr != null && remoteServiceAttr.IsEnabledFor(controllerType))
{
ConfigureRemoteService(controller, configuration);
}
}
}
}
protected virtual void ConfigureRemoteService(ControllerModel controller, [CanBeNull] ConventionalControllerSetting configuration)
{
ConfigureApiExplorer(controller);
ConfigureSelector(controller, configuration);
ConfigureParameters(controller);
}
} IAbpServiceConvention接口
看看IAbpServiceConvention接口的定义:
public interface IAbpServiceConvention : IApplicationModelConvention
{
}可以看到这个接口是继承自aspnet core的IApplicationModelConvention。这个接口有一个Apply方法,该方法,可以简单的理解为应用规约替换默认的应用模型。源码如下:
public interface IApplicationModelConvention
{
//
// 摘要:
// Called to apply the convention to the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.ApplicationModels.ApplicationModel.
//
// 参数:
// application:
// The Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.ApplicationModels.ApplicationModel.
void Apply(ApplicationModel application);
}AbpServiceConvention类
回到AbpServiceConvention类,这个类的构造函数就是用过Options模式获取到aspnetcoremvcoption类的实例,主要就是在ApplyForController方法上,顾名思义,就是应用于控制器。先看看这个方法:
protected virtual void ApplyForControllers(ApplicationModel application)
{
foreach (var controller in application.Controllers)
{
var controllerType = controller.ControllerType.AsType();
var configuration = GetControllerSettingOrNull(controllerType);
//TODO: We can remove different behaviour for ImplementsRemoteServiceInterface. If there is a configuration, then it should be applied!
//TODO: But also consider ConventionalControllerSetting.IsRemoteService method too..!
if (ImplementsRemoteServiceInterface(controllerType))
{
controller.ControllerName = controller.ControllerName.RemovePostFix(ApplicationService.CommonPostfixes);
configuration?.ControllerModelConfigurer?.Invoke(controller);
ConfigureRemoteService(controller, configuration);
}
else
{
var remoteServiceAttr = ReflectionHelper.GetSingleAttributeOrDefault(controllerType.GetTypeInfo());
if (remoteServiceAttr != null && remoteServiceAttr.IsEnabledFor(controllerType))
{
ConfigureRemoteService(controller, configuration);
}
}
}
} 在这个方法里面遍历应用模型里面的控制器(Controller)集合,根据控制器去检索规约控制器配置(ConventionalControllerSetting),上面也提到了这个类,就是一些约定的配置,如果我们配置了控制器模型(ConventionModel),那么就会在这里被调用。接下来最重要的就是ConfigureRemoteService方法。
ConfigureRemoteService方法
源码如下:
protected virtual void ConfigureRemoteService(ControllerModel controller, [CanBeNull] ConventionalControllerSetting configuration)
{
ConfigureApiExplorer(controller);
ConfigureSelector(controller, configuration);
ConfigureParameters(controller);
}在这里就是为我们的远程服务也就是XXXAppServices类配置详细的api信息。首先就是配置ApiExplorer,主要就是开放Api检索,swagger就是调用这个的。Selector就是配置Api的HTTPMethod和路由模型。Parameters则配置Action的参数,主要就是配置复杂类型的参数。
ConfigureApiExplorer
The ApiExplorer contains functionality for discovering and exposing metadata about your MVC application. 这句话是摘自博客 Introduction to the ApiExplorer in ASP.NET Core。我们翻译过来就是:ApiExplorer包含发现和公开MVC应用程序元数据的功能。从命名我们也能看出来这用来检索Api的。abp中是如何处理ApiExplorer的呢?
protected virtual void ConfigureApiExplorer(ControllerModel controller)
{
if (controller.ApiExplorer.GroupName.IsNullOrEmpty())
{
controller.ApiExplorer.GroupName = controller.ControllerName;
}
if (controller.ApiExplorer.IsVisible == null)
{
var controllerType = controller.ControllerType.AsType();
var remoteServiceAtt = ReflectionHelper.GetSingleAttributeOrDefault(controllerType.GetTypeInfo());
if (remoteServiceAtt != null)
{
controller.ApiExplorer.IsVisible =
remoteServiceAtt.IsEnabledFor(controllerType) &&
remoteServiceAtt.IsMetadataEnabledFor(controllerType);
}
else
{
controller.ApiExplorer.IsVisible = true;
}
}
foreach (var action in controller.Actions)
{
ConfigureApiExplorer(action);
}
}
protected virtual void ConfigureApiExplorer(ActionModel action)
{
if (action.ApiExplorer.IsVisible == null)
{
var remoteServiceAtt = ReflectionHelper.GetSingleAttributeOrDefault(action.ActionMethod);
if (remoteServiceAtt != null)
{
action.ApiExplorer.IsVisible =
remoteServiceAtt.IsEnabledFor(action.ActionMethod) &&
remoteServiceAtt.IsMetadataEnabledFor(action.ActionMethod);
}
}
} 这个方法中并没有做其余的事情,只是检索RemoteAttribute,然后去配置ApiExplorerModel类的IsVisible,默认的是true,也就是开放出来,提供检索。swagger就是通过这个来枚举api的。
ConfigureSelector
这个比较难理解,先看看aspnet core中的SelectorModel源码:
public class SelectorModel
{
public SelectorModel();
public SelectorModel(SelectorModel other);
public IList ActionConstraints { get; }
public AttributeRouteModel AttributeRouteModel { get; set; }
//
// 摘要:
// Gets the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.ApplicationModels.SelectorModel.EndpointMetadata
// associated with the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.ApplicationModels.SelectorModel.
public IList 分析下这个类,首先是ActionConstrains,这是一个接口其中就有一个实现HttpMethodActionConstraint,这个类就是约束了Action的HTTP类型,也就是平时在action上标记的[HTTPGet],一般标记了此特性,aspnetcore会默认实例化一个SelectorModel对象。然后就是最重要的AttributeRouteModel,这个就是路由特性,即平时在action上标记的[Route("xxx/xxx")],同时也实例化了一个SelectorModel对象。看看ConfigureSelector方法:
protected virtual void ConfigureSelector(ControllerModel controller, [CanBeNull] ConventionalControllerSetting configuration)
{
if (controller.Selectors.Any(selector => selector.AttributeRouteModel != null))
{
return;
}
var rootPath = GetRootPathOrDefault(controller.ControllerType.AsType());
foreach (var action in controller.Actions)
{
ConfigureSelector(rootPath, controller.ControllerName, action, configuration);
}
}
protected virtual void ConfigureSelector(string rootPath, string controllerName, ActionModel action, [CanBeNull] ConventionalControllerSetting configuration)
{
if (!action.Selectors.Any())
{
AddAbpServiceSelector(rootPath, controllerName, action, configuration);
}
else
{
NormalizeSelectorRoutes(rootPath, controllerName, action, configuration);
}
}
protected virtual void AddAbpServiceSelector(string rootPath, string controllerName, ActionModel action, [CanBeNull] ConventionalControllerSetting configuration)
{
var httpMethod = SelectHttpMethod(action, configuration);
var abpServiceSelectorModel = new SelectorModel
{
AttributeRouteModel = CreateAbpServiceAttributeRouteModel(rootPath, controllerName, action, httpMethod, configuration),
ActionConstraints = { new HttpMethodActionConstraint(new[] { httpMethod }) }
};
action.Selectors.Add(abpServiceSelectorModel);
}如果我们配置了路由特性,那么直接返回,否则,我们首先获取到默认的根目录(默认是app)。接下来就去配置abp的Selector,首先是选择HTTPMethod,这个是按照约定来的选择的,如下:
public static Dictionary ConventionalPrefixes { get; set; } = new Dictionary
{
{"GET", new[] {"GetList", "GetAll", "Get"}},
{"PUT", new[] {"Put", "Update"}},
{"DELETE", new[] {"Delete", "Remove"}},
{"POST", new[] {"Create", "Add", "Insert", "Post"}},
{"PATCH", new[] {"Patch"}}
}; 根据Action的名称来选择(默认是POST),然后实例化一个HttpMethodActionConstraint类,传入的参数就是HTTPMethod,这个就是前面说到的SelectorModel,最后就是创建路由模型了,我们会去计算一个路由模板,根据这个模板实例化RouteAttribute,再通过这个去实例化AttributeRouteModel,从而构造了SelectorModel的两个重要属性。路由模板的计算规则如下:
protected virtual string CalculateRouteTemplate(string rootPath, string controllerName, ActionModel action, string httpMethod, [CanBeNull] ConventionalControllerSetting configuration)
{
var controllerNameInUrl = NormalizeUrlControllerName(rootPath, controllerName, action, httpMethod, configuration);
var url = $"api/{rootPath}/{controllerNameInUrl.ToCamelCase()}";
//Add {id} path if needed
if (action.Parameters.Any(p => p.ParameterName == "id"))
{
url += "/{id}";
}
//Add action name if needed
var actionNameInUrl = NormalizeUrlActionName(rootPath, controllerName, action, httpMethod, configuration);
if (!actionNameInUrl.IsNullOrEmpty())
{
url += $"/{actionNameInUrl.ToCamelCase()}";
//Add secondary Id
var secondaryIds = action.Parameters.Where(p => p.ParameterName.EndsWith("Id", StringComparison.Ordinal)).ToList();
if (secondaryIds.Count == 1)
{
url += $"/{{{secondaryIds[0].ParameterName}}}";
}
}
return url;
}首先,Abp的动态控制器约束是以AppService、ApplicationService、Service结尾的控制器,在这里要注意两点,如果action参数是id,或者以id结尾且仅有一个参数,那么路由就是:
api/app/xxx/{id}/{action}
或
api/app/xxx/{action}/{id}构造完url之后就去实例化RouteAttribute特性,构造路由:
return new AttributeRouteModel(
new RouteAttribute(
CalculateRouteTemplate(rootPath, controllerName, action, httpMethod, configuration)
)
);如果没有按照abp的action命名约束命名,并标记了HTTPMethod特性,那么就会调用aspnet core默认的路由,源码如下:
protected virtual void NormalizeSelectorRoutes(string rootPath, string controllerName, ActionModel action, [CanBeNull] ConventionalControllerSetting configuration)
{
foreach (var selector in action.Selectors)
{
var httpMethod = selector.ActionConstraints
.OfType()
.FirstOrDefault()?
.HttpMethods?
.FirstOrDefault();
if (httpMethod == null)
{
httpMethod = SelectHttpMethod(action, configuration);
}
if (selector.AttributeRouteModel == null)
{
selector.AttributeRouteModel = CreateAbpServiceAttributeRouteModel(rootPath, controllerName, action, httpMethod, configuration);
}
if (!selector.ActionConstraints.OfType().Any())
{
selector.ActionConstraints.Add(new HttpMethodActionConstraint(new[] {httpMethod}));
}
}
} ConfigureParameters
顾名思义,这是用来配置action的参数,默认是调用aspnetcore mvc本身的参数绑定机制:
protected virtual void ConfigureParameters(ControllerModel controller)
{
/* Default binding system of Asp.Net Core for a parameter
* 1. Form values
* 2. Route values.
* 3. Query string.
*/
foreach (var action in controller.Actions)
{
foreach (var prm in action.Parameters)
{
if (prm.BindingInfo != null)
{
continue;
}
if (!TypeHelper.IsPrimitiveExtended(prm.ParameterInfo.ParameterType))
{
if (CanUseFormBodyBinding(action, prm))
{
prm.BindingInfo = BindingInfo.GetBindingInfo(new[] { new FromBodyAttribute() });
}
}
}
}
}如此,整个abp集成aspnetcore mvc创建并管理自己的api流程便大致的分析完了。