【iOS】Mapkit的使用:地图显示、定位、大头针、气泡等
标签:iOS地图mapkit
1.显示地图
(1)首先我们要像下图这样子打开地图功能:
XCode会自动给我们的项目进行配置,例如会自动给我们添加MapKit.frameworks。
(2)在需要使用地图的类中
#import
(3)显示地图有两种方法:
<1>使用Interface Builder, 拖一个Map view对象到View中
<2>使用纯代码,创建一个MKMapView的实例,使用initWithFrame:来进行初始化,最后将它作为subview添加到windows或者其它UIView上。
因为一个map view是一个UIView子类,所以可以像操作其它View那样操作map view,因此可以给map view添加任何subview,但是添加的subview并不会随着地图内容的移动而移动,如果需要跟随移动,必须使用annotations 或者 overlays。
新建的地图,默认只是显示地图数据以及响应用户手势。通过创建MKMapCamera实例,可以进行3D地图显示,通过设置mapType属性可以设置地图来显示卫星地图、卫星地图和地图数据的混合视图,通过改变属性rotateEnabled, pitchEnabled, zoomEnabled,scrollEnabled 等,可以限制用户的控制权限。通过实现代理MKMapViewDelegate ,可以响应用户的手势操作。
以下为使用第<2>种方法来显示地图:
[objc]view plaincopy
mapView = [[MKMapViewalloc]initWithFrame:self.view.bounds];
[self.viewaddSubview:mapView];
运行效果如下:
2.设置地图的默认显示区域
步骤1中添加的地图,默认会显示整个地球的视图,可以通过修改它的Region属性来设置地图初始化时默认的显示区域,这个属性是一个MKCoordinateRegion结构体,定义如下:
[objc]view plaincopy
typedefstruct{
CLLocationCoordinate2D center;
MKCoordinateSpan span;
} MKCoordinateRegion;
其中span是使用度、分、秒为单位的,一度约等于111km,但是我们一般习惯使用的是长*宽的数据,因此可以使用MKCoordinateRegionMakeWithDistance方法将常用的长和宽数据转化为需要的以度为单位的数据。下面就是将地图的显示范围设置为中心点为经纬度(29.454686,106.529259),南北方向和东西方向均为5km的区域
[objc]view plaincopy
[mapViewsetRegion:MKCoordinateRegionMakeWithDistance(CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(29.454686,106.529259),5000,5000)animated:YES];
添加上面一句代码后,步骤1中的视图变成了下图的效果:
3.显示3D地图
3D地图是从某个海拔高度点以一定角度俯瞰2D地图的视图,在iOS7和OSX10.9及以后版本,可以使用MKMapCamera类来调整3D地图。
一个MKMapCamera实例类camera,使用下面的属性来确定3D地图:
• 海拔高度(Altitude). camera的距离2D地图平面的高度,单位米
• 斜度(Pitch).camera相对于地面倾斜的角度(其中0度表示垂直往下看,所以效果是标准的2D地图)
• 方向(Heading). camera面对的方向
• 中心(Center). 显示在屏幕正中间的地图表面的点
或许举一个例子就秒懂了,下面的代码就是实现从经纬度(29.545686,106.628259),高度为100的空中俯瞰经纬度(29.454686,106.529259)的效果:
[objc]view plaincopy
// Create a coordinate structure for the location.
CLLocationCoordinate2D ground = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(29.454686,106.529259);
// Create a coordinate structure for the point on the ground from which to view the location.
CLLocationCoordinate2D eye = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(29.545686,106.628259);
// Ask Map Kit for a camera that looks at the location from an altitude of 100 meters above the eye coordinates.
MKMapCamera*myCamera = [MKMapCameracameraLookingAtCenterCoordinate:groundfromEyeCoordinate:eyeeyeAltitude:100];
// Assign the camera to your map view
mapView.camera= myCamera;
4.滑动和缩放地图内容
通过滑动和缩放可以随时改变地图的显示区域
• 通过滑动地图,改变map view或者camera的centerCoordinate值,或者直接调用map view的setCenterCoordinate:animated:或者setCamera:animated:方法
• 改变放大级别,改变map view的region属性的值,或者调用setRegion:animated:方法,你也可以在3D地图中改变camera的海拔高度的值(设置海拔高度为双倍或者一半,大约等于放大或缩小一个级别)。
例如,下面的代码将地图往左移动当前地图宽度的一半的距离,并且带有移动的动画效果。
[objc]view plaincopy
CLLocationCoordinate2D mapCenter = mapView.centerCoordinate;
mapCenter = [mapViewconvertPoint:
CGPointMake(1, (mapView.frame.size.width/2.0))
toCoordinateFromView:mapView];
[mapViewsetCenterCoordinate:mapCenteranimated:YES];
通过修改地图的region属性的span的值进行地图缩放。如果要放大(拉近镜头),将span设置为一个更小的值,如果要缩小(拉远镜头),将span设置为一个更大的值。以下为缩小的示例代码:
[objc]view plaincopy
MKCoordinateRegion theRegion = myMapView.region;
// Zoom out
theRegion.span.longitudeDelta*=2.0;
theRegion.span.latitudeDelta*=2.0;
[myMapViewsetRegion:theRegionanimated:YES];
5.在地图上显示用户当前位置
要在地图上显示用户位置,先设置map view的showsUserLocation属性为Yes
[objc]view plaincopy
mapView.showsUserLocation=YES;
以上代码只是告诉mapView要显示用户位置,但mapView并不知道用户的位置,因此还需要通过CLLocationManager来使用定位服务:创建一个CLLocationManager的实例,设置它的desiredAccuracy(期望的定位精度)和distanceFilter(距离过滤)属性。为了接收到位置更新的通知,设置代理CLLocationManagerDelegate,并调用startUpdatingLocation方法来注册接收定位更新(调用stopUpdatingLocation取消接收定位更新)。另外在iOS8中,需要向用户请求定位权限,示例代码如下:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (void)startStandardUpdates{
// Create the location manager if this object does not
// already have one.
if(nil== locationManager)
locationManager = [[CLLocationManageralloc]init];
locationManager.delegate=self;
locationManager.desiredAccuracy= kCLLocationAccuracyBest;
if([[[UIDevicecurrentDevice]systemVersion]floatValue] >=8.0){
[locationManagerrequestWhenInUseAuthorization];
}
if(![CLLocationManagerlocationServicesEnabled]){
NSLog(@"请开启定位:设置 > 隐私 > 位置 > 定位服务");
}
if([locationManagerrespondsToSelector:@selector(requestAlwaysAuthorization)]) {
[locationManagerrequestAlwaysAuthorization];// 永久授权
[locationManagerrequestWhenInUseAuthorization];//使用中授权
}
[locationManagerstartUpdatingLocation];
}
效果如图:
关于iOS定位的详细讲解(后台持续定位),请看我的另一篇博文:http://blog.csdn.net/dolacmeng/article/details/45064939
6.创建一个地图快照
有时候,我们的需求并不需要一个功能完整的map view视图。例如,如果app只是想用户在一个地图图像的滚动列表中选择,那就不需要实现地图的交互功能。另一个创建一个静态地图图像的原因是为了实现绘图功能。在上面提到的需求中,我们可以使用MKMapSnapshotter对象来异步地创建一个静态的地图图像。
一般的,通过下面的步骤来创建一个地图快照
1.确保网络连接正常并且app正在前台运行
2.创建一个MKMapSnapshotOptions对象,并设置地图外观、输出大小等
3.创建一个MKMapSnapshotter对象并用上一步的实例对象初始化进行初始化。
4.调用startWithCompletionHandler:方法来开始异步的快照任务
5.当任务完成,从block中取回地图快照,并添加需要的覆盖物或者标注。
示例代码:
[objc]view plaincopy
-(void)shot{
MKMapSnapshotOptions*options = [[MKMapSnapshotOptionsalloc]init];
options.region= mapView.region;
options.size= mapView.frame.size;
options.scale= [[UIScreenmainScreen]scale];
MKMapSnapshotter*snapshotter = [[MKMapSnapshotteralloc]initWithOptions:options];
// Initialize the semaphore to 0 because there are no resources yet.
dispatch_semaphore_t snapshotSem = dispatch_semaphore_create(0);
// Get a global queue (it doesn't matter which one).
dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT,0);
// Create variables to hold return values. Use the __block modifier because these variables will be modified inside a block.
__blockMKMapSnapshot*mapSnapshot =nil;
__blockNSError*error =nil;
// Start the asynchronous snapshot-creation task.
[snapshotterstartWithQueue:queue
completionHandler:^(MKMapSnapshot*snapshot,NSError*e) {
mapSnapshot = snapshot;
error = e;
// The dispatch_semaphore_signal function tells the semaphore that the async task is finished, which unblocks the main thread.
dispatch_semaphore_signal(snapshotSem);
}];
// On the main thread, use dispatch_semaphore_wait to wait for the snapshot task to complete.
dispatch_semaphore_wait(snapshotSem, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
if(error) {// Handle error. }
// Get the image from the newly created snapshot.
//UIImage *image = mapSnapshot.image;
// Optionally, draw annotations on the image before displaying it.
}
UIImage*image = mapSnapshot.image;
UIImageView*imageView = [[UIImageViewalloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(50,50,200,200)];
imageView.image= image;
[self.viewaddSubview:imageView];
}
效果如下:
7.添加大头针(下文中统一称作标注)
(1)为了在地图上添加标注,app必须提供两个明确的对象
•一个annotation 对象, 遵从MKAnnotation代理,管理标注的数据(只是存储标注的数据,不涉及视图)
•一个annotation view, 用来在地图上画annotation的表现形式(用来显示标注数据的视图)
(2)明确了(1)中的要求后,得到添加标注的步骤:
<1>使用下面任何一个对象(annotation 对象)来确定一个合适的标注
•使用MKPointAnnotation类来实现一个标注,这种类型的标注包含显示在标注弹出气泡标题和副标题的属性。
•定义一个自定义的遵从MKAnnotation代理的对象,自定义的标注可以包含任何我们想存贮的数据类型。详细看Defining a Custom Annotation Object
<2>定义一个 annotation view来在屏幕上显示标注的数据。怎么定义annotation view 取决于我们的需求,可以是下面的任何一个:
•如果是要使用标准的大头针标注,创建一个MKPinAnnotationView类的实例。
•如果标注用自定义的静态图片来展示,创建一个MKAnnotationView类的实例,设置它的image属性为展示的图片。
•如果一张静态图片不足够来展现标注,新建一个MKAnnotationView的子类,实现自定义的绘制方法。
<3>实现mapView:viewForAnnotation:代理方法。
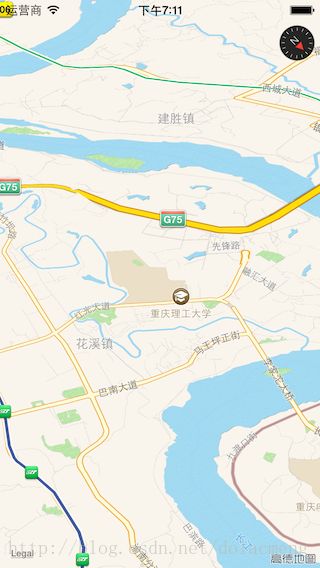
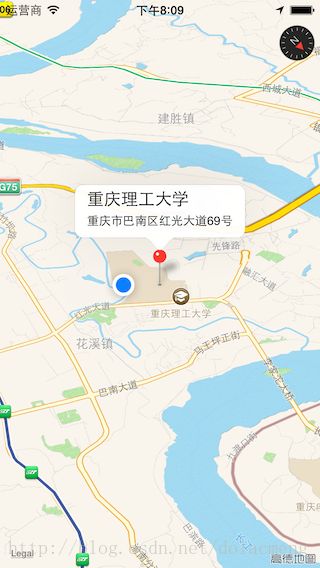
这个方法返回一个MKAnnotationView类型的视图,来显示标注的信息, 如果不实现这个代理方法或者return nil,就会用默认的 annotation view进行数据显示(也就是显示红色大头针、title、subtitle,效果请看下面的例子1)。
<4>使用addAnnotation: (或者 addAnnotations:)方法来添加标注到地图。
上面都是直接从官方文档翻译的,感觉有点晦涩难懂,还是上例子吧,比较比较容易理解~
(例子1)使用MKPointAnnotation类来作为标注,并使用默认的annotation view(不用实现mapView:viewForAnnotation:方法,或者return nil),代码及效果如下:
[objc]view plaincopy
MKPointAnnotation*annotation0= [[MKPointAnnotationalloc]init];
[annotation0setCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(29.454686,106.529259)];
[annotation0setTitle:@"重庆理工大学"];
[annotation0setSubtitle:@"重庆市巴南区红光大道69号"];
[mapViewaddAnnotation:annotation0];
(例子2)使用MKPointAnnotation类来作为标注(还是用例子1中的代码),并使用默认的自定义MKPinAnnotationView,将大头针设置为紫色,设置气泡左边的图像,并在右边添加一个按钮(实现View:viewForAnnotation:方法,并返回一个MKPinAnnotationView实例),在例子1中增加代码及效果如下:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (MKAnnotationView*)mapView:(MKMapView*)mapViewviewForAnnotation:(id)annotation{
// If the annotation is the user location, just return nil.(如果是显示用户位置的Annotation,则使用默认的蓝色圆点)
if([annotationisKindOfClass:[MKUserLocationclass]])
returnnil;
if([annotationisKindOfClass:[MKPointAnnotationclass]]) {
// Try to dequeue an existing pin view first.(这里跟UITableView的重用差不多)
MKPinAnnotationView*customPinView = (MKPinAnnotationView*)[mapView
dequeueReusableAnnotationViewWithIdentifier:@"CustomPinAnnotationView"];
if(!customPinView){
// If an existing pin view was not available, create one.
customPinView = [[MKPinAnnotationViewalloc]initWithAnnotation:annotation
reuseIdentifier:@"CustomPinAnnotationView"];
}
//iOS9中用pinTintColor代替了pinColor
customPinView.pinColor= MKPinAnnotationColorPurple;
customPinView.animatesDrop=YES;
customPinView.canShowCallout=YES;
UIButton*rightButton = [[UIButtonalloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0,0,80,50)];
rightButton.backgroundColor= [UIColorgrayColor];
[rightButtonsetTitle:@"查看详情"forState:UIControlStateNormal];
customPinView.rightCalloutAccessoryView= rightButton;
// Add a custom image to the left side of the callout.(设置弹出起泡的左面图片)
UIImageView*myCustomImage = [[UIImageViewalloc]initWithImage:[UIImageimageNamed:@"myimage"]];
customPinView.leftCalloutAccessoryView= myCustomImage;
returncustomPinView;
}
returnnil;//返回nil代表使用默认样式
}
为了响应“查看详情”的点击事件,只要实现以下代理方法:
[objc]view plaincopy
-(void)mapView:(MKMapView*)mapViewannotationView:(MKAnnotationView*)viewcalloutAccessoryControlTapped:(UIControl*)control{
NSLog(@"点击了查看详情");
}
(例子3)使用MKPointAnnotation类来作为标注(还是用例子1中的代码),并使用默认的自定义MKAnnotationView
,将大头针设置为自定义图像,(实现View:viewForAnnotation:方法,并返回一个MKAnnotationView实例),例1中新增代码及效果如下:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (MKAnnotationView*)mapView:(MKMapView*)mapViewviewForAnnotation:(id)annotation
{
// If the annotation is the user location, just return nil.
if([annotationisKindOfClass:[MKUserLocationclass]])
returnnil;
if([annotationisKindOfClass:[MKPointAnnotationclass]]) {
MKAnnotationView* aView = [[MKAnnotationViewalloc]initWithAnnotation:annotationreuseIdentifier:@"MKPointAnnotation"];
aView.image= [UIImageimageNamed:@"myimage"];
aView.canShowCallout=YES;
returnaView;
}
returnnil;
}
(例子4)这个例子较前面的例子要复杂些:
1. 使用实现MKAnnotation代理的自定义对象(MyCustomAnnotation)来作为标注(能存储任意的数据,例如存储一家餐厅的名字、地址、好评率、距离等属性,上面三个例子中的MKPointAnnotation只能存储title和subtitle,这里的例子定义了两个属性:maintitle和subtitle)。
2.使用继承自MKAnnotationView的类(MyCustomAnnotationView)来自定义气泡视图(实现View:viewForAnnotation:方法,并返回一个继承自MKAnnotationView的实例,其中,MKAnnotationView包含一个UIViewController的属性,这个view controller用来管理气泡的视图和响应事件,并且这个例子使用xib来设计界面)。
3.在MyCustomAnnotationView中要实现hitTest:和setSelected:animated:方法,来显示或隐藏气泡。
代码及效果如下:
MyCustomAnnotation.h文件
[objc]view plaincopy
#import
#import
@interfaceMyCustomAnnotation : NSObject {
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate;
}
@property(nonatomic,readonly) CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSString*maintitle;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSString*secondtitle;
- (id)initWithLocation:(CLLocationCoordinate2D)coord;
@end
MyCustomAnnotation.m文件
[objc]view plaincopy
#import "MyCustomAnnotation.h"
@implementationMyCustomAnnotation
@synthesizecoordinate;
- (id)initWithLocation:(CLLocationCoordinate2D)coord {
self= [superinit];
if(self) {
coordinate = coord;
}
returnself;
}
@end
MyCustomAnnotationView.h
[objc]view plaincopy
#import
#import "CustomCalloutViewController.h"
@classMyCustomAnnotation;
@interfaceMyCustomAnnotationView : MKPinAnnotationView
- (id)initWithAnnotation:(id)annotationreuseIdentifier:(NSString*)reuseIdentifier;
@property(strong,nonatomic)CustomCalloutViewController*calloutViewController;
@property(strong,nonatomic)MyCustomAnnotation*myCustomAnnotation;
@end
MyCustomAnnotationView.m
[objc]view plaincopy
#import "MyCustomAnnotationView.h"
#import "MyCustomAnnotation.h"
@implementationMyCustomAnnotationView
- (id)initWithAnnotation:(id)annotationreuseIdentifier:(NSString*)reuseIdentifier
{
self= [superinitWithAnnotation:annotationreuseIdentifier:reuseIdentifier];
if(self)
{
// Set the frame size to the appropriate values.
CGRect myFrame =self.frame;
myFrame.size.width=20;
myFrame.size.height=20;
self.frame= myFrame;
// The opaque property is YES by default. Setting it to
// NO allows map content to show through any unrendered parts of your view.
self.opaque=NO;
self.canShowCallout=NO;
self.calloutViewController= [[CustomCalloutViewControlleralloc]initWithNibName:@"CustomCalloutView"bundle:nil];
self.myCustomAnnotation= (MyCustomAnnotation*)annotation;
}
returnself;
}
- (UIView*)hitTest:(CGPoint)pointwithEvent:(UIEvent*)event
{
UIView*hitView = [superhitTest:pointwithEvent:event];
if(hitView ==nil&&self.selected) {
CGPoint pointInAnnotationView = [self.superviewconvertPoint:pointtoView:self];
UIView*calloutView =self.calloutViewController.view;
hitView = [calloutViewhitTest:pointInAnnotationViewwithEvent:event];
}
returnhitView;
}
- (void)setSelected:(BOOL)selectedanimated:(BOOL)animated
{
[supersetSelected:selectedanimated:YES];
// Get the custom callout view.
UIView*calloutView =self.calloutViewController.view;
if(selected) {
self.calloutViewController.maintitle.text=self.myCustomAnnotation.maintitle;
self.calloutViewController.secondtitle.text=self.myCustomAnnotation.secondtitle;
CGRect annotationViewBounds =self.bounds;
CGRect calloutViewFrame = calloutView.frame;
if(calloutViewFrame.origin.x==annotationViewBounds.origin.x) {
// Center the callout view above and to the right of the annotation view.
calloutViewFrame.origin.x-= (calloutViewFrame.size.width- annotationViewBounds.size.width) *0.5;
calloutViewFrame.origin.y-= (calloutViewFrame.size.height);
calloutView.frame= calloutViewFrame;
}
[selfaddSubview:calloutView];
}else{
[calloutViewremoveFromSuperview];
}
}
@end
CustomCalloutViewController.h文件
[objc]view plaincopy
@interfaceCustomCalloutViewController : UIViewController{
UILabel*labTitle;
}
@property(weak,nonatomic) IBOutletUILabel*maintitle;
@property(weak,nonatomic) IBOutletUILabel*secondtitle;
@end
CustomCalloutViewController.m文件
[objc]view plaincopy
@implementationCustomCalloutViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[superviewDidLoad];
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[superdidReceiveMemoryWarning];
}
@end
View:viewForAnnotation:代理方法:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (MKAnnotationView*)mapView:(MKMapView*)mapView
viewForAnnotation:(id)annotation
{
MyCustomAnnotationView*annotationView = (MyCustomAnnotationView*)[mapViewdequeueReusableAnnotationViewWithIdentifier:@"MyCustomAnnotationView"];
if(!annotationView) {
annotationView = [[MyCustomAnnotationViewalloc]initWithAnnotation:annotationreuseIdentifier:@"MyCustomAnnotationView"];
annotationView.image= [UIImageimageNamed:@"myimage"];
}
returnannotationView;
}
另外,还能实现导航等功能,有时间再继续写。