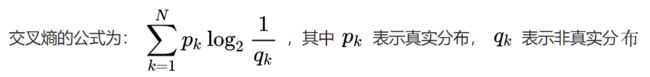1.交叉熵
逻辑斯蒂回归这个模型采用的是交叉熵,通俗点理解交叉熵
推荐一篇文章讲的很清楚:
https://www.zhihu.com/question/41252833
因此,交叉熵越低,这个策略就越好,最低的交叉熵也就是使用了真实分布所计算出来的信息熵,因为此时 ,交叉熵 = 信息熵。这也是为什么在机器学习中的分类算法中,我们总是最小化交叉熵,因为交叉熵越低,就证明由算法所产生的策略最接近最优策略,也间接证明我们算法所算出的非真实分布越接近真实分布
2.代码解释
1 import warnings 2 warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') 3 import numpy as np 4 import tensorflow as tf 5 # 样本集 6 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data 7 8 # 加载数据,目标值变成概率的形式,ont-hot 9 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('./',one_hot=True) 10 # 训练数据 (55000, 784) 11 mnist.train.images.shape 12 # 测试数据 (10000, 784) 13 mnist.test.images.shape 14 # 目标值 ont-hot形式 15 mnist.train.labels[:10] 16 17 # 构建方程 18 X = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float64,shape = (None,784),name = 'data') 19 y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float64,shape = (None,10),name = 'target') 20 W = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.zeros(shape =(784,10),dtype = tf.float64)) 21 b = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.zeros(shape = (10),dtype = tf.float64)) 22 y_pred = tf.matmul(X,W) + b 23 24 # 构建损失函数 25 # y 和 y_pred对比 26 # y表示是概率 [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.] 27 # y_pred,矩阵运算求解的目标值 28 # 要将y_pred转化成概率,softmax 29 y_ = tf.nn.softmax(y_pred) 30 # 此时y和y_表示概率 31 # y和y_越接近,说明预测函数越准确 32 # 此时分类问题,交叉熵,表示损失函数 33 # 熵:表示的系统混乱程度 34 # 损失函数,越小越好 35 # 平均交叉熵------->可以比较大小的数 36 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(y,tf.log(1/y_)),axis = -1)) 37 38 # 最优化 39 opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(loss) 40 41 # 训练 42 # 训练次数 43 epoches = 100 44 # 保存 45 saver = tf.train.Saver() 46 with tf.Session() as sess: 47 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) 48 for i in range(epoches): 49 c = 0 50 for j in range(100): 51 # 一次取550个,分100次取完数据 next_batch方法 52 X_train,y_train = mnist.train.next_batch(550) 53 opt_,cost = sess.run([opt,loss],feed_dict = {X:X_train,y:y_train}) 54 c += cost/100 55 # 计算准确率 56 X_test,y_test = mnist.test.next_batch(2000) 57 y_predict = sess.run(y_,feed_dict={X:X_test}) 58 y_test = np.argmax(y_test,axis = -1) 59 y_predict = np.argmax(y_predict,axis = 1) 60 accuracy = (y_test == y_predict).mean() 61 print('执行次数:%d。损失函数是:%0.4f。准确率是:%0.4f'%(i+1,c,accuracy)) 62 if accuracy > 0.91: 63 saver.save(sess,'./model/estimator',global_step=i) 64 print('---------------------------模型保存成功----------------------------')
保存了模型,在上一次的基础上继续进行学习,这样的话可以直接从上次的准确率开始
1 # 其实代码是一样的,只是加了个saver.restore还原 2 with tf.Session() as sess: 3 # 还原到sess会话中 4 saver.restore(sess,'./model/estimator-99') 5 6 for i in range(100,200): 7 c = 0 8 for j in range(100): 9 X_train,y_train = mnist.train.next_batch(550) 10 opt_,cost = sess.run([opt,loss],feed_dict = {X:X_train,y:y_train}) 11 c += cost/100 12 13 # 计算准确率 14 X_test,y_test = mnist.test.next_batch(2000) 15 16 y_predict = sess.run(y_,feed_dict={X:X_test}) 17 18 y_test = np.argmax(y_test,axis = -1) 19 y_predict = np.argmax(y_predict,axis = 1) 20 21 accuracy = (y_test == y_predict).mean() 22 print('执行次数:%d。损失函数是:%0.4f。准确率是:%0.4f'%(i+1,c,accuracy)) 23 24 if accuracy > 0.91: 25 saver.save(sess,'./model/estimator',global_step=i) 26 print('---------------------------模型保存成功----------------------------')