Nagios
监控
在互联网日益发展的今天,监控的重要性已经不言而喻。可能打开一个URL要经过6-7层的处理,如果出了问题而没有监控将很难定位到问题所在。那哪些内容需要监控呢?
1.本地资源
(1) 负载:uptime;
(2) CPU:top,sar,cpu温度;
(3) 磁盘:df;
(4) 内存:free;
(5) IO:iostat;
(6) RAID
(7) passwd文件的变化(本地所有文件指纹识别)。
2.网络服务
端口、URL、ping丢包、进程数、IDC网络流量
3.其他设备
路由器、交换机端口流量、打印机、windows等
4.业务数据
用户登录失败次数,用户登录网站次数,输入验证码失败次数、某个API接口流量并发,电商网站订单,支付交易的数量等。这个获取的过程可能是开发或者架构师完成的,但添加的过程就是运维;
监控软件本身仅仅是一个平台,我们想监控的内容,理论上只要在服务器命令行可以获取到就可以被监控软件监控。
1.1 Nagios简介
Nagios又被称为难够死,因为很难。Nagios是一款开源的网络及服务的监控工具,其功能强大、灵活性强。能有效监控windows、Linux和Unix等系统的主机各种状态信息,交换机、路由器等网络设备,以及主机端口及URL服务等。根据不同业务故障级别发出告警信息(邮件、微信、短信、语音报警、飞信、MSN)给管理员,当故障恢复时也会发出恢复消息给管理员。
Nagios服务端可以在Unix及类Unix系统上运行,目前无法运行在windows。Windows可以作为被监控的主机,但是无法作为监控服务器。
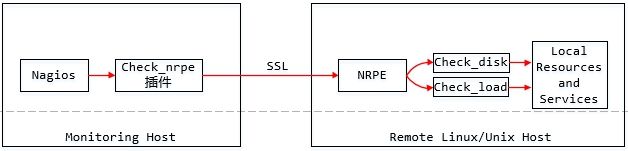
1.2 Nagios构成
Nagios不好的地方在于它只做核心,很多其他功能都是通过插件来实现的。Nagios一般由一个主程序(Nagios),一个插件程序(Nagios-plugins)和一些可选的附加程序(NRPE,NSClient++,NSCA,NDOUtils)等。Nagios本身就是一个监控的平台而已,其具体的监控工作都是通过插件(Nagios-plugins,也可自己编写)来实现的。因此,Nagios主程序和Nagios-plugins插件都是Nagios服务端必须安装的程序组件,并且Nagios-plugins一般也要安装于被监控端。几个附加程序的描述如下:
1. NRPE:半被动模式
(1) 存在位置:工作在被监控端,操作系统为Linux/Unix;
(2) 作用:用于在被监控的远程Linux/Unix主机上执行脚本插件获取数据回传给服务器端,以实现对这些主机资源的监控。主要用于监控本地资源;
(3) 存在形式:守护进程(agent)模式,开启的端口为5666.
2. NSClient++:半被动模式
(1) 存在位置:监控Windows主机;
(2) 作用:相当于Linux下的NRPE;
3. NDOUtils:不推荐使用
(1) 存在位置:Nagios服务器端;
(2)作用:用于将Nagios的配置信息和各event产生的数据存入数据库以实现对这些数据的检索和处理。但是存入数据库还不如存放在磁盘上,因此推荐使用;
4. NSCA:纯被动模式的监控
(1)存在位置:同时安装在Nagios的服务器端和客户端;
(2) 作用:用于让被监控的远程Linux/Unix主机主动将监控到的信息发送给Nagios服务器。在分布式监控集群模式中要用到,300台服务器以内可以不考虑;
1.3 原理
1.4 安装
1.4.1 服务端
调整字符集,如果不安装后面安装一些插件会有错误:
[root@nagios ~]# echo 'exprot LC_ALL=C' >>/etc/profile[root@nagios ~]# . /etc/profile
关闭防火墙:
[root@nagios ~]# /etc/init.d/iptables stop[root@nagios ~]# chkconfig iptables off
关闭selinux:
[root@nagios ~]# setenforce 0[root@nagios ~]# sed -ri 's#^(SELINUX=).*#\1disabled#g' /etc/selinux/config
时间同步,监控的时间同步很重要:
echo '# time sync' >>/var/spool/cron/rootecho '*/10 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate pool.ntp.org &>/dev/null' >>/var/spool/cron/root
需要安装web展示相关软件:
[root@nagios ~]# yum install -y gcc glibc glibc-common gd gd-devel httpd php php-gd mysql*
gcc glibc glibc-common gcc编译器 gd gd-devel画图用的 httpd php \php-gd php环境,官方推荐LAMP,不要改成Nginx mysql* 生成MySQL的插件,MySQL不需要启动
准备所需软件:
[root@nagios hadoop]# tree.|-- Class-Accessor-0.31.tar.gz # iostat监控插件所需|-- Config-Tiny-2.12.tar.gz # 同上|-- Math-Calc-Units-1.07.tar.gz # 同上|-- Nagios-Plugin-0.34.tar.gz # 同上|-- Params-Validate-0.91.tar.gz # 同上|-- Regexp-Common-2010010201.tar.gz # 同上|-- check_iostat # 用于监控的插件|-- check_memory.pl # 用于监控的插件|-- check_mysql # 用于监控的插件|-- libart_lgpl-2.3.17.tar.gz # iostat监控插件所需|-- nagios-3.5.1.tar.gz # 主程序|-- nagios-plugins-1.4.16.tar.gz # 插件管理|-- nrpe-2.12.tar.gz # agent|-- pnp-0.4.14.tar.gz # 画图的web程序,这个是展示`-- rrdtool-1.2.14.tar.gz # pnp的辅助程序,这个才是画图的
软件包下载 密码:usyr
创建所需用户,并将apache和nagios同属于一个组,方便一起管理:
useradd -m nagiosgroupadd nagcmdusermod -a -G nagcmd nagiosusermod -a -G nagcmd apache
安装:
[root@nagios hadoop]# tar xf nagios-3.5.1.tar.gz[root@nagios hadoop]# cd nagios[root@nagios nagios]# ./configure --with-command-group=nagcmd[root@nagios nagios]# make all[root@nagios nagios]# make install… make install-init - This installs the init script in /etc/rc.d/init.d make install-commandmode - This installs and configures permissions on the directory for holding the external command file make install-config - This installs sample config files in /usr/local/nagios/etcmake[1]: Leaving directory `/admin/hadoop/nagios'
这是编译后出现的信息提示,可以时候以上三种编译方式生成启动脚本、命令和配置文件样例
[root@nagios nagios]# make install-init && make install-config && make install-commandmode[root@nagios nagios]# make install-webconf # 生成了如何在httpd中显示Nagios的配置文件/usr/bin/install -c -m 644 sample-config/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf # 就是这个文件
配置web认证:
htpasswd -cb /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users oldboy 123456
# -b:非交互
安装插件:
yum install -y perl-develtar xf nagios-plugins-1.4.16.tar.gzcd nagios-plugins-1.4.16./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios --enable-perl-modulesmake && make installcd ..ls /usr/local/nagios/libexec/|wc -l # 插件有61个,多比少好
安装NRPE,之所以服务端也安装NRPE,一是是因为要在…/nagios/libexec/目录下生成check_nrpe命令;二是服务端也要通过NRPE进行监控:
tar xf nrpe-2.12.tar.gzcd nrpe-2.12./configuremake allmake install-pluginmake install-daemonmake install-daemon-configcd ..
最后启动,Nagios是不会监听端口的,因为不会有程序发数据给它。
/etc/init.d/httpd start/etc/init.d/nagios startlsof -i :80ps aux |grep nagios
1.4.2 被监控端
调整字符集,如果不安装后面安装一些插件会有错误:
echo 'exprot LC_ALL=C' >>/etc/profile. /etc/profile
关闭防火墙:
/etc/init.d/iptables stopchkconfig iptables off
时间同步,监控的时间同步很重要:
echo '# time sync' >>/var/spool/cron/rootecho '*/10 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate pool.ntp.org &>/dev/null' >>/var/spool/cron/root
创建用户:
[root@lamp ~]# useradd -m nagios -s /sbin/nologin
安装perl
yum install -y perl-devel perl-CPAN openssl*yum install -y mysql-server # 这是为了解决报错
安装插件:
tar xf nagios-plugins-1.4.16.tar.gzcd nagios-plugins-1.4.16./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nagios --enable-perl-modules --enable-redhat-pthread-workaround #--with-mysql=/usr/bin/mysql# --enable-redhat-pthread-workaround:如果redhat系统不加这个会很慢# --with-mysql是为了解决make: *** [all] Error 2make && make installcd ..ls /usr/local/nagios/libexec/|wc -l # 结果为59而不是61估计跟MySQL有关
安装NRPE:
tar xf nrpe-2.12.tar.gzcd nrpe-2.12./configuremake allmake install-pluginmake install-daemonmake install-daemon-configcd ..
安装iostat:
tar xf Params-Validate-0.91.tar.gzcd Params-Validate-0.91perl Makefile.PLmakemake installcd ..tar xf Class-Accessor-0.31.tar.gzcd Class-Accessor-0.31perl Makefile.PLmake && make installcd ..tar xf Config-Tiny-2.12.tar.gzcd Config-Tiny-2.12perl Makefile.PLecho $?make && make installcd ..tar xf Math-Calc-Units-1.07.tar.gzcd Math-Calc-Units-1.07perl Makefile.PLmake && make installcd ..tar xf Regexp-Common-2010010201.tar.gzcd Regexp-Common-2010010201perl Makefile.PLmake && make installcd ..tar xf Nagios-Plugin-0.34.tar.gzcd Nagios-Plugin-0.34perl Makefile.PLmakemake installcd ..yum install -y sysstatcp /root/tools/check_memory.pl /usr/local/nagios/libexec/cp /root/tools/check_iostat /usr/local/nagios/libexec/chmod 755 /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_memory.plchmod 755 /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_iostatyum install -y dos2unixdos2unix /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_iostatdos2unix /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_memory.pl
修改客户端的配置文件:
cd /usr/local/nagios/etc/cp nrpe.cfg{,.bak}sed -ri 's@^allowed_hosts.*@&,10.0.0.1@g' nrpe.cfg # 允许10.0.0.1监控sed -ri '199,203d' nrpe.cfg
# 以下是用来告诉NRPE这个守护进程怎么去监控
echo "command[check_load]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_load -w 15,10,6 -c 30,25,20" >>nrpe.cfgecho "command[check_mem]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_memory.pl -w 6% -c 3%" >>nrpe.cfgecho "command[check_disk]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 8% -p /" >>nrpe.cfgecho "command[check_swap]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_swap -w 20% -c 10%" >>nrpe.cfgecho "command[check_iostat]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_iostat -w 6 -c 10" >>nrpe.cfg
# [check_load]:相当于模块名
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_load:获取资源的命令
# 也就是说通过调用check_load就相当于执行/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_load这个命令
启动NRPE:
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d
# -c:指定配置文件
# -d:daemon
echo "# nagios nrpe process cmd" >>/etc/rc.local # 开机自启echo "/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d" >>/etc/rc.localss -lnt|grep 5666
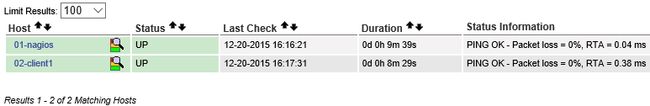
1.5 开始监控
监控之前也要在服务器端安装客户端软件。
Nagios安装生成的文件:
[root@nagios nagios]# pwd/usr/local/nagios[root@nagios nagios]# tree -L 1.|-- bin|-- etc|-- libexec # 插件|-- sbin # CGI程序|-- share # Nagios界面展示的php程序等内容的目录,被Nagios在httpd配置文件目录生成的配置文件所调用 `-- var # 日志和数据6 directories, 0 files
配置文件目录:
[root@nagios nagios]# tree etc/etc/|-- cgi.cfg # 被主配置文件包含|-- nagios.cfg # 主配置文件|-- objects # 被主配置文件包含| |-- commands.cfg # 存放Nagios命令相关配置(也可指定commands目录),这里的命令不是系统命令| |-- contacts.cfg| |-- localhost.cfg # 对本机的监控,我们不使用它进行监控,而是将本机当成客户端来监控| |-- printer.cfg # 打印机| |-- switch.cfg # 交换机| |-- templates.cfg # 模板配置文件| |-- timeperiods.cfg| `-- windows.cfg # windows`-- resource.cfg # 被主配置文件包含,这里面是Nagios内置变量的定义,如$USER1$,$USER2$,$USER3$等
内容解释:
#
commands.cfg:存放Nagios命令相关配置(也可指定commands目录),这里的命令不是系统命令,而是实现把Nagios中定义的命令和Linux系统中的插件命令关联的一个文件。如oldboy=/bin/cat,oldboy就是Nagios命令,而/bin/cat则是系统命令;services.cfg:存放具体被监控的服务相关的配置内容(对哪些服务进行监控),上百台以上可指定services目录,默认不存在;hosts.cfg:存放具体被监控的主机相关配置,上百台以上可指定hosts目录,默认不存在;contacts.cfg:存放报警联系人相关配置的文件;timeperiods.cfg:存放报警周期时间等相关配置;template.cfg:模板配置文件,模板的存在是为了方便的配置服务器配置,类似shell里的函数功能
编辑主配置文件:
# 主配置文件是通过cfg_file来包含其他配置文件的,我们可以让其包含上述两个并不存在的配置文件:
[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri '33acfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/hosts.cfg' nagios.cfg[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri '33acfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/services.cfg' nagios.cfg
# 注释掉localhost
[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri 's@cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/localhost.cfg@#&@g' nagios.cfg
# 主配置文件还可以包含目录,只要目录下面存在以.cfg结尾的文件都会被包含进来。在配置文件很多时还是可以使用的:
[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri 's@#(cfg_dir=/usr/local/nagios/etc/servers)@\1@g' nagios.cfg
创建目录和文件:
mkdir serverschown -R nagios.nagios servers/cd objects/head -51 localhost.cfg >hosts.cfgchown nagios.nagios hosts.cfgtouch services.cfg # 暂时留空chown nagios.nagios services.cfg
加入被监控主机:
# 编辑hosts.cfg配置文件,也就是head localhost文件生成的
[root@nagios objects]# vim hosts.cfgdefine host{ use host_name 02-client1 alias 02-client1 address 10.0.0.2 }define host{ # 将本机也加入监控 use linux-server host_name 01-nagios alias 01-nagios address 10.0.0.1 }
解释:
这一个标签就是一个被监控的主机
use表示一个使用名为linux-server的模板,该模板就是和hosts.cfg在同一个目录下的timeperiods.cfg,在该文件中可以搜索到linux-server定义的属性。可以也可以将该模板中定义的熟悉写在define
host{}标签内,如果在该标签中定义了,那么就以该标签中的内容为准;如果没定义就会模板配置文件中找。使用模板配置文件的好处就在于在现在这个标签内只需定义四行即可。
define hostgroup{ # 再将两个客户端加入一个组 hostgroup_name linux-servers alias Linux Servers members 02-client1,01-nagios }
检查配置文件:
# 检查配置文件的方法有两种,第一种为:
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
# 第二种:
/etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig
# 其实第二种就是调用第一种的命令,但是它将信息都定义到了/dev/null中了,根本看不出来什么地方出错了,因此我们可以修改启动脚本中的内容:
[root@nagios objects]# vim /etc/init.d/nagios +183 checkconfig) printf "Running configuration check..." $NagiosBin -v $NagiosCfgFile # 将后面的重定向去掉
# 执行命令
[root@nagios objects]# /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig...Error: There are no services defined! # 这就是错误,没有定义服务。下面就是统计的...Total Warnings: 2 # 警告无所谓Total Errors: 1 # 但是错误一定要解决...
# 既然没有定义服务,那我们就定义一个:
define service { use generic-service # 模板 host_name 02-client1,01-nagios # 被监控主机 service_description Disk Partition # 检查磁盘分区 check_command check_nrpe!check_disk}
# check_nrpe:Nagios的命令,需要在commands.cfg文件中定义
# check_disk:调用客户端配置文件nrpe.cfg中[check_disk]标签后面的命令
command[check_disk]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 8%
-p /
# 继续编辑commands.cfg配置文件,在配置文件的结尾加入以下几行:
# 'check_nrpe' command definitiondefine command{ command_name check_nrpe command_line $USER1$/check_nrpe -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -c $ARG1$ }
# -c:指定一个参数,这个参数就是check_disk
# 其实定义这么多的参数无非就是为了执行这一条命令:
[root@nagios objects]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 10.0.0.2 -c check_diskDISK OK - free space: / 57841 MB (95% inode=97%);| /=2760MB;51080;58742;0;63851
# 再次检查配置文件,结果ok:
[root@nagios objects]# /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig
启动服务并访问web界面:
/etc/init.d/nagios start/etc/init.d/httpd start
我们点击左边的services,会出现报错信息,解决办法就是编辑cgi.cfg: 
[root@nagios etc]# pwd /usr/local/nagios/etc[root@nagios etc]# grep nagiosadmin cgi.cfgauthorized_for_system_information=nagiosadminauthorized_for_configuration_information=nagiosadminauthorized_for_system_commands=nagiosadminauthorized_for_all_services=nagiosadminauthorized_for_all_hosts=nagiosadminauthorized_for_all_service_commands=nagiosadminauthorized_for_all_host_commands=nagiosadmin
# 从以上信息可以看出nagiosadmin就是Nagios的管理员,我们现在是没有权限,因此我们可以将nagiosadmin改为我们一开始添加的认证的用户oldboy。当然也可以使用nagiosadmin作为认证用户:
[root@nagios etc]# sed -i 's/nagiosadmin/oldboy/g' cgi.cfg[root@nagios etc]# grep oldboy cgi.cfgauthorized_for_system_information=oldboyauthorized_for_configuration_information=oldboyauthorized_for_system_commands=oldboyauthorized_for_all_services=oldboyauthorized_for_all_hosts=oldboyauthorized_for_all_service_commands=oldboyauthorized_for_all_host_commands=oldboy
重启服务:
[root@nagios etc]# /etc/init.d/nagios reload
1.5.1 刷新时间的定义
status_update_interval=3 # 默认10s刷新状态之类的数据[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri 's/(^status_u.*=).*/\13/g' nagios.cfgmax_service_check_spread=10 # 最大的服务检查间隔[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri 's/(^max_s.*=).*/\110/g' nagios.cfgauto_rescheduling_interval=5 # 尝试自动检查的时间间隔[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri 's/(^auto_rescheduling_i.*=).*/\15/g' nagios.cfgcommand_check_interval=-1 # -1的意思是尽可能的经常检查,但这不是我们想要的[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri 's/(^command_c.*=).*/\12s/g' nagios.cfg # 改为2sretention_update_interval=10[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri 's/(^rete.*=).*/\110/g' nagios.cfginterval_length=10[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri 's/(^in.*=).*/\110/g' nagios.cfgservice_freshness_check_interval=10[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri 's/(^service_f.*=).*/\110/g' nagios.cfghost_freshness_check_interval=10[root@nagios etc]# sed -ri 's/(^host_f.*=).*/\110/g' nagios.cfg
1.5.2 一些排错的思路
(1) 客户端获取值失败:
[root@client1 ~]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 10.0.0.2 -c check_diskCHECK_NRPE: Error - Could not complete SSL handshake. # 握手失败
# 这种问题的解决办法很简单,只需要执行下面这条命令即可:
[root@client1 ~]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c check_disk
# 如果能够获得值,那就是没有添加网卡地址,在nrpe.cfg中修改allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1这一行
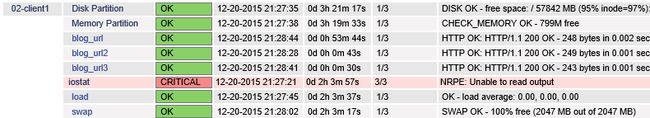
(2) 状态为CRITICAL  # 这种问题就是连接失败,要么是
# 这种问题就是连接失败,要么是服务没起,要么就是防火墙没关。我们可以现在本地执行:
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 10.0.0.2 -c check_disk
# 当然ip和参数都可以改,通过该命令就能得到答案,因为改命令就是Nagios获取监控值的过程
(3) 命令行执行能够获取数值,但是web界面去获取不到。
define service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1,01-nagios service_description Disk Partition check_command check_nrpe!check_disk # 肯定是这个参数定义错了}
(4) Unable to read output
![]()
# 出现这种问题的原因就是获取值的插件没有执行权限,或者是这插件就是有问题的,总之就是插件的错。
command[check_mem]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_memory.pl -w 6% -c 3% # check_memory.pl就是插件[root@nagios libexec]# chmod +x check_memory.pl # 执行该命令,如果还是不行,那就是插件本身的问题了
总结,当web界面显示出现问题时:
(1) Nagios自身和配置文件;
(2) 在服务器端执行: /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 被监控主机地址-c 获取值的命令
(3) 在客户端本地执行: /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c获取值的命令
(4) 执行nrpe.cfg配置文件中的获取值的命令:
command[check_disk]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 8%
-p / # 执行该命令
老男孩老师补几个提醒:
(1) 检查客户端系统自带的防火强,是否drop了5666端口;
(2) nrpe添加完命令后,有没有真正重启;
(3) nrpe.cfg配置文件中的allow_hosts这行的ip千万不要加错了。
1.5.3 添加其他监控项
[root@nagios objects]# cat services.cfgdefine service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1,01-nagios service_description Disk Partition check_command check_nrpe!check_disk}define service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1,01-nagios service_description Memory Partition check_command check_nrpe!check_mem}define service { use generic-service host_name 01-nagios,02-client1 service_description load check_command check_nrpe!check_load}define service { use generic-service host_name 01-nagios,02-client1 service_description swap check_command check_nrpe!check_swap}define service { use generic-service host_name 01-nagios,02-client1 service_description iostat check_command check_nrpe!check_iostat}
1.6 主动模式
按照监控的行为,老男孩老师把Nagios的监控分为主动监控和被动监控(NRPE半被动和NSCA全被动)。
(1) 主动监控:所谓的主动模式就是Nagios服务器端发起的监控,如URL地址、端口监控等。主动模式获取值的命令无需经过nrpe,Nagios自身能够直接发起,也就是说不需要在客户端安装任何插件。当然,主动监控模式也能配置成被动模式。
(2) 半被动监控:我们把对负载、内存、硬盘、虚拟内存、磁盘IO、温度、风扇转速等这些本地资源而非系统对外提供的服务的监控称为半被动模式。半被动模式的特点是对于这些本地资源的监控一般由Nagios插件定时去连接client的NRPE服务,定期获取信息发回Nagios服务器端。基本上只要安装了类似NRPE的agent端,且通过插件的方式的监控我们都认为是半被动监控。
上面讲到的都是被动模式。
如何选择主动和被动?
(1) 对于本地资源的监控,一般都使用被动模式。如负载、磁盘、内存、虚拟内存、磁盘IO、温度、风扇等的监控(我们也可以通过snmp来监控部分系统资源);
(2) 对于web服务、数据库这种能对外提供服务的监控,一般采用主动模式。如监控http、ssh、MySQL、rsync等服务;
(3) 主动和被动是相对的,并且是可以相互转换的。即主动模式的服务可以改成被动的;而被动模式有时也可以改为主动。
总之:
(a) 主动模式就和NRPE无关了,就是利用服务端本地插件直接获取信息;
(b) 被动模式则是Nagios主程序通过check_nrpe插件和客户端NRPE进程沟通,调用本地插件获取数据。
主动模式有check_tcp和check_http这两个非常常用的插件,一个是检查端口,另一个则是检查URL,它们都能够使用–help查看使用帮助。
[root@nagios libexec]# ./check_http --help[root@nagios libexec]# ./check_tcp --help
# 以下是最基本的使用方法
[root@nagios libexec]# ./check_tcp -H 10.0.0.2 -p 22TCP OK - 0.000 second response time on port 22|time=0.000299s;;;0.000000;10.000000[root@nagios libexec]# ./check_http -I 10.0.0.2HTTP OK: HTTP/1.1 200 OK - 248 bytes in 0.024 second response time |time=0.023816s;;;0.000000 size=248B;;;0
1.6.1 监控一个域名或URI
先说说使用主配置文件包含一个目录的好处:
(1) 该目录下的所有所有以.cfg为后缀的配置文件都会被Nagios加载,因此当我们不想使用其中的配置文件时,只需要改变其后缀名即可;
(2) 我们一个以一个服务名为目录名,下面的配置文件都是监控这个服务的;还可以以一个主机命名,下面的配置文件都是监控这个主机的。可以根据业务需要进行配置。
1. 添加一个服务:
[root@nagios etc]# vim servers/http.cfg # server是主配置文件中包含的目录define service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1 service_description blog_url check_command check_weburl!-I 10.0.0.2max_check_attempts 3normal_check_interval 2retry_check_interval 1check_period 24x7notification_interval 30notification_period 24x7notification_options w,u,c,rcontact_groups admins}
check_weburl:check_weburl这个可以直接换成check_http,但是也可以在commands.cfg文件中定义,让它和这个check_http关联起来; -I 10.0.0.2 可以使用域名而非ip,工作中肯定是使用域名的,这里只是测试
2. 编辑commands.cfg,加入check_weburl
[root@nagios etc]# vim objects/commands.cfg# 'check_http' command definition # 这里面已经存在了check_http,因此可以直接替换上面的check_weburldefine command{ command_name check_http command_line $USER1$/check_http -I $HOSTADDRESS$ $ARG1$ }# 'check_weburl' command definitiondefine command{ command_name check_weburl command_line $USER1$/check_http $ARG1$ -w 10 -c 30 }
# 之所以重新定义check_weburl,是为了增加-w 10 -c 30,10秒钟之内返回结果为警告,30秒内返回结果那就很严重了
3. 重新加载配置文件:
[root@nagios etc]# /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig[root@nagios etc]# /etc/init.d/nagios reload
以上是ip,下面是域名:
[root@nagios etc]# cat servers/http.cfgdefine service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1 service_description blog_url check_command check_weburl!-I 10.0.0.2max_check_attempts 3normal_check_interval 2retry_check_interval 1check_period 24x7notification_interval 30notification_period 24x7notification_options w,u,c,rcontact_groups admins}define service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1 service_description blog_url2 check_command check_weburl!-H blog.etiantian.org # 域名 max_check_attempts 3 normal_check_interval 2 retry_check_interval 1 check_period 24x7 notification_interval 30 notification_period 24x7 notification_options w,u,c,r contact_groups admins}define service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1 service_description blog_url3 check_command check_weburl!-H blog.etiantian.org -u "/exec/test" # URI max_check_attempts 3 normal_check_interval 2 retry_check_interval 1 check_period 24x7 notification_interval 30 notification_period 24x7 notification_options w,u,c,r contact_groups admins}
# 编辑hosts文件,域名都有公网DNS解析了,为什么还要添加hosts呢?因为使用公网DNS很容易误报,如果监控服务器本身DNS出问题了就会导致误报。缺点是不能监控到DNS导致的域名解析故障。
[root@nagios etc]# vim /etc/hosts127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 nagios::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain610.0.0.2 blog.etiantian.org
# curl一下,看看是否有问题
[root@nagios etc]# curl blog.etiantian.orgblog.etiantian.org
# 再次检查:
[root@nagios etc]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_http -H blog.etiantian.orgHTTP OK: HTTP/1.1 200 OK - 249 bytes in 0.001 second response time |time=0.000688s;;;0.000000 size=249B;;;0
# 这是对URL做监控
[root@nagios etc]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_http -H blog.etiantian.org -u /exec/test HTTP OK: HTTP/1.1 200 OK - 243 bytes in 0.001 second response time |time=0.000784s;;;0.000000 size=243B;;;0
# 重载配置文件:
[root@nagios etc]# /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig [root@nagios etc]# /etc/init.d/nagios reload
如果不是监控域名而是URI的话,当该URI有特殊符号,也就是没有做伪静态时,使用这个URL一定要用引号一起来不然就会报错:
define service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1 service_description blog_url check_command check_weburl!-H blog.etiantian.org -u "/main_free.jsp?dirId=32234&gId=3"
我们可以删除URI中的文件,查看监控的反应: ![]()
1.6.2 监控端口
监控端口使用的是check_tcp这个插件,这个命令已经在commands.cfg中定义了,我们直接拿来用就行。比如监听80端口:
[root@nagios etc]# vim servers/http.cfgdefine service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1 service_description blog_prot_80 check_command check_tcp!80 # 已经在commands.cfg中定义了 max_check_attempts 3 normal_check_interval 2 retry_check_interval 1 check_period 24x7 notification_interval 30 notification_period 24x7 notification_options w,u,c,r contact_groups admins}
# 重载配置文件
[root@nagios etc]# /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig [root@nagios etc]# /etc/init.d/nagios reload
所有端口都可以这么监控,只需要改个描述和端口号即可。
1.6.3 集群节点控制
利用别名实现对集群下面同样的节点的URL监控,因为相同的域名下所有节点都是一样的,这是就可以通过别名区分同一个域名解析下的所有主机:
web1 blog.etiantian.org,blog1.etiantian.org
web2 blog.etiantian.org,blog2.etiantian.org
1.6.4 小结
一般客户端对外开启的服务,用主动模式监控。如port,url。
主动模式的监控配置过程:
(1) 在服务端的命令行把要监控的命令先调试好;
(2) 在commands.cfg中定义Nagios命令,同时调用命令行的插件;
(3) 在服务的配置文件中定义要监控的服务,调用commands.cfg中定义Nagios的监控命令。
1.6.5 被动模式监控端口
被动模式就要在客户端进行
1) 先测试命令在命令行是否执行成功:
[root@client1 etc]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_tcp -H 10.0.0.2 -p 80TCP OK - 0.000 second response time on port 80|time=0.000132s;;;0.000000;10.000000
2) 然后加入到nrpe.cfg中:
[root@client1 etc]# echo "command[check_port_80]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_tcp -H 10.0.0.2 -p 80 -w 5 -c 10" >>nrpe.cfg
3) 重启服务:
ps aux|grep nrpepkill nrpeps aux|grep nrpe/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -dps aux|grep nrpe
4) 在服务端命令测试:
[root@nagios libexec]# ./check_nrpe -H 10.0.0.2 -c check_port_80TCP OK - 0.000 second response time on port 80|time=0.000162s;5.000000;10.000000;0.000000;10.000000
5) 添加一个services:
[root@nagios etc]# vim servers/http.cfgdefine service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1 service_description blog_prot_80_passive check_command check_nrpe!check_port_80 max_check_attempts 3 normal_check_interval 2 retry_check_interval 1 check_period 24x7 notification_interval 30 notification_period 24x7 notification_options w,u,c,r contact_groups admins}
6) 重载配置文件
[root@nagios etc]# /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig [root@nagios etc]# /etc/init.d/nagios reload
![]()
1.7 服务分组
先定义一个配置文件,然后写入配置:
[root@nagios etc]# vim servers/servergroup.cfgdefine servicegroup{servicegroup_name swap # 这个swap要和前面定义的服务名对应上alias Linux Serversmembers 02-client1,swap,01-nagios,swap # 监控的主机,服务的组名,第二个监控主机,服务的组名... 这样就达到了服务分组的目的}
重载服务后,在哪里查看呢?点击左侧栏的Service Groups: 
今后就能够通过这种方式进行分组了,比如将所有要监控swap、cpu、磁盘等等的主机放在一个组里面。但是这个并不是太重要。
1.8 Nagios日志
Nagios也可以通过日志排查问题,日志所在位置为/usr/local/nagios/var/nagios.log,但是排错的思路前面已经讲到了,无需看日志。
1.9 主机和服务监控的重要参数
主机:
define host { # 定义主机 use linux-server # 主机使用的模板,详见templates.cfg host_name 02-client1 # 这个主机名和关键,很多监控的定义都会引用这个主机名alias 02-client1 # 主机别名address 10.0.0.2 # ip check_command check-host-alive # 检测主机存活的命令,来自commands.cfgmax_check_attempts 3 # 故障后的最大检测次数normal_check_interval 2 # 正常的检查间隔,默认单位为分钟retry_check_interval 1 # 故障后重试的检查间隔,默认单位为分钟check_period 24x7 # 检查周期24x7,具体详见timeperiods.cfgnotification_interval 30 # 故障后,两次报警的通知间隔,默认单位为分钟notification_period 24x7 # 一天之内通知的周期,如全天、半天等,详见timeperiods.cfgnotification_options d,u,r # 哪些问题会报警,d-down,u-unreachable(不可达),r-recovery(主机恢复)contact_groups admins # 报警到admins用户组,在contacts.cfg中定义}
服务:
define service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1 service_description blog_prot_80_passive # 报警服务的描述 check_command check_nrpe!check_port_80 # 检查服务的命令 max_check_attempts 3 normal_check_interval 2 retry_check_interval 1 check_period 24x7 notification_interval 30 notification_period 24x7 notification_options w,u,c,r # w-warning,u-unknown(状态不知道),c-critical(特别严重),r-recovery(恢复) contact_groups adminsprocess_perf_data 1 # PNP出图记录数据相关}
1.9.1 服务模板
不管是服务还是主机,一半只会定义前四项,其他参数都会定义在模板文件中。如果我们对监控的服务进行分类的话,甚至可以只写两行。我们来看看模板文件中的内容:
[root@nagios objects]# vim templates.cfgdefine service{ name generic-service # 这就是服务的模板 active_checks_enabled 1 passive_checks_enabled 1 parallelize_check 1 obsess_over_service 1 check_freshness 0 notifications_enabled 1 event_handler_enabled 1 flap_detection_enabled 1 failure_prediction_enabled 1 process_perf_data 1 retain_status_information 1 retain_nonstatus_information 1 is_volatile 0 check_period 24x7 max_check_attempts 3 normal_check_interval 10 retry_check_interval 2 contact_groups admins notification_options w,u,c,r notification_interval 60 notification_period 24x7 register 0 }
1.9.2 监控周期模板
查看监控周期timeperiods.cfg文件:
define timeperiod{ timeperiod_name 24x7 # 24x7只是一个名字而已,真正的时间在下面定义 alias 24 Hours A Day, 7 Days A Week sunday 00:00-24:00 monday 00:00-24:00 tuesday 00:00-24:00 wednesday 00:00-24:00 thursday 00:00-24:00 friday 00:00-24:00 saturday 00:00-24:00 }# 'workhours' timeperiod definitiondefine timeperiod{timeperiod_name workhours # 这是工作时间的,老外真爽alias Normal Work Hoursmonday 09:00-17:00tuesday 09:00-17:00wednesday 09:00-17:00thursday 09:00-17:00friday 09:00-17:00}
# workhours用于监控磁盘的报警,也就是说磁盘的监控是7x24小时的,但是报警时间一般为8点到23点。
1.9.3 联系人模板
模板文件名为contacts.cfg,记录报警信息发送的对象:
[root@nagios objects]# vim contacts.cfgdefine contact{ contact_name nagiosadmin # 联系人的名字 use generic-contact # 使用的模板 alias Nagios Admin email nagios@localhost}define contactgroup{ # 联系人组contactgroup_name admins # 可以向这个组内的所有成员报警alias Nagios Administratorsmembers nagiosadmin # 组中的成员}
# 可以添加一个运维组,将所有运维人员都添加到该组中;还可以添加一个老大的邮箱,当某些报警信息不希望老大收到时就不把他写上去。
1.10 报警的过程
templates.cfg:[root@nagios objects]# cat templates.cfgdefine contact{name generic-contact # 这是联系人的模板service_notification_period 24x7host_notification_period 24x7service_notification_options w,u,c,r,f,shost_notification_options d,u,r,f,sservice_notification_commands notify-service-by-email # 这是服务发送Email的命令,在command.cfg中定义host_notification_commands notify-host-by-email # 这是主机报警的命令,同上register 0}contacts.cfg:[root@nagios objects]# vim contacts.cfgdefine contact{ contact_name nagiosadmin use generic-contact # 联系人模板从这里引用 alias Nagios Admin email nagios@localhost}commands.cfg:[root@nagios objects]# vim commands.cfg# 'notify-host-by-email' command definitiondefine command{ command_name notify-host-by-email # 主机报警的命令,最终调用的是系统的mail命令 command_line /usr/bin/printf "%b" "***** Nagios *****\n\nNotification Type: $NOTIFICATIONTYPE$\nHost: $HOSTNAME$\nState: $HOSTSTATE$\nAddress: $HOSTADDRESS$\nInfo: $HOSTOUTPUT$\n\nDate/Time: $LONGDATETIME$\n" | /bin/mail -s "** $NOTIFICATIONTYPE$ Host Alert: $HOSTNAME$ is $HOSTSTATE$ **" $CONTACTEMAIL$ }# 'notify-service-by-email' command definitiondefine command{ command_name notify-service-by-email # 服务报警的命令 command_line /usr/bin/printf "%b" "***** Nagios *****\n\nNotification Type: $NOTIFICATIONTYPE$\n\nService: $SERVICEDESC$\nHost: $HOSTALIAS$\nAddress: $HOSTADDRESS$\nState: $SERVICESTATE$\n\nDate/Time: $LONGDATETIME$\n\nAdditional Info:\n\n$SERVICEOUTPUT$\n" | /bin/mail -s "** $NOTIFICATIONTYPE$ Service Alert: $HOSTALIAS$/$SERVICEDESC$ is $SERVICESTATE$ **" $CONTACTEMAIL$ }
1.11 自定义开发插件
自定义插件可以使用任意语言开发,只要能在命令行给出结果,就能够使用Nagios监控。什么是插件呢?我们在前文安装的nagios-plugins-1.4.16.tar.gz,这个软件包就是Nagios的插件安装包,插件都安装…/nagios/libexec目录下。只所以使用自定义插件的原因有:
(1) Nagios自带的插件满足不了需要;
(2) 由于插件是我们写的,因此它有哪些缺点和BUG我们都清楚。
写自定义插件的规则:
(1) 插件要有一个退出状态码,它用于被Nagios主程序作为判断被监控系统服务状态的依据;
(2) 插件在控制台打印的第一行数据,该数据可以被Nagios主程序作为被监控系统服务状态的补充说明,会显示在管理界面。 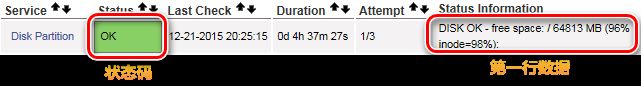
Nagios主程序可识别的状态码和说明如下: OK:退出状态码0,表示服务正常工作; WARNING:退出状态码1,表示服务处于警告状态; CRITICAL:退出状态码2,表示服务处于严重状态; UNKNOWN:退出状态码3,表示服务处于未知状态。
状态码定义的方法可以在libexec目录下执行head -7 utils.sh:
[root@nagios libexec]# head -7 utils.sh#! /bin/shSTATE_OK=0STATE_WARNING=1STATE_CRITICAL=2STATE_UNKNOWN=3STATE_DEPENDENT=4
不同语言的系统退出函数示例如下:
Java:System.exit(int status)
php:exit(status)
python:sys.exit(int status)
C/C++:return int status
bash:exit int status
不同语言打印第一行数据:
Java:System.out.println(String msg)
php:echo msg
python:printf msg
C/C++:printf(“%s”,msg)
bash:echo msg(printf)
使用shell开发第一个插件,监控passwd文件的变化:
# 先写脚本
[root@client1 ~]# md5sum /etc/passwd >/etc/oldboy.md5[root@client1 ~]# cd /usr/local/nagios/libexec/[root@client1 libexec]# vim check_passwd#!/bin/bashchar=`md5sum -c /etc/oldboy.md5|grep "OK"|wc -l`if [ $char -eq 1 ];then echo "passwd is ok" exit 0else echo "passwd is changed" exit 2fi[root@client1 libexec]# chmod +x check_passwd
# 添加到监控,只能使用被动监控
[root@client1 ~]# echo "command[check_passwd]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_passwd" >>/usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg[root@client1 libexec]# pkill nrpe[root@client1 libexec]# ps aux|grep nrpe[root@client1 libexec]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d[root@nagios nagios]# ./libexec/check_nrpe -H 10.0.0.2 -c check_passwd # 在服务器端先测试[root@nagios nagios]# vim etc/objects/services.cfg # 在服务端配置define service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1 service_description passwd check_command check_nrpe!check_passwd}[root@nagios nagios]# /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig[root@nagios nagios]# /etc/init.d/nagios reload
# 最终结果: ![]()
1.12 图形显示和管理
虽然能显示能报警,但是企业工作中需要一个历史趋势图。Nagios本身只是实现了核心功能,因此它不具备出图的能力,和Nagios配合出图的工具有很多,但是最好的还是pnp。想要使用pnp出图,但是也需要其他软件的支持。我们先安装图形显示管理的依赖库:
[root@nagios ~]# yum install -y cairo pango zlib zlib-devel freetype freetype-devel gd gd-devel
1.12.1 安装软件
pnp出图实际上是利用rrdtool(轮询的数据库工具)这个软件,但是安装之前我们先安装rrdtool的依赖库。我们可以使用yum install libart_lgpl libart_lgpl-devel安装,这里我们使用编译安装的方式(软件包中都有):
tar xf libart_lgpl-2.3.17.tar.gzcd libart_lgpl-2.3.17./configuremake && make installcp -r /usr/local/include/libart-2.0/ /usr/include/cd ..
安装rrdtools,rrdtools是真正画图的软件,这个工具虽然冷门,但是很多软件的画图都是靠它:
tar xf rrdtool-1.2.14.tar.gzcd rrdtool-1.2.14./configure --prefix=/usr/local/rrdtool --disable-python --disable-tclmake && make installcd ..ll /usr/local/rrdtool/bin/ # 3个程序
现在才是真正的安装pnp,pnp的作用就是收集数据然后告诉rrdtool,然后rrdtool画完图后还要通过pnp进行展示:
tar xf pnp-0.4.14.tar.gzcd pnp-0.4.14./configure \--with-rrdtool=/usr/local/rrdtool/bin/rrdtool \ # 画图的命令--with-perfdata-dir=/usr/local/nagios/share/perfdata # 出图的路径make allmake installmake install-configmake install-initll /usr/local/nagios/libexec/|grep process
# configure出现WARNING不用理会
1.12.2 修改配置
软件都准备好了,接下来要做的就是编辑主配置文件:
cd /usr/local/nagios/etc/cp nagios.cfg nagios.cfg.baksed -ri 's@(^pro.*=).*@\11@g' nagios.cfgsed -ri 's@^#(host_perfdata_c.*)@\1@g' nagios.cfgsed -ri 's@^#(service_perfdata_c.*)@\1@g' nagios.cfg
# 这是修改后的内容
process_performance_data=1host_perfdata_command=process-host-perfdataservice_perfdata_command=process-service-perfdata
修改commands.cfg文件:
# 将这两段内容删除:
# 'process-host-perfdata' command definitiondefine command{ command_name process-host-perfdata command_line /usr/bin/printf "%b" "$LASTHOSTCHECK$\t$HOSTNAME$\t$HOSTSTATE$\t$HOSTATTEMPT$\t$HOSTSTATETYPE$\t$HOSTEXECUTIONTIME$\t$HOSTOUTPUT$\t$HOSTPERFDATA$\n" >> /usr/local/nagios/var/host-perfdata.out }# 'process-service-perfdata' command definitiondefine command{ command_name process-service-perfdata command_line /usr/bin/printf "%b" "$LASTSERVICECHECK$\t$HOSTNAME$\t$SERVICEDESC$\t$SERVICESTATE$\t$SERVICEATTEMPT$\t$SERVICESTATETYPE$\t$SERVICEEXECUTIONTIME$\t$SERVICELATENCY$\t$SERVICEOUTPUT$\t$SERVICEPERFDATA$\n" >> /usr/local/nagios/var/service-perfdata.out }
# 替换成:
# 'process-host-perfdata' command definitiondefine command{ command_name process-host-perfdata command_line /usr/local/nagios/libexec/process_perfdata.pl # 其实就是该这一行 }# 'process-service-perfdata' command definitiondefine command{ command_name process-service-perfdata command_line /usr/local/nagios/libexec/process_perfdata.pl }
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec可以用$USER1$进行替换
重载配置文件后访问10.0.0.1/nagios/pnp/index.php,出现以下界面表示安装成功:
/etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig/etc/init.d/nagios reload
只要等一会,图上就有数据显示了,只所以会有数据出现在图上,是因为模板配置文件中一个参数决定的:
[root@nagios etc]# vim objects/templates.cfgdefine service{ name generic-service active_checks_enabled 1 passive_checks_enabled 1 parallelize_check 1 obsess_over_service 1 check_freshness 0 notifications_enabled 1 event_handler_enabled 1 flap_detection_enabled 1 failure_prediction_enabled 1 process_perf_data 1 # 就是这个参数
1.12.3 将二者结合
目前监控和趋势图二者是分离的,我们现在要将它们结合起来。
在主机监控中整合:
[root@nagios objects]# vim hosts.cfgdefine host{ use linux-server host_name 02-client1 alia 02-client1 address 10.0.0.2 action_url /nagios/pnp/index.php?host=$HOSTNAME$ # 增加这一行,定义URL }
# 在模板中添加更省事
重载配置文件后访问10.0.0.1/nagios,可以看到多了一个按钮,点进去就是该主机所有的趋势图了: 
服务出图:
[root@nagios objects]# vim services.cfgdefine service { use generic-service host_name 02-client1,01-nagios service_description Disk Partition check_command check_nrpe!check_disk action_url /nagios/pnp/index.php?host=$HOSTNAME$&srv=$SERVICEDESC$ # 增加一行}
1.13 报警
邮件报警:这是必须会的,生产环境中应尽量使用自己公司的信箱作为报警信箱,或者建立一个邮箱组(邮件列表)。尽量不用非公司信箱作为报警信箱,如126、qq等,因为这些信箱是免费的,对报警的频率等会有限制,很有可能会拒收或当成垃圾邮件,导致报警延时或无法收到。适用于重要且不紧急的业务报警;
邮件转短信报警:收到邮件会短信提醒,就相当于短信报警的功能。这是由邮箱提供商提供的一个功能,但报警内容长度有限制;
http短信网关:有专门的公司提供直接发送信息到手机的短信网关,常用的报警就是一个URL地址携带信息,收短信费。这是推荐的报警方式;
购买短信猫:类似于手机终端一样的客户端硬件设备,早期报警选用的方式,收短信费;
电话语音报警:先将报警语音录下来,报警时直接打电话到报警负责人,播放报警语音;也可以用语音识别软件,将文字识别为语音;
QQ/微信:模拟QQ,微信发信息的功能,QQ不太稳定;微信实际上就是将微信和邮箱绑定,当邮箱收到邮件时,微信会提醒
在生产环境中,一般会根据业务的紧急程度不同,多个报警策略结合使用。对于不需要紧急处理的业务一般选择邮件报警,如内存、磁盘空间的剩余率;对于重要且紧急的业务,会使用邮件加上短信同时报警。使用邮件报警便于记录故障详细信息,短息报警时及时提醒,优点是及时。短信报警的缺点是报警内容有限,所以在工作中如果接到严重报警时,我们紧急处理之前也会开启邮件系统先查看邮件细节。
其中http短信网关是老男孩老师最优先推荐使用的短信报警方式,原因:
(1) 简单、易用;
(2) 稳定、可靠;
(3) 收费合理,类似个人手机一样,收取发送费用。
老男孩老师的思想:花一定的费用把业务做到最好是正常工作的思维,如果总想着免费,那么如果业务报警收不到,损失可能会更大。
1.13.1 报警分级
A类:磁盘空间、cpu、内存报警等为一般报警,运维内部采取常规处理方式;
B类:网站域名不能打开为严重报警,需协调技术部相关人员会诊处理。
若收到A类报警,原则上限制处理时间,但以不影响服务为前提,进行即使处理;或收到B类报警短信,值班人员需在10分钟内邮件周知运维全体同事及相关技术人员,并解决。纯值班人员可能没有处理权限,只能电话及邮件周知运维人员,有的公司根据业务分配好报警的人。
1.13.2 配置报警
配置报警就是配置contacts.cfg文件。可以将公司所有的运维人员都加入到这个文件中,如果有需要还可以分组。
配置报警的步骤:
(1) 添加联系人及联系组contacts.cfg;
define contact{contact_name oldboy-pager use generic-contactalias Nagios usersemail 18901398229}
(2) 添加报警的命令commands.cfg
define command {command_name notify-host-by-pagercommand_line $USER1$/sms_send "$HOSTSTATE$ alert for $HOSTNAME$" $CONTACTOAGER$}define command {command_name notify-service-by-pagercommand_line $USER1$/sms_send "$HOSTALIAS$/$SERVICEDESC$ is $SERVICESTATE$" $CONTACTOAGER$}
(3) 调整联系人模板,添加报警的命令(来自于commands.cfg):
define contact{name generic-contactservice_notification_period 24x7host_notification_period 24x7service_notification_options w,u,c,r,f,shost_notification_options d,u,r,f,sservice_notification_commands notify-service-by-email,notify-service-by-pagerhost_notification_commands notify-host-by-email,notify-host-by-pagerregister 0}
(4) 在hosts.cfg和service.cfg配置文件中添加报警联系人及组,或者在模板中添加
contact_groups admins,group1,group2,user1
总结:总体来说nagios还是不错的一款监控软件,但是相比zabbix 就没有zabbix那样配置简单。只需要在图形化界面点点就可以完成。