课程笔记文集地址:Udemy课程:The Complete iOS 9 Developer Course - Build 18 Apps
用老师的原话来说,这是一个大项目,好吧,视频的长度是46分钟,也算是大项目吧!
一、Storyboard 布局
新建工程,使用一个 Navigation Controller ,这是之前的课程里没有讲过的知识点,设为 Initial View Controller,Segue(show) 连接一个 Map View Controller(点击 Bar Button Item 跳转到 Map View Controller。
注意这个 Navigation Controller 自带一个 TableViewController.
)
Map View Controller 拖入 MKMapView 控件,设置 AutoLayout 约束。创建 Outlet 连接。
二、新建类文件
给 Storyboard 里每个界面创建类文件,去 Storyboard 中关联一下。TableViewController 拖动简历 delegate 和 datasource。
TableViewController 类文件里完成必须要有的 2 个 datasource 方法。
三、获取用户位置需要进行的操作。
获取用户的位置需要进行的操作之前的课程里已经讲过了,也写到笔记里了,我在这里再重复一遍。
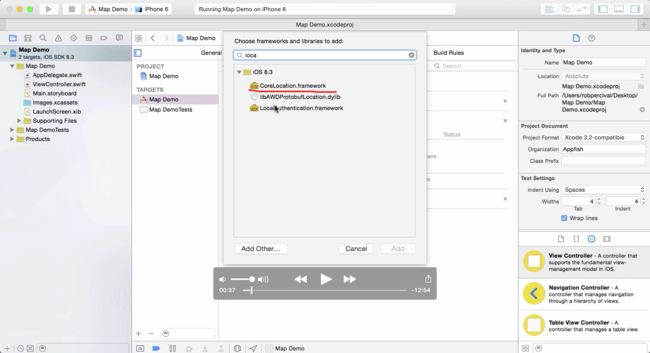
1、引入 CoreLocation.framework
步骤如下图,5步点击 + 号按钮:
点击 + 后,弹出框里输入查询:
选择 CoreLocation.framework,最终效果如下图:
这两个地方有了变化。
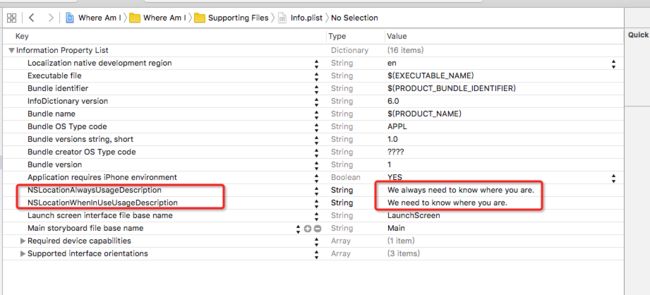
2、设置 plist 文件,请求用户权限
只在需要用的时候才获取用户的位置信息,NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription
如下图,两个里只需写一个即可:
Value 一栏输入的内容,是你在想用户请求获取位置信息权限时,显示给用户的一段内容,这段内容的目的是告诉用户为什么要使用你的位置,从而用户能够根据你说的理由决定是否给你这个权限。
3、类文件的代码
在与Map View Controller 关联的类文件里开始写代码,如下图中所标出的内容:
然后在 viewDidLoad 里写入下列代码:
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
//创建实例
manager = CLLocationManager()
//协议委托
manager.delegate = self
//设置用户位置的精确度
manager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest
//请求权限(这里和plist文件里的设置要一致)
manager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
//开始获取位置
manager.startUpdatingLocation()
}
四、获取用户位置之后进行处理
在这一部分里,所有的操作都是在与Map View Controller 关联的类文件进行的。
1、让地图控件显示的图像正好是用户位置的周围
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
let userLocation:CLLocation = locations[0] as! CLLocation
let latitude:CLLocationDegrees = userLocation.coordinate.latitude
let longitude:CLLocationDegrees = userLocation.coordinate.longitude
let latDelta:CLLocationDegrees = 0.01
let lonDelta:CLLocationDegrees = 0.01
let span:MKCoordinateSpan = MKCoordinateSpanMake(latDelta, lonDelta)
let coordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2D = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude)
let region:MKCoordinateRegion = MKCoordinateRegionMake(coordinate, span)
map.setRegion(region, animated: false)
}
2、创建手势
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
...
let uilpgr = UILongPressGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: #selector(ViewController.action(_:)))
uilpgr.minimumPressDuration = 2.0
map.addGestureRecognizer(uilpgr)
}
创建 action 方法,和之前课程学到的方法差不多,不过多了一个 if 判断。这个好处就是,长按立马进行操作,而不是长按,抬起手指,然后再进行操作。能够提高用户体验,没有 if ,用户会觉得等待时间过长了。
func action(gestureRecognizer: UIGestureRecognizer) {
//提高用户体验的关键点
if gestureRecognizer.state == UIGestureRecognizerState.Began {
//记录用户长按所在的点的位置
var touchPoint = gestureRecognizer.locationInView(self.map)
//将手指所在的点的位置转换成地图上的2D坐标数值
var newCoordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2D = map.convertPoint(touchPoint, toCoordinateFromView: self.map)
let location = CLLocation(latitude: newCoordinate.latitude, longitude: newCoordinate.longitude)
CLGeocoder().reverseGeocodeLocation(location, completionHandler: { (placemarks, error) -> Void in
//在后面的部分,我们会在这个闭包里进行大量的代码编程,闭包之外的代码在后面的会省略掉
})
//这之后的代码都是添加图钉标记,在后面的操作里会发现,这部分放到了闭包里
var annotation = MKPointAnnotation()
annotation.coordinate = newCoordinate
annotation.title = "New Place"
map.addAnnotation(annotation)
}
}
�3、处理闭包里的操作
闭包里的有关操作在 78 课里讲过一部分,这里又根据这次的需求添加了一些变化:
CLGeocoder().reverseGeocodeLocation(location, completionHandler: { (placemarks, error) -> Void in
var title = ""
if (error == nil) {
//if statement was changed
if let p = placemarks?[0] {
var subThoroughfare:String = ""
var thoroughfare:String = ""
if p.subThoroughfare != nil {
subThoroughfare = p.subThoroughfare!
}
if p.thoroughfare != nil {
thoroughfare = p.thoroughfare!
}
title = "\(subThoroughfare) \(thoroughfare)"
}
}
if title.stringByTrimmingCharactersInSet(NSCharacterSet.whitespaceCharacterSet()) == "" {
title = "Added \(NSDate())"
}
//这个 places 是一个全局数组变量,数组的类型是词典类型,词典的键值都是 String 类型,老师在 TableViewController 里创建的,不过既然是全局变量,在这个类的上面创建也是一样的
//给数组添加了两个元素
places.append(["name":title,"lat":"\(newCoordinate.latitude)","lon":"\(newCoordinate.longitude)"])
//是的,把添加图钉的操作放到了闭包里了
print(places)
let annotation = MKPointAnnotation()
annotation.coordinate = newCoordinate
annotation.title = title
self.map.addAnnotation(annotation)
})
五、完善 TableViewController
1、全局数组变量
刚刚提到的 places 全局数组变量,这行代码要鞋子 class 之外:
var places = [Dictionary()]
2、修改 datasource 的两个方法
现在,可以使用 places 数组了。
override func tableView(tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return places.count
}
override func tableView(tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAtIndexPath indexPath: NSIndexPath) -> UITableViewCell {
let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier("Cell", forIndexPath: indexPath) as UITableViewCell
cell.textLabel?.text = places[indexPath.row]["name"]
return cell
}
3、数组的第一个元素是空的字典
是的,我一开始没有看懂为什么要添加这个代码:
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
if places.count == 1 {
places.removeAtIndex(0)
places.append(["name":"Taj Mahal","lat":"27.175277","lon":"78.042128"])
}
}
于是,我加上几个 print 来查看一下原因,如下图:
看到控制台输入的打印信息了吗?你还没有创建任何新的地点,这个数组里已经有一个元素了,所以需要这段代码去掉第一个元素,新建一个默认的地点(当然你也可以没有默认地点,一开始就空白,不过这个操作会稍微复杂一丁点)。
六、地图显示某个点的位置
我感觉到这一步才开始学习新东西,前面那些都是之前课程里涉及过的。。。是的,这节视频长达 46 分钟,到 37分钟才开发讲新的东西。。。实际上新东西只有10来分钟而已嘛!!
需求如下:点击 TableViewController 上某一行地点,跳转地图界面,且地图显示的就是刚刚选择的地点。
1、创建 Segue
选中 cell,拖到地图界面,点击 show(Selection Segue,别选错了),如下图:
2、记住用户点击了哪一行
创建全局变量,在 places 下面写下:
var activePlace = -1
然后使用 TableView 里的一个方法:
override func tableView(tableView: UITableView, willSelectRowAtIndexPath indexPath: NSIndexPath) -> NSIndexPath? {
activePlace = indexPath.row
return indexPath
}
3、通过 Segue 传值
在 Storyboard 中,对点击 + 产生的 Segue 输入 identifier:newPlace
override func prepareForSegue(segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: AnyObject?) {
if segue.identifier == "newPlace" {
activePlace = -1
}
}
这样,如果 active 值是 -1,则是在新建图钉,如果不是 -1,则是在查看已有地点的信息。
4、确保 TableView 上的数据是最新的
这个简单:
override func viewWillAppear(animated: Bool) {
tableView.reloadData()
}
5、区分新建和查看
这上面的需要是要查看已有的地点信息,点击 + 则是要新建地点,都是在这个 Map View Controller 进行,所以需要区分哪个请求是新建,哪个是查看。
区分方法如下,用 if 语句来判断:
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
manager = CLLocationManager()
manager.delegate = self
manager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest
//如果值为 -1,则是在新建图钉
if activePlace == -1 {
manager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
manager.startUpdatingLocation()
//如果不是 -1,则是在查看之前记录的地点
} else {
//把字典里的字符串转换成数值
let latitude = NSString(string: places[activePlace]["lat"]!).doubleValue
//把字典里的字符串转换成数值
let longitude = NSString(string: places[activePlace]["lon"]!).doubleValue
//这往下的内容没有什么变化了,之前都学过了
let coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude)
let latDelta:CLLocationDegrees = 0.01
let lonDelta:CLLocationDegrees = 0.01
let span:MKCoordinateSpan = MKCoordinateSpanMake(latDelta, lonDelta)
let region:MKCoordinateRegion = MKCoordinateRegionMake(coordinate, span)
self.map.setRegion(region, animated: true)
let annotation = MKPointAnnotation()
annotation.coordinate = coordinate
annotation.title = places[activePlace]["name"]
self.map.addAnnotation(annotation)
}
let uilpgr = UILongPressGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: #selector(ViewController.action(_:)))
uilpgr.minimumPressDuration = 2.0
map.addGestureRecognizer(uilpgr)
}
七、结束
恩,最后十分钟的讲解还是不错的!之前有些拖沓了,就当是巩固吧。