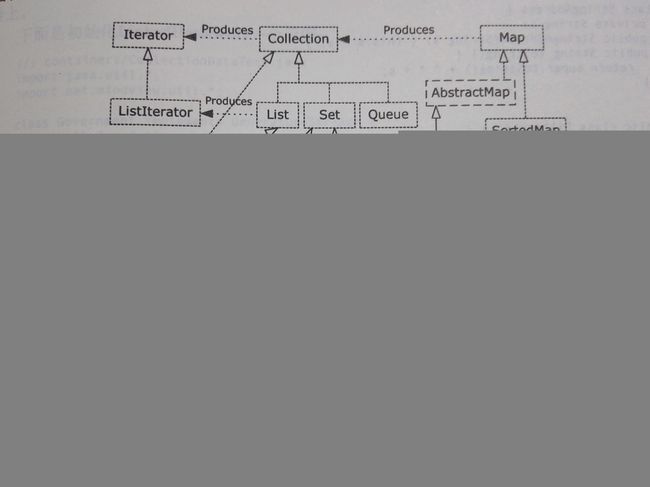
集合类:list(特定顺序) set(元素不重复) queue(一端插入,一端移除) map(键值对)
Collection collection = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
Integer[] moreInts = { 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
collection.addAll(Arrays.asList(moreInts));
// Runs significantly faster, but you can't
// construct a Collection this way:
Collections.addAll(collection, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15);
Collections.addAll(collection, moreInts);
// Produces a list "backed by" an array:
List list = Arrays.asList(16, 17, 18, 19, 20);
list.set(1, 99); // OK -- modify an element
// list.add(21); // Runtime error because the
// underlying array cannot be resized.
Collection.addAll():只能接受另一个Collection对象作参数
Collections.addAll():参数列表可变,运行速度更快
Arrays.asList():参数列表可变,直接使用方法返回是一个固定大小的数组
list
Arraylist:随机访问快,插入和移除慢
Linkedlist:利于插入和移除,随机访问慢
注意List有些方法行为依赖于equals()方法
迭代器
迭代器(一种设计模式),它可以遍历并选择序列中的对象,而不用关心序列底层的结构。
不用知道容器的确切类型,统一了对容器的访问方式
iterator()
next()
hasNext()
remove()
List pets = Pets.arrayList(12);
Iterator it = pets.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Pet p = it.next();
System.out.print(p.id() + ":" + p + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// A simpler approach, when possible:
for(Pet p : pets)
System.out.print(p.id() + ":" + p + " ");
System.out.println();
// An Iterator can also remove elements:
it = pets.iterator();
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
it.next();
it.remove();
}
System.out.println(pets);
/* Output:
0:Rat 1:Manx 2:Cymric 3:Mutt 4:Pug 5:Cymric 6:Pug 7:Manx 8:Cymric 9:Rat 10:EgyptianMau 11:Hamster
0:Rat 1:Manx 2:Cymric 3:Mutt 4:Pug 5:Cymric 6:Pug 7:Manx 8:Cymric 9:Rat 10:EgyptianMau 11:Hamster
[Pug, Manx, Cymric, Rat, EgyptianMau, Hamster]
*///:~
ListItertor
Iterator 只能向前移动
ListItertor 可以双向移动,能指向当前位置的前一个和后一个索引,set()方法替换它访问的过的后一个元素,
listIterator()方法指向开始处, 或用listIterator(n)方法一开始就指向n的索引。
List pets = Pets.arrayList(8);
ListIterator it = pets.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext())
System.out.print(it.next() + ", " + it.nextIndex() +
", " + it.previousIndex() + "; ");
System.out.println();
// Backwards:
while(it.hasPrevious())
System.out.print(it.previous().id() + " ");
System.out.println();
System.out.println(pets);
it = pets.listIterator(3);
while(it.hasNext()) {
it.next();
it.set(Pets.randomPet());
}
System.out.println(pets);
/* Output:
Rat, 1, 0; Manx, 2, 1; Cymric, 3, 2; Mutt, 4, 3; Pug, 5, 4; Cymric, 6, 5; Pug, 7, 6; Manx, 8, 7;
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
[Rat, Manx, Cymric, Mutt, Pug, Cymric, Pug, Manx]
[Rat, Manx, Cymric, Cymric, Rat, EgyptianMau, Hamster, EgyptianMau]
*///:~
LinkedList
执行插入和移除效率较高,不适合随机访问
Set
不保存重复的元素
Set中最常被使用的是测试归属性,查找是set最重要的操作
Set具有与Collection完全一样的接口,实际上Set就是Collection,只是行为不用(继承与多态思想的典型应用:表现不同的行为)
Queue
队列常被当作一种可靠的将对象从程序的某个区域传输到另一个区域的途径,队列在并发编程中特别重要
peek() 返回队头 队列为空返回null
element() 返回队头 队列为空抛出异常
poll() 移除并返回队头 队列为空返回null
remove() 移除并返回队头 队列为空抛出异常
PriorityQueue 优先级队列声明下一个弹出的元素是最需要的元素(优先级最高的),可用Comparator来设置自己的排序规则
Map
Map和Collection唯一的重叠就是Map可以使用entrySet()和values()方法来产生Collection。
Foreach与迭代器
foreach语法主要用于数组,但它也可以应用于任何Collection对象。实质是任何实现Iterable的类,都可以用foreach
这不意味数组是一个Iterable,把数组当做一个Iterable参数传递会导致失败。说明不存在任何数组到Iterable的自动转换,必须手动转换
//: holding/ArrayIsNotIterable.java
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayIsNotIterable {
static void test(Iterable ib) {
for(T t : ib)
System.out.print(t + " ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
String[] strings = { "A", "B", "C" };
// An array works in foreach, but it's not Iterable:
//! test(strings);
// You must explicitly convert it to an Iterable:
test(Arrays.asList(strings));
}
}
/* Output:
1 2 3 A B C
*///:~
*///:~
适配器方法惯用法
向Iterable类添加一个或多种使用foreach的方式
如果直接继承这个类,并覆盖iterator()方法。只能替换现有的方法,而不能实现选择,因此添加一个能够产生Iterable对象的方法,该对象能够用于foreach语句
//: holding/MultiIterableClass.java
// Adding several Adapter Methods.
import java.util.*;
public class MultiIterableClass extends IterableClass {
public Iterable reversed() {
return new Iterable() {
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Iterator() {
int current = words.length - 1;
public boolean hasNext() { return current > -1; }
public String next() { return words[current--]; }
public void remove() { // Not implemented
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
};
}
};
}
public Iterable randomized() {
return new Iterable() {
public Iterator iterator() {
List shuffled =
new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(words));
Collections.shuffle(shuffled, new Random(47));
return shuffled.iterator();
}
};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiIterableClass mic = new MultiIterableClass();
for(String s : mic.reversed())
System.out.print(s + " ");
System.out.println();
for(String s : mic.randomized())
System.out.print(s + " ");
System.out.println();
for(String s : mic)
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
}
/* Output:
banana-shaped. be to Earth the know we how is that And
is banana-shaped. Earth that how the be And we know to
And that is how we know the Earth to be banana-shaped.
*///:~
注意,第二个方法random()是直接返回被打乱的list中的Iterator。
从输出中可以看到,Collection.shuffle()方法没有影响到原来的数组,只是打乱了shuffed中的引用,这是因为用一个Arraylist将Arrays.aslist()方法的结果包装起来了,如果直接用Arrays.aslist()方法产生,它将会修改底层的数组。因为Arrays.aslist()方法产生list对象会使用底层数组作为其物理实现。
如果不想原来的数组被修改,那就应该在另一个容器创建一个副本。
//: holding/ModifyingArraysAsList.java
import java.util.*;
public class ModifyingArraysAsList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random rand = new Random(47);
Integer[] ia = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
List list1 =
new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(ia));
System.out.println("Before shuffling: " + list1);
Collections.shuffle(list1, rand);
System.out.println("After shuffling: " + list1);
System.out.println("array: " + Arrays.toString(ia));
List list2 = Arrays.asList(ia);
System.out.println("Before shuffling: " + list2);
Collections.shuffle(list2, rand);
System.out.println("After shuffling: " + list2);
System.out.println("array: " + Arrays.toString(ia));
}
}
/* Output:
Before shuffling: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
After shuffling: [4, 6, 3, 1, 8, 7, 2, 5, 10, 9]
array: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
Before shuffling: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
After shuffling: [9, 1, 6, 3, 7, 2, 5, 10, 4, 8]
array: [9, 1, 6, 3, 7, 2, 5, 10, 4, 8]
*///:~