源码阅读是基于JDK7,本篇主要涉及ArrayList常用方法源码分析。
1.概述
ArrayList是List接口的可调整大小的数组实现,可以包含任何类型的元素,包括null。除了实现List接口中的方法,它还提供了调整元素数组大小的方法。这个类除了非同步的特性,大体上和Vector是相同的。它的size、isEmpty、get、set方法运行时间为常数,而add方法运行开销为分摊的常数,添加n个元素的时间复杂度是O(n)。每个ArrayList的实例都有自己的容量,这个容量即用于存储List元素的数组大小,它的大小要大于等于数组实际存储的元素数,当元素被添加到ArrayList时,它的容量会自动扩容。当需要添加大量的元素到ArrayList中,最好提前给ArrayList设置合适的初始容量,这样可以减少增量式的内存再分配次数。ArrayList的实现方式是非同步的(非线程安全的),所以当多线程同时访问的时候,如果有线程从结构上做了修改(指任何添加或删除一个或多个元素的操作,或者显式调整底层数组的大小,仅仅设置元素的值不是结构上的修改),需要在使用它的地方做同步控制,源码里提供了使用List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(...))方式做同步,这个不推荐,这种方式只是在原有方法上加了同步控制,对于有些使用场景没有针对性,如果真的需要线程安全的操作,推荐使用Vector或concurrent并发包下的CopyOnWriteArrayList。
2.数据结构
ArrayList类的声明代码如下,
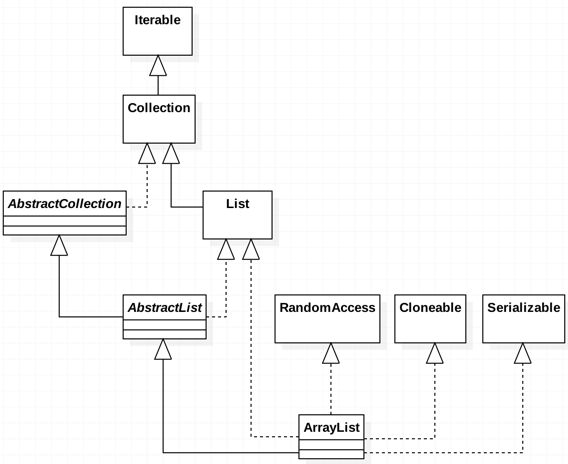
public class ArrayList extends AbstractList
implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
由上面的代码段可以得出如下所示的类图,
ArrayList中声明了如下一些属性,
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private transient Object[] elementData;
private int size;
protected transient int modCount = 0;
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
(1)DEFAULT_CAPACITY为默认的初始容量,即数组的默认大小;
(2)elementData数组用于存储元素;
(3)size为ArrayList中实际元素个数;
(4)modCount从AbstractList继承而来,用于记录从结构上修改此ArrayList的次数。
(5)EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA空数组;
3.构造方法
提供了三个构造函数可供使用。
//initialCapacity指定初始容量大小
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
//无参构造方法,elementData指向EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
public ArrayList() {
super();
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
//构造一个包含指定元素的list,这些元素的是按照Collection的迭代器返回的顺序排列的
public ArrayList(Collection c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
4.扩容
当添加元素的时候,检查数组容量是否需要扩容。
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
//可分配的最大数组大小(一些虚拟机保留一些字节头,所以减8)
//试图分配较大容量的数组可能会导致OutOfMemoryError
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
//扩展容量的时候要确保能容纳minCapacity参数指定的元素的数量
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//准备新扩容的数组长度为旧容量的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
5.size方法
public int size() {
return size;
}
返回ArrayList中元素的个数。
6.isEmpty方法
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
判断ArrayList中元素的个数是否为0。
7.contains方法
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
从前向后遍历elementData数组,匹配第一个和o相等的元素,如果存在返回对应元素的下标序号,否则返回-1。这里需要注意的是o.equals(elementData[i]),这里是Objetc的equals方法,比较的是引用。
8.toArray方法
public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
该方法返回一个新的数组,数组中的元素按照ArrayList中的第一个到最后一个顺序排列,修改返回的数组不会影响原ArrayList中的数据。
9.get方法
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
10.set方法
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
set方法就是给数组的指定下标成员重新赋值。
11.add方法
//首先进行扩容(是否扩容由ensureCapacityInternal方法决定)
//给数组的size++位置赋值为e
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
//检查给定的index是否正确
//进行扩容(是否扩容由ensureCapacityInternal方法决定)
//index位置后面的元素向后移动(数组复制实现)
//给index下标成员重新赋值
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
12.remove方法
//删除指定位置的元素
//原理:将index+1位置开始到末尾的元素向前移动一位,最后一位赋值为null,GC进行回收
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
//删除指定内容的元素,删除匹配的第一个元素
//原理:将匹配的第一个元素的位置下标加1开始到末尾的元素向前移动一位,最后一位赋值为null,GC进行回收
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//将index+1位置开始到末尾的元素向前移动一位,最后一位赋值为null,GC进行回收
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
13.clear方法
public void clear() {
modCount++;
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
size = 0;
}
将数组所有元素引用设置了null,ArrayList的元素个数置为0;
14.iterator方法和listIterator方法
//返回Iterator用于遍历ArrayList
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator {
int cursor; // 下一个元素的索引下标
int lastRet = -1; // 最后一个元素的下标,如果不存在则返回-1
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
//从index下标开始返回一个ListIterator
public ListIterator listIterator(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
public ListIterator listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0);
}
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
在执行iterator或listIterator方法时,如果有线程从结构上做了修改(指任何添加或删除一个或多个元素的操作,或者显式调整底层数组的大小,仅仅设置元素的值不是结构上的修改),这两个方法会fail-fast,将会抛出ConcurrentModificationException。迭代器的快速失败行为无法得到保证,因为一般来说,不可能对是否出现不同步并发修改做出任何硬性保证。快速失败操作会尽最大努力抛出ConcurrentModificationException。因此,为提高此类操作的正确性而编写一个依赖于此异常的程序是错误的做法,正确做法是:ConcurrentModificationException应该仅用于检测bug。抛异常就是为了避免数据问题而存在的,其实就是检查modCount是否是期望值,如果不是,则说明ArrayList数组被从结构上修改了。这里是经常会遇到的问题,使用Java的For Each方式遍历元素时删除匹配的元素,会抛出ConcurrentModificationException。Java中的For Each实际上使用的是iterator进行处理的,而iterator是不允许集合在iterator使用期间删除的。
小结:
1.ArrayList是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构。
2.ArrayList在每次增加元素时,都要进行扩容判断,扩容时都要确保足够的容量。当容量不足以容纳当前的元素个数时,就设置新的容量为旧的容量的1.5倍,如果新容量还不够,则新容量设置为传入的参数,如果新容量还不够,则新容量为最大容量。从中可以看出,当容量不够时,都要将原来的元素拷贝到一个新的数组中,耗时而且还需要重新分配内存,因此建议在事先能确定元素数量的情况下,明确指明容量大小。
3.ArrayList基于数组实现,可以通过下标索引直接查找到指定位置的元素,因此查找效率高,但每次插入或删除元素,就要大量地移动元素,效率低。