完整代码
Word2Vec核心观念
- 相似的词具有相似的上下文
-
cat climbed a treeandkitten climbed a tree - 则数据为
(input:cat,output:tree)and(input:kitten,output:tree), - So
catandkitty的向量表示会很接近
skip-gram 简介
- word 预测 context(word)
- The dog barked at the mailman
- 当skip_window=2,dog 预测(the barked at)
- 数据输入为
(input:dog,output:the),(input:dog,output:barked),(input:dog,output:at)
说明
- 对text8进行word2vec
- 对词向量降为可视化
代码解释
- 首先下载并验证text8数据集
- 读取数据集,转化为列表vocabulary(每个元素为单词)
- 根据vocabulary建立data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary
- 按照skip-gram要求生成batch train data
- 建立模型并训练(每disp_step输出一些相近的词向量)
- stne降维并可视化
首先下载并验证text8数据集
import collections
import math
import os
import random
import zipfile
import numpy as np
from six.moves import urllib
from six.moves import xrange # pylint: disable=redefined-builtin
import tensorflow as tf
print(tf.__version__)
# Step 1: Download the data.
url = 'http://mattmahoney.net/dc/'
def maybe_download(filename, expected_bytes):
"""
Download a file if not present,
and make sure it's the right size.
"""
if not os.path.exists(filename):
filename, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(url + filename, filename)
statinfo = os.stat(filename)
if statinfo.st_size == expected_bytes:
print('Found and verified', filename)
else:
print(statinfo.st_size)
raise Exception(
'Failed to verify ' + filename + \
'. Can you get to it with a browser?')
return filename
filename = maybe_download('text8.zip', 31344016)
读取数据集,转化为列表vocabulary(每个元素为单词)
# Read the data into a list of strings.
def read_data(filename):
"""
Extract the first file enclosed in a zip file as a list of words.
"""
with zipfile.ZipFile(filename) as f:
data = tf.compat.as_str(f.read(f.namelist()[0])).split()
return data
vocabulary = read_data(filename)
print('Data size', len(vocabulary))
根据vocabulary建立data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary
# Step 2: Build the dictionary and replace rare words with UNK token.
vocabulary_size = 50000
def build_dataset(words, n_words):
"""Process raw inputs into a dataset."""
count = [['UNK', -1]]
count.extend(collections.Counter(words).most_common(n_words - 1))
dictionary = dict()
for word, _ in count:
dictionary[word] = len(dictionary)
data = list()
unk_count = 0
for word in words:
if word in dictionary:
index = dictionary[word]
else:
index = 0 # dictionary['UNK']
unk_count += 1
data.append(index)
count[0][1] = unk_count
reversed_dictionary = dict(zip(dictionary.values(),
dictionary.keys()))
return data, count, dictionary, reversed_dictionary
data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary = build_dataset(vocabulary,
vocabulary_size)
del vocabulary # Hint to reduce memory.
print('Most common words (+UNK)', count[:5])
print('Sample data', data[:10],
[reverse_dictionary[i] for i in data[:10]])
data_index = 0
按照skip-gram要求生成batch train data
- num_skips : 从窗口中选取多少个(input, output)
# Step 3: Function to generate a training batch for the skip-gram model.
* num_skips : 从窗口中选取多少个(input, )
def generate_batch(batch_size, num_skips, skip_window):
global data_index
assert batch_size % num_skips == 0
assert num_skips <= 2 * skip_window
batch = np.ndarray(shape=(batch_size), dtype=np.int32)
labels = np.ndarray(shape=(batch_size, 1), dtype=np.int32)
span = 2 * skip_window + 1 # [ skip_window target skip_window ]
buffer = collections.deque(maxlen=span)
for _ in range(span):
buffer.append(data[data_index])
data_index = (data_index + 1) % len(data)
for i in range(batch_size // num_skips):
target = skip_window # target label at the center of the buffer
targets_to_avoid = [skip_window]
for j in range(num_skips):
while target in targets_to_avoid:
target = random.randint(0, span - 1)
targets_to_avoid.append(target)
batch[i * num_skips + j] = buffer[skip_window]
labels[i * num_skips + j, 0] = buffer[target]
buffer.append(data[data_index])
data_index = (data_index + 1) % len(data)
# Backtrack a little bit to avoid skipping words in the end of a batch
data_index = (data_index + len(data) - span) % len(data)
return batch, labels
batch, labels = generate_batch(batch_size=8, num_skips=2,
skip_window=1)
for i in range(8):
print(batch[i], reverse_dictionary[batch[i]],
'->', labels[i, 0], reverse_dictionary[labels[i, 0]])
建立模型并训练
# Step 4: Build and train a skip-gram model.
batch_size = 128
embedding_size = 128 # Dimension of the embedding vector.
skip_window = 1 # How many words to consider left and right.
num_skips = 2
# How many times to reuse an input to generate a label.
# We pick a random validation set to sample nearest neighbors. Here we limit the
# validation samples to the words that have a low numeric ID, which by
# construction are also the most frequent.
valid_size = 16
# Random set of words to evaluate similarity on.
valid_window = 100
# Only pick dev samples in the head of the distribution.
valid_examples = np.random.choice(valid_window, valid_size,
replace=False)
# 从np.arange(valid_window)中选valid——size个
num_sampled = 64 # Number of negative examples to sample.
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
# Input data.
train_inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size])
train_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size, 1])
valid_dataset = tf.constant(valid_examples, dtype=tf.int32)
# Ops and variables pinned to the CPU because of
# missing GPU implementation
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
# Look up embeddings for inputs.
embeddings = tf.Variable(
tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0))
embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, train_inputs)
# Construct the variables for the NCE loss
nce_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, embedding_size],
stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(embedding_size)))
nce_biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([vocabulary_size]))
# Compute the average NCE loss for the batch.
# tf.nce_loss automatically draws a new sample of the negative labels each
# time we evaluate the loss.
loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.nce_loss(weights=nce_weights,
biases=nce_biases,
labels=train_labels,
inputs=embed,
num_sampled=num_sampled,
num_classes=vocabulary_size))
# Construct the SGD optimizer using a learning rate of 1.0.
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1.0).minimize(loss)
# Compute the cosine similarity between minibatch examples and all embeddings.
norm = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(embeddings), 1, keep_dims=True))
normalized_embeddings = embeddings / norm
valid_embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(
normalized_embeddings, valid_dataset)
similarity = tf.matmul(
valid_embeddings, normalized_embeddings, transpose_b=True)
# Add variable initializer.
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Step 5: Begin training.
num_steps = 100001
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as session:
# We must initialize all variables before we use them.
init.run()
print('Initialized')
average_loss = 0
for step in xrange(num_steps):
batch_inputs, batch_labels = generate_batch(
batch_size, num_skips, skip_window)
feed_dict = {train_inputs: batch_inputs, train_labels: batch_labels}
# We perform one update step by evaluating the optimizer op (including it
# in the list of returned values for session.run()
_, loss_val = session.run([optimizer, loss], feed_dict=feed_dict)
average_loss += loss_val
if step % 2000 == 0:
if step > 0:
average_loss /= 2000
# The average loss is an estimate of the loss over the last 2000 batches.
print('Average loss at step ', step, ': ', average_loss)
average_loss = 0
# Note that this is expensive (~20% slowdown if computed every 500 steps)
if step % 10000 == 0:
sim = similarity.eval()
for i in xrange(valid_size):
valid_word = reverse_dictionary[valid_examples[i]]
top_k = 8 # number of nearest neighbors
nearest = (-sim[i, :]).argsort()[1:top_k + 1]
log_str = 'Nearest to %s:' % valid_word
for k in xrange(top_k):
close_word = reverse_dictionary[nearest[k]]
log_str = '%s %s,' % (log_str, close_word)
print(log_str)
final_embeddings = normalized_embeddings.eval()
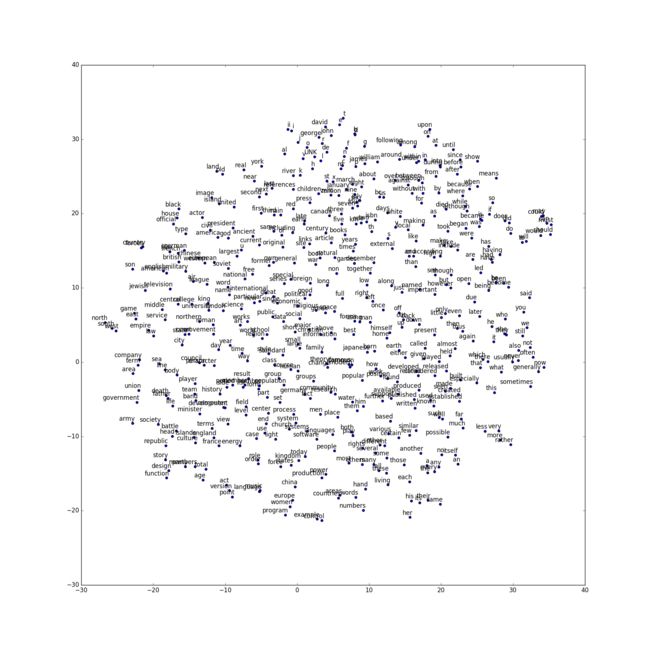
tsne 降维可视化
# Step 6: Visualize the embeddings.
def plot_with_labels(low_dim_embs, labels, filename='tsne.png'):
assert low_dim_embs.shape[0] >= len(labels), 'More labels than embeddings'
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 18)) # in inches
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
x, y = low_dim_embs[i, :]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.annotate(label,
xy=(x, y),
xytext=(5, 2),
textcoords='offset points',
ha='right',
va='bottom')
plt.savefig(filename)
try:
# pylint: disable=g-import-not-at-top
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
tsne = TSNE(perplexity=30, n_components=2, init='pca', n_iter=5000)
plot_only = 500
low_dim_embs = tsne.fit_transform(final_embeddings[:plot_only, :])
labels = [reverse_dictionary[i] for i in xrange(plot_only)]
plot_with_labels(low_dim_embs, labels)
except ImportError:
print('Please install sklearn, matplotlib, and scipy to show embeddings.')
运行结果
- 部分代码输出
- 可视化词向量
1.0.1
Found and verified text8.zip
Data size 17005207
Most common words (+UNK) [['UNK', 418391], ('the', 1061396), ('of', 593677), ('and', 416629), ('one', 411764)]
Sample data [5242, 3082, 12, 6, 195, 2, 3137, 46, 59, 156] ['anarchism', 'originated', 'as', 'a', 'term', 'of', 'abuse', 'first', 'used', 'against']
3082 originated -> 12 as
3082 originated -> 5242 anarchism
12 as -> 6 a
12 as -> 3082 originated
6 a -> 12 as
6 a -> 195 term
195 term -> 2 of
195 term -> 6 a
Average loss at step 2000 : 113.561805058
Average loss at step 4000 : 52.6443465168
Average loss at step 6000 : 33.354344763
Average loss at step 8000 : 23.1323922411
Average loss at step 10000 : 18.2816311638
Nearest to b: marriage, authorities, anti, punts, molecules, unionists, province, traffic,
Nearest to can: majesty, archie, review, antonym, arabs, robeson, healthy, factors,
Nearest to first: agave, boroughs, in, restaurant, of, symbol, apiaceae, developed,
参考文献
- http://www.thushv.com/natural_language_processing/word2vec-part-1-nlp-with-deep-learning-with-tensorflow-skip-gram/
高级版本的word2vec实现
https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/tutorials/embedding/word2vec.py