本文根据Jiang教授讲授《how to write sci-tech paper in English》课程时,记录的课堂笔记整理而成。之前有分享过大框架的思维导图,时隔一年,终于将所有笔记整理好,若有错误烦请指正。公诸同好,希望对您的英文论文写作有所帮助,祝学业顺利!
先介绍一下本文目录及说明。
Summarize(介绍科技论文分类、写作的一些规则等)
Commonly used words & expressions(区分常用的词语及句子)
Sentence patterns(常用句型)
Figures and tables(图形和表格表示方法)
English tense & English voice(英语时态及语态)
Some details need to know(数字、缩写和符号表示方法)
Main functional types of writing(写作类型及方法)
writing type: cause-effect relationship(因果关系类型)
How to Read papers (a three-pass approach) (如何读文献)
Presentation skill(英语演讲技巧)
Structure of research papers(论文结构,并逐一说明)
1.title
2.Author/Authors
3.abstract(summary)&keywords(index terms)
4.introduction
5.theory&solution (material and method)
6.experiments &analysis (results & discussion)
7.conclusion&discussion
8.acknowledgment
9.reference(bibliography)
Literature review (文献综述)
Summarize
Classification of scientific and technical papers.
-according to the contents: review papers, theoretical papers, opinion papers, policy papers, research papers (experiments, techniques, algorithms, system designs, etc.)
-according to the usage: conference(proceeding)papers, (conference, symposium, meeting, workshop, etc.), journal papers(journal, magazine, transaction), degree paper(thesis, dissertation)
Sample research papers-A
A conference paper: E. Dubois, “Filter Design for Adaptive Frequency-Domain Bayer Demosaicking,” Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Image Processing(ICIP’06), AHanta, GA, USA, Oct,2006,pp,2705-2708.
Sample research papers-B
A journal paper: S.P. Metkar and S.N. Talbar,”Fast Motion Estimation Using Modified or Thogonal Search Algorithm for Video Processing,”vol.4,no.2,pp,123-128,June 2010.
Master the basis of organized writing.
Paragraph: ordered set of topically-related sentences.
Lead sentence: setting context for paragraph. Tied to precious paragraph.
Sentences in paragraph: following the logical narrative flow. Relating to the lead sentence/theme/topic.
Words: arranged into phrases, clauses, and sentences. Obeying grammar and punctuation rules.
Writing style – common rules
1.同样的意思能用简单词汇描述,就不用长的。
2.如果不必要,就用尽量短的,简单的句子。
3.不要创造一些缩写词、反复用。
4.公式也不要范用,如果可以用一句或两句叙述替代,就不用公式。
5.深奥的理论,如果写得好,也能携程“常识”感。
评价一个论文最重要的特点
well-written, well-organized, research related, contribution(创新点)
什么是创新?
Introduce a new idea, explain something old in a new way, synthesize familiar ideas in a new way, present something new.
Categories of research papers
Provide a solution for: an algorithm, a system structure(a system design, a software system, a protocol), a performance evaluation(through analyses, simulation or measurements), a theory(a collection of theorems)
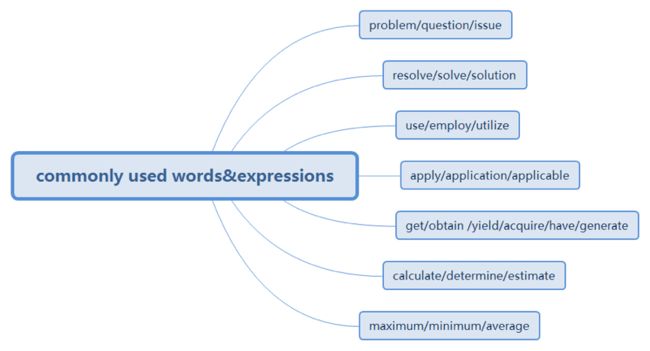
Commonly used words & expressions
Problem:The problem was dealt with by the provision of a novel CFA Bayer filter.(有一定难度、需要克服的)
Question: The question is how to design a proper CFR Bayer filter to reconstruct the color images.
Issue: The main point of the issue is whether the color images can be perfectly reconstructed with current available filters.
Resolve: The solar energy converter will surely help us resolver many industrial problems in the area lacking fuel.(问题有一定难度,解决问题是逐步的)
Solve: knowing certain values enables us to solve the problem.
Solution: the diagram will help in the solution of some of these problems.
Use: this instrument has been widely used in the satellite communication laboratory.
Employ: the 3D HDTV systems employ the parallax of human being’s eyes to display the depth information of the scenes.
Utilize: different types of electronic computers are utilized for various purpose in the modern society.
Apply: these principles are applied to the study of electromagnetic field attribution and propagation.
Applicable: the formula of kinesin energy is applicable to any object that is moving.
Application: the application of the new technology to printing is carried out in this factory.
Get:获得
Obtain: the optimized additive distortion is obtained by setting x = 2u + z. (更正式,目的性获得、推导时间)
Yield: an application of sockets’ theorem yields the Ampere’s law in the integration form.
Acquire: F could be acquired by replacing O by S in the equation. (经过一段时间、过程取得的结果)
Have:更注重于得到后,有条件达到相应的状态。
Generate:产生、得到。
Maximum: the PSNR reaches a maximum at R = 200 Mb/s.
The maximum value of this parameter is 30.
复数maxima,形容词maximal
Minimum: The minimum temperature is about 35 centigrade.
复数minima,形容词minimal
Average: note that all data are in average in Table 3.4
In most cases, this ratio averages less than 15 dB.
Expressions for the purpose of comparison(比较相同的或不同的)
As…as… : Line AB is 3 times as long as lineCD.
Less/more…than: sound travels less faster than light.
The… the… : the higher the resistance, the lower the conductivity.
Expressions for the purpose of contrast(显示不同点、显示明显的差别)
While/whereas
Some substances are soluble, while others are not.
On the one hand… on the other hand
In contrast to/with
Sentence patterns
*The theory is not applicable to …
(a)The new theory
The newly developed theory
The previous theory
The theory of
(b)does not apply to
is not applicable to
could not be applied to
is not valid for
is not true for
does not prove to be valid for
does not hold true for
(c)situations like those mentioned earlier
individuals whose characters differ from
circumstances totally different from
cases of …
*To deal with a problem in some aspect
(a)It is easy
It seems difficult
It is impossible
It does seem possible
(b)to present the problem
to review all aspects
to discuss the problem
to analyze all aspects
(c)in all its complexity
In all its immensity
In every detail
*for the purpose of… the studies are made to a certain extent.
(a)several experimental studies
Many comprehensive studies
No thorough investigations
No fundamental investigations
(b)are made
are now being carried out
were then performed
have been undertaken
have been attempted
have been initiated
Figures and tables
(1)use a capital F or T when it is associated with a number; otherwise, use lower cases.
e.g. seeFigure 1 an dTable 2.
(2)the abbreviations for Figure and Figures are Fig. and Figs. , avoid abbreviating the word Table.
e.g. see Fig2a and b. → see Figs.2a and 2b.
(3)be concise when introducing or making reference to a figure or table.
e.g. the snapshot depicted in Figure 3 shows a view of the architecture.
→ Figure 3 shows the architecture.
(4)where possible, use the active form rather than the passive.
Figure 2 shows the initial settings.
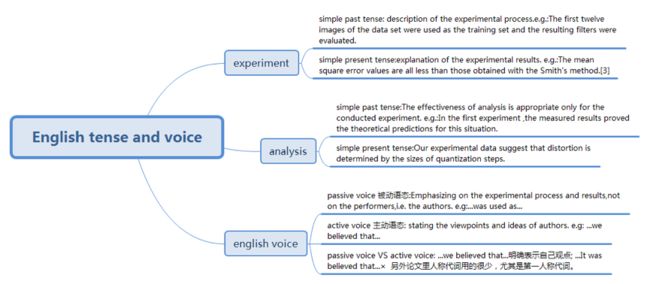
English tense & English voice
英文语态(主动、被动)科技论文,主要用主动语态
e.g.
*pressures and heating rates, normalized with respect to surface conditions, are shown in figures 2 and 3.
*Figures 2 and 3 show pressures and heating rates, normalized with respect to surface conditions.
Some details need to know
Don’t overstate/understate your results.
Overstatement mistake: When only actually shown for one case or small/limited cases.
e.g.
“it shows that x is prevalent in the application.”
“it shows that A is better than B.”
understatement mistake:轻描淡写
fail to consider broader implications of your work.
If your results are less significant, the reviewer and readers will be less interested in your paper.
Numbers: word vs digits
1.When you use numbers from one to ten within a text, write them as words rather than digits.
e.g. for this reason, three samples were measured. (3 samples ✘)
Two hundred samples were examined. (虽然不是1-9,但在句子开头,因此用单词,而非200)
2.Use digits not words when numbers are in association with percentages, abbreviations for measurements, tables and figures etc.(与测量单位、特殊词连写时用数字)
e.g. 20m, 9kg, 9.9%, Table2
In Table 1 and 2, 20 samples with… ✘
In Table 1 and 2, twenty samples with… (减少歧义,让读者易于理解
2,20
)
Between 4 and 12
5 out of 34
abbreviations and symbols (缩写和符号)
numbers before abbreviations and symbols must be digits.
e.g. the platform weighed 8kg and was 50cm wide.(8kgs ✘,测量单位无负数形式)
the image sequence lasted10min.(ten ✘)
测量单位、缩写都是小写,但字节bytes(e.g. KB, GB),温度temperature(C, F)除外。
The device is 65kg in weight.(65Kg ✘)
Three devices weighed 12kg, 14kg and 15kg.(12,14 and 15kg ✘)
From 12 to 50kg(12kg to 50kg✘)
A few kilograms (e.g. 3kg)…(a few kg ✘)
Singular or plural with numbers
1.whole numbers don’t require an-s to indicate the plural an d no preposition is used between the number and the noun.整数表示不加s,分数加s
e.g.
four thousands of experiments have been conducted so far. ✘)
four thousand experiments have been conducted so far.
One and half hours, three quarters of an hour, four fifths of a liter, nine tenths
2.for reasons of readability, make single digits plural using ‘s, however, for other numbers simply add an s.
e.g. the table contains only 0s and 1s. ✘
the table contains only 0’s and 1’s.一位数字时,数字复数加’s
1990s
a five megabytes memory… ✘
a five-megabyte memory…作为定语,不加复数,加连字符。
Main functional types of writing
Perspective/viewpoint
Defining concepts or objects
Presenting data in classification
Describing process in sequences
Presenting things in time order
Describing certain relationships
Exposing cause-effort connections
Making comparisons and contrasts
Defining concepts
Introduction: some specialized words andexpressions.
Readers may not understand their meanings, they have different meanings in different special subjects.
The author needs to supply the readers with his definition of these term, to make sure that he and his readers are talking and thinking about the same thing.
Definition structure: formal definition.
_____Is a form of/kind of/species of…_____ that/which____.
e.g.: Copper is a kind of substance which is easily shaped, and allows heat and electricity to pass through it.
Naming definition
____that/which____ is known/called/named… as____.
e.g.: The type of electricity that dischargers from a solid material after it has been rubbed with another material is known as static electricity.
Expandingthe definition
It is often necessary to expand the definition description of a concept by adding extra information.
e.g.: by using brackets or dashes.
Tungsten is a metal-used in filament in electric light bulbs-which retains hardness at red heat.
____.Therefore/Consequently/As a result, it is used in____.
e.g.:Aluminum is a metal which is light in weight.Consequently, it is used in the manufacture of aircraft.
Describing processes
introduction: process descriptions often appear in papers.
A process consists of stages moving forward in a logical step-by-step.
e.g.: A Flow Diagram of a partial process of previous information processing.
A process involves linear relationships in a sequence.
Sequencers make the process clear in a sequence.
e.g.: to begin with…next…then…after this…
beginning/first/firstly/to begin with/initially
middle steps/secondly/thirdly/next/then/subsequently/after this/before this/at the same time
end/lastly/finally
Top-to-down design
·Good organization is the key to good writing.
Starting with an outline and working out the details is the normal way of paper writing. It is always better to develop the body paragraphs form an outline instead of doing it directly from the roughly noted points.
Enhancing writing skills
Studying writing styles and effective communication.
Imitating the best native writers in your area: sample papers.
Establishing your own writing databases.
Common words and phrases, sentence patterns, ways of citing references.
Good writing takes times, taking times to enhance writing skills.
writing type: cause-effect relationship
introduction
Exposing cause and effect relation is at the heart of all scientific disciplines.
Cause are harder to identify, or are confused with effects, or researchers do not agree about the causes.
Causes always precede effects (linear relationship).
Expressions for cause-effect relationships
A simple way of showing causal relationship: because + clause (contains verb)
e.g.: The war started because the economic situation was desperate.
Or because of /on account of + phrase
e.g.: The war started because of the desperate economic situation.
Some common words/phrases clearly making the cause and effect relationships:
Verbs: cause/result in/result form
Adverbs: consequently/therefore/hence/thus
Conjunction: because/since/for/so/as
Phrases: be responsible for/be due to/as a result of
Examples of causal relationship descriptions:
*This could cause the downfall of the internet.
*A set of processes of threads is deadlocked since one process is waiting for another one to act.
*This is equivalent to a system setting and consequently saves your effort of setting it in the designer.
Emphasizing on the cause or the effect : be placed first
e.g.: A set of threads is deadlocked since one process is waiting for another one to act.
Different degree of certainty: we need to vary the degree of certainty
e.g.: Because the earth is round, the sun’s energy does not fall evenly over the earth.
Complete:
verbs: is/will/must
Adverbs: certainly/definitely/clearly/undoubtedly/actually
Partial:(strong→less strong)
Verbs: can/could/should/may/might
Adverbs: probably/likely/unlikely/presumably/possibly/perhaps
Impersonal:(i.e.no commitment of self)
It is said that…
X reports that…
There is evidence to suggest that…
Organizing texts: general-specific
A general statement(generalization), starts off a piece of writing/paragraph.
Generalizations introduce many points of details in one statement.
If you read the generalization, you would expect reader to it.
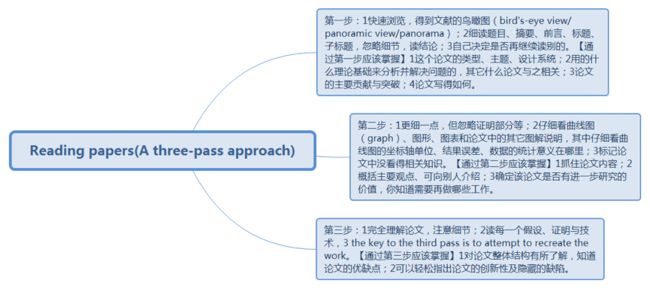
How to Read papers (a three-pass approach)
Presentation skill
To improve communication of key ideas in a presentation.
To provide guidelines for the design preparation and delivery of …
1.Define the desired topic
Specify the subject matter that will be the focus of the presentation. Based on the reason why you will.
2.Define the target audience
Determine type of audience, professionals or general public.
Determine extent of knowledge of your topic.
Estimate size of audience.
Predict audience trigger points.
3.Set presentation time limits.
Set time for presentation components, introduction/main body of presentation/extra presentation aids/questions.
·Predict the number of slides required.
10-15 slides for a 20 minute presentation.
25-30 slides for a 25 minute presentation.
40-45 slides for a 60 minute presentation.
·Basic format guidelines
Backgrounds: use no backgrounds if presentation is black& write.
Use dark backgrounds if presentation is in color.
·Font type and size
Select 2 or 3 fonts for presentation.
All important facts should be 24pt or larger.
Avoid italics.
·Headings format.
Use different color/font for headings.
Heading size is larger than text (e.g. 36pt)
·Content format
最多10-12行,最多3-5个标题,避免长句。
·Animation and video
Avoid complex animation effects.
Design animation to complement presentation.
Speed up or slow down presentation by video.
·Color
Use color to enhance communication of concepts in presentation.
Minimize color used for aesthetic purposes.
Use a maximum of 2-4 colors per slide.
Utilize same color arrangement for heading, subheadings and content.
Step1.
Select background, font type, font size, headings and content format.
Step2.
Develop rough skeleton of presentation including major heading and subheading.
Step3.
Add content to the presentation from information organized.
Step4.
Review presentation and add any missing parts.
Step5.
Add animation and video clips.
Step6.
Review the presentation using animation/video.
Step7.
Perform practice run of presentation and record time.
Step8.
Modify presentation to fit to time limits.
Step9.
Perform practice run in front of sample audience.
Step10.
Modify presentation based on suggestions.
·The dangers of practicing
Practicing too little:
usually presentation will exceed time limit.
Presenter may be forced to refer to notes.
Presenter will likely not be able to answer questions with confidence.
Practicing too much:
Presentation delivery is too mechanical.
Presenter is less spontaneous.
Usually presentation will proceed too quickly.
·Preparing yourself for your presentation
Step1.Print presentation slides(3 to 6slides per page)
Step2.make notes in the printout.
Step3.practice presentation(as discussed)
Step4. verigy that you have supporting material to confidently answer field questions.
·Setting ready for presentation
Step1.reserve presentation media in advance.
Step2.make certain abstract or notice of presentation has been sent with the proper information.
Step3.set up presentation media well before presentation.
·The moments before you present.
Step1.run presentation in your mind using the printed copy of slides with your notes.
Step2.clear your thoughts and retain a sense of calm.
Remember its normal to be nervous, learn to channel the nervous energy to drive you to deliver an outstanding presentation.
·Delivering your presentation
Introduction:
Introduce yourself and your topic clearly.
Clarity of speech:
Make certain that the entire audience can hear you.
Position in front of screen:
Make certain you are facing audience avoid covering the screen.
Monitoring your progress:
Use designated slides to monitor timing during delivery.
Sensing and adapting to audience:
Slowing or speeding presentation based on audience.
Acknowledgements:
Take time to sincerely thank contributors and audience.
Answering questions:
Maintain calm: take your time to think through answers, answer the question only, do not expand on answer unless very confident.
Face questions you can’t answer:
Remain confident and inform the audience that you can’t answer the question at this time, but you are willing to provide the answers later.
Finalizing presentation:
Thanking audience, take your time to thank the audience for participating.
Providing contact information:
Inform audience that they can contact you for further information.
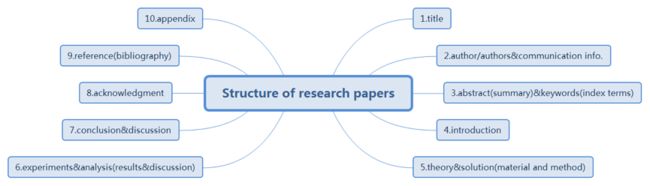
Structure of research papers
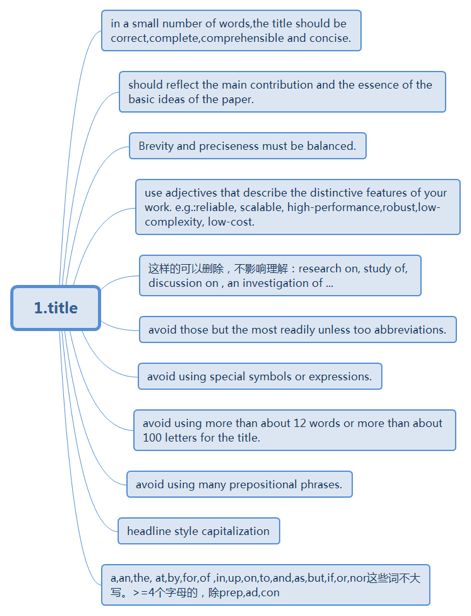
1.title
·capitalize the first and last words:
e.g. Procedure After All Questionnaires Are In
·capitalize both elements of a tow-element hyphenated compound word except the second element of a compound numeral:
e.g. EM-Imaging Systems for In-Class Flour Visualization
Evaluation of Twenty-one High-Resolution Graphics Work Stations
·in a hyphenated phrase of three or more words, the first element and other elements that are principal words are capitalized.
e.g. Design of a State-of-the ArtInterference Alleviation System for…
·if a normally lowercase short word is used parallel with a capitalized word of like significance, the short word should be capitalized:
e.g. Electromagnetic Radiation In and Around Airports
·capitalize the infinitive to (note that some authorities recommend lower case for the infinitive)
e.g. In-Loop Deblocking Filter To Improve Subjective Quality of Compressed Video.
In-Loop Deblocking Filter Improving Subjective Quality of Compressed Video.
·Normally lowercase abbreviations should always be left lowercase, particularly abbreviations for units of measure:
e.g. Toughness of 1-ft by 1.5-ftSpecimens
Toughness of 0.5-cm-Thick Specimens
Noise Exposure From 10:00p.m.to 6:00a.m.
But
Multiple Diffractions from the 0.3-Meter(因为不是缩写而是全写)Obstacle
·Headline style capitalization is used for proper nouns
·As a matter of preferred style, the following elements may be capitalized in headline style, applied, e.g. in NASA reports:
Table titles: e.g. Table 4. Test Results for HP-9420.
·Improving titles
Consider replacing or clarifying word with vague meaning such as method, system, facility, use or approach the following example illustrates this point:
·title: An Instrumentation System for Measuring Phase Fluctuation Coefficients
·revision: A Digital Vector Instrumentation System for Measuring Phase Fluctuation Coefficients
·Majority of titles: Noun phrases
A prepositional phrase can be changed to a modifier.
e.g. Analysis of Antenna Array of Waveguides Filled withHydrogen Using Differential Equation Representation
revision: Antenna Array Analysis of Hydrogen-Filled Waveguides Using Differential Equation Representation
·主标题+副标题,更有强调作用;动词→动名词,使意思更清晰。
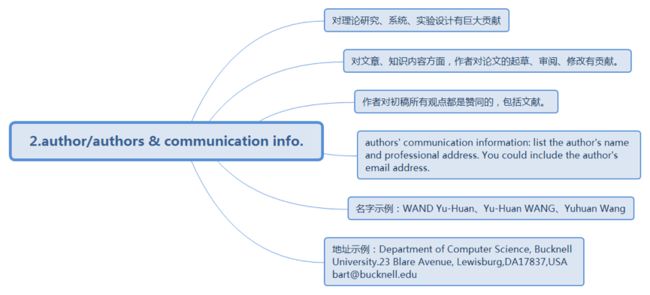
2.Author/Authors
3.abstract(summary)&keywords(index terms)
Requirement: the abstract should summarize the research paper by briefly conveying the essential information presented in the paper.
Content:
1.the kind of proof (theoretical, experimental, simulations, implementations, etc.) provided to show that the proposed solution is really better than the existing ones.
2.Each component is flexible and brief in length without a fixed order.
3.Avoid equations and math.
摘要时态的问题:
E.g. this paper presents a unique technique for…
Previous research has provided that…
And yet has not confirmed that…
This research investigated how…
We describe a new approach to test…
The experimental results indicate that…
We suggest that this technique could beapplied to …
4.introduction
description of the problem
A brief description of the problem the paper is addressing.
A clear statement why the problem is important (or interesting).
Forming the problem description or statement in a professional way.
Review of related research work
A survey, usually brief compared to the rest part of the paper, only addressing a narrow area of the field.
Describing clearly what has been done before for solving the addressed problem.
Naturally citing or incorporating the relevant reference material into the review.
Clarifying the remaining shortcomings
Stating the shortcomings remaining in the current solutions.
Indicating the troubles, the remaining shortcomings bring about for the solution to the addressed problem.
Outlining the proposed approach & solution.
A brief summary of the proposed method and solution to the addressed problem (and perhaps ever a general description of results).
Describing clearly what is new in your solution (identifying reported new knowledge, the novel aspects of the solution or contributions).
Identifying the significance of the results. (the improvements and impact they suggest).
Summarizing the organization of the paper.
Outline of the rest parts of the paper.
e.g. “the remainder of the paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we introduce…Section 3 describes… Finally, we describe future work in Section 5.” (Note that section is capitalized)
Vary your expression between “Section” being the subject of the sentence, as in “Section2 discusses…” and “In Section, we discuss…”
Things to avoid
1.Too many motivational materials. Three reasons are enough and they should be described very briefly.
2.Describing unnecessary details.
A detail is unnecessary, if its omission will not harm the reader’s ability to understand the important novel aspects of the result.
3.spelling errors. With the availability of spell checker, there is no reason to have spelling errors red-underlined in a manuscript.
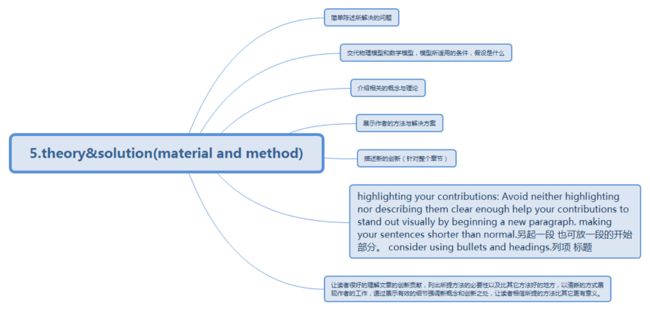
5.theory&solution (material and method)
Objective: describing contributions so that readers can understand them well.
Tips:
Advance previous work? Introduce new concepts?
“An article is finished not when there is nothing more to add, but when there is nothing more that can be taken away.”
A good paper usually addresses exactly one topic
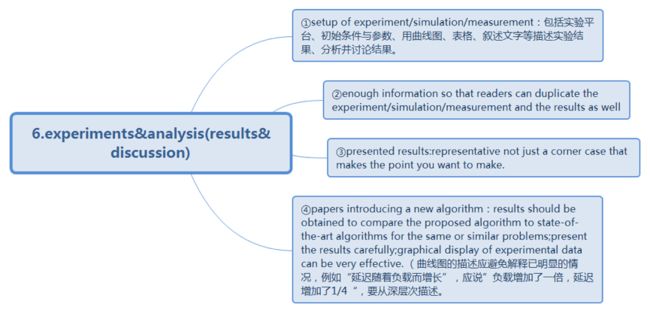
6.experiments &analysis (results & discussion)
Purpose: support your solution.
Presenting the experiment/simulation/measurement results in sufficient details to establish their validity to support the research contributions.
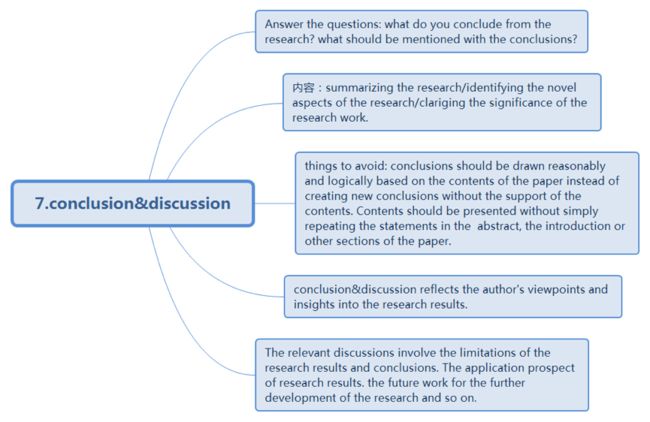
7.conclusion&discussion
Objective: presenting the conclusions drawn from the research and discussing on the relevant issues.
Sentence patterns – conclusion &discussion
The research demonstrates that…
(a)the research we have done
The investigation we have carried out
The study we have performed
(b)demonstrates
shows
indicates
suggests
reveals
confirms
(c)that…
an improved
performance of
an overall performance improvement of
an increase in
an enhancement in
a superior performance of… over…
This scheme has certain advantages over…
(a)this novel
Technique
The newly developed method
The proposed algorithm
The presented scheme
The procedure we followed
(b)has certain advantages over the existing techniques
has some advantages over the old method used for…?
has several advantages over the previous algorithm suggested by…?
has many advantages as compared with…?
is advantageous in some respects
outperforms the generic scheme provided by…
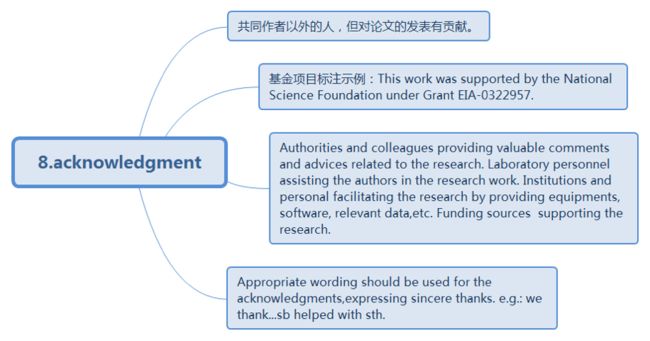
8.acknowledgment
Notes:
·Specifying as possible the contributions received from those your acknowledgments are addressed to.
·Avoiding the embarrassment of acknowledging someone who do not agree with the viewpoints made in the paper.
·Generally, reviewers, especially anonymous reviewers, don’t get acknowledged, unless they really provided an exceptional level of feedback or insight.
·Appropriate words should be used for the acknowledgments, expressing sincere thanks. Such as: We thank…sb. Helped with sth.
Sample:
This work was supported by the NationalScience and Engineering Research Council. The author acknowledges the assistance of Brian Jones and Eric Smith of British Columbia University in running some of the experiments and the help of Bill Tayler of the UIVA lab in providing the software of the compared Naxior scheme.
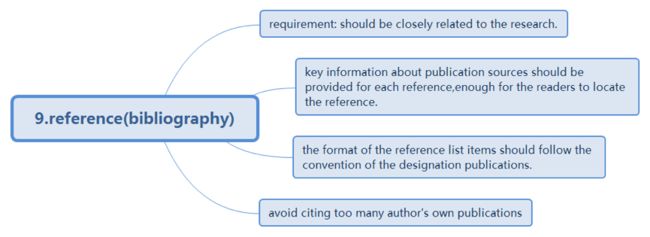
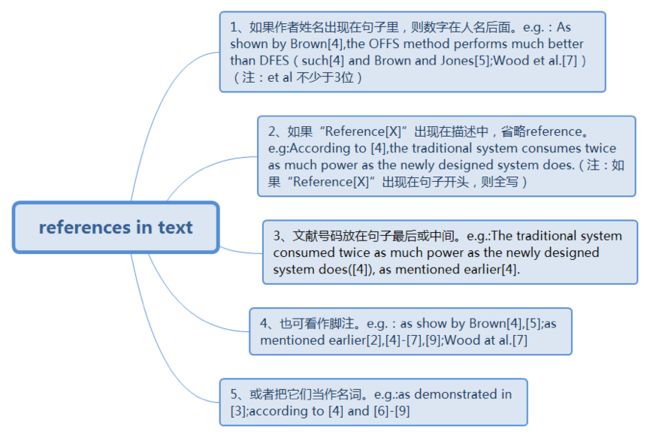
9.reference(bibliography)
·Notes:
·for a journal paper: author, title, journal name, volume, issue and page numbers, month year.
·conference: author, title, conference full name and location, conf. month. year, page numbers.
·book citations: author, book title, publisher, publication place and year, but no ISBN
·priority of reference selection: specific authors’ papers inmost recent, specific periodicals and proceedings.
It is now acceptable to include URLs to materials as references.
·Things to avoid
Avoid citing too many author’s own publications.
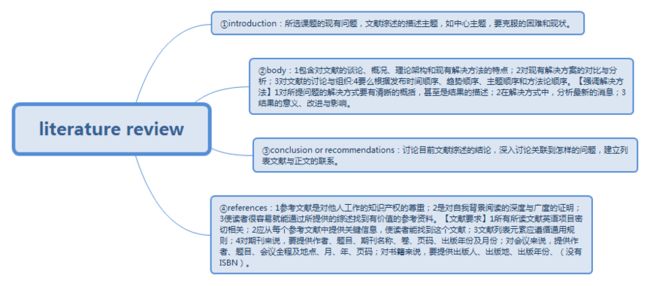
Literature review
usage:
*自成一体的,独立的;
*研究报告的基本引言;
*合同计划的要求部分;
*论文的一章节。
写作顺序分类:时间顺序、方法论顺序、按主题。