线程属性
初始化与销毁属性
int pthread_attr_init(pthread_attr_t *attr);
int pthread_attr_destroy(pthread_attr_t *attr);获取与设置分离属性
int pthread_attr_getdetachstate(const pthread_attr_t *attr, int *detachstate);
int pthread_attr_setdetachstate(pthread_attr_t *attr, int detachstate);
detachstate :
PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED
PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE获取与设置栈大小
int pthread_attr_setstacksize(pthread_attr_t *attr, size_t stacksize);
int pthread_attr_getstacksize(const pthread_attr_t *attr, size_t *stacksize);获取与设置栈溢出保护区大小
int pthread_attr_setguardsize(pthread_attr_t *attr, size_t guardsize);
int pthread_attr_getguardsize(const pthread_attr_t *attr, size_t *guardsize);获取与设置线程竞争范围
int pthread_attr_setscope(pthread_attr_t *attr, int scope);
int pthread_attr_getscope(const pthread_attr_t *attr, int *scope);
scope :
PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM
PTHREAD_SCOPE_PROCESS获取与设置调度策略
int pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(pthread_attr_t *attr, int policy);
int pthread_attr_getschedpolicy(const pthread_attr_t *attr, int *policy);
policy :
SCHED_FIFO : 如果线程优先级相同,按照先进先出的原则来调度
SCHED_RR : 如果线程优先级相同,按照抢占式的原则来调度
SCHED_OTHER : 其它情况
获取与设置继承的调度策略
int pthread_attr_setinheritsched(pthread_attr_t *attr, int inheritsched);
int pthread_attr_getinheritsched(const pthread_attr_t *attr, int *inheritsched);
inheritsched :
PTHREAD_INHERIT_SCHED
PTHREAD_EXPLICIT_SCHED获取与设置调度参数
int pthread_attr_setschedparam(pthread_attr_t *attr, const struct sched_param *param);
int pthread_attr_getschedparam(const pthread_attr_t *attr, struct sched_param *param);
struct sched_param {
int sched_priority; /* Scheduling priority 调度优先级*/
};获取与设置并发级别
int pthread_setconcurrency(int new_level);
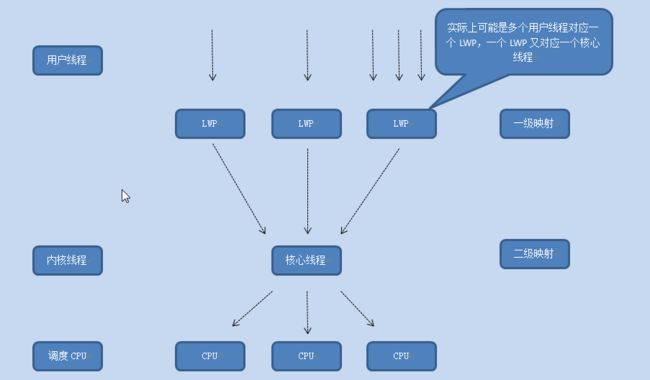
int pthread_getconcurrency(void); 仅在N:M线程模型中,设置并发级别,给内核一个提示;表示提供给定级别数量的核心线程来映射用户线程是高效的。
默认是0,表示内核按照自己合适的规则来映射
pthread_attr.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do \
{ \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while (0)
int main(void)
{
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
int state;
pthread_attr_getdetachstate(&attr, &state);
if(state == PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE)
printf("state : PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE\n");
else if(state == PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED)
printf("state : PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED");
size_t size;
pthread_attr_getstacksize(&attr, &size);
printf("stacksize : %lu\n",size);
size_t guardsize;
pthread_attr_getguardsize(&attr, &guardsize);
printf("guardsize : %lu\n",guardsize);
int scope;
pthread_attr_getscope(&attr, &scope);
if(scope == PTHREAD_SCOPE_PROCESS)
printf("scope : PTHREAD_SCOPE_PROCESS\n");
else if(scope == PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM);
printf("scope : PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM\n");
int policy;
pthread_attr_getschedpolicy(&attr, &policy);
if(policy == SCHED_FIFO)
printf("policy : SCHED_FIFO\n");
else if(policy == SCHED_RR)
printf("policy : SCHED_RR\n");
else if(policy == SCHED_OTHER)
printf("policy : SCHED_OTHER\n");
int inheritsched;
pthread_attr_getinheritsched(&attr, &inheritsched);
if(inheritsched == PTHREAD_EXPLICIT_SCHED)
printf("inheritsched : PTHREAD_EXPLICIT_SCHED\n");
else if(inheritsched == PTHREAD_INHERIT_SCHED)
printf("inheritsched : PTHREAD_INHERIT_SCHED\n");
struct sched_param param;
pthread_attr_getschedparam(&attr, ¶m);
printf("sched_param : %d\n",param.__sched_priority);
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
int level;
level = pthread_getconcurrency();
printf("level : %d\n", level);
return 0;
} 线程特定数据
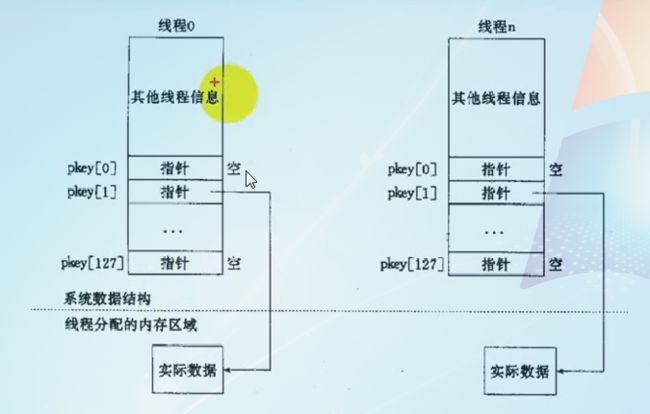
- 在单线程程序中,我们经常要用到“全局变量”以实现多个函数间共享数据
- 在多线程环境下,由于数据空间是共享的,因此全局变量也为所有线程共有。
- 但有时应用程序设计中有必要提供线程私有的全局变量,仅在某个线程中有效,但却可以跨多个函数访问
- POSIX线程库通过维护一定的数据结构来解决这个问题,这些数据称为(Thread-specific Data, 或TSD)
pthread_key_create
功能:
从TSD池中分配一项,将其值赋给key供以后访问使用(每个线程都有128个key)
原型:
int pthread_key_create(pthread_key_t *key, void (*destructor)(void*));
参数:
key : thread-specific data
destructor : 如果destructor不为空,在线程退出(pthread_exit())时将以key所关联的数据为参数调用destructor,以释放分配的缓冲区。
返回值:
成功 : 将创建的键值存放到key,返回0
失败 : 返回错误码pthread_key_delete
功能:
删除一个key
原型:
int pthread_key_delete(pthread_key_t key);
参数:
key : thread-specific data
返回值:
成功 : 将创建的键值存放到key,返回0
失败 : 返回错误码pthread_getspecific
功能:
获取线程特定数据
原型:
void *pthread_getspecific(pthread_key_t key);
参数:
key : thread-specific data
返回值:
成功 : 返回线程特定数据
失败 : NULLpthread_setspecific
功能:
获取线程特定数据
原型:
int pthread_setspecific(pthread_key_t key, const void *value);
参数:
key : thread-specific data
value : 要设置的线程特定数据
返回值:
成功 : 0
失败 : 错误码pthread_once
功能:
使用初值为PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT的once_control变量保证init_routine()函数在本进程执行序列中仅执行一次
原型:
int pthread_once(pthread_once_t *once_control, void (*init_routine)(void));
pthread_once_t once_control = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
参数:
once_control : 表示是否执行过
init_routine : 线程执行函数
返回值:
成功 : 0
失败 : 错误码pthread_key.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do \
{ \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while (0)
typedef struct tsd
{
pthread_t tid;
char *str;
}tsd_t;
pthread_key_t key_tsd;
pthread_once_t once_control = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
void destructor_toutime(void* value)
{
printf("destory ...\n");
free(value);
}
void init_routine(void)
{
pthread_key_create(&key_tsd, destructor_toutime);
printf("key init success\n");
}
void* thread_routine(void *arg)
{
//保证只有一个线程会去调用init_routine,具体哪一个是不确定的
pthread_once(&once_control,init_routine);
tsd_t *value = (tsd_t*)malloc(sizeof(tsd_t));
value->tid = pthread_self();
value->str = (char*)arg;
pthread_setspecific(key_tsd, value);
printf("%s setspecific %p\n", (char*)arg, value);
value = pthread_getspecific(key_tsd);
printf("%s id : %lu str : %s\n",(char*)arg, value->tid, value->str);
sleep(2);
value = pthread_getspecific(key_tsd);
printf("%s id : %lu str : %s\n",(char*)arg, value->tid, value->str);
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
//在主线程中创建key
// pthread_key_create(&key_tsd, destructor_toutime);
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_routine, "thread1");
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_routine, "thread2");
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_key_delete(key_tsd);
return 0;
}