- 1.OkHttp源码解析(一):OKHttp初阶
- 2 OkHttp源码解析(二):OkHttp连接的"前戏"——HTTP的那些事
- 3 OkHttp源码解析(三):OKHttp中阶之线程池和消息队列
- 4 OkHttp源码解析(四):OKHttp中阶之拦截器及调用链
- 5 OkHttp源码解析(五):OKHttp中阶之OKio简介
- 6 OkHttp源码解析(六):OKHttp中阶之缓存基础
- 7 OkHttp源码解析(七):OKHttp中阶之缓存机制
- 8 OkHttp源码解析(八):OKHttp中阶之连接与请求值前奏
- 9 OkHttp源码解析(九):OKHTTP连接中三个"核心"RealConnection、ConnectionPool、StreamAllocation
- 10 OkHttp源码解析(十) OKHTTP中连接与请求
- 11 OkHttp的感谢
本篇文章主要讲解OKHttp的interceptor调用链,大体内容分为
- 1.interceptor调用链的入口
- 2.interceptor接口和RealInterceptorChain类
- 3.Anddress类详解
- 4.Route类详解
- 5.RouteDatabase详解
- 6.RouteSelector详解
- 7.RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor类详解
- 8.BridgeInterceptor类详解
一、interceptor调用链的入口
那我们书接上文。上篇文章已经说明了OKHttp有两种调用方式,一种是阻塞的同步请求,一种是异步的非阻塞的请求。但是无论同步还是异步都会调用下RealCall的 getResponseWithInterceptorChain方法来完成请求,同时将返回数据或者状态通过Callback来完成。源代码如下:
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
//添加 在配置 OkHttpClient 时设置的 interceptors
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
//添加 负责失败重试以及重定向的 RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor;
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
//添加 负责把用户构造的请求转换为发送到服务器的请求、把服务器返回的 响应转换为用户友好的响应的 BridgeInterceptor;
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
//添加 负责读取缓存直接返回、更新缓存的 CacheInterceptor;
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
//添加 负责和服务器建立连接的 ConnectInterceptor;
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
//如果不是webSocket
if (!forWebSocket) {
//添加 OkHttpClient 时设置的 networkInterceptors;
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
//最后 添加 负责向服务器发送请求数据、从服务器读取响应数据的 CallServerInterceptor。
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(
interceptors, null, null, null, 0, originalRequest);
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
从上面可知,无论同步还是异步,他们的入口都是从RealCall的getResponseWithInterceptorChain进来的。
一、interceptor接口和RealInterceptorChain类
(一)、interceptor接口详解
Interceptor 负责拦截和分发
- 1.1 先来看看Intercepor本身文档的含义:观察,修改以及可能短路的请求输出和响应请求的回来。通常情况下拦截器用来添加,移除或者转换请求或者回应的头部信息
- 1.2 拦截器,就像水管一样,把一节一节的水管(拦截器)连起来,形成一个回路,实际上client到server也是如此,通过一个又一个的interceptor串起来,然后把数据发送到服务器,又能接受返回的数据,每一个拦截器(水管)都有自己的作用,分别处理不同东西,比如消毒,净化,去杂质,就像一层层过滤网一样。
/**
* Observes, modifies, and potentially short-circuits requests going out and the corresponding
* responses coming back in. Typically interceptors add, remove, or transform headers on the request
* or response.
*/
public interface Interceptor {
//负责拦截
Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException;
interface Chain {
Request request();
//负责分发、前行
Response proceed(Request request) throws IOException;
Connection connection();
}
}
- 2.1 Interceptor是一个接口,主要是对请求和相应的过滤处理,其中有一个抽象方法即Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException负责具体的过滤。
- 2.2 而在他的子类里面又调用了Chain,从而实现拦截器调用链(chain),所以真正实现拦截作用的是其内部接口Chain
Interceptor.Chain的实现类都是RealInterceptorChain,也就说说处理调用过程的实现是RealInterceptorChain。所以RealInterceptorChain持有一个List的Interceptor,通过对这个List的Interceptor进行迭代和递归推进。让我们看看源码实现。
/**
* A concrete interceptor chain that carries the entire interceptor chain: all application
* interceptors, the OkHttp core, all network interceptors, and finally the network caller.
*/
public final class RealInterceptorChain implements Interceptor.Chain {
private final List interceptors;
private final Request request;
// 下面属性会在执行各个拦截器的过程中一步一步赋值
private final StreamAllocation streamAllocation;//在RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor中new的
private final HttpCodec httpCodec; //在ConnectInterceptor中new的
private final RealConnection connection; //在ConnectInterceptor中new的
private final int index; //通过index + 1
private int calls; //通过call++
public RealInterceptorChain(List interceptors, StreamAllocation streamAllocation,
HttpCodec httpCodec, RealConnection connection, int index, Request request) {
this.interceptors = interceptors;
this.connection = connection;
this.streamAllocation = streamAllocation;
this.httpCodec = httpCodec;
this.index = index;
this.request = request;
}
@Override public Connection connection() {
return connection;
}
public StreamAllocation streamAllocation() {
return streamAllocation;
}
public HttpCodec httpStream() {
return httpCodec;
}
@Override public Request request() {
return request;
}
// 实现了父类proceed方法
@Override public Response proceed(Request request) throws IOException {
return proceed(request, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection);
}
//处理调用
public Response proceed(Request request, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, HttpCodec httpCodec,
RealConnection connection) throws IOException {
// 1、迭代拦截器集合
if (index >= interceptors.size()) throw new AssertionError();
//2、创建一次实例,call+1
calls++;
// If we already have a stream, confirm that the incoming request will use it.
if (this.httpCodec != null && !this.connection.supportsUrl(request.url())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("network interceptor " + interceptors.get(index - 1)
+ " must retain the same host and port");
}
// If we already have a stream, confirm that this is the only call to chain.proceed().
if (this.httpCodec != null && calls > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("network interceptor " + interceptors.get(index - 1)
+ " must call proceed() exactly once");
}
// Call the next interceptor in the chain.
// 3、创建一个RealInterceptorChain实例
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(
interceptors, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection, index + 1, request);
//4、取出下一个 interceptor
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
//5、执行intercept方法,拦截器又会调用proceed()方法
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
// Confirm that the next interceptor made its required call to chain.proceed().
if (httpCodec != null && index + 1 < interceptors.size() && next.calls != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("network interceptor " + interceptor
+ " must call proceed() exactly once");
}
// Confirm that the intercepted response isn't null.
if (response == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("interceptor " + interceptor + " returned null");
}
return response;
}
}
看到了上述源码,给大家分析一下就是:
- 第一步,先判断是否超过list的size,如果超过则遍历结束,如果没有超过则继续执行
- 第二步calls+1
- 第三步new了一个RealInterceptorChain,其中然后下标index+1
- 第四步 从list取出下一个interceptor对象
- 第五步 执行interceptor的intercept方法
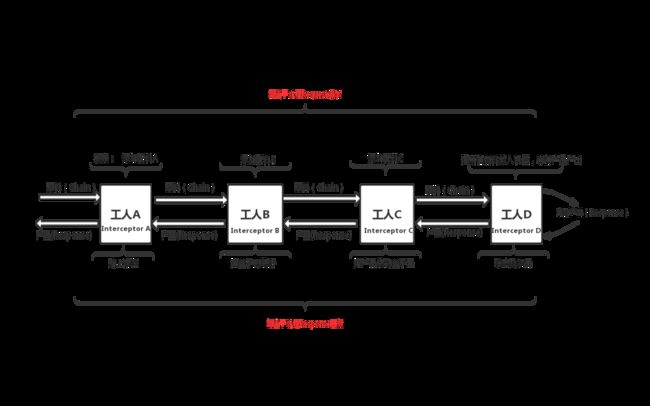
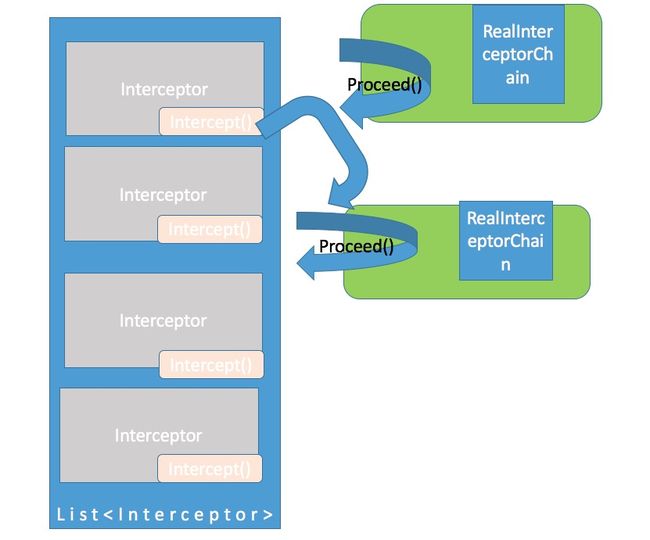
总结一下就是每一个RealInterceptorChain对应一个interceptor,然后每一个interceptor再产生下一个RealInterceptorChain,直到List迭代完成。所以上面基本上就是迭代+递归,找了一些图片有助于大家理解如下图
PS:
这里的拦截器有点像安卓里面的触控反馈的Interceptor。既一个网络请求,按一定的顺序,经由多个拦截器进行处理,该拦截器可以决定自己处理并且返回我的结果,也可以选择向下继续传递,让后面的拦截器处理返回它的结果。这个设计模式叫做责任链模式。
与Android中的触控反馈interceptor的设计略有不同的是,后者通过返回true 或者 false 来决定是否已经拦截。而OkHttp这里的拦截器通过函数调用的方式,讲参数传递给后面的拦截器的方式进行传递。这样做的好处是拦截器的逻辑比较灵活,可以在后面的拦截器处理完并返回结果后仍然执行自己的逻辑;缺点是逻辑没有前者清晰。
三、Address类详解
老规矩,先来看他的类注释
/**
* A specification for a connection to an origin server. For simple connections, this is the
* server's hostname and port. If an explicit proxy is requested (or {@linkplain Proxy#NO_PROXY no
* proxy} is explicitly requested), this also includes that proxy information. For secure
* connections the address also includes the SSL socket factory, hostname verifier, and certificate
* pinner.
*
* HTTP requests that share the same {@code Address} may also share the same {@link Connection}.
*/
翻译如下:与服务器连接的格式,对于简单的链接,这里是服务器的主机名和端口号。如果是通过代理(Proxy)的链接,则包含代理信息(Proxy)。如果是安全链接,则还包括SSL socket Factory、hostname验证器,证书等。
通过翻译大家可以理解为一个地址的包装类,封装了地址的所有可能,说白了address描述了建立连接的所有配置信息
再来看下它的字段构造函数
final HttpUrl url;
final Dns dns;
final SocketFactory socketFactory;
final Authenticator proxyAuthenticator;
final List protocols;
final List connectionSpecs;
final ProxySelector proxySelector;
final Proxy proxy;
final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory;
final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier;
final CertificatePinner certificatePinner;
public Address(String uriHost, int uriPort, Dns dns, SocketFactory socketFactory,
SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory, HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier,
CertificatePinner certificatePinner, Authenticator proxyAuthenticator, Proxy proxy,
List protocols, List connectionSpecs, ProxySelector proxySelector) {
this.url = new HttpUrl.Builder()
.scheme(sslSocketFactory != null ? "https" : "http")
.host(uriHost)
.port(uriPort)
.build();
if (dns == null) throw new NullPointerException("dns == null");
this.dns = dns;
if (socketFactory == null) throw new NullPointerException("socketFactory == null");
this.socketFactory = socketFactory;
if (proxyAuthenticator == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("proxyAuthenticator == null");
}
this.proxyAuthenticator = proxyAuthenticator;
if (protocols == null) throw new NullPointerException("protocols == null");
this.protocols = Util.immutableList(protocols);
if (connectionSpecs == null) throw new NullPointerException("connectionSpecs == null");
this.connectionSpecs = Util.immutableList(connectionSpecs);
if (proxySelector == null) throw new NullPointerException("proxySelector == null");
this.proxySelector = proxySelector;
this.proxy = proxy;
this.sslSocketFactory = sslSocketFactory;
this.hostnameVerifier = hostnameVerifier;
this.certificatePinner = certificatePinner;
}
果然和咱们想的一样,就是一个地址的包装类,包含了三种请求类型的封装1直连,2走代理,3ssl 。
这里先简单的说下Address的构造函数,咱们回想一下什么时候new的Address对象,记忆好的同学可能想起来了,在RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor类里面,我们曾经创建过StreamAllocation类,在构造这个StreamAllocation的对象的时候,需要传入一个Addres对象,而在RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor类中则是通过createAddress来创建的Address对象的
private Address createAddress(HttpUrl url) {
SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory = null;
HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier = null;
CertificatePinner certificatePinner = null;
if (url.isHttps()) {
sslSocketFactory = client.sslSocketFactory();
hostnameVerifier = client.hostnameVerifier();
certificatePinner = client.certificatePinner();
}
return new Address(url.host(), url.port(), client.dns(), client.socketFactory(),
sslSocketFactory, hostnameVerifier, certificatePinner, client.proxyAuthenticator(),
client.proxy(), client.protocols(), client.connectionSpecs(), client.proxySelector());
}
通过构createAddress方法,我们发现除了uriHost和uriPort外的所有构造函数的参数均来自OkHttpClient,而Address的url字段正式根据这两个字段构造的,由此可见,Address的url字段仅仅包含HTTP请求的url的schema+host+port三部分的信息,而不包含path和query等信息。
让我们再来看下它的一个重要方法equalsNonHost
boolean equalsNonHost(Address that) {
return this.dns.equals(that.dns)
&& this.proxyAuthenticator.equals(that.proxyAuthenticator)
&& this.protocols.equals(that.protocols)
&& this.connectionSpecs.equals(that.connectionSpecs)
&& this.proxySelector.equals(that.proxySelector)
&& equal(this.proxy, that.proxy)
&& equal(this.sslSocketFactory, that.sslSocketFactory)
&& equal(this.hostnameVerifier, that.hostnameVerifier)
&& equal(this.certificatePinner, that.certificatePinner)
&& this.url().port() == that.url().port();
}
用来返回两个Address是否是同一个地址,这个方法什么时候会被调用那,会在连接池复用的时候调用,因为只有两个Address相同才能说明这两个连接的配置信息是一直的,才能使用RealConnection的复用。看到方法内部大家发现,这个"相同"的要求还是很严格的,必须所有配置信息都一直才可以。
至此这个类基本已经讲解完毕,后续流程涉及到再提及。
四、Route
老规矩先看类的注释
/**
* The concrete route used by a connection to reach an abstract origin server. When creating a
* connection the client has many options:
*
*
* - HTTP proxy: a proxy server may be explicitly configured for the client.
* Otherwise the {@linkplain java.net.ProxySelector proxy selector} is used. It may return
* multiple proxies to attempt.
*
- IP address: whether connecting directly to an origin server or a proxy,
* opening a socket requires an IP address. The DNS server may return multiple IP addresses
* to attempt.
*
*
* Each route is a specific selection of these options.
*/
简单翻译下就是:
连接使用的路由到抽象服务器。创建连接时,客户端有很多选择
1、HTTP proxy(http代理):已经为客户端配置了一个专门的代理服务器,否则会通过net.ProxySelector proxy selector尝试多个代理
2、IP address(ip地址):无论是通过直连还是通过代理,DNS服务器可能会尝试多个ip地址。
每一个路由都是上述路由的一种格式
所以我的理解就是OkHttp3中抽象出来的Route是描述网络数据包传输的路径,最主要还是描述直接与其建立TCP连接的目标端点。
现在看下他的字段和构造函数
final Address address;
final Proxy proxy;
final InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress;
public Route(Address address, Proxy proxy, InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress) {
if (address == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("address == null");
}
if (proxy == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("proxy == null");
}
if (inetSocketAddress == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("inetSocketAddress == null");
}
this.address = address;
this.proxy = proxy;
this.inetSocketAddress = inetSocketAddress;
}
所以咱咱们知道Route通过代理服务器的信息proxy,及链接的目标地址Address来描述路由即Route,连接的目标地址inetSocketAddress根据代理类型的不同而有着不同的含义,这主要是通过不同代理协议的差异而造成的。对于无需代理的情况,连接的目标地址inetSocketAddress中包含HTTP服务器经过DNS域名解析的IP地址以及协议端口号;对于SOCKET代理其中包含HTTP服务器的域名及协议端口号;对于HTTP代理,其中则包含代理服务器经过域名解析的IP地址及端口号。
这里面说一个后面能用到的requiresTunnel()方法
/**
* Returns true if this route tunnels HTTPS through an HTTP proxy. See RFC 2817, Section 5.2.
*/
public boolean requiresTunnel() {
//是HTTP请求,但是还有SSL
return address.sslSocketFactory != null && proxy.type() == Proxy.Type.HTTP;
}
即对于设置了HTTP代理,且安全的连接(SSL)需要请求代理服务器,建立一个到目标HTTP服务器的隧道连接,客户端与HTTP代理建立TCP连接,以此请求HTTP代理服务器在客户端与HTTP服务器之间进行数据的盲目转发
即对于设置了HTTP代理,且安全的连接 (SSL) 需要请求代理服务器建立一个到目标HTTP服务器的隧道连接,客户端与HTTP代理建立TCP连接,以此请求HTTP代理服务在客户端与HTTP服务器之间进行数据的盲转发。
五、RouteDatabase
先来看看类注释
/**
* A blacklist of failed routes to avoid when creating a new connection to a target address. This is
* used so that OkHttp can learn from its mistakes: if there was a failure attempting to connect to
* a specific IP address or proxy server, that failure is remembered and alternate routes are
* preferred.
*/
简单翻译一下就是:
当在创建与目标地址的链接时,为了避免重复出现路由故障而创建的黑名单,如果尝试链接特定的IP或者代理服务器最后失败了,将记住这些故障。
这个类很简单, 大家看下
private final Set failedRoutes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
/** Records a failure connecting to {@code failedRoute}. */
public synchronized void failed(Route failedRoute) {
failedRoutes.add(failedRoute);
}
/** Records success connecting to {@code failedRoute}. */
public synchronized void connected(Route route) {
failedRoutes.remove(route);
}
/** Returns true if {@code route} has failed recently and should be avoided. */
public synchronized boolean shouldPostpone(Route route) {
return failedRoutes.contains(route);
}
看了代码,相信大家都知道了,这个类,内部维护了一个LinkHashSet().如果链接失败了,就放进去,如果成功就删除,还提供了一个判断是否包含路由的方法,用来判断该rount是否存在于LinkedHashSet()里面
六、RouteSelector
(1)先来看注释:
/**
* Selects routes to connect to an origin server. Each connection requires a choice of proxy server,
* IP address, and TLS mode. Connections may also be recycled.
*/
翻译一下就是:
这个类主要是选择连接到服务器的路由,每个连接应该是代理服务器/IP地址/TLS模式 三者中的一种。连接月可以被回收
所以可以把RouteSelector理解为路由选择器.
(2)那为什么需要RouteSelector那?
因为HTTP请求处理过程中所需的TCP连接建立过程,主要是找到一个Route,然后依据代理协议规则与特定目标建立TCP连接。对于无代理的情况,是与HTTP服务器建立TCP连接,对于SOCKS代理和http代理,是与代理服务器建立tcp连接,虽然都是与代理服务器建立tcp连接,但是SOCKS代理协议和http代理协议又有一定的区别。
而且借助于域名做负均衡已经是网络中非常常见的手法了,因而,常常会有域名对应不同IP地址的情况。同时相同系统也可以设置多个代理,这使Route的选择变得非常复杂。
在OKHTTP中,对Route连接有一定的错误处理机制。OKHTTP会逐个尝试找到Route建立TCP连接,直到找到可用的哪一个。这样对Route信息有良好的管理。OKHTTP中借助RouteSelector类管理所有路由信息,并帮助选择路由。
(3)看一下它的字段和构造函数
private final Address address;
private final RouteDatabase routeDatabase;
/* The most recently attempted route. */
private Proxy lastProxy;
private InetSocketAddress lastInetSocketAddress;
/* State for negotiating the next proxy to use. */
private List proxies = Collections.emptyList();
private int nextProxyIndex;
/* State for negotiating the next socket address to use. */
private List inetSocketAddresses = Collections.emptyList();
private int nextInetSocketAddressIndex;
/* State for negotiating failed routes */
private final List postponedRoutes = new ArrayList<>();
public RouteSelector(Address address, RouteDatabase routeDatabase) {
this.address = address;
this.routeDatabase = routeDatabase;
resetNextProxy(address.url(), address.proxy());
}
/** Prepares the proxy servers to try. */
private void resetNextProxy(HttpUrl url, Proxy proxy) {
if (proxy != null) {
//第一种方式
// If the user specifies a proxy, try that and only that.
proxies = Collections.singletonList(proxy);
} else {
//第二种方式
// Try each of the ProxySelector choices until one connection succeeds.
List proxiesOrNull = address.proxySelector().select(url.uri());
proxies = proxiesOrNull != null && !proxiesOrNull.isEmpty()
? Util.immutableList(proxiesOrNull)
: Util.immutableList(Proxy.NO_PROXY);
}
nextProxyIndex = 0;
}
RouteSelector这个类的字段和构造函数比较简单,但是在构造函数里面调用了resetNextProxy()方法
收集路由主要分为两个步骤:第一步收集所有的代理;第二步则是收集特定的代理服务器选择所有的连接目标的地址。
收集代理的过程正如上面的这段代码所示,有两种方式:
一是外部通过address传入代理,此时代理集合将包含这唯一的代理。address的代理最终来源于OkHttpClient,我们可以在构造OkHttpClient时设置代理,来指定该client执行的所有请求特定的代理。
二是,借助于ProxySelectory获得多个代理。ProxySelector最终也来源于OkHttpClient用户当然也可以对此进行配置。但通常情况下,使用系统默认收集的所有代理保存在列表proxies中
为OkHttpClient配置Proxy或ProxySelector的场景大概是,需要让连接使用代理,但不使用系统的代理配置情况。
PS:proxies是在这时候被初始化的。inetSocketAddresses也是在这里被初始化,并且添加的第一个元素
(4)hasNext()方法
/**
* Returns true if there's another route to attempt. Every address has at least one route.
*/
public boolean hasNext() {
return hasNextInetSocketAddress()
|| hasNextProxy()
|| hasNextPostponed();
}
/** Returns true if there's another proxy to try. */
//是否还有代理
private boolean hasNextProxy() {
return nextProxyIndex < proxies.size();
}
/** Returns true if there's another socket address to try. */
//是否还有socket地址
private boolean hasNextInetSocketAddress() {
return nextInetSocketAddressIndex < inetSocketAddresses.size();
}
/** Returns true if there is another postponed route to try. */
//是否还有延迟路由
private boolean hasNextPostponed() {
return !postponedRoutes.isEmpty();
}
hasNext()表明是否有可以使用的路由
里面做了三个判断,如果满足一条就可以表明有可以使用的路由 :1是否还有代理、2是否还有Socket、3是否还有延迟路由,如果三者都没有,则认为没有了。
(5)next()方法
下面介绍一下他的一个重要方法next()方法。
收集 一个特定代理服务器选择下的 连接目标地址 ,因代理类型的不同而不同,这里主要分3种情况:
- 1、对于没有配置代理的情况,会对HTTP服务器的域名进行DNS域名解析,并为每个解析到的IP地址创建 连接的目标地址
- 2、对于SOCKS代理,直接以HTTP的服务器的域名以及协议端口创建 连接目标地址
- 3、对于HTTP代理,则会对HTTP代理服务器的域名进行DNS域名解析,并为每个解析到的IP地址创建 连接的目标地址
这里其实就是OkHttp发生DNS域名解析的场所。对于使用代理的场景,没有对HTTP服务器的域名做DNS域名解析,也就意味着HTTP服务器的域名解析要由代理服务器完成。
代理服务器的收集是在创建RouteSelector完成的;而一个特定的代理服务器选择下,连接目标地址 收集则是在选择Route时根据需要完成的。
代码如下:
public Route next() throws IOException {
// Compute the next route to attempt.
if (!hasNextInetSocketAddress()) {
if (!hasNextProxy()) {
if (!hasNextPostponed()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return nextPostponed();
}
lastProxy = nextProxy();
}
lastInetSocketAddress = nextInetSocketAddress();
Route route = new Route(address, lastProxy, lastInetSocketAddress);
if (routeDatabase.shouldPostpone(route)) {
postponedRoutes.add(route);
// We will only recurse in order to skip previously failed routes. They will be tried last.
return next();
}
return route;
}
这个方法主要是通过收集路由来选择路由。里面分了三种情况
- 1、如果hasNextPostponed(),则return nextPostponed()。
- 2、如果hasNextProxy(),则通过nextProxy()获取上一个代理,并用他去构造一个route,如果在失败链接的数据库里面有这个route,则最后通过递归调用next(),否则返回route
- 3、如果hasNextInetSocketAddress(),则通过nextInetSocketAddress()获取上一个InetSocketAddress,并用他去构造一个route,如果在这个失败里面数据中有这个路由,然后继续通过递归调用next()方法,或者直接返回route。
那么首先我们来看下nextPostponed()这个方法
/** Returns the next postponed route to try. */
private Route nextPostponed() {
return postponedRoutes.remove(0);
}
postponedRoutes是一个list,里面存放的是之前失败链接的路由,目的是在前所有不符合的情况,把之前失败的路由再试一次。
再来看一下nextProxy()方法
/** Returns the next proxy to try. May be PROXY.NO_PROXY but never null. */
private Proxy nextProxy() throws IOException {
if (!hasNextProxy()) {
throw new SocketException("No route to " + address.url().host()
+ "; exhausted proxy configurations: " + proxies);
}
Proxy result = proxies.get(nextProxyIndex++);
resetNextInetSocketAddress(result);
return result;
}
这个就是从proxies里面去一个出来,proxies是在构造函数里面方法resetNextProxy()来赋值的。
咱们再来看下nextInetSocketAddress()方法
/** Returns the next socket address to try. */
private InetSocketAddress nextInetSocketAddress() throws IOException {
if (!hasNextInetSocketAddress()) {
throw new SocketException("No route to " + address.url().host()
+ "; exhausted inet socket addresses: " + inetSocketAddresses);
}
return inetSocketAddresses.get(nextInetSocketAddressIndex++);
}
这个就是从inetSocketAddresses里面取一个出来,proxies是在构造函数里面方法resetNextProxy()来赋值的。
(6)connectFailed()方法
通过维护失败的路由信息,以避免浪费时间去连接一切不可用的路由。RouteSelector借助于RouteDatabase维护失败的路由信息。
综上所述RouteSelector在OkHttp里面主要负责三件事,1收集路由信息,2选择路由,3维护失败路由。
七、 RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor 类详解
RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor 负责失败重连以及重定向
/**
* This interceptor recovers from failures and follows redirects as necessary. It may throw an
* {@link IOException} if the call was canceled.
*/
public final class RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor implements Interceptor {
/**
* How many redirects and auth challenges should we attempt? Chrome follows 21 redirects; Firefox,
* curl, and wget follow 20; Safari follows 16; and HTTP/1.0 recommends 5.
*/
//最大恢复追逐次数:
private static final int MAX_FOLLOW_UPS = 20;
public RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor(OkHttpClient client, boolean forWebSocket) {
this.client = client;
this.forWebSocket = forWebSocket;
}
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request request = chain.request();
// 三个参数分别对应:(1)全局的连接池,(2)连接线路Address, (3)堆栈对象
streamAllocation = new StreamAllocation(
client.connectionPool(), createAddress(request.url()), callStackTrace);
int followUpCount = 0;
Response priorResponse = null;
while (true) {
if (canceled) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new IOException("Canceled");
}
Response response = null;
boolean releaseConnection = true;
try {
// 执行下一个拦截器,即BridgeInterceptor
// 这里有个很重的信息,即会将初始化好的连接对象传递给下一个拦截器,也是贯穿整个请求的连击对象,上面我们说过,在拦截器执行过程中,RealInterceptorChain的几个属性字段会一步一步赋值
response = ((RealInterceptorChain) chain).proceed(request, streamAllocation, null, null);
releaseConnection = false;
} catch (RouteException e) {
// The attempt to connect via a route failed. The request will not have been sent.
// 如果有异常,判断是否要恢复
if (!recover(e.getLastConnectException(), false, request)) {
throw e.getLastConnectException();
}
releaseConnection = false;
continue;
} catch (IOException e) {
// An attempt to communicate with a server failed. The request may have been sent.
boolean requestSendStarted = !(e instanceof ConnectionShutdownException);
if (!recover(e, requestSendStarted, request)) throw e;
releaseConnection = false;
continue;
} finally {
// We're throwing an unchecked exception. Release any resources.
if (releaseConnection) {
streamAllocation.streamFailed(null);
streamAllocation.release();
}
}
// Attach the prior response if it exists. Such responses never have a body.
if (priorResponse != null) {
response = response.newBuilder()
.priorResponse(priorResponse.newBuilder()
.body(null)
.build())
.build();
}
// 检查是否符合要求
Request followUp = followUpRequest(response);
if (followUp == null) {
if (!forWebSocket) {
streamAllocation.release();
}
// 返回结果
return response;
}
//不符合,关闭响应流
closeQuietly(response.body());
// 是否超过最大限制
if (++followUpCount > MAX_FOLLOW_UPS) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new ProtocolException("Too many follow-up requests: " + followUpCount);
}
if (followUp.body() instanceof UnrepeatableRequestBody) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new HttpRetryException("Cannot retry streamed HTTP body", response.code());
}
// 是否有相同的连接
if (!sameConnection(response, followUp.url())) {
streamAllocation.release();
streamAllocation = new StreamAllocation(
client.connectionPool(), createAddress(followUp.url()), callStackTrace);
} else if (streamAllocation.codec() != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Closing the body of " + response
+ " didn't close its backing stream. Bad interceptor?");
}
request = followUp;
priorResponse = response;
}
}
我们知道每个拦截器都实现了接口interceptor,interceptor.intercept()方法就是子类用来处理自己的业务逻辑,所以我们仅仅需要分析这个方法即可。看源码我们得出了如下流程
1 根据url创建一个Address对象,初始化一个Socket连接对象,基于Okio
private Address createAddress(HttpUrl url) {
SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory = null;
HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier = null;
CertificatePinner certificatePinner = null;
if (url.isHttps()) {
sslSocketFactory = client.sslSocketFactory();
hostnameVerifier = client.hostnameVerifier();
certificatePinner = client.certificatePinner();
}
return new Address(url.host(), url.port(), client.dns(), client.socketFactory(),
sslSocketFactory, hostnameVerifier, certificatePinner, client.proxyAuthenticator(),
client.proxy(), client.protocols(), client.connectionSpecs(), client.proxySelector());
}
2 用前面创建的address作为参数去实例化StreamAllocation
PS:此处还没有真正的去建立连接,只是初始化一个连接对象
3 开启一个while(true)循环
4 如果取消,释放资源并抛出异常,结束流程
5 执行下一个拦截器,一般是BridgeInterceptor
6 如果发生异常,走到catch里面,判断是否继续请求,不继续请求则退出
7 如果priorResponse不为空,则说明前面已经获取到了响应,这里会结合当前获取的Response和先前的Response
8 调用followUpRequest查看响应是否需要重定向,如果不需要重定向则返回当前请求
9 重定向次数+1,同时判断是否达到最大限制数量。是:退出
10 检查是否有相同的链接,是:释放,重建创建
11 重新设置request,并把当前的Response保存到priorResponse,继续while循环
我们来看下重定向的判断followUpRequest
/**
* Figures out the HTTP request to make in response to receiving {@code userResponse}. This will
* either add authentication headers, follow redirects or handle a client request timeout. If a
* follow-up is either unnecessary or not applicable, this returns null.
*/
private Request followUpRequest(Response userResponse) throws IOException {
if (userResponse == null) throw new IllegalStateException();
Connection connection = streamAllocation.connection();
Route route = connection != null
? connection.route()
: null;
int responseCode = userResponse.code();
final String method = userResponse.request().method();
switch (responseCode) {
case HTTP_PROXY_AUTH:
Proxy selectedProxy = route != null
? route.proxy()
: client.proxy();
if (selectedProxy.type() != Proxy.Type.HTTP) {
throw new ProtocolException("Received HTTP_PROXY_AUTH (407) code while not using proxy");
}
return client.proxyAuthenticator().authenticate(route, userResponse);
case HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED:
return client.authenticator().authenticate(route, userResponse);
case HTTP_PERM_REDIRECT:
case HTTP_TEMP_REDIRECT:
// "If the 307 or 308 status code is received in response to a request other than GET
// or HEAD, the user agent MUST NOT automatically redirect the request"
if (!method.equals("GET") && !method.equals("HEAD")) {
return null;
}
// fall-through
case HTTP_MULT_CHOICE:
case HTTP_MOVED_PERM:
case HTTP_MOVED_TEMP:
case HTTP_SEE_OTHER:
// Does the client allow redirects?
if (!client.followRedirects()) return null;
String location = userResponse.header("Location");
if (location == null) return null;
HttpUrl url = userResponse.request().url().resolve(location);
// Don't follow redirects to unsupported protocols.
if (url == null) return null;
// If configured, don't follow redirects between SSL and non-SSL.
boolean sameScheme = url.scheme().equals(userResponse.request().url().scheme());
if (!sameScheme && !client.followSslRedirects()) return null;
// Most redirects don't include a request body.
Request.Builder requestBuilder = userResponse.request().newBuilder();
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(method)) {
final boolean maintainBody = HttpMethod.redirectsWithBody(method);
if (HttpMethod.redirectsToGet(method)) {
requestBuilder.method("GET", null);
} else {
RequestBody requestBody = maintainBody ? userResponse.request().body() : null;
requestBuilder.method(method, requestBody);
}
if (!maintainBody) {
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Transfer-Encoding");
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Length");
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Type");
}
}
// When redirecting across hosts, drop all authentication headers. This
// is potentially annoying to the application layer since they have no
// way to retain them.
if (!sameConnection(userResponse, url)) {
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Authorization");
}
return requestBuilder.url(url).build();
case HTTP_CLIENT_TIMEOUT:
// 408's are rare in practice, but some servers like HAProxy use this response code. The
// spec says that we may repeat the request without modifications. Modern browsers also
// repeat the request (even non-idempotent ones.)
if (userResponse.request().body() instanceof UnrepeatableRequestBody) {
return null;
}
return userResponse.request();
default:
return null;
}
}
这里主要是根据响应码(code)和响应头(header),查看是否需要重定向,并重新设置请求,当然,如果是正常响应则直接返回Response停止循环
/**
* Report and attempt to recover from a failure to communicate with a server. Returns true if
* {@code e} is recoverable, or false if the failure is permanent. Requests with a body can only
* be recovered if the body is buffered or if the failure occurred before the request has been
* sent.
*/
private boolean recover(IOException e, boolean requestSendStarted, Request userRequest) {
streamAllocation.streamFailed(e);
// 1. 应用层配置不在连接,默认为true
// The application layer has forbidden retries.
if (!client.retryOnConnectionFailure()) return false;
// 2. 请求Request出错不能继续使用
// We can't send the request body again.
if (requestSendStarted && userRequest.body() instanceof UnrepeatableRequestBody) return false;
// 是否可以恢复的
// This exception is fatal.
if (!isRecoverable(e, requestSendStarted)) return false;
// 4. 没用更多线路可供选择
// No more routes to attempt.
if (!streamAllocation.hasMoreRoutes()) return false;
// For failure recovery, use the same route selector with a new connection.
return true;
}
private boolean isRecoverable(IOException e, boolean requestSendStarted) {
// If there was a protocol problem, don't recover.
if (e instanceof ProtocolException) {
return false;
}
// If there was an interruption don't recover, but if there was a timeout connecting to a route
// we should try the next route (if there is one).
if (e instanceof InterruptedIOException) {
return e instanceof SocketTimeoutException && !requestSendStarted;
}
// Look for known client-side or negotiation errors that are unlikely to be fixed by trying
// again with a different route.
if (e instanceof SSLHandshakeException) {
// If the problem was a CertificateException from the X509TrustManager,
// do not retry.
if (e.getCause() instanceof CertificateException) {
return false;
}
}
if (e instanceof SSLPeerUnverifiedException) {
// e.g. a certificate pinning error.
return false;
}
// An example of one we might want to retry with a different route is a problem connecting to a
// proxy and would manifest as a standard IOException. Unless it is one we know we should not
// retry, we return true and try a new route.
return true;
}
看上面代码可以这样理解:判断是否可以恢复如果下面几种条件符合,则返回true,代表可以恢复,如果返回false,代表不可恢复。
- 应用层配置不在连接(默认为true),则不可恢复
- 请求Request是不可重复使用的Request,则不可恢复
- 根据Exception的类型判断是否可以恢复的 (isRecoverable()方法)
3.1、如果是协议错误(ProtocolException)则不可恢复
3.2、如果是中断异常(InterruptedIOException)则不可恢复
3.3、如果是SSL握手错误(SSLHandshakeException && CertificateException)则不可恢复
3.4、certificate pinning错误(SSLPeerUnverifiedException)则不可恢复 - 没用更多线路可供选择 则不可恢复
如果上述条件都不满足,则这个request可以恢复
综上所述:
一个循环来不停的获取response。每循环一次都会获取下一个request,如果没有,则返回response,退出循环。而获取下一个request的逻辑,是根据上一个response返回的状态码,分别作处理。
四 BridgeInterceptor 类详解
BridgeInterceptor :负责对Request和Response报文进行加工,具体如下:
- 1、请求从应用层数据类型类型转化为网络调用层的数据类型。
- 2、将网络层返回的数据类型 转化为 应用层数据类型。
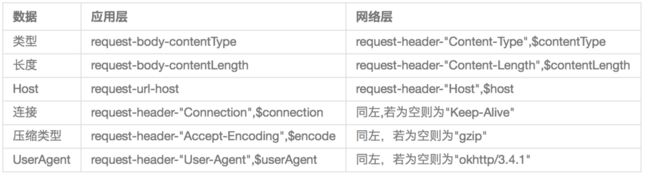
- 3、补充:Keep-Alive 连接:
区别如下图:
看下源码:
@Override
// 主要方法,其他略
// 此拦截器较为简单,其中有两点比较重要,1、cookie的处理 2Gzip
public Response intercept(Interceptor.Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request userRequest = chain.request();
Request.Builder requestBuilder = userRequest.newBuilder();
RequestBody body = userRequest.body();
if (body != null) {
MediaType contentType = body.contentType();
if (contentType != null) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Type", contentType.toString());
}
long contentLength = body.contentLength();
if (contentLength != -1) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Length", Long.toString(contentLength));
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Transfer-Encoding");
} else {
requestBuilder.header("Transfer-Encoding", "chunked");
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Length");
}
}
if (userRequest.header("Host") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Host", hostHeader(userRequest.url(), false));
}
if (userRequest.header("Connection") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Connection", "Keep-Alive");
}
// If we add an "Accept-Encoding: gzip" header field we're responsible for also decompressing
// the transfer stream.
boolean transparentGzip = false;
if (userRequest.header("Accept-Encoding") == null && userRequest.header("Range") == null) {
transparentGzip = true;
requestBuilder.header("Accept-Encoding", "gzip");
}
// 所以返回的cookies不能为空,否则这里会报空指针
List cookies = cookieJar.loadForRequest(userRequest.url());
if (!cookies.isEmpty()) {
// 创建Okhpptclitent时候配置的cookieJar,
requestBuilder.header("Cookie", cookieHeader(cookies));
}
if (userRequest.header("User-Agent") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("User-Agent", Version.userAgent());
}
// 以上为请求前的头处理
Response networkResponse = chain.proceed(requestBuilder.build());
// 以下是请求完成,拿到返回后的头处理
// 响应header, 如果没有自定义配置cookie不会解析
HttpHeaders.receiveHeaders(cookieJar, userRequest.url(), networkResponse.headers());
Response.Builder responseBuilder = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.request(userRequest);
// 前面解析完header后,判断服务器是否支持gzip压缩格式,如果支持将交给Okio处理
if (transparentGzip
&& "gzip".equalsIgnoreCase(networkResponse.header("Content-Encoding"))
&& HttpHeaders.hasBody(networkResponse)) {
GzipSource responseBody = new GzipSource(networkResponse.body().source());
Headers strippedHeaders = networkResponse.headers().newBuilder()
.removeAll("Content-Encoding")
.removeAll("Content-Length")
.build();
responseBuilder.headers(strippedHeaders);
// 处理完成后,重新生成一个response
responseBuilder.body(new RealResponseBody(strippedHeaders, Okio.buffer(responseBody)));
}
return responseBuilder.build();
}
读了源码发现这个interceptor比较简单,可以分为发送请求和响应两个阶段来看:
1.在发送阶段BridgeInterceptor补全了一些header包括Content-Type、Content-Length、Transfer-Encoding、Host、Connection、Accept-Encoding、User-Agent。
2.如果需要gzip压缩则进行gzip压缩
3.加载Cookie
4.随后创建新的request并交付给后续的interceptor来处理,以获取响应。
5.首先保存Cookie
6.如果服务器返回的响应content是以gzip压缩过的,则会先进行解压缩,移除响应中的header Content-Encoding和Content-Length,构造新的响应返回。
7 否则直接返回response
其中* CookieJar来自 OkHttpClient*,他是OKHttp的Cookie管理类,负责Cookie的存取。
public interface CookieJar {
/** A cookie jar that never accepts any cookies. */
CookieJar NO_COOKIES = new CookieJar() {
@Override public void saveFromResponse(HttpUrl url, List cookies) {
}
@Override public List loadForRequest(HttpUrl url) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
};
/**
* Saves {@code cookies} from an HTTP response to this store according to this jar's policy.
*
* Note that this method may be called a second time for a single HTTP response if the response
* includes a trailer. For this obscure HTTP feature, {@code cookies} contains only the trailer's
* cookies.
*/
void saveFromResponse(HttpUrl url, List cookies);
/**
* Load cookies from the jar for an HTTP request to {@code url}. This method returns a possibly
* empty list of cookies for the network request.
*
* Simple implementations will return the accepted cookies that have not yet expired and that
* {@linkplain Cookie#matches match} {@code url}.
*/
List loadForRequest(HttpUrl url);
}
由于OKHttpClient默认的构造过程可以看到,OKHttp默认是没有提供Cookie管理功能的,所以如果想增加Cookie管理需要重写里面的方法,PS:如果重写CookieJar()需要注意loadForRequest()方法的返回值不能为null
public static void receiveHeaders(CookieJar cookieJar, HttpUrl url, Headers headers) {
// 没有配置,不解析
if (cookieJar == CookieJar.NO_COOKIES) return;
// 此处遍历,解析Set-Cookie的值,比如max-age
List cookies = Cookie.parseAll(url, headers);
if (cookies.isEmpty()) return;
// 然后保存,即自定义
cookieJar.saveFromResponse(url, cookies);
}