SpringBoot2.x—SpringCache(1)集成
SpringBoot2.x—SpringCache(2)使用
SpringBoot2.x—SpringCache(3) CacheManager源码
SpringBoot2.x—SpringCache(4)集成SpringCache保证Redis的数据一致性
SpringBoot2.x—SpringCache(5)使用多级缓存
SpringBoot2.x—SpringCache(6)缓存注意事项
SpringCache如何保证数据一致性的呢?
@Cacheable一般用于优化方法,而@CachePut一般用于填充缓存。
@CachePut一般用于更新/插入方法。理论上是在此处实现数据库与缓存的一致性。
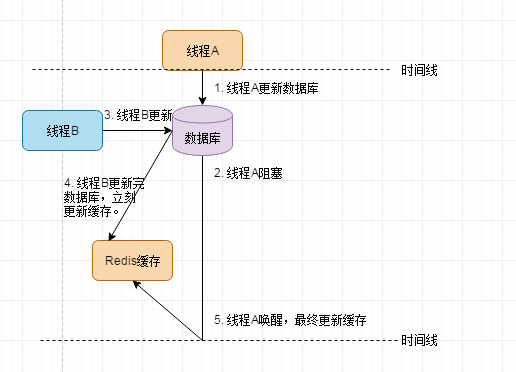
翻看源码:实际上SpringCache采用的是先更新数据库,再更新缓存的策略。这会导致:
线程A先更新DB,准备更新Redis时,被阻塞。线程B更新DB,并更新Redis后,线程A拿着旧值填充Redis,造成Redis与DB数据不一致。
//源码:org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheAspectSupport#execute(org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheOperationInvoker, java.lang.reflect.Method, org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheAspectSupport.CacheOperationContexts)
// 将@CachePut和@Cacheable miss的值保存到缓存中。
for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) {
cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue);
}
//会执行Cache的put操作,将数据放入到缓存中。
public void apply(@Nullable Object result) {
if (this.context.canPutToCache(result)) {
for (Cache cache : this.context.getCaches()) {
doPut(cache, this.key, result);
}
}
}
//doPut操作最终会自执行org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCache#put方法,若是缓存中已经存在记录,
//会将该记录更新。
@Override
public void put(Object key, @Nullable Object value) {
Object cacheValue = preProcessCacheValue(value);
if (!isAllowNullValues() && cacheValue == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"Cache '%s' does not allow 'null' values. Avoid storing null via '@Cacheable(unless=\"#result == null\")' or configure RedisCache to allow 'null' via RedisCacheConfiguration.",
name));
}
cacheWriter.put(name, createAndConvertCacheKey(key), serializeCacheValue(cacheValue), cacheConfig.getTtl());
}
选择什么策略去保证数据一致性问题呢?
分布式之数据库和缓存双写一致性方案解析
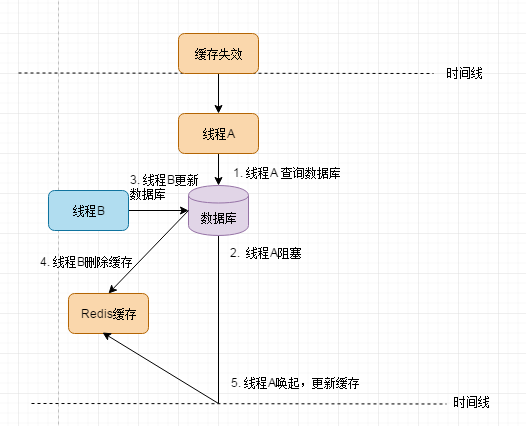
采用的是先更新数据库,在删除缓存的策略。一般情况下因为DB写操作比读操作耗时。即更新操作(2)一般会在查询操作(3)之后。
遇到上述问题,我们可以在开启一个定时线程,1s(根据业务方法执行时间来大概推算)后再次删除Redis的缓存。
如何对源码二次开发
SpringCache中,Cache对象是真正的对缓存进行增改删除的对象,所以我们的目的就是装饰RedisCache对象。
Cache对象是由CacheManager对象生产的。Spring使用模板方法模式实现CacheMananger接口,留给我们可扩展的方法大概是:
- 项目启动时,读取Cache的配置,创建Cache对象;
- 查询Cache得不到时,根据默认配置创建Cache对象;
- 装饰Cache对象;
咋一看3中可以满足我们的需求,但是源码中已经使用事务装饰了Cache对象。我们不能再次重写该方法。
只能在生成Cache时去装饰。无论是项目启动时还是查询Cache得不到,都需要调用RedisCache#createRedisCache去生成Cache对象,于是我们可以去重写该方法,装饰Cache对象。
public class LocalRedisCacheManager extends RedisCacheManager {
public LocalRedisCacheManager(RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter, RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration, Map initialCacheConfigurations) {
super(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration, initialCacheConfigurations);
}
//子类重写该方法,装饰生成的Cache对象。
@Override
protected RedisCache createRedisCache(String name, RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig) {
return new LocalRedisCache(super.createRedisCache(name, cacheConfig));
}
}
@Slf4j
public class LocalRedisCache extends RedisCache {
private RedisCache cache;
private RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter;
private String name;
/**
* 调用父类的方法
*
* @param cache
*/
public LocalRedisCache(RedisCache cache) {
super(cache.getName(), cache.getNativeCache(), cache.getCacheConfiguration());
this.cache = cache;
this.cacheWriter = cache.getNativeCache();
this.name = cache.getName();
}
@Override
public void put(Object key, Object value) {
//插入之前,若是缓存中已经存在值
byte[] oldValue = cacheWriter.get(name, createAndConvertCacheKey(key));
//先更新数据库,其次删除缓存
if (oldValue != null) {
log.warn("该数据存在,推测为@CachePut操作。进行移除缓存,确保缓存一致性!");
cache.evict(key);
//可以增加线程,实现延迟双删
return;
}
log.warn("数据不存在,填入缓存");
//若不存在,则插入缓存
cache.put(key, value);
}
private byte[] createAndConvertCacheKey(Object key) {
return serializeCacheKey(createCacheKey(key));
}
}
//配置文件
RedisCacheWriter redisCacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.lockingRedisCacheWriter(connectionFactory);
LocalRedisCacheManager localRedisCache = new LocalRedisCacheManager(redisCacheWriter,
customProtoStuffRedisCacheConfiguration(Duration.ofSeconds(6000)),
cacheConfigurations);