app架构之应用层架构
期望
view和model是可以复用的,业务逻辑是可以测试的。模块的代码应该职责清晰便于后期维护和扩展。
应用层架构定义
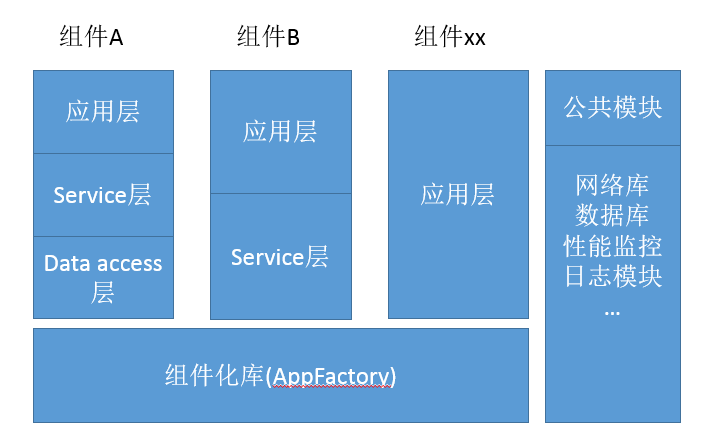
一个颇具规模的app必然会涉及到组件化、分层设计、公共模块等等。如下图:
组件化方案: 目前采用工APFFactory库,通过trrgierEvent事件通知、goPage页面跳转、dataProvider数据获取进行组件间的交互、数据共享。
公共模块: 数据库 采用FMDB,网络库采用restDao,流量监控等
三层划分: 应用层,service层,data access层
- 应用层:也就是我们常常用到的UIViewController,负责数据的展示,用户交互的处理,数据的采集等等
- service层:位于应用层的下面,为应用层提供公共的服务接口,对应用层来说就像是一个server,一般来说会包含业务数据的处理,网络接口的调用
- data access层:负责处理我们app的基础数据,提供数据库交互所需的api
下面讨论的主要是针对应用层
MVC模式
- M:即Model,不仅仅只是数据模型也可能是一个Model层也是数据层。Model它负责对数据的存取操作,例如对数据库的读写,网络的数据的请求等
- V:是显示数据(model)并且将用户指令(events)传送到C
- C:负责View的创建和展示以及业务逻辑
优点
- V与M相互隔离,复用性高
- 针对简单的界面功能,架构清晰,代码量少
缺点
- Controller随着业务的演进很容易臃肿,难以维护和扩展
- 没有区分业务逻辑和业务展示,很难去做单元测试
推荐架构
MVVM/MVCVM模式
- V:UI布局和数据显示
- C: 胶水层代码,做UI和VM的数据绑定和协调工作
- VM:承担业务逻辑工作
- M: 即Model,不仅仅只是数据模型也可能是一个Model层也是数据层。Model它负责对数据的存取操作,例如对数据库的读写,网络的数据的请求等
优点
- 针对MVC,将展示和业务逻辑分离
- 业务逻辑放在VM层,VM层可测试
代码例子
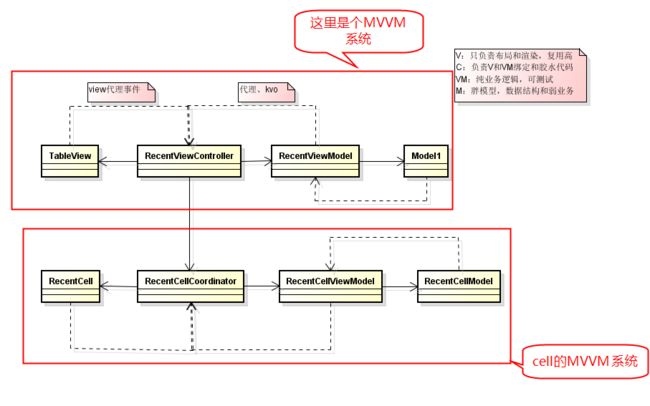
一个很常见的业务功能,如下图:
注解
这是一个典型的列表场景,用tableView视图实现,但是如果把所有业务包括cellView的业务逻辑都堆积到一个MVVM架构中显然会显得臃肿不合适,因此会把他拆分tableView、controller、tablViewModel为一个MVVM架构模式,其中每个tableCellView又是一个小型的MVVM架构如图:
[图片上传失败...(image-d844f2-1524550781161)]
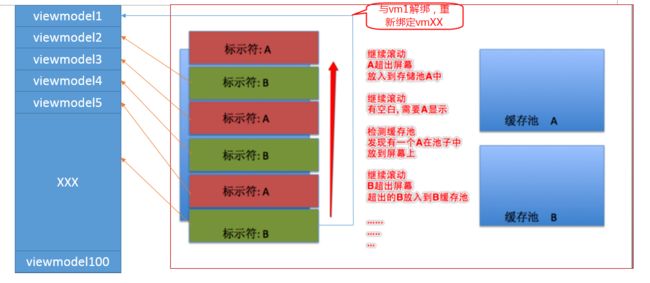
但是这里有个比较大的问题,tableView的mvvm和tableCellView的mvvm如何衔接起来哪?众所周知苹果的tableCellView是有复用机制的如图:
即tableCellView只会创建屏幕能显示的个数,而cellViewModel会创建完整的数量。那协调器cellCoordinator的他们直接的关系哪?如果cellCoordinator与cellViewmodel保持一一对应那么会有两个问题,有两份内存,对cellViewModel的增删同时要对应的对cellCoordinator做增。其二当cell超出屏幕被放入回收池,cellCoordinator不知道解绑。因此cellCoordinator应该与cellView一一对应,即用一个NSDictory保存key是cellView,value是cellCoordinator。这样既能减少内存占用,在cellView复用的时候能找到对应的cellCoordinator不能解除绑定。如下图:
具体代码如下:
1.1 ViewController & View
@interface RecentViewController ()
@property(nonatomic, strong) RecentViewModel *viewModel;
@property(nonatomic, strong) UITableView *tableView;
@property(nonatomic, strong) NSDictionary *coordinatorDic; //用于保存cell协调器,用于和cell一一对应
@end
@implementation RecentViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[self addSubView];
[self bindData];
[self fetchData];
}
- (void)addSubView {
self.tableView = [[UITableView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectZero];
self.tableView.tableFooterView = [[UIView alloc] init];
self.tableView.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor];
self.tableView.dataSource = self;
self.tableView.delegate = self;
self.tableView.separatorStyle = UITableViewCellSeparatorStyleNone;
[self.view addSubview:self.tableView];
[self.tableView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.equalTo(self.view);
}];
}
- (void)bindData {
[self.kvoController observe:self.viewModel keyPath:@"cellViewModelList" options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew | NSKeyValueObservingOptionInitial block:^(id observer, id object, NSDictionary *change) {
@strongify(self);
[self.tableView reloadData];
}];
}
- (void)fetchData {
[self.viewModel fetchData];
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return [self.viewModel.cellViewModelList count];
}
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
id viewModel = MUPArrayObjectAtIndex(self.viewModel.cellViewModelList, indexPath.row);
return [viewModel cellHeight];
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
id viewModel = MUPArrayObjectAtIndex(self.viewModel.cellViewModelList, indexPath.row);
NSString *identifier = @"ChatPlainTextCell";
RecentCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:identifier];
if (!cell) {
cell = [[RecentCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleSubtitle reuseIdentifier:identifier];
}
RecentCellCoordinator *cellCoordinator = = [self getCoordinatorWithCell:cell];
[cellCoordinator bind:viewModel];
return cell;
}
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:indexPath];
RecentCellCoordinator *cellCoordinator = [self.coordinatorDic objectForKey:cell];
[cellCoordinator didSelectCellView];
}
@end
- (void)getCoordinatorWithCell:(UITableViewCell *)cell {
RecentCellCoordinator *cellCoordinator = [self.coordinatorDic objectForKey:cell];
if (!cellCoordinator) {
cellCoordinator = [[RecentCellCoordinator alloc] initWithCellView:cell];
[self.coordinatorDic setObject:cellCoordinator forKey:cell];
}
return cellCoordinator;
}
1.2 ViewModel & Model
@interface RecentViewModel
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSArray *cellViewModelList; //Model
- (void)fetchData;
@end
@interface RecentViewModel ()
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray *cellViewModelList;
@end
@implementation RecentViewModel
- (void)fetchData {
//从数据源(dataSource类)获取数据
NSArray *array = [self.dataSource fetchDataList];
//将数据转换为CellViewModel
self.dataList = [self convertToCellViewModels:array];
}
- (NSArray *)convertToCellViewModels:(NSArray *)array {
NSMutableArray *cellVMArray = [NSMutableArray array];
for (int i=0; i<[array count]; i++) {
Model *model = array[i];
RecentCellViewModel *cellViewModel = [TableCellViewModelFactory createCellViewModel:model];
[cellVMArray addObject:cellViewModel];
}
return cellVMArray;
}
@end
这里面的RecentViewModel只做业务逻辑,而视图的绑定和事件代理者有RecentViewController负责,因此RecentViewModel是可以测试。
1.1.1 CellView
@protocol SWTableViewCellDelegate
- (void)swipeableTableViewCell:(SWTableViewCell *)cell didTriggerRightUtilityButtonWithIndex:(NSInteger)index;
@end
@protocol RecentCellDelegate
@optional
- (void)onAvatarClick:(NSInterger)uid;
@end
@interface RecentCell
@property(nonatomic, assign) NSInterger uid;
@property(nonatomic, strong) NSString *title;
@property(nonatomic, strong) NSString *timeText;
@property(nonatomic, strong) NSString *content;
@property(nonatomic, strong) NSString *rightButtonTitle;
@property(nonatomic, weak) id swDelegate;
@property(nonatomic, weak) id delegate;
@end
1.1.2 CellViewModel & Model
@interface RecentCellViewModel
@property(nonatomic, strong) NSString *title;
@property(nonatomic, strong) NSString *timeText;
@property(nonatomic, strong) NSString *content;
@property(nonatomic, assign) BOOL isFollowing;
- (instancetype)initWithConversation:(IMSConversation *)conv;
- (void)follow;
@end
@implementation RecentCellViewModel
- (void)follow {
if(_isFollowing) {
self.isFollowing = YES;
[PSPManager ShareInstance] unFollow:_uid complete:^(NSError *error, id result) {
if (error) { self.isFollowing = NO; }//follow失败 状态回退
//...略
}
} else {
//flow PSP
}
}
@end
1.1.3 协调器,负责绑定View和ViewModel
@interface RecentCellCoordinator ()
@property(nonatomic, weak) RecentCell *cell;
@property(nonatomic, weak) RecentCellViewModel *cellViewModel;
@property(nonatomic, strong) FBKVOController *kvoController;
@end
@implementation RecentCellCoordinator
- (instanceType)initWithCellView:(RecentCell *)cell {
if (self = [super init]) {
self.cell = cell;
self = cell.delegate;
self = cell.swDelegate;
}
}
- (void)bind:(RecentCellViewModel *)viewModel {
self.cellViewModel = viewModel;
self.cell.title = viewModel.title;
//... 设置其他属性
[kvoController observe:viewModel keyPath:@"isFollowing" options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew | NSKeyValueObservingOptionInitial block:^(id observer, id object, NSDictionary *change) {
//修改recentCell的展示内容
self.cell.rightButtonTitle = self.viewModel.isFollowing ? @"取消关注" : @"关注";
}];
}
- (void)swipeableTableViewCell:(SWTableViewCell *)cell didTriggerRightUtilityButtonWithIndex:(NSInteger)index {
[self.cellViewModel follow];
}
- (void)onAvatarClick:(NSInterger)uid {
//调转个人主页
PersonMainController *ctl = [[PersonMainController allooc] initWithUid:uid];
//push ctl;
}
@end
这里每个cell又是一个独立的MVVM,其业务和胶水代码写在自己的模块中。其中RecentCell只做布局和渲染,并将点击代理开给CellCoordinator,RecentCell的复用性贼好。而RecentCellViewModel制作业务逻辑测试性高,RecentCellCoordinator做绑定和事件代理代码简洁可读性也会提高。
当页面足够复杂时如下图聊天界面
其主要功能如下:
- 导航栏部分:显示聊天对方的名字、在线状态、用户信息、聊天养成等等功能
- 中间消息展示部分:显示各种不同的消息
- 底部输入框:显示文本、语音以及各功能入口
- 聊天页面:展示鲜花、打赏入口,聊天动态浮窗等
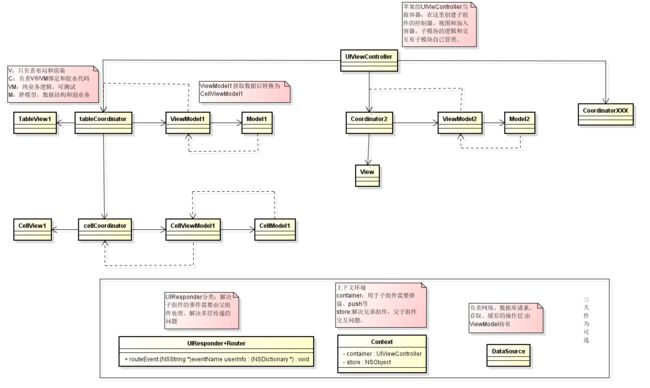
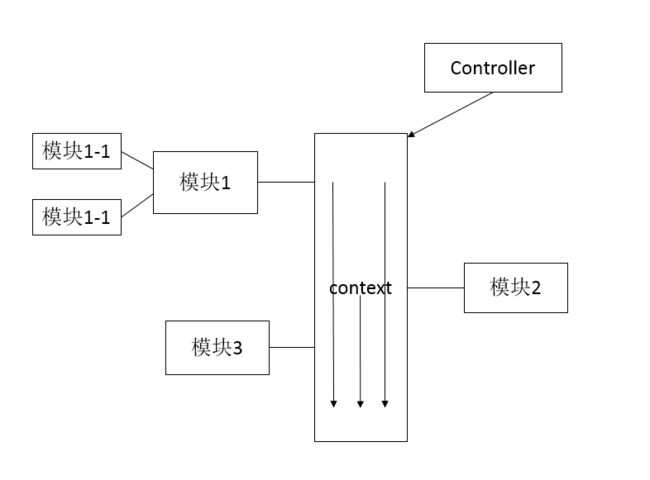
解决问题的核心是按照功能等维度进行==拆分==,以低耦合的方式分散代码复杂度。将UI、交互、事件都放到各自子模块中处理。如下图:
同时引入新的问题这些子模块怎么通信和交互?
对子模块的交互进行归类,主要有两种方式:
- 通知其他子模块,如:滚动tableview到底部等
- 子模块需要共享、监听数据的变动,如:多选状态、页面展示样式等
针对第一个问题,我们可以借鉴苹果系统的事件响应链的方式来解决多层传递的麻烦问题
@protocol UIResponderEventProtocol
- (void)routeEvent:(NSString *)eventName userInfo:(NSDictionary *)userInfo;
@end
@interface UIResponder (Router)
@property(nonatomic, weak) id eventDelegate;
- (void)routeEvent:(NSString *)eventName userInfo:(NSDictionary *)userInfo
@end
@implementation UIResponder (Router)
//沿着响应者链将事件往父视图传递, 事件最终被拦截处理 或者 无人处理直接丢弃
- (void)routeEvent:(NSString *)eventName userInfo:(NSDictionary *)userInfo {
if([self.eventDelegate respondsToSelector:@selector(routeEvent:userInfo:)]) {
[self.eventDelegate routeEvent:eventName userInfo:userInfo];
}
[self.nextResponder routeEvent:eventName userInfo:userInfo];
}
@end
针对第二种交互方式采用如下图所示,引入context(上下文)概念,保存UIViewController(控制器)、共享数据模型等。子模块可通过监听或获取context的数据模型来做相应的展示,通过UIViewController做吐司、push等操作。
代码例子:
3.1 context类
//聊天上下文,提供共享数据等
@interface ChatContext
@property(nonatomic, weak) UIViewController *controller;
@property(nonatomic, strong) BOOL selectModel; //编辑模式
@end
3.2 table协调器
//tableView的协调器,处理tableView和ViewModel的胶水代码
@interface TableViewCoordinator()
- (void)scrollToPositionWithMessageId:(NSNumber *)mid;
@end
3.2.1 tableCell协调器
//tableCell的协调器,处理tableCell和cellViewModel的胶水代码
@interface ChatCellCoordinator()
@end
@implementation ChatCellCoordinator
- (void)onMenuForward:(ChatCell *)cell {
SelectViewController *selectVC = [[SelectViewController alloc] init];
[self.context.controller push:selectVC];
}
- (void)onMenuMultiSelect {
self.context.selectModel = YES;
}
@end
3.3 输入框协调器
@implementation InputPanelViewCoordinator
- (void)bindData {
[self.kvoController observe:self.context keyPath:@"selectModel" options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew | NSKeyValueObservingOptionInitial block:^(id observer, id object, NSDictionary *change) {
@strongify(self);
[self.view.hidden = YES;
}];
}
@end
- 聊天会话页面中的消息ChatCell长按会弹出菜单列表,选择转发按钮ChatCell的协调器ChatCellCoordinator可直接通过context的controller跳转到选人页面。
- 聊天会话页面中的消息ChatCell长按会弹出菜单列表,选择多选按钮进入编辑选择状态,协调器ChatCellCoordinator设置context的selectModel为YES切换为选择模式,输入面板子模块监听选择状态后隐藏同时显示跳转到啊选人界面的入口。聊天消息ChatCell也监听选择状态线束勾选按钮。
3.4 头部协调器
@interface HeaderViewCoordinator()
@property(nonatomic, strong) PromptView *view;
@property(nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *unReadMaxMessageID;
@end
@implementation HeaderViewCoordinator
- (void)onClickPromptView {
//滚动到置顶位置
NSDictory *dic = @{@"unReadMaxMessageID", self.unReadMaxMessageID};
[self.view routeEvent:@"ScrollToPosition" userInfo:dic];
}
@end
3.5 ViewController
@interface ChatViewController ()
@property(nonatomic, strong) ChatContext *context;
@property(nonatomic, strong) HeaderViewCoordinator *headerCoordinator;
@property(nonatomic, strong) TableViewCoordinator *tableViewCoordinator;
@property(nonatomic, strong) InputPanelViewCoordinator *inputPanelViewCoordinator;
@end
@implementation
- (void)viewDidLoad {
self.view.eventDelegate = self;
[self config];
}
- (void)routeEvent:(NSString *)eventName userInfo:(NSDictionary *)userInfo {
NSNumber mid = [userInfo objectForKey:@"ScrollToPosition"];
[self.tableViewCoordinator scrollToPositionWithMessageId:mid];
}
- (void)config {
UITableView *tableView = [[UITableView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectZero];
[self.view addSubView:tableView];
//做布局
self.tableViewCoordinator = [[TableViewCoordinator alloc] initWithTableView:tableView context:self.context];
InputPanelView *inputView = [[InputPanelView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectZero];
[self.view addSubView:inputView];
//做布局
self.inputPanelViewCoordinator = [[InputPanelViewCoordinator alloc] initWithTableView:inputView context:self.context];
//其他模块配置
}
@end
顶部未读消息弹框点击后由HeaderViewCoordinator代理执行点击事件,发现自己执行不了需要通知tableView子模块滚动。于是调用view的routeEvent: userInfo:事件路由通过视图的响应链到ChatViewController的view视图,ChatViewController拦截view的事件作为中介者调用tableViewCoordinator提供的滚动tableview的接口。于是完成功能。
通过上面的拆解职责分工清楚,减少代码臃肿提供代码的可读性和可维护性。
页面间数据流
如B页面设置了会话为免扰模式,A页面需要监听免扰模式从而做不同的视图展现。可以将免扰模式这个数据下沉到SDK中,然后开出免扰变动监听的接口。
Demo
[demo传送门]https://github.com/hubjf/AppFrameworkKit
FAQ
关于context传递问题
- 可以借用View视图的树形结构模型,在子视图调用context往父视图遍历找到根节点的context从而解决context一层层传递问题。
具体代码如下:
UIView分类头文件
@protocol ContextProtocol
@property(nonatomic, weak, readonly) UIViewController *controller;
- (instancetype)initWithViewController:(UIViewController *)controller;
@end
@interface UIView (Context)
@property(nonatomic, strong) id context;
@end
UIView分类实现文件
static char *ContextProtocolKey = "ContextProtocolKey";
@implementation UIView (Context)
- (void)setContext:(id)delegate {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, ContextProtocolKey, delegate, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
- (id)context {
id context = [self p_context:self];
if (!context) {
context = [self parentContext:self.superview];
}
return context;
}
- (id)parentContext:(UIView *)parentView {
if (!parentView) {
return nil;
}
id context = [parentView p_context:parentView];
if (!context) {
context = [self parentContext:parentView.superview];
} else {
self.context = context;
}
return context;
}
- (id)p_context:(id)object {
id context = objc_getAssociatedObject(object, ContextProtocolKey);
return context;
}
创建业务的上下文ChatContext
@interface ChatContext : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) ChatBackGroundStyle bgStyle;
@end
然后在ViewController里面创建context并赋值
//ChatViewController.m文件
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.view.context = [[ChatContext alloc] initWithViewController:self];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
[self installSubModule];
}
使用者在Coordinator里面直接调用自己的View的context
//InputPanelCoordinator.m文件
- (void)bindData {
ChatContext *context = (ChatContext *)self.inputView.context;
}
关于context共享属性大家够随意修改问题
- 如果在context的属性如bgStyle属性直接声明可读、可写,那么
可能会有多处地方修改从而引起不可控,因此需要对bgStyle对外声明可读,context的实现类通过@synthesize bgStyle = chatContext_bgStyle; 将其和私有变量绑定,同时重写私有变量chatContext_bgStyle的set方法。然后在需要写的子模块里面通过KVC方式修改该属性。具体代码如下
//ChatContext.h文件
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) ChatBackGroundStyle bgStyle;
//ChatContext.m文件
@interface ChatContext ()
{
ChatBackGroundStyle chatContext_bgStyle;
}
@end
@implementation ChatContext
@synthesize bgStyle = chatContext_bgStyle;
- (void)setChatContext_bgStyle:(ChatBackGroundStyle)style {
[self willChangeValueForKey:@"bgStyle"];
chatContext_bgStyle = style;
[self didChangeValueForKey:@"bgStyle"];
}
@end
推广使用
上述文章讲解了具体的思想和解决方案以及对应的代码实现,后续会提供工具类、架构模板,使用者只要创建文件的时候根据场景选择对应的架构就能够帮你创建整个架构文件,然后只需要在里面写业务逻辑即可。
设计思想
- 所有的模块角色只会有三种:数据管理者(Model)、数据加工者(Controller)、数据展示者(View),这些五花八门的思想,不外乎就是制订了一个规范,规定了这三个角色应当如何进行数据交换。
- 要提高代码的复用度则需要将数据展示者、数据管理者隔离(即不互相依赖),要达到可测试性则需要将数据展示者和数据加工者剥离。
- 当一个页面足够复杂则需要将其按照功能拆分多个MVC/MVVM/MVP。