列出定单之间的平均天数
drop table job_history;
create table job_history(
employee_id number primary key not null,
start_date date,
end_date date,
ename varchar2(30),
job varchar2(30)
);
delete from job_history;
insert into job_history values(1,to_date('2014-07-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2015-07-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'polly','sales');
insert into job_history values(8,to_date('2015-07-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2018-07-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'polly','finance');
insert into job_history values(2,to_date('2014-06-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2015-06-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'hanmeimei','secrectory');
insert into job_history values(9,to_date('2015-06-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2017-06-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'hanmeimei','finance');
insert into job_history values(3,to_date('1985-06-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('1987-02-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'litao','engineer');
insert into job_history values(10,to_date('1987-06-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2000-02-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'litao','operations person');
insert into job_history values(4,to_date('2003-06-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2006-04-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'lilei','manager');
insert into job_history values(11,to_date('2006-08-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2009-04-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'lilei','ceo');
insert into job_history values(5,to_date('1999-01-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('1999-08-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'uncle wang','cto');
insert into job_history values(12,to_date('2009-05-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2010-08-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'uncle wang','sales');
insert into job_history values(6,to_date('2001-07-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2005-06-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'jim','police');
insert into job_history values(13,to_date('2005-07-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2009-10-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'jim','sales');
insert into job_history values(7,to_date('2004-09-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2008-06-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'green','waiter');
insert into job_history values(14,to_date('2008-09-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),to_date('2015-06-07','yyyy-mm-dd'),'green','waiter');
select distinct employee_id, ename
from job_history j1
where not exists
(select null
from job_history j2
where j2.employee_id = j1.employee_id
and round(months_between(j2.start_date, j2.end_date) / 12, 0) <>
round(months_between(j1.start_date, j1.end_date) / 12, 0));
select employee_id
from job_history
group by employee_id
having min(round(months_between(start_date, end_date) / 12, 0)) = max(round(months_between(start_date, end_date) / 12, 0));
SQL是基于集合理论的,集合中的行没有预先确定顺序,排序就必须在符合查询条件的数据行都从集合中抽取出来之后再单独进行。
准备测试数据
--创建orders表
drop table orders;
create table orders(
order_id number primary key,
customer_id number,
sales_rep_id number,
order_total number,
order_date date
);
drop sequence seq;
create sequence seq;
--准备测试数据
delete from orders;
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,1,4,10000,to_date('2017-03-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,2,4,10000,to_date('2004-03-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,2,4,10000,to_date('2017-08-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,1,4,10000,to_date('2010-03-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,1,4,10000,to_date('2012-03-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,2,4,10000,to_date('1999-08-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,2,4,10000,to_date('1998-09-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,1,4,10000,to_date('1995-07-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,1,4,10000,to_date('2008-03-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,2,4,10000,to_date('2009-03-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,3,4,10000,to_date('2017-08-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,3,4,10000,to_date('2016-03-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,3,4,10000,to_date('2015-03-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,3,4,10000,to_date('2018-02-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,3,4,10000,to_date('2017-01-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,3,4,10000,to_date('2014-03-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,4,4,10000,to_date('2014-02-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,4,4,10000,to_date('2014-06-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,5,4,10000,to_date('2014-08-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,5,4,10000,to_date('2014-09-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,5,5,10000,to_date('2014-02-06 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,5,4,100,to_date('2011-02-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,5,7,10800,to_date('2013-02-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
insert into orders VALUES(seq.nextval,5,8,1000,to_date('2016-02-05 18:26','yyyy-mm-dd HH24:MI'));
SELECT * from orders;
commit;
面向过程的思维方式
--列出客户的定单数
select customer_id, order_date from orders where customer_id = 5;
--根据当前行的日期决定之前的日期
select customer_id,
order_date,
lag(order_date, 1, order_date) over(partition by customer_id order by order_date) as pre_order_date
from orders
where customer_id = 5;
--决定定单之间的天数
select trunc(order_date)-trunc(pre_order_date) days_between from (
select customer_id,
order_date,
lag(order_date, 1, order_date) over(partition by customer_id order by order_date) as pre_order_date
from orders
where customer_id = 5
);
--放在一起做平均数,得到最终答案
select avg(trunc(order_date)-trunc(pre_order_date)) avg_days_between from (
select customer_id,
order_date,
lag(order_date, 1, order_date) over(partition by customer_id order by order_date) as pre_order_date
from orders
where customer_id = 5
);
基于集合的思维方式
select (max(trunc(order_date)) - min(trunc(order_date))) / count(*) as avg_days_between
from orders
where customer_id = 5;
计算定单之间的平均天数,只需计算第一笔和最后一笔的定单天数以及总的定单数即可。不需要一个个计算定单,一个个汇总。
集合运算
集合运算符将两个或更多select语句的结果合并形成一个结果集。
联结是用来将不同表中的列组合起来形成一行。
集合运算比较所输入查询的所有行并返回一个包含重复值的行集。
所有的集合运算都必须符合下面的条件:
- 所有的输入查询必须返回相同数目的列
- 每一列的数据类型必须与对应的其它输入查询一致
- order by子句不能在某个单独的查询中应用,只能用在整个查询的最后,用来排序整个集合运算的结果集
- 列名源自第一个输入查询
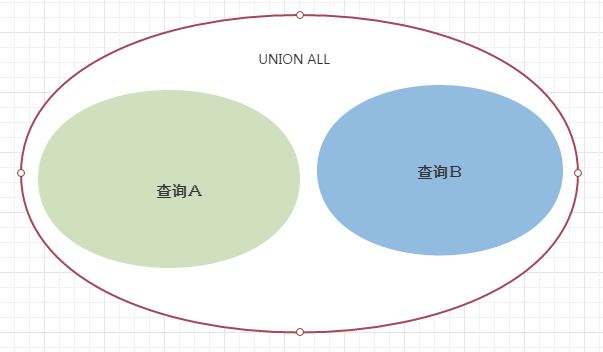
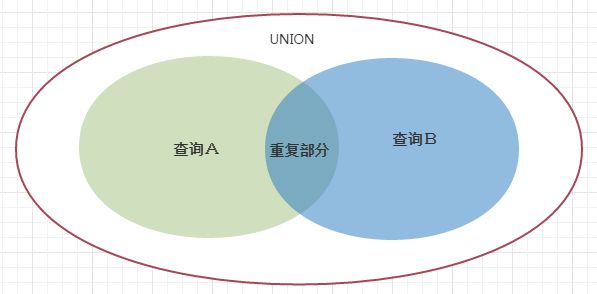
oracle支持4种集合运算符: union all,union, minus,intersect
-
union all: 返回两个集合中的所有行,包含重复。
--例1
SQL> select 'tomluo' as name from dual
2 union all
3 select 'tomluo' as name from dual;
NAME
------
tomluo
tomluo
--例2
create table table1(
id_pk integer not null primary key,
color varchar(10) not null
);
create table table2(
id_pk integer not null primary key,
color varchar(10) not null
);
create table table3(
color varchar(10) not null
);
insert into table1 values(1,'red');
insert into table1 values(2,'red');
insert into table1 values(3,'orange');
insert into table1 values(4,'orange');
insert into table1 values(5,'orange');
insert into table1 values(6,'yellow');
insert into table1 values(7,'green');
insert into table1 values(8,'blue');
insert into table1 values(9,'blue');
insert into table1 values(10,'violet');
insert into table2 values(1,'red');
insert into table2 values(2,'red');
insert into table2 values(3,'blue');
insert into table2 values(4,'blue');
insert into table2 values(5,'blue');
insert into table2 values(6,'green');
commit;
select color from table1
union all
select color from table2;
select color from table1;
- union: 返回来自所有输入查询的不包含重复的结果集
SQL> select 'tomluo' as name from dual
2 union
3 select 'tomluo' as name from dual;
NAME
------
tomluo
select color from table1
union
select color from table2;
select color from table3;
select color from table1
union
select color from table3;
--下面的有错,列不一样
select * from table1
union
select color from table2;
-
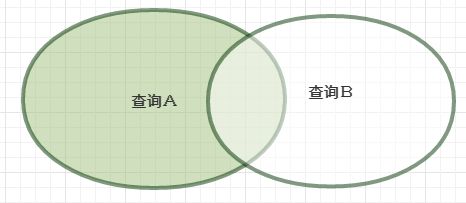
minus:返回在第一个输入查询中存在但接下来的查询中不存在的非重复数据行
将第一个查询的结果集作为基础数据集减去另一个查询结果集。minus通用来替代not exists(反联结)查询。
select color from table1
minus
select color from table2;
select color from table1
minus
select color from table3;
- intersect: 返回在所有输入查询中都存在的重复行
intersect用来返回在所有输入查询中都存在的唯一行集。intersect通常用来代替exists(半联结)。
select color from table1
intersect
select color from table2;
集合与空值
空值: 空值并不是一个值,最多是一个标记,可以理解为‘我不知道’。
--列出所有的行从tem表中
select * from emp;
--列出部门号为1,2,3,4的用户
select * from emp where deptno in (1, 2, 3, 4);
--列出部门号不为1,2,3,4的用户
select * from emp where deptno not in (1, 2, 3, 4);
--列出部门号不为1,2,3,4的用户或部门为空值的用户
select * from emp where deptno not in (1, 2, 3, 4);
除非显式声明,它们不会被包含在结果集中。
空值不能用来比较,空值不能与任何东西进行加,减,乖,除运算。
select * from emp where deptno is null;
select * from emp where deptno = null;
insert into emp
(empno, ename, deptno, job, mgr, hiredate, sal)
values
(10, 'jiantao', 4, 'engineer', 2, sysdate, 5800);
select sal,comm,sal+comm as tot_cmp from emp where deptno=4;
关系模型是基于两个值(真,假)的逻辑关系,但是SQL语言支持3个值(真,假和未知)的逻辑。空值代表未知,所以很可能返回错误的值。
空值与集合运算
--空值与集合运算
select null from dual
union
select null from dual;
select null from dual
union all
select null from dual;
select null from dual
intersect
select null from dual;
select null from dual
minus
select null from dual;
select 1 from dual
union
select null from dual;
select 1 from dual
union all
select null from dual;
select 1 from dual
intersect
select null from dual;
select 1 from dual
minus
select null from dual;
当具有空值的两行进行联合时,你只会得到一行。这就表明这两行是相等等的,因此在进行联合时重复行就可以被去掉了。
集合运算将所有的空值作为相等的值来对待。
空值与group by 、order by
group by和order by子句也将空值作为可以用等式进行比较的值来对等。空值总是会像其他己知值那样被放在一起。
select comm, count(*) str from scott.emp group by comm;
select comm, count(*) str from scott.emp group by comm order by comm;
select comm, count(*) str
from scott.emp
group by comm
order by comm nulls first;
select ename, sal, comm from scott.emp order by comm, ename;
默认的排序规则是把空值排到最后。
空值与聚合函数
当在聚合函数如sum,count,avg,min以及max等包含的列中出现空值时,它们将会被从聚合中去掉。如果去掉后集合变成空的,聚合则会返回空值。
select count(*) row_ct,
count(comm) comm_ct,
avg(comm) avg_comm,
min(comm) min_comm,
max(comm) max_comm,
sum(comm) sum_comm
from scott.emp;
count()和count(comm)的区别: 使用得到所有的行数。而使用comm是comm值为非空的行数。如果在计算avg,min,max及sum值时,如果有空值,所有的这些函数最后只返回一个结果。如果空值没有被去掉,这些函数将会返回空值。
要想写出简单易懂且性能会过程化方法更好的SQL语句,需要掌握的核心技心就是以集合的方式来思考。如果按照过程化的方式思考时,就会尝试强制让非过程化的SQL语言按照不必要的方式来实现其功能。