引言
以下内容是笔者学习了Udacity的android数据库基础课程有关SQLite的学习笔记,感谢Udacity提供优秀的课程内容。
使用方法
Training中使用SQLite分为两步:
- Define a Schema and Contract(class)
- Using a SQL Helper to create db
What is Schema?
在我上一篇关于PC上使用sqlite命令里面使用了Schema查看的时候可以看到显示的就是我们创建db时候用的sql语句,所以不难理解定义好Schema就是要求我们在使用数据库的时候要先把数据库里面的表结构建好,(让我想起了林老师讲的第一范式第二范式等等,真的是我在大学遇到的最好的老师),总之写代码前先分析好我们的数据都有哪些,什么类型。
What is Contract?
Contract就是我们为数据列先定义好的一个规范,比如我们要创建一个表Student,列名有name,gender,s_id等等,那么我们就可以在Contract中定义一个字符串常量(英文用constant)将我们要表达的这个列名规范化,以下是在udacity中的一个示例的代码:
//定义pet数据库中的表和列的信息常量
public final class PetsContract {
//not allow to create a instance
private PetsContract(){}
//为pet表定义列名常量
public static final class petsEntry implements BaseColumns{
/**
* table name
*/
public static final String COLUMN_NAME = "pets";
/**
* column of the table
* name:pets'name
* breed:you should feed what kind of food
* gender:male 1 female 2 unknown 0
* weight:the weight of pet
*/
public static final String _ID = BaseColumns._ID;
public static final String COLUMN_NAME_ = "name";
public static final String COLUMN_BREED = "breed";
public static final String COLUMN_GENDER = "gender";
public static final String COLUMN_WEIGHT = "weight";
/**
* Possible values for the gender
*/
public static final int GENDER_UNKNOWN = 0;
public static final int GENDER_MALE = 1;
public static final int GENDER_FEMALE = 2;
}
}
确定范围的有限个数据可以使用整数标识,然后在我们的这个contract中规范好就行,比如上面代码中的gender就使用这种方法。
contract的思想在android中的很多地方都使用到,目的就是方便我们app在未来的更新维护。
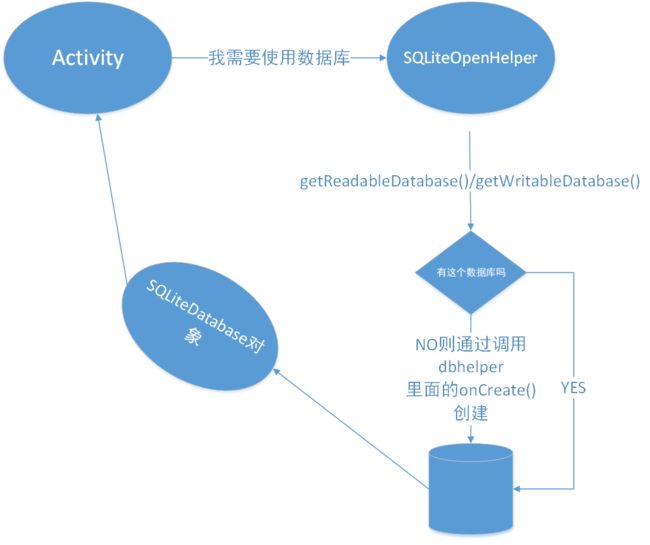
使用SQLiteHelper
SQLiteHelper做什么的:
- 第一次使用的时候创建数据库
- 连接已经存在的数据库
- 帮助修改Schema
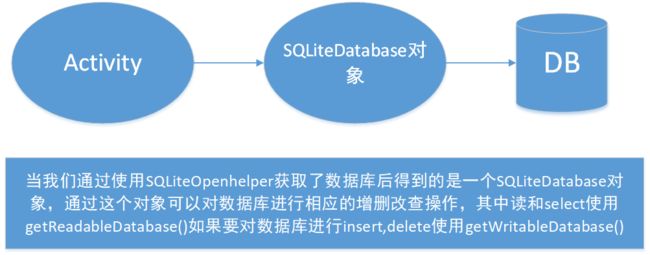
获取数据库对象后:
有了数据库对象SQLitedatabase,我们就可以使用各种CRUD啦!这节课我主要学习了insert和read的方法接下来就复习一下
INSERT
先上代码:
//当用户点击insert按钮后会执行此代码
private void insert() {
//获取dbHelpter
PetsdbHelper dbHelper = new PetsdbHelper(this);
//获取SQLite数据库
SQLiteDatabase petsdb = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
//使用content value创建values
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(petsEntry.COLUMN_NAME_,"jasper");
values.put(petsEntry.COLUMN_BREED,"carrot");
values.put(petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER,petsEntry.GENDER_MALE);
values.put(petsEntry.COLUMN_WEIGHT,70);
petsdb.insert(petsEntry.TABLE_NAME,null,values);
}
insert方法第一个参数就是我们先前在contract中定义好的表名,第二个参数通常为null,详情点击这里 ,第三个参数就是我们要插入的值,只不过这个值使用ContentValues通过键值对的方式包装了一下。代码中put就是将我们要放入的值放在对应的列中。
Cursor
代码:
private void displayDatabaseInfo() {
// To access our database, we instantiate our subclass of SQLiteOpenHelper
// and pass the context, which is the current activity.
PetsdbHelper mDbHelper = new PetsdbHelper(this);
// Create and/or open a database to read from it
SQLiteDatabase db = mDbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
String[] projection ={
petsEntry._ID,
petsEntry.COLUMN_BREED,
petsEntry.COLUMN_NAME_,
petsEntry.COLUMN_WEIGHT,
petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER,
};
String selection = petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER + "=?";
String[] selectionArgs = new String[]{ "" + petsEntry.GENDER_MALE };
Cursor cursor = db.query(petsEntry.TABLE_NAME,projection,selection,selectionArgs,null,null,null);
try {
int pets_id_index = cursor.getColumnIndex(petsEntry._ID);
int pets_breed_index = cursor.getColumnIndex(petsEntry.COLUMN_BREED);
int pets_name_index = cursor.getColumnIndex(petsEntry.COLUMN_NAME_);
int pets_weight_index = cursor.getColumnIndex(petsEntry.COLUMN_WEIGHT);
int pets_gender_index = cursor.getColumnIndex(petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER);
TextView displayView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_view_pet);
while(cursor.moveToNext()) {
int pets_gender = cursor.getInt(pets_gender_index);
String pets_breed = cursor.getString(pets_breed_index);
String pets_name = cursor.getString(pets_name_index);
int pets_weight = cursor.getInt(pets_weight_index);
int pets_id = cursor.getInt(pets_id_index);
displayView.append("id: " + pets_id + " gender: " + pets_gender + " breed: " + pets_breed + " name: " + pets_name + " weight: " + pets_weight + "\n\n");
}
} finally {
// Always close the cursor when you're done reading from it. This releases all its
// resources and makes it invalid.
cursor.close();
}
}
使用query获取cursor对象,获取到的这个cursor就是根据query中的参数构成的SQL语句查询到的内容,这样我们通过操作cursor处理我们查询到的内容就行了。query参数部分请看这里 。
关于Cursor示例中的一些问题:
第一个问题:
当初是为了当我们从子Activity返回时候也可以看到上面查询的内容,所以我在onCreate和onStart方法中都调用了这个方法,而我在这个方法中还使用了append方法将内容加载到屏幕上,这就导致了每次调用该方法都会再appand一下,让同样的内容重复了很多次。所以以后一定要注意的是Activity的生命周期,和收尾的一些工作(比如把cursor关掉防止内存泄漏等等...)。
第二个问题:
关于SQLitedatabase对象调用query中有关selectionArgs的问题:
String[] projection ={
petsEntry._ID,
petsEntry.COLUMN_BREED,
petsEntry.COLUMN_NAME_,
petsEntry.COLUMN_WEIGHT,
petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER,
};
String selection = petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER + "=" + petsEntry.GENDER_MALE;
//String[] selectionArgs = new String[]{ petsEntry.GENDER_UNKNOWN };
// String selection = "?=petsEntry.GENDER_MALE";
// String[] selectionArgs = {"petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER"};
Cursor cursor = db.query(petsEntry.TABLE_NAME,projection,selection,null,null,null,null);
上面代码中我的selectionArgs应该是一个整数,可是因为selectionArgs必须要用String[]所以以下两个代码都不能正确查询到内容:
这个代码会报错
String selection = "?=petsEntry.GENDER_MALE";
String[] selectionArgs = {"petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER"};
Caused by: android.database.sqlite.SQLiteException: no such column: petsEntry.GENDER_MALE (Sqlite code 1): , while compiling: SELECT _id, breed, name, weight, gender FROM pets WHERE ?=petsEntry.GENDER_MALE, (OS error - 2:No such file or directory)
下面的代码可以正常运行但是不能查询到:
String selection = petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER + "=?";
String[] selectionArgs = new String[]{ "petsEntry.GENDER_UNKNOWN" };
下面的代码因为String[]不是String所以直接报错:
String selection = petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER + "=?";
String[] selectionArgs = new String[]{ petsEntry.GENDER_UNKNOWN };
改正方法(使用""+int 强行将int转化为String 一步步分析试过来,看来java一些小技巧还挺好用):
String selection = petsEntry.COLUMN_GENDER + "=?";
String[] selectionArgs = new String[]{ "" + petsEntry.GENDER_MALE };