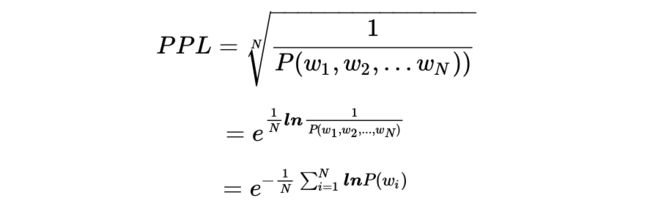通过前面的两篇博客,我们已经获取了训练数据和字向量,还了解了RNN单元的原理和代码实现。
这篇博客继续讲解如何实现一个RNN起名器(使用LSTM)。
1. 网络结构
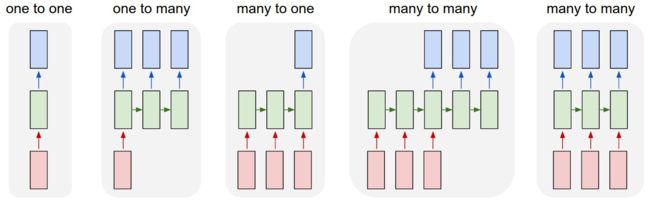
先看下RNN网络常用的基础结构,图片来自karpathy:
解释:
- (1) 简单的一对一。(严格的说不属于RNN)
- (2) 序列输出 (例如输入一张图片,输出一句句子)。
- (3) 序列输入 (例如输入一句话,做情感分类)。
- (4) 序列输入,序列输出 (典型例子:Machine Translation)。
- (5) 同步的序列输入和输出 (例如视频分类,给视频的每一帧画面打label)。
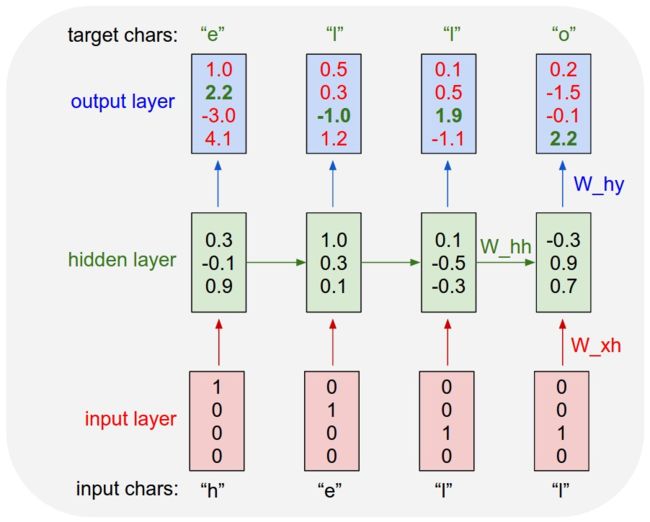
我们的起名器使用的是最后一种同步序列输入和输出。
2. lstm最终实现
上一篇介绍了lstm的基本实现。
接下来,我们看下我们的最终实现:
with self.graph.as_default():
# Parameters:
# Embedding layer
with tf.name_scope("embedding"):
self.Vector = tf.Variable(initial_value=self.W_value, name="Vector")
# input to all gates
U = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([self.embedding_dim, self.hidden_dim * 4], -0.1, 0.1), name='x')
# memory of all gates
W = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([self.hidden_dim, self.hidden_dim * 4], -0.1, 0.1), name='m')
# biases all gates
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, self.hidden_dim * 4]))
# Variables saving state across unrollings.
saved_output = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.batch_size, self.hidden_dim]), trainable=False)
saved_state = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.batch_size, self.hidden_dim]), trainable=False)
# Classifier weights and biases.
w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([self.hidden_dim, self.vocabulary_size], -0.1, 0.1))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.vocabulary_size]))
self.keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="kb")
# Definition of the cell computation.
def lstm_cell(i, o, state):
i = tf.nn.dropout(x=i, keep_prob=self.keep_prob)
mult = tf.matmul(i, U) + tf.matmul(o, W) + biases
input_gate = tf.sigmoid(mult[:, :self.hidden_dim])
forget_gate = tf.sigmoid(mult[:, self.hidden_dim:self.hidden_dim * 2])
update = mult[:, self.hidden_dim * 3:self.hidden_dim * 4]
state = forget_gate * state + input_gate * tf.tanh(update)
output_gate = tf.sigmoid(mult[:, self.hidden_dim * 3:])
output = tf.nn.dropout(output_gate * tf.tanh(state), self.keep_prob)
return output, state
上面的代码把iU,fU,cU,oU堆叠成U,把iW,fW,cW,oW堆叠成W。
这样,矩阵乘法:
tf.matmul(i, iU) + tf.matmul(o, iW) + ib
tf.matmul(i, fU) + tf.matmul(o, fW) + fb
tf.matmul(i, cU) + tf.matmul(o, cW) + cb
tf.matmul(i, oU) + tf.matmul(o, oW) + ob
就可以合成下面的一步:
mult = tf.matmul(i, U) + tf.matmul(o, W) + biases
3. mini-batch
如果不使用mini-batch,一个一个样本训练,速度会很慢。
为了加快训练速度,RNN通常也会采用mini-batch的方式训练。
但是问题来了,不同的训练语句长度不一样怎么办?一般采用固定batch长度,不够的zero padding补上;多出的分割成多个。
下面的代码生成batch数据:
class BatchGenerator(object):
"""Batch 生成器"""
def __init__(self, X_value, Y_value, batch_size,
num_unrollings, vocabulary_size, char_to_index):
self.X_value = X_value
self.Y_value = Y_value
self.data_len = len(X_value)
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.num_unrollings = num_unrollings
self.vocabulary_size = vocabulary_size
self.char_to_index = char_to_index
self.start = 0
self.end = batch_size - 1
print "data length:", len(X_value)
def next(self):
X_all = self.X_value[[i % self.data_len for i in range(self.start, self.end + 1)]]
Y_all = self.Y_value[[i % self.data_len for i in range(self.start, self.end + 1)]]
X_all = [x + list(np.zeros(self.num_unrollings - len(x), dtype=int)) for x in X_all if len(x) != self.num_unrollings]
Y_all = [y + list(np.zeros(self.num_unrollings - len(y), dtype=int)) for y in Y_all if len(y) != self.num_unrollings]
X_batchs = list()
Y_batchs = list()
for step in range(self.num_unrollings):
X_batch = list()
Y_batch = np.zeros(shape=(self.batch_size, self.vocabulary_size), dtype=np.float)
for b in range(self.batch_size):
X_batch.append(X_all[b][step])
Y_batch[b, Y_all[b][step]] = 1.0
X_batchs.append(np.array(X_batch))
Y_batchs.append(Y_batch)
self.start = self.end + 1
self.end += self.batch_size
return X_batchs, Y_batchs
因为要使用字向量,所以X_batch数据是字的index(根据index查询char embedding),而Y_batch数据是one hot向量。
所以X_batchs的尺寸是:(5, 50),即num_unrollings×batch_size;
Y_batchs的尺寸是:(5, 50, 5273),即num_unrollings×batch_size×num_chars。
4.损失函数和模型评估
损失函数:根据softmax的输出和label计算交叉熵
logits = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(tf.concat(0, outputs), w, b)
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits, tf.concat(0, self.train_labels)))
评估指标:perplexity
perplexity 衡量概率模型的采样的有多好,数值越小,概率模型越好(语言模型常用)。
def logprob(predictions, labels):
"""
计算perplexity时用到。
Log-probability of the true labels in a predicted batch.
"""
predictions[predictions < 1e-10] = 1e-10
return np.sum(np.multiply(labels, -np.log(predictions))) / labels.shape[0]
print('Minibatch perplexity: %.2f' % float(
np.exp(logprob(predictions, np.concatenate(Y_batchs)))))
5. 生成名字(sample)
def sample_distribution(distribution):
"""Sample one element from a distribution assumed to be an array of normalized
probabilities.
sample按照distribution的概率分布采样下标,这里的采样方式是针对离散的分布,相当于连续分布中求CDF。
"""
r = random.uniform(0, 1)
s = 0
for i in range(len(distribution)):
s += distribution[i]
if s >= r:
return i
return len(distribution) - 1
def sample(prediction, vocabulary_size):
"""Turn a (column) prediction into 1-hot encoded samples.
根据sample_distribution采样得的下标值,转换成1-hot的样本
"""
p = np.zeros(shape=[1, vocabulary_size], dtype=np.float)
p[0, sample_distribution(prediction[0])] = 1.0
return p
def sample_name(self, first_name, ckpt_file=MODEL_PRE):
"""根据现有模型,sample生成名字"""
with tf.Session(graph=self.graph) as session:
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.restore(session, ckpt_file)
for _ in range(NAME_NUM):
name = first_name
sample_input = self.char_to_index[first_name[-1]]
self.reset_sample_state.run()
for _ in range(NAME_LEN-1):
prediction = self.sample_prediction.eval({self.sample_input: [sample_input], self.keep_prob: 1.0})
one_hot = sample(prediction, self.vocabulary_size)
sample_input = self.char_to_index[prob_to_char(one_hot, self.index_to_char)[0]]
name += prob_to_char(one_hot, self.index_to_char)[0]
print name
根据输入的姓,和名字长度,获取名字。
6. 结果展示
完整代码
训练模型在main函数中执行train_all()
生成名字在main函数中执行namer_lstm_c2v()
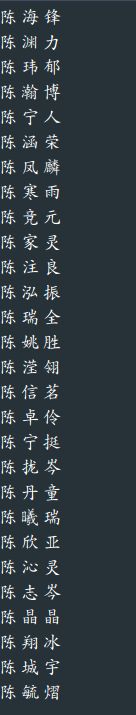
生成的陈姓男孩名字: