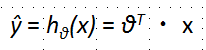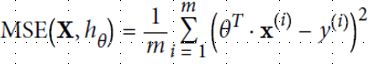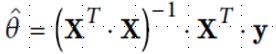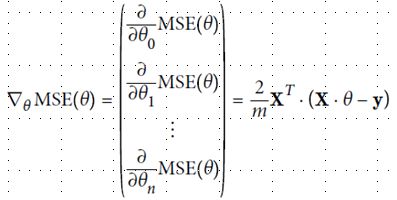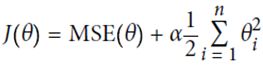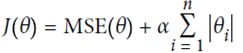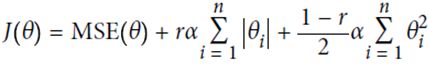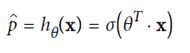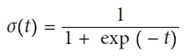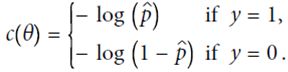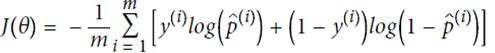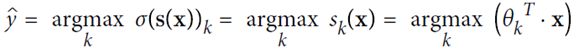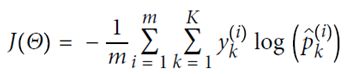一、Linear Regression
线性回归是相对简单的一种,表达式如下
![]()
其中,θ0表示bias,其他可以看做weight,可以转换为如下形式
为了更好回归,定义损失函数,并尽量缩小这个函数值,使用MSE方法(mean square equal)
缩小方法采用梯度下降法,即不断地向现在站立的山坡往下走,走的速度就是学习速率η(learning rate),太小耗尽计算资源,太大走过了山谷。
(1)Normal Equation
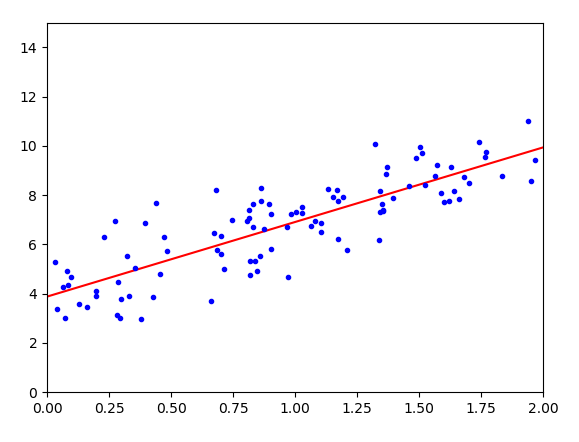
1 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 5 # 数据集 6 X = 2*np.random.rand(100, 1) 7 y = 4+3*X+np.random.randn(100,1) 8 9 # X每个元素加1 10 X_b = np.c_[np.ones((100,1)), X] 11 theta_best = np.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(y) 12 13 # 训练 14 lin_reg = LinearRegression() 15 lin_reg.fit(X, y) 16 print(lin_reg.intercept_, lin_reg.coef_) 17 18 # 测试数据 19 X_new = np.array([[0],[2]]) 20 X_new_b = np.c_[np.ones((2,1)), X_new] 21 y_predict = X_new_b.dot(theta_best) 22 print(y_predict) 23 24 # 画图 25 plt.plot(X_new, y_predict, "r-") 26 plt.plot(X, y, "b.") 27 plt.axis([0,2,0,15]) 28 plt.show()
(2)Batch Gradient Descent
基本算是遍历了所有数据,不适用于数据规模大的数据
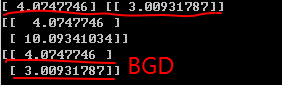
1 # BGD梯度下降 2 eta = 0.1 3 n_iterations = 1000 4 m = 100 5 theta = np.random.randn(2,1) 6 for iteration in range(n_iterations): 7 gradients = 2/m * X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y) 8 theta = theta - eta*gradients 9 print(theta)
(3)Stochastic Gradient Descent
可以避免局部最优结果,但是会震来震去。为了防止这种震荡,让学习速率η不断减小(类似模拟退火)
# SGD梯度下降 m = 100 n_epochs = 50 t0, t1 = 5, 50 # η初始值0.1 def learning_schedule(t): return t0 / (t + t1) theta = np.random.randn(2,1) # random initialization for epoch in range(n_epochs): for i in range(m): random_index = np.random.randint(m) xi = X_b[random_index:random_index+1] yi = y[random_index:random_index+1] gradients = 2 * xi.T.dot(xi.dot(theta) - yi) eta = learning_schedule(epoch * m + i) theta = theta - eta * gradients print(theta) # sklearn 提供了SGDRegressor的方法 from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressor sgd_reg = SGDRegressor(max_iter=50, penalty=None, eta0=0.1) sgd_reg.fit(X, y.ravel()) print(sgd_reg.intercept_, sgd_reg.coef_)
(4)Min-batch Gradient Descent
使用小批随机数据,结合SGD与BGD优点
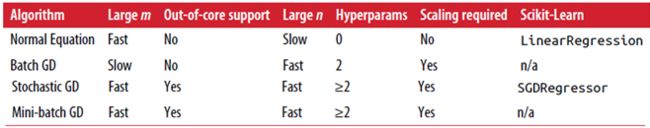
以下是各种方法对比
二、Polynomial Regression
但有的时候,y本身是由x取平方所得,无法找出来一条合适的线性回归线来拟合数据,该怎么办呢?
我们可以尝试将x取平方,取3次方等方法,多加尝试
三、误差分析
四、防止过拟合
用惩罚系数(penalty),即正则项(regularize the model)
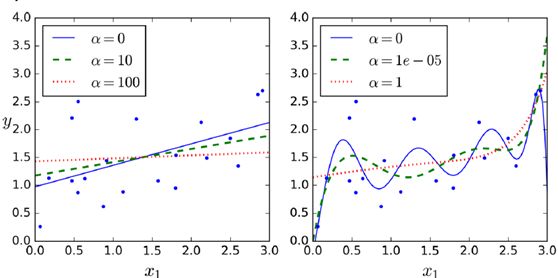
(1)岭回归ridge regression
控制参数自由度,减少模型复杂度。所控制的α=α![]() ,越大控制结果越强
,越大控制结果越强
优势:直接用公式可以计算出结果
1 from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge 2 ridge_reg = Ridge(alpha=1, solver="cholesky") 3 ridge_reg.fit(X, y)
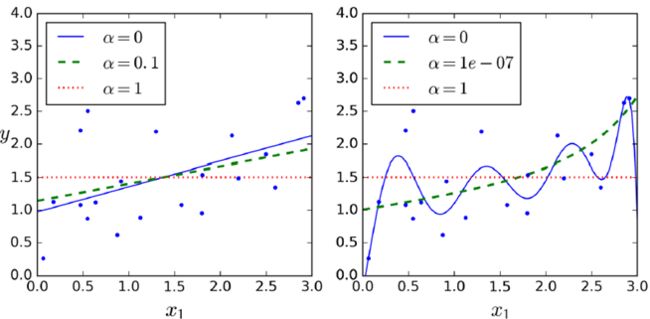
(2)Lasso Regression(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression)
正则化项同ridge regression不同,正则化的控制更强
1 # Lasso Regression 2 from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso 3 lasso_reg = Lasso(alpha=0.1) 4 lasso_reg.fit(X, y) 5 lasso_reg.predict([[1.5]])
对于高阶degree regularize尤为明显,是一个sparse model,很多高阶参数项成为了0
(3)Elastic Net(一般推荐使用)
相当于ridge和lasso regression的结合,用超参数r来控制其平衡
1 # Elastic Net 2 from sklearn.linear_model import ElasticNet 3 elastic_net = ElasticNet(alpha=0.1, l1_ratio=0.5) 4 elastic_net.fit(X, y)
(4)Early Stopping
找到开始上升的点,从那里停止(整体找到,取最优的)
1 from sklearn.base import clone 2 sgd_reg = SGDRegressor(n_iter=1, warm_start=True, penalty=None, 3 learning_rate="constant", eta0=0.0005) 4 minimum_val_error = float("inf") 5 best_epoch = None 6 best_model = None 7 for epoch in range(1000): 8 sgd_reg.fit(X_train_poly_scaled, y_train) # continues where it left off 9 y_val_predict = sgd_reg.predict(X_val_poly_scaled) 10 val_error = mean_squared_error(y_val_predict, y_val) 11 if val_error < minimum_val_error: 12 minimum_val_error = val_error 13 best_epoch = epoch 14 best_model = clone(sgd_reg)
五、Logistic Regression(可用作分类)
定义cost function,由于p在(0,1)之间,故最前面加一个符号,保证代价始终为正的。p值越大,整体cost越小,预测的越对
不存在解析解,故用偏导数计算
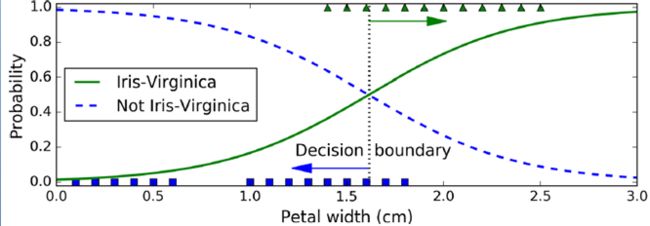
以Iris花的种类划分为例
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 2 from sklearn import datasets 3 iris = datasets.load_iris() 4 print(list(iris.keys())) 5 # ['DESCR', 'data', 'target', 'target_names', 'feature_names'] 6 X = iris["data"][:, 3:] # petal width 7 y = (iris["target"] == 2).astype(np.int) # 1 if Iris-Virginica, else 0 8 9 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 10 log_reg = LogisticRegression() 11 log_reg.fit(X, y) 12 X_new = np.linspace(0, 3, 1000).reshape(-1, 1) 13 # estimated probabilities for flowers with petal widths varying from 0 to 3 cm: 14 y_proba = log_reg.predict_proba(X_new) 15 16 plt.plot(X_new, y_proba[:, 1], "g-", label="Iris-Virginica") 17 plt.plot(X_new, y_proba[:, 0], "b--", label="Not Iris-Virginica") 18 plt.show() 19 # + more Matplotlib code to make the image look pretty
六、Softmax Regression
可以用做多分类
X = iris["data"][:, (2, 3)] # petal length, petal width y = iris["target"] softmax_reg = LogisticRegression(multi_class="multinomial",solver="lbfgs", C=10) softmax_reg.fit(X, y) print(softmax_reg.predict([[5, 2]])) # array([2]) print(softmax_reg.predict_proba([[5, 2]])) # array([[ 6.33134078e-07, 5.75276067e-02, 9.42471760e-01]])