章节目录
- Spring MVC DispatcherServlet 与 HttpServlet 关系类图
- Spring MVC 源码分析Request 请求映射、执行、视图解析流程
- 总结-Spring MVC 运行流程图
1.Spring MVC DispatcherServlet 与 HttpServlet 关系类图
1.1 什么是DispatcherServlet
源码注释如下所示:
Central dispatcher for HTTP request handlers/controllers, e.g. for web UI controllers or HTTP-based remote service exporters. Dispatches to registered handlers for processing a web request, providing convenient mapping and exception handling facilities.
译文如下:
DispatcherServlet 是HTTP请求处理程序/控制器的中央调度程序(将请求映射到具体处理器(handler)上 ),例如用于Web UI控制器或基于HTTP的远程服务导出器(webService),调度器会将请求路由至已经注册好的具体的hadler,使得handler可以处理执行相关的web请求,提供了请求与处理器之间的映射关系功能,其实就是路由映射功能。
1.2 什么是HttpServlet
HttpServlet 是处理相关基于Http请求的处理程序,请求的相关信息被封装成
HttpServletRequest对象,其中Service() 方法通过获取 HttpServletRequest 中的方法名 如GET、POST、PUT等 request-method信息的获取,去invoke具体的doGet()、doPost()、doPut()方法,最终将执行完业务逻辑获取到的处理数据通过HttpServletResponse对象返回给客户端。所以最终request请求结果还是从HttpServlet中的service()返回的
那么这两者之间有什么关系呢?
如下图所示DispatcherServlet与HttpServlet之间的类图关系:
其中最重要的是FrameworkServlet。
源码注释如下:
Base servlet for Spring's web framework. Provides integration with
a Spring application context, in a JavaBean-based overall solution.
译文如下:
Spring web 框架中的基础Servlet,将Spring 相关的ApplicationContext 集成进来。方便我们在后期使用Spring IOC 容器中注册的各种属性的类对象。
FrameworkServlet 整合Spring WebApplicationContext 对象源码如下:
/**
* Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet.
* Delegates to {@link #createWebApplicationContext} for actual creation
* of the context. Can be overridden in subclasses.
* @return the WebApplicationContext instance
* @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #setContextClass
* @see #setContextConfigLocation
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
...
return wac;
}
其中获取web应用程序上下文的代码段为:
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
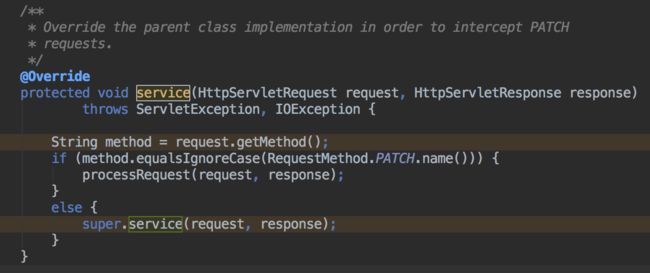
FrameworkServlet 对 extends 自 HttpServlet 的service()方法进行了override()
super.service()即调用HttpServlet中的Service()方法
可以看到Service()方法根据request.method 去调用具体的doxxx()方法,这里FrameworkServlet 对 doxxx()方法也进行了override()。
如下为FrameworkServlet 中doGet()方法源码
其中的processRequest()方法源码如下所示:
/**
* Process this request, publishing an event regardless of the outcome.
* The actual event handling is performed by the abstract
* {@link #doService} template method.
*/
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
}
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
- 其中最重要的是doService()方法,这个doService()方法被声明为抽象方法,在DispatcherServlet 做具体实现。
源码实现如下:
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap();
Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
//为请求设置具体的属性。
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try {
//调用doDispatch(),将请求分配给具体的handler去处理。实际上第二节会具体分析doDispatch()方法
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
1.3 Spring Web 对Request的执行流程
所以请求的整个执行流程依据之前的HttpServlet知识积累(未debug)可以大致总结如下(第二节会debug源码,用来验证我们总结的这个流程)
即:
1.请求到达dispatcherServlet,(非初次请求,初次请求会涉及dispatcherServlet初始化,调用init()方法)。
2.dispatcherServlet 执行service()方法,因Dispatcher类继承FrameworkServlet,所以调用父类的service()方法。
3.service()调用FrameworkServlet 中具体的doxxx()方法
4.FrameworkServlet 具体的 doxxx()方法调用processRequest()方法。
5.processRequest()方法调用dispatcherServlet 的 doService()方法。
6.dispatcherServlet 的 doService()方法调用doDispatch()方法。
注意:上述根方法-service()方法被servlet容器 Servlet container显示调用。
2.Spring MVC 源码分析Request 请求映射、执行、视图解析流程
简单的helloword级别的web项目,搭建方式可以略过。主要是debug开始的地方我们需要确定,因为有HttpServlet源码分析的积累,那么我们直接在DispatcherServlet中的Service方法中打断点就可以了,因为DispatcherServlet继承了FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet对HttpServlet中的service()方法进行了override,所以程序入口断点应该打在FrameworkServlet 中的service() 方法,接下来就是实操演示:
注意:本源码分析的是Spring 4.1版本
2.0 debug的目的
了解 request 到具体 handler 的执行流程。
2.1 FrameworkServlet 中 service() 打断点
2.2 开启debug模式
2.3 开始debug
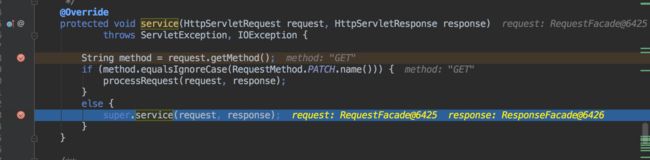
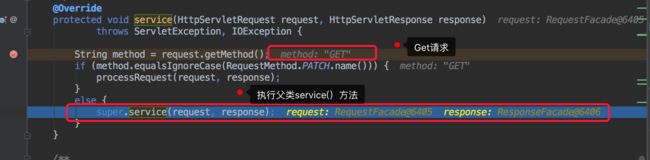
执行父类service()方法
执行doGet()方法
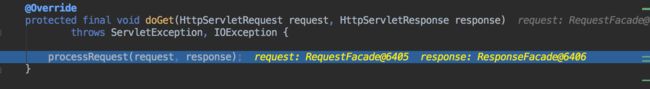
执行processRequest()方法
执行doService()方法
执行doDispatch方法
获取请求对应的handler
继续debug hm.getHandler(request)看看这其中发生了什么?
通过SimpleUrlHandlerMapping, 发现并不能获取到 对应的 handler(HandlerExcutionChain对象),
继续foreach
通过EndpointHandlerMapping, 发现并不能获取到 对应的 handler(HandlerExcutionChain对象),
继续foreach
最终我们通过RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象获取到了对应的handler对象。
可以看下handler对象是什么东东?
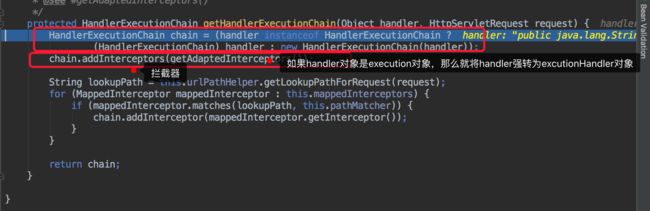
所以handlerExcutionChain 对象 包含有handler对象、interceptor对象。
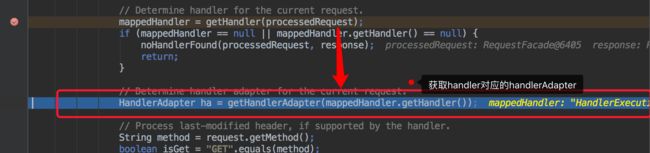
到此我们通过requestMappingHandlerMapping 获取到了请求对应的handler。
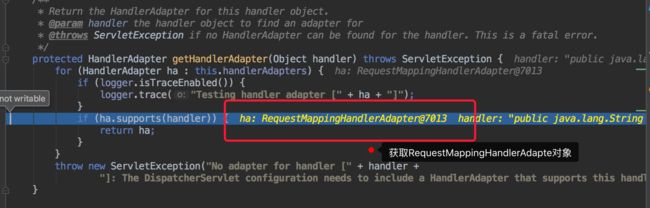
接下来需要以handler为参数获取真正处理请求的handlerAdaptor
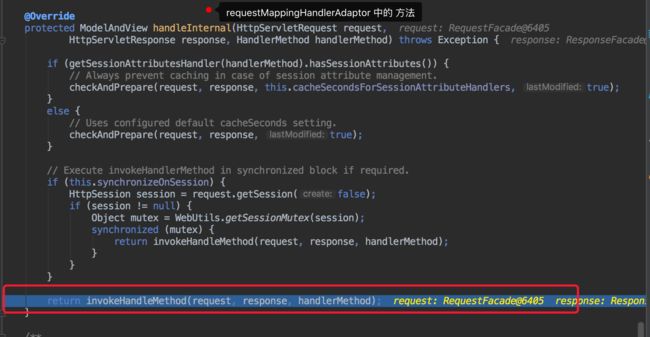
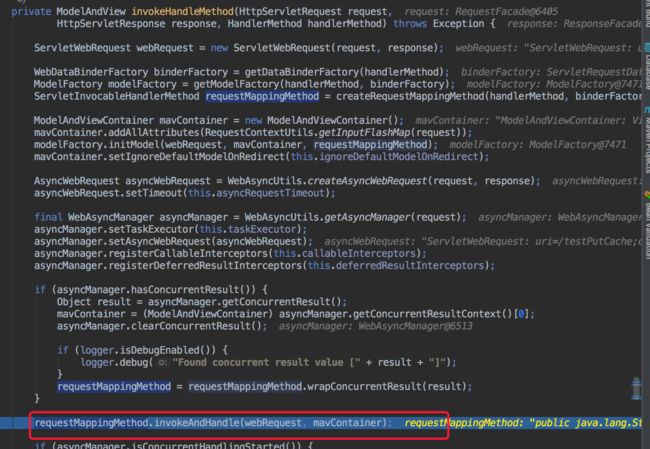
接下来执行 handlerAdaptor 中 handler()方法
返回mv,需要注意的是,返回mv 其实是对Controller 中业务方法的调用其实使用到了反射。
注意在返回mv之前 通过handlerExcutionChain对象可以调用applyPreHandler 方法,可以在返回mv之前做预先处理工作。
返回mv之后,可以通过handlerExcutionChain对象可以调用applyPreHandler 方法对返回的mv做修改。我们只需要实现 handlerInterceptor类并实现配置就可以了。
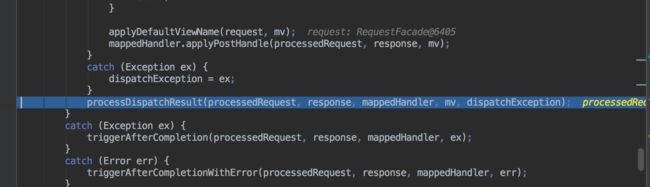
最后一步执行视图渲染的工作,这一步是在dispatcherServlet中完成的。
最终请求结果
注意:由于返回结果为String 类型的value,不涉及视图解析,所以render 方法并没有执行。
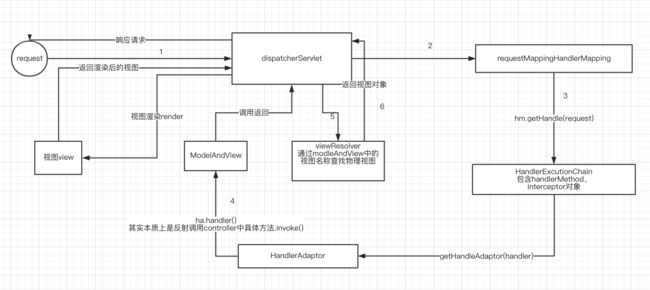
3.总结-Spring MVC 运行流程图
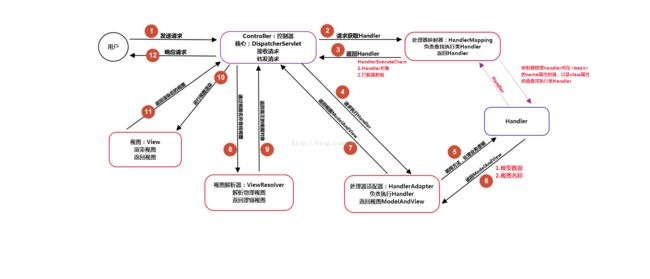
对上述流程图的解释:
- 用户发起请求到前端控制器(Controller)
- 前端控制器没有处理业务逻辑的能力,需要找到具体的模型对象处理(Handler),到处理器映射器(HandlerMapping)中查找Handler对象(Model)。
- HandlerMapping返回执行链,包含了2部分内容: ① Handler对象、② 拦截器数组
- 前端处理器通过处理器适配器包装后执行Handler对象。
- 处理业务逻辑。
- Handler处理完业务逻辑,返回ModelAndView对象,其中view是视图名称,不是真正的视图对象。
- 将ModelAndView返回给前端控制器。
- 视图解析器(ViewResolver)返回真正的视图对象(View)。
- (此时前端控制器中既有视图又有Model对象数据)前端控制器根据模型数据和视图对象,进行视图渲染。
- 返回渲染后的视图(html/json/xml)返回。
- 给用户产生响应。