- 设计模式 23 访问者模式
WineMonk
#设计模式设计模式访问者模式
设计模式23创建型模式(5):工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、单例模式、建造者模式、原型模式结构型模式(7):适配器模式、桥接模式、组合模式、装饰者模式、外观模式、享元模式、代理模式行为型模式(11):责任链模式、命令模式、解释器模式、迭代器模式、中介者模式、备忘录模式、观察者模式、状态模式、策略模式、模板方法模式、访问者模式文章目录设计模式23访问者模式(VisitorPattern)1定义2结构3
- Android面试从新手到架构师,一篇解析就够(1),跳槽字节跳动
m0_60607609
程序员androidjava面试后端
5.抽象工厂模式:结构型(7):描述如何将类或对象按某种规则组成更大的结构1.桥接模式:对于两个或以上纬度独立变化的场景,将抽象与具体实现分离,实例:用不同颜色画不同形状2.外观模式:对外有一个统一接口,外部不用关心内部子系统的具体实现,这是"迪米特原则"的典型应用3.适配器模式:改变类的接口,使原本由于接口不匹配而无法一起工作的两个类能够在一工作,实例:RecycleView的Adapter不管
- Java基础 --- 多线程&JUC,以及一些常用的设计模式总结
lzhlizihang
java设计模式
文章目录一、多线程1、线程和进程的区别2、创建多线程的四种方式3、集合中的线程安全二、设计模式1、单例模式2、装饰者模式(IO流缓冲流)3、适配器模式4、模板模式一、多线程1、线程和进程的区别进程是操作系统资源分配的基本单位,而线程是处理器任务调度和执行的基本单位,一个进程可以运行多个线程多进程:操作系统中同时运行的多个程序多线程:在同一个进程中同时运行的多个任务2、创建多线程的四种方式Runna
- Java设计模式之单例模式/饿汉式/懒汉式/DCL双重检测锁模式/静态内部类实现单例模式/使用反射破坏单例模式/枚举类实现单例模式
ZaynFox
#JavaSE
一、概念设计模式:是在大量的实践中总结和理论化之后优选的代码结构、编程风格、以及解决问题的思考方式。设计模式就像是经典的棋谱,不同的棋局,我们用不同的棋谱,免去我们自己再思考和摸索。共有23种设计模式:创建型模式,共5种:工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、单例模式、建造者模式、原型模式。结构型模式,共7种:适配器模式、装饰器模式、代理模式、外观模式、桥接模式、组合模式、享元模式。行为型模式,共11种:策
- Unity3d学习笔记
明月海子
Mecanin动画系统.pngNavigation导航系统.pngShader渲染基础.png面向对象六大原则.png策略模式Strategy.png工厂模式Factory产品工厂.png观察者Observer.png结构设计模式总结.png模板方法模式TemplateMethod.png适配器模式Adapter.png外观模式Facade.png职责连模式ChainofResponsibilit
- 软考 - 系统架构设计师 - 设计模式
小林想被监督学习
系统架构设计师系统架构设计模式
目录概念创建型设计模式抽象工厂模式(AbstractFactoryPattern)优点缺点应用场景总结构建器模式(BuilderPattern)优点缺点应用场景工厂方法模式(factorymethod)优点缺点应用场景原型模式(prototype)优点缺点应用场景单例模式(Singleton)优点缺点应用场景结构型设计模式适配器模式(Adapter)优点缺点应用场景桥接模式(Bridge)优点缺点
- java设计模式---中介者模式
奔跑的扫地僧
Java设计模式java
首先我们了解下设计模式的总览:GoF提出的设计模式总共有23种,根据目的准则分类分为三大类:创建型模式,共五种:单例模式、工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、建造者模式、原型模式。结构型模式,共七种:适配器模式、装饰模式、代理模式、外观模式、桥接模式、组合模式、享元模式。行为型模式,共十一种:策略模式、模板方法模式、观察者模式、迭代器模式、责任链模式、命令模式、备忘录模式、状态模式、访问者模式、中介者模式
- 2024最新Android大厂面试真题大全(附答案)
imtokenmax合约众筹
2024年程序员面试android面试职场和发展
五、架构设计和设计模式1.谈谈你对Android设计模式的理解2.MVCMVPMVVM原理和区别3.你所知道的设计模式有哪些?4.项目中常用的设计模式5.手写生产者/消费者模式6.写出观察者模式的代码7.适配器模式,装饰者模式,外观模式的异同?8.用到的一些开源框架,介绍一个看过源码的,内部实现过程。9.谈谈对RxJava的理解10.Rxjava发送事件步骤11.RxJava的作用,与平时使用的异
- 软考-常见的23种设计模式整理
ppliu600
软件架构数据仓库数据库数据挖掘
参考:23种设计模式总结设计模式可以将复用别人的解决方案。一、设计模式的分类创建型模式,共5种:单例模式、工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、建造者模式、原型模式。结构型模式,共7种:适配器模式、组合模式、代理模式、享元模式、外观模式、桥接模式、装饰器模式、行为型模式,共11种:观察者模式、策略模式、模板方法模式、迭代子模式、责任链模式、命令模式、备忘录模式、状态模式、访问者模式、中介者模式、解释器模式。
- 【小结】利用filter做统一编码转换
桌面很乱
思路一:静态代理在filter中做一个内部类继承HttpServletRequestWrapper(此类采用了适配器模式,全部方法均为引用构造方法中传递的ServletRequest),进行静态代理(装饰者模式)。注意区分get和post请求的编码处理方式。加强(重写)request.getParameter(Stringkey),最后将包装过的request对象(MyRequest)传递给ser
- Python之最常用的16种设计模式
ModelBulider
Python基础(千锋篇)python设计模式javascript
文章目录一、设计模式与面向对象介绍1.1设计模式1.2复习:面向对象1.3接口二、面向对象设计SOLID原则三、设计模式分类四、创造型模式4.1简单工厂模式4.2工厂方法模式4.3抽象工厂模式4.4建造者模式4.5单例模式4.6创建型模式小结五、结构型模式5.1适配器模式5.2桥模式5.3组合模式5.4外观模式5.5代理模式六、行为型模式6.1责任链模式6.2观察者模式6.3策略模式6.4模板方法
- 深入解析:23种软件设计模式详解及其分类(创建型、结构型、行为型)附代码示例DEMO
J^T
设计模式C/C++设计模式装饰器模式组合模式观察者模式单例模式23种设计模式
目录引言一、创建型模式1.简单工厂模式(SimpleFactoryPattern)2.抽象工厂模式(AbstractFactoryPattern)3.单例模式(SingletonPattern)4.建造者模式(BuilderPattern)5.原型模式(PrototypePattern)二、结构型模式1.适配器模式(AdapterPattern)2.桥接模式(BridgePattern)3.装饰器
- 【设计模式】第四章:原型模式详解及应用案例
Bummon.
设计模式原型模式设计模式
系列文章【设计模式】七大设计原则【设计模式】第一章:单例模式【设计模式】第二章:工厂模式【设计模式】第三章:建造者模式【设计模式】第四章:原型模式【设计模式】第五章:适配器模式【设计模式】第六章:装饰器模式【设计模式】第七章:代理模式【设计模式】第八章:桥接模式【设计模式】第九章:外观模式/门面模式【设计模式】第十章:组合模式【设计模式】第十一章:享元模式【设计模式】第十二章:观察者模式【设计模式
- 八、适配器模式
磊-
设计模式适配器模式
适配器模式(AdapterPattern)是一种结构型设计模式,它允许不兼容的接口之间进行合作。适配器模式通过创建一个适配器类来转换一个接口的接口,使得原本由于接口不兼容无法一起工作的类可以一起工作。
- 设计模式总结:适配器、桥接、组合和迭代器模式
空青726
设计模式迭代器模式java后端架构面试考研
在之前的对话中,我们讨论了五种常见的Java设计模式:单例、工厂、策略、装饰器和观察者模式。现在,让我们继续探索其他四种设计模式:适配器、桥接、组合和迭代器模式。适配器模式概念:适配器模式是一种结构型设计模式,用于将一个类的接口转换为另一个类期望的接口。适配器模式可以让原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的类可以进行交互。使用场景:当你需要将一个类的接口转换为另一个类期望的接口时。当你想要重用一些现有
- 初识Java设计模式学习
「已注销」
Java设计模式eclipsejava设计模式springstruts
Title:Java设计模式学习Author:ychhh_文章目录@[toc]设计模式概述设计模式目的七大原则单一职责原则接口隔离原则依赖倒转原则(面向接口编程)里氏替换原则开闭原则迪米特法则合成复用原则UML类图设计模式基本概念单例模式饿汉式懒汉式双重检查静态内部类枚举类单例模式注意工厂模式简单工厂模式工厂方法模式抽象工厂模式原型模式建造者模式适配器模式对象适配器接口适配器(缺省适配器模式)桥接
- 设计模式-结构性模式
$驽马十驾$
设计模式
结构型模式1.适配器模式(AdapterPattern)2.桥接模式(BridgePattern)3.装饰器模式(DecoratorPattern)步骤1:定义咖啡接口步骤2:具体的咖啡类步骤3:装饰器抽象类步骤4:具体的装饰器类步骤5:使用装饰器4.组合模式(CompositePattern)4.1定义组件接口4.2实现基本的图形4.3实现复合图形4.4客户端代码5.外观模式(FacadePat
- 设计模式 15 解释器模式
WineMonk
#设计模式设计模式解释器模式
设计模式15创建型模式(5):工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、单例模式、建造者模式、原型模式结构型模式(7):适配器模式、桥接模式、组合模式、装饰者模式、外观模式、享元模式、代理模式行为型模式(11):责任链模式、命令模式、解释器模式、迭代器模式、中介者模式、备忘录模式、观察者模式、状态模式、策略模式、模板方法模式、访问者模式文章目录设计模式15解释器模式(InterpreterPattern)1定义
- 设计模式 18 备忘录模式
WineMonk
#设计模式设计模式备忘录模式
设计模式18创建型模式(5):工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、单例模式、建造者模式、原型模式结构型模式(7):适配器模式、桥接模式、组合模式、装饰者模式、外观模式、享元模式、代理模式行为型模式(11):责任链模式、命令模式、解释器模式、迭代器模式、中介者模式、备忘录模式、观察者模式、状态模式、策略模式、模板方法模式、访问者模式文章目录设计模式18备忘录模式(MementoPattern)1定义2结构3
- 23种设计模式(GOF)
gb4215287
javajava
设计模式(GOF)分为三种类型,共23类。1、单例模式(Singleton)2、原型模式(Prototype)简单工厂模式(SimpleFactoryMode)3、工厂方法模式(FactoryMethod)4、抽象工厂模式(AbstractFactory)5、建造者模式(Builder)6、代理模式(Proxy)7、适配器模式(Adapter)8、桥接模式(Bridge)9、装饰器模式(Decor
- 设计模式- 代理模式(Proxy Pattern)结构|原理|优缺点|场景|示例
TsengOnce
设计模式设计模式代理模式
设计模式(分类)设计模式(六大原则)创建型(5种)工厂方法抽象工厂模式单例模式建造者模式原型模式结构型(7种)适配器模式装饰器模式代理模式外观模式桥接模式组合模式享元模式行为型(11种)策略模式模板方法模式观察者模式迭代器模式责任链模式命令模式备忘录模式状态模式访问者模式中介者模式代理模式(ProxyPattern)是一种结构型设计模式,它为其他对象(被代理对象)提供一个代理对象,并由代理对象控制
- 简谈设计模式之适配器模式
Yonagi833
设计模式设计模式适配器模式java
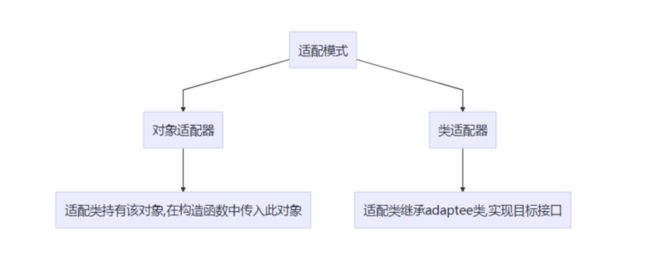
适配器模式是结构型设计模式之一,用于将一个类的接口转换成客户期望的另一个接口.通过使用适配器模式,原本由于接口不兼容而无法一起工作的类可以协同工作适配器模式通常有两种实现方式类适配器模式(ClassAdapterPattern):使用继承来实现适配器。**对象适配器模式(ObjectAdapterPattern)**:使用组合来实现适配器。适配器模式结构目标接口:当前系统业务所期待的接口,可以是抽
- 设计模式 11 享元模式
WineMonk
#设计模式设计模式享元模式
设计模式11创建型模式(5):工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、单例模式、建造者模式、原型模式结构型模式(7):适配器模式、桥接模式、组合模式、装饰者模式、外观模式、享元模式、代理模式行为型模式(11):责任链模式、命令模式、解释器模式、迭代器模式、中介者模式、备忘录模式、观察者模式、状态模式、策略模式、模板方法模式、访问者模式文章目录设计模式11享元模式(FlyweightPattern)1定义2结构
- 结构型模式:代理/适配器/装饰者/桥接/外观模式
架构师成长进阶空间
外观模式
5,结构型模式结构型模式描述如何将类或对象按某种布局组成更大的结构。它分为类结构型模式和对象结构型模式,前者采用继承机制来组织接口和类,后者釆用组合或聚合来组合对象。由于组合关系或聚合关系比继承关系耦合度低,满足“合成复用原则”,所以对象结构型模式比类结构型模式具有更大的灵活性。结构型模式分为以下7种:代理模式适配器模式装饰者模式桥接模式外观模式组合模式享元模式5.1代理模式5.1.1概述由于某些
- 【Java设计模式】Java 中的适配器模式:无缝集成不兼容系统
道长不会写代码
Java设计模式java设计模式适配器模式
文章目录Java中的适配器模式:无缝集成不兼容系统一、概述二、适配器设计模式的别名三、适配器设计模式的意图四、适配器模式的详细解释及实际示例五、Java中适配器模式的编程示例六、Java中何时使用适配器模式七、适配器模式的优点和权衡八、Java中适配器模式的实际应用九、源码下载Java中的适配器模式:无缝集成不兼容系统一、概述在Java开发中,适配器模式(AdapterPattern)是一种非常有
- 游戏开发设计模式之原型模式
Ctrl+CV九段手
游戏开发设计模式设计模式原型模式pythonjavac++c#游戏开发
目录原型模式的实现步骤原型模式的优点原型模式的应用场景总结原型模式在游戏开发中的具体应用案例是什么?如何在不同编程语言中实现原型模式?JavaC#PythonC++JavaScript原型模式与其他创建型设计模式(如建造者模式、适配器模式)的比较优劣是什么?原型模式的优点:原型模式的缺点:建造者模式的优点:建造者模式的缺点:适配器模式的优点:适配器模式的缺点:总结:在大型游戏项目中,原型模式对开发
- 设计模式(Kotlin)
找藉口是失败者的习惯
设计模式kotlin开发语言
设计模式创造型设计模式(5种)1、工厂方法模式2、抽象工厂模式3、单例模式4、建造者模式5、原型模式结构型设计模式(7种)1、适配器模式2、桥接模式3、组合模式4、装饰者模式5、外观模式6、享元模式7、代理模式行为型模式(11种)1、模板方法模式2、策略模式3、状态模式4、观察者模式5、备忘录模式6、迭代器模式7、访问者模式8、解释器模式9、责任链模式10、命令模式11、中介者模式以下我会以And
- 【Kotlin设计模式】Kotlin实现适配器模式
一方贝地
Kotlin设计模式kotlin设计模式适配器模式
前言适配器模式(AdapterPattern)的核心将某个类的接口转换成客户端期望的另一个接口表示,使得客户端能够通过自己期望的接口与不兼容的类进行交互。适配器模式有三种实现方式,分别是类适配器模式、对象适配器模式、接口适配器模式。我们假设有个视频输出盒子,当前只能接收和输出HDMI信号,现在客户的输入设备只能输出VGA信号,则我们可以通过转换器(要适配的类),将VGA信号转换成HDMI信号做输出
- Java 22种设计模式详解
冲上云霄的Jayden
Javajava设计模式单例模式工程模式代理模式适配器模式桥接模式
22种设计模式详解创建型模式单例模式工厂方法模式抽象工厂模式建造者模式原型模式结构型模式适配器模式桥接模式组合模式装饰器模式装饰器模式与桥接模式代理模式代理模式与装饰器模式外观模式享元模式享元模式原理:享元模式角色:示例代码:行为型模式模板方法模式原理角色示例代码命令模式迭代器模式观察者模式中介者模式备忘录模式解释器模式状态模式策略模式访问者模式设计模式通常分为三类:创建型(Creational)
- 设计模式 7 桥接模式
WineMonk
#设计模式设计模式桥接模式
设计模式7创建型模式(5):工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、单例模式、建造者模式、原型模式结构型模式(7):适配器模式、桥接模式、组合模式、装饰者模式、外观模式、享元模式、代理模式行为型模式(11):责任链模式、命令模式、解释器模式、迭代器模式、中介者模式、备忘录模式、观察者模式、状态模式、策略模式、模板方法模式、访问者模式文章目录设计模式7桥接模式(BridgePattern)1定义2结构3示例代码
- sql统计相同项个数并按名次显示
朱辉辉33
javaoracle
现在有如下这样一个表:
A表
ID Name time
------------------------------
0001 aaa 2006-11-18
0002 ccc 2006-11-18
0003 eee 2006-11-18
0004 aaa 2006-11-18
0005 eee 2006-11-18
0004 aaa 2006-11-18
0002 ccc 20
- Android+Jquery Mobile学习系列-目录
白糖_
JQuery Mobile
最近在研究学习基于Android的移动应用开发,准备给家里人做一个应用程序用用。向公司手机移动团队咨询了下,觉得使用Android的WebView上手最快,因为WebView等于是一个内置浏览器,可以基于html页面开发,不用去学习Android自带的七七八八的控件。然后加上Jquery mobile的样式渲染和事件等,就能非常方便的做动态应用了。
从现在起,往后一段时间,我打算
- 如何给线程池命名
daysinsun
线程池
在系统运行后,在线程快照里总是看到线程池的名字为pool-xx,这样导致很不好定位,怎么给线程池一个有意义的名字呢。参照ThreadPoolExecutor类的ThreadFactory,自己实现ThreadFactory接口,重写newThread方法即可。参考代码如下:
public class Named
- IE 中"HTML Parsing Error:Unable to modify the parent container element before the
周凡杨
html解析errorreadyState
错误: IE 中"HTML Parsing Error:Unable to modify the parent container element before the child element is closed"
现象: 同事之间几个IE 测试情况下,有的报这个错,有的不报。经查询资料后,可归纳以下原因。
- java上传
g21121
java
我们在做web项目中通常会遇到上传文件的情况,用struts等框架的会直接用的自带的标签和组件,今天说的是利用servlet来完成上传。
我们这里利用到commons-fileupload组件,相关jar包可以取apache官网下载:http://commons.apache.org/
下面是servlet的代码:
//定义一个磁盘文件工厂
DiskFileItemFactory fact
- SpringMVC配置学习
510888780
springmvc
spring MVC配置详解
现在主流的Web MVC框架除了Struts这个主力 外,其次就是Spring MVC了,因此这也是作为一名程序员需要掌握的主流框架,框架选择多了,应对多变的需求和业务时,可实行的方案自然就多了。不过要想灵活运用Spring MVC来应对大多数的Web开发,就必须要掌握它的配置及原理。
一、Spring MVC环境搭建:(Spring 2.5.6 + Hi
- spring mvc-jfreeChart 柱图(1)
布衣凌宇
jfreechart
第一步:下载jfreeChart包,注意是jfreeChart文件lib目录下的,jcommon-1.0.23.jar和jfreechart-1.0.19.jar两个包即可;
第二步:配置web.xml;
web.xml代码如下
<servlet>
<servlet-name>jfreechart</servlet-nam
- 我的spring学习笔记13-容器扩展点之PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
aijuans
Spring3
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer是个bean工厂后置处理器的实现,也就是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的一个实现。关于BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor类似。我会在其他地方介绍。PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer可以将上下文(配置文件)中的属性值放在另一个单独的标准java P
- java 线程池使用 Runnable&Callable&Future
antlove
javathreadRunnablecallablefuture
1. 创建线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
2. 执行一次线程,调用Runnable接口实现
Future<?> future = executorService.submit(new DefaultRunnable());
System.out.prin
- XML语法元素结构的总结
百合不是茶
xml树结构
1.XML介绍1969年 gml (主要目的是要在不同的机器进行通信的数据规范)1985年 sgml standard generralized markup language1993年 html(www网)1998年 xml extensible markup language
- 改变eclipse编码格式
bijian1013
eclipse编码格式
1.改变整个工作空间的编码格式
改变整个工作空间的编码格式,这样以后新建的文件也是新设置的编码格式。
Eclipse->window->preferences->General->workspace-
- javascript中return的设计缺陷
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJS
代码1:
<script>
var gisService = (function(window)
{
return
{
name:function ()
{
alert(1);
}
};
})(this);
gisService.name();
&l
- 【持久化框架MyBatis3八】Spring集成MyBatis3
bit1129
Mybatis3
pom.xml配置
Maven的pom中主要包括:
MyBatis
MyBatis-Spring
Spring
MySQL-Connector-Java
Druid
applicationContext.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
&
- java web项目启动时自动加载自定义properties文件
bitray
javaWeb监听器相对路径
创建一个类
public class ContextInitListener implements ServletContextListener
使得该类成为一个监听器。用于监听整个容器生命周期的,主要是初始化和销毁的。
类创建后要在web.xml配置文件中增加一个简单的监听器配置,即刚才我们定义的类。
<listener>
<des
- 用nginx区分文件大小做出不同响应
ronin47
昨晚和前21v的同事聊天,说到我离职后一些技术上的更新。其中有个给某大客户(游戏下载类)的特殊需求设计,因为文件大小差距很大——估计是大版本和补丁的区别——又走的是同一个域名,而squid在响应比较大的文件时,尤其是初次下载的时候,性能比较差,所以拆成两组服务器,squid服务于较小的文件,通过pull方式从peer层获取,nginx服务于较大的文件,通过push方式由peer层分发同步。外部发布
- java-67-扑克牌的顺子.从扑克牌中随机抽5张牌,判断是不是一个顺子,即这5张牌是不是连续的.2-10为数字本身,A为1,J为11,Q为12,K为13,而大
bylijinnan
java
package com.ljn.base;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class ContinuousPoker {
/**
* Q67 扑克牌的顺子 从扑克牌中随机抽5张牌,判断是不是一个顺子,即这5张牌是不是连续的。
* 2-10为数字本身,A为1,J为1
- 翟鸿燊老师语录
ccii
翟鸿燊
一、国学应用智慧TAT之亮剑精神A
1. 角色就是人格
就像你一回家的时候,你一进屋里面,你已经是儿子,是姑娘啦,给老爸老妈倒怀水吧,你还觉得你是老总呢?还拿派呢?就像今天一样,你们往这儿一坐,你们之间是什么,同学,是朋友。
还有下属最忌讳的就是领导向他询问情况的时候,什么我不知道,我不清楚,该你知道的你凭什么不知道
- [光速与宇宙]进行光速飞行的一些问题
comsci
问题
在人类整体进入宇宙时代,即将开展深空宇宙探索之前,我有几个猜想想告诉大家
仅仅是猜想。。。未经官方证实
1:要在宇宙中进行光速飞行,必须首先获得宇宙中的航行通行证,而这个航行通行证并不是我们平常认为的那种带钢印的证书,是什么呢? 下面我来告诉
- oracle undo解析
cwqcwqmax9
oracle
oracle undo解析2012-09-24 09:02:01 我来说两句 作者:虫师收藏 我要投稿
Undo是干嘛用的? &nb
- java中各种集合的详细介绍
dashuaifu
java集合
一,java中各种集合的关系图 Collection 接口的接口 对象的集合 ├ List 子接口 &n
- 卸载windows服务的方法
dcj3sjt126com
windowsservice
卸载Windows服务的方法
在Windows中,有一类程序称为服务,在操作系统内核加载完成后就开始加载。这里程序往往运行在操作系统的底层,因此资源占用比较大、执行效率比较高,比较有代表性的就是杀毒软件。但是一旦因为特殊原因不能正确卸载这些程序了,其加载在Windows内的服务就不容易删除了。即便是删除注册表中的相 应项目,虽然不启动了,但是系统中仍然存在此项服务,只是没有加载而已。如果安装其他
- Warning: The Copy Bundle Resources build phase contains this target's Info.plist
dcj3sjt126com
iosxcode
http://developer.apple.com/iphone/library/qa/qa2009/qa1649.html
Excerpt:
You are getting this warning because you probably added your Info.plist file to your Copy Bundle
- 2014之C++学习笔记(一)
Etwo
C++EtwoEtwoiterator迭代器
已经有很长一段时间没有写博客了,可能大家已经淡忘了Etwo这个人的存在,这一年多以来,本人从事了AS的相关开发工作,但最近一段时间,AS在天朝的没落,相信有很多码农也都清楚,现在的页游基本上达到饱和,手机上的游戏基本被unity3D与cocos占据,AS基本没有容身之处。so。。。最近我并不打算直接转型
- js跨越获取数据问题记录
haifengwuch
jsonpjsonAjax
js的跨越问题,普通的ajax无法获取服务器返回的值。
第一种解决方案,通过getson,后台配合方式,实现。
Java后台代码:
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String ca
- 蓝色jQuery导航条
ini
JavaScripthtmljqueryWebhtml5
效果体验:http://keleyi.com/keleyi/phtml/jqtexiao/39.htmHTML文件代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>jQuery鼠标悬停上下滑动导航条 - 柯乐义<
- linux部署jdk,tomcat,mysql
kerryg
jdktomcatlinuxmysql
1、安装java环境jdk:
一般系统都会默认自带的JDK,但是不太好用,都会卸载了,然后重新安装。
1.1)、卸载:
(rpm -qa :查询已经安装哪些软件包;
rmp -q 软件包:查询指定包是否已
- DOMContentLoaded VS onload VS onreadystatechange
mutongwu
jqueryjs
1. DOMContentLoaded 在页面html、script、style加载完毕即可触发,无需等待所有资源(image/iframe)加载完毕。(IE9+)
2. onload是最早支持的事件,要求所有资源加载完毕触发。
3. onreadystatechange 开始在IE引入,后来其它浏览器也有一定的实现。涉及以下 document , applet, embed, fra
- sql批量插入数据
qifeifei
批量插入
hi,
自己在做工程的时候,遇到批量插入数据的数据修复场景。我的思路是在插入前准备一个临时表,临时表的整理就看当时的选择条件了,临时表就是要插入的数据集,最后再批量插入到数据库中。
WITH tempT AS (
SELECT
item_id AS combo_id,
item_id,
now() AS create_date
FROM
a
- log4j打印日志文件 如何实现相对路径到 项目工程下
thinkfreer
Weblog4j应用服务器日志
最近为了实现统计一个网站的访问量,记录用户的登录信息,以方便站长实时了解自己网站的访问情况,选择了Apache 的log4j,但是在选择相对路径那块 卡主了,X度了好多方法(其实大多都是一样的内用,还一个字都不差的),都没有能解决问题,无奈搞了2天终于解决了,与大家分享一下
需求:
用户登录该网站时,把用户的登录名,ip,时间。统计到一个txt文档里,以方便其他系统调用此txt。项目名
- linux下mysql-5.6.23.tar.gz安装与配置
笑我痴狂
mysqllinuxunix
1.卸载系统默认的mysql
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa | grep mysql
mysql-libs-5.1.66-2.el6_3.x86_64
mysql-devel-5.1.66-2.el6_3.x86_64
mysql-5.1.66-2.el6_3.x86_64
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -e mysql-libs-5.1