ES6 中的Class
基本用法
ES5 的写法
function Point(x, y) {
this.x = x; this.y = y; } Point.prototype.toString = function () { return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')'; }; var p = new Point(1, 2);ES6 的写法
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x; this.y = y; } toString() { return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')'; } }在类的实例上面调用方法,其实就是调用原型上的方法。
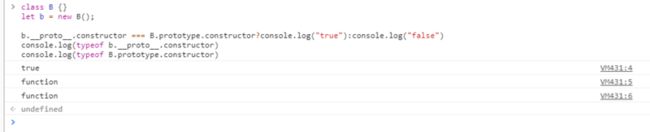
class B {}
let b = new B(); b.__proto__.constructor === B.prototype.constructor?console.log("true"):console.log("false") console.log(typeof b.__proto__.constructor) console.log(typeof B.prototype.constructor)注:类的内部所有定义的方法,都是不可枚举的
constructor 方法
constructor方法是类的默认方法,通过new命令生成对象实例时,自动调用该方法。一个类必须有constructor方法,如果没有显式定义,一个空的constructor方法会被默认添加。
注意点
-
constructor方法默认返回实例对象(即this),完全可以指定返回另外一个对象。
class Foo { constructor() { return Object.create(null); } } new Foo() instanceof Foo // false
-
类必须使用new调用,否则会报错。
class book{ constructor(){ this._year=2004; this.edition=1; } get year(){ return this._year; } set year(newVal){ if(newVal>2004){ this._year=newVal; this.edition+=newVal-2004; } } } let b=new book(); b.year = 2004; //2 console.log(b.edition);
取值函数(getter)和存值函数(setter)
class book{
constructor(){
this._year=2004; this.edition=1; } get year(){ return this._year; } set year(newVal){ if(newVal>2004){ this._year=newVal; this.edition+=newVal-2004; } } } let b=new book(); b.year = 2004; //2 console.log(b.edition);