SpringBoot进阶
1. Idea springBoot多模块
1.1 parent:管理版本
<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId> <version>2.0.5.RELEASEversion> <type>pomtype> <scope>importscope> dependency> dependencies> dependencyManagement>
1.2 子模块
指定父模块
<parent> <groupId>cn.dyiergroupId> <artifactId>springboot-parentartifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion> parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> dependencies>
1.3 打包运行
<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId> <configuration> <mainClass>cn.itsource.AppmainClass> configuration> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>repackagegoal> goals> execution> executions> plugin> plugins> build>
2. SpringBoot配置
2.1 yml基本语法
k:(空格)v:表示一对键值对(空格必须有);
以空格的缩进来控制层级关系;只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的
server:
port: 8081
path: /hello
属性和值也是大小写敏感;
2.2 yml值的语法
1)字面量:普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔)
k: v:字面直接来写;
字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号;
"":双引号;不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符;特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思
name: "zhangsan \n lisi":输出;zhangsan 换行 lisi
'':单引号;会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
name: ‘zhangsan \n lisi’:输出;zhangsan \n lisi
2)k: v:在下一行来写对象的属性和值的关系;注意缩进
对象还是k: v的方式
friends:
lastName: zhangsan
age: 20
3)数组(List、Set):
用- 值表示数组中的一个元素
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
2.2 读取配置文件
1) 读取单个值:
@Vaule(“${对象.字段}”)
@Value("${person.lastName}")
2) 批量注入配置文件中的属性
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “对象”)
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
3) @ConfigurationProrperties 与 @Vaule的区别
2.3 读取指定的properties配置文件
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:person.properties")
2.4 profile多环境支持
1) 定义多套环境
---
server:
port: 8080
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles: test
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: prod
2) 启用默认环境
spring:
profiles:
active: test
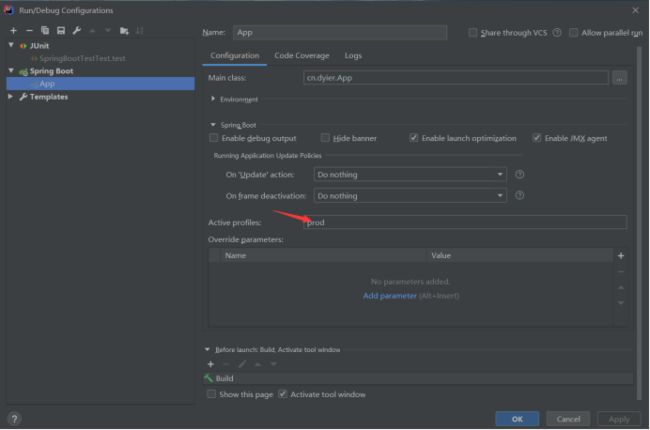
3) idea开发时切换环境
4) 打包时启动时切换环境
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod
3. springBoot测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = App.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = App.class) //这是一个Spring测试,会加载该类的包及子子孙孙包里面的类