在 App 中,如果分享、发布、上传功能涉及到图片,必不可少会对图片进行一定程度的压缩。笔者最近在公司项目中恰好重构了双端(iOS&Android)的图片压缩模块。本文会非常基础的讲解一些图片压缩的方式和思路。
图片格式基础
点阵图&矢量图
- 点阵图:也叫位图。用像素为单位,像素保存颜色信息,排列像素实现显示。
- 矢量图:记录元素形状和颜色的算法,显示时展示算法运算的结果。
颜色
表示颜色时,有两种形式,一种为索引色(Index Color),一种为直接色(Direct Color)
- 索引色:用一个数字索引代表一种颜色,在图像信息中存储数字到颜色的映射关系表(调色盘 Palette)。每个像素保存该像素颜色对应的数字索引。一般调色盘只能存储有限种类的颜色,通常为 256 种。所以每个像素的数字占用 1 字节(8 bit)大小。
- 直接色:用四个数字来代表一种颜色,数字分别对应颜色中红色,绿色,蓝色,透明度(RGBA)。每个像素保存这四个纬度的信息来代表该像素的颜色。根据色彩深度(每个像素存储颜色信息的 bit 数不同),最多可以支持的颜色种类也不同,常见的有 8 位(R3+G3+B2)、16 位(R5+G6+B5)、24 位(R8+G8+B8)、32 位(A8+R8+G8+B8)。所以每个像素占用 1~4 字节大小。
移动端常用图片格式
图片格式中一般分为静态图和动态图
静态图
JPG:是支持 JPEG( 一种有损压缩方法)标准中最常用的图片格式。采用点阵图。常见的是使用 24 位的颜色深度的直接色(不支持透明)。
PNG:是支持无损压缩的图片格式。采用点阵图。PNG 有 5 种颜色选项:索引色、灰度、灰度透明、真彩色(24 位直接色)、真彩色透明(32 位直接色)。
WebP:是同时支持有损压缩和无所压缩的的图片格式。采用点阵图。支持 32 位直接色。移动端支持情况如下:
| 系统 | 原生 | WebView | 浏览器 |
|---|---|---|---|
| iOS | 第三方库支持 | 不支持 | 不支持 |
| Android | 4.3 后支持完整功能 | 支持 | 支持 |
动态图
GIF:是支持无损压缩的图片格式。采用点阵图。使用索引色,并有 1 位透明度通道(透明与否)。
APNG:基于 PNG 格式扩展的格式,加入动态图支持。采用点阵图。使用 32 位直接色。但没有被官方 PNG 接纳。移动端支持情况如下:
| 系统 | 原生 | WebView | 浏览器 |
|---|---|---|---|
| iOS | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
| Android | 第三方库支持 | 不支持 | 不支持 |
- Animated Webp:Webp 的动图形式,实际上是文件中打包了多个单帧 Webp,在 libwebp 0.4 后开始支持。移动端支持情况如下:
| 系统 | 原生 | WebView | 系统浏览器 |
|---|---|---|---|
| iOS | 第三方库支持 | 不支持 | 不支持 |
| Android | 第三方库支持 | 不支持 | 不支持 |
而由于一般项目需要兼容三端(iOS、Android、Web 的关系),最简单就是支持 JPG、PNG、GIF 这三种通用的格式。所以本文暂不讨论其余图片格式的压缩。
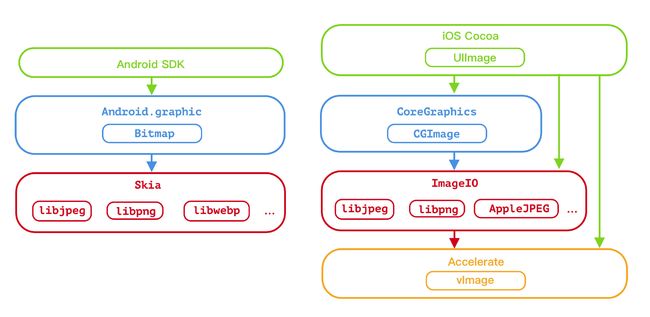
移动端系统图片处理架构
根据我的了解,画了一下 iOS&Android 图片处理架构。iOS 这边,也是可以直接调用底层一点的框架的。
iOS 的 ImageIO
本文 iOS 端处理图片主要用 ImageIO 框架,使用的原因主要是静态图动态图 API 调用保持一致,且不会因为 UIImage 转换时会丢失一部分数据的信息。
ImageIO 主要提供了图片编解码功能,封装了一套 C 语言接口。在 Swift 中不需要对 C 对象进行内存管理,会比 Objective-C 中使用方便不少,但 api 结果返回都是 Optional(实际上非空),需要用 guard/if,或者 !进行转换。
解码
1. 创建 CGImageSource
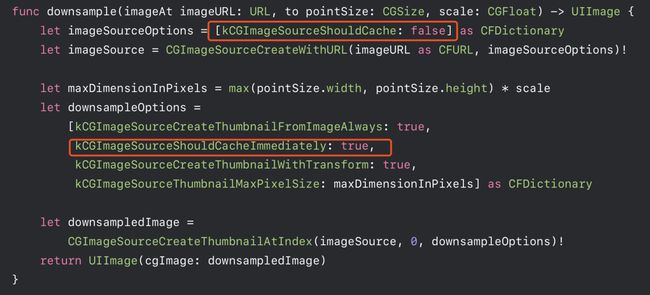
CGImageSource 相当于 ImageIO 数据来源的抽象类。通用的使用方式 CGImageSourceCreateWithDataProvider: 需要提供一个 DataProvider,可以指定文件、URL、Data 等输入。也有通过传入 CFData 来进行创建的便捷方法 CGImageSourceCreateWithData:。方法的第二个参数 options 传入一个字典进行配置。根据 Apple 在 WWDC 2018 上的 Image and Graphics Best Practices 上的例子,当不需要解码仅需要创建 CGImageSource 的时候,应该将 kCGImageSourceShouldCache 设为 false。
2. 解码得到 CGImage
用 CGImageSourceCreateImageAtIndex: 或者 CGImageSourceCreateThumbnailAtIndex: 来获取生成的 CGImage,这里参数的 Index 就是第几帧图片,静态图传入 0 即可。
编码
1. 创建 CGImageDestination
CGImageDestination 相当于 ImageIO 数据输出的抽象类。通用的使用方式 CGImageDestinationCreateWithDataConsumer: 需要提供一个 DataConsumer,可以置顶 URL、Data 等输入。也有通过传入 CFData 来进行创建的便捷方法 CGImageDestinationCreateWithData:,输出会写入到传入的 Data 中。方法还需要提供图片类型,图片帧数。
2. 添加 CGImage
添加 CGImage 使用 CGImageDestinationAddImage: 方法,动图的话,按顺序多次调用就行了。
而且还有一个特别的 CGImageDestinationAddImageFromSource: 方法,添加的其实是一个 CGImageSource,有什么用呢,通过 options 参数,达到改变图像设置的作用。比如改变 JPG 的压缩参数,用上这个功能后,就不需要转换成更顶层的对象(比如 UIImage),减少了转换时的编解码的损耗,达到性能更优的目的。
3. 进行编码
调用 CGImageDestinationFinalize: ,表示开始编码,完成后会返回一个 Bool 值,并将数据写入 CGImageDestination 提供的 DataConsumer 中。
压缩思路分析
位图占用的空间大小,其实就是像素数量x单像素占用空间x帧数。所以减小图片空间大小,其实就从这三个方向下手。其中单像素占用空间,在直接色的情况下,主要和色彩深度相关。在实际项目中,改变色彩深度会导致图片颜色和原图没有保持完全一致,笔者并不建议对色彩深度进行更改。而像素数量就是平时非常常用的图片分辨率缩放。除此之外,JPG 格式还有特有的通过指定压缩系数来进行有损压缩。
- JPG:压缩系数 + 分辨率缩放 + 色彩深度降低
- PNG: 分辨率缩放 + 降低色彩深度
- GIF:减少帧数 + 每帧分辨率缩放 + 减小调色盘
判断图片格式
后缀扩展名来判断其实并不保险,真实的判断方式应该是通过文件头里的信息进行判断。
| JPG | PNG | GIF |
|---|---|---|
| 开头:FF D8 + 结尾:FF D9 | 89 50 4E 47 0D 0A 1A 0A | 47 49 46 38 39/37 61 |
简单判断用前三个字节来判断
iOS
extension Data{
enum ImageFormat {
case jpg, png, gif, unknown
}
var imageFormat:ImageFormat {
var headerData = [UInt8](repeating: 0, count: 3)
self.copyBytes(to: &headerData, from:(0..<3))
let hexString = headerData.reduce("") { $0 + String(($1&0xFF), radix:16) }.uppercased()
var imageFormat = ImageFormat.unknown
switch hexString {
case "FFD8FF": imageFormat = .jpg
case "89504E": imageFormat = .png
case "474946": imageFormat = .gif
default:break
}
return imageFormat
}
}
iOS 中除了可以用文件头信息以外,还可以将 Data 转成 CGImageSource,然后用 CGImageSourceGetType 这个 API,这样会获取到 ImageIO 框架支持的图片格式的的 UTI 标识的字符串。对应的标识符常量定义在 MobileCoreServices 框架下的 UTCoreTypes 中。
| 字符串常量 | UTI 格式(字符串原始值) |
|---|---|
| kUTTypePNG | public.png |
| kUTTypeJPEG | public.jpeg |
| kUTTypeGIF | com.compuserve.gif |
Andorid
enum class ImageFormat{
JPG, PNG, GIF, UNKNOWN
}
fun ByteArray.imageFormat(): ImageFormat {
val headerData = this.slice(0..2)
val hexString = headerData.fold(StringBuilder("")) { result, byte -> result.append( (byte.toInt() and 0xFF).toString(16) ) }.toString().toUpperCase()
var imageFormat = ImageFormat.UNKNOWN
when (hexString) {
"FFD8FF" -> {
imageFormat = ImageFormat.JPG
}
"89504E" -> {
imageFormat = ImageFormat.PNG
}
"474946" -> {
imageFormat = ImageFormat.GIF
}
}
return imageFormat
}
色彩深度改变
实际上,减少深度一般也就是从 32 位减少至 16 位,但颜色的改变并一定能让产品、用户、设计接受,所以笔者在压缩过程并没有实际使用改变色彩深度的方法,仅仅研究了做法。
iOS
在 iOS 中,改变色彩深度,原生的 CGImage 库中,没有简单的方法。需要自己设置参数,重新生成 CGImage。
public init?(width: Int, height: Int, bitsPerComponent: Int, bitsPerPixel: Int, bytesPerRow: Int, space: CGColorSpace, bitmapInfo: CGBitmapInfo, provider: CGDataProvider, decode: UnsafePointer?, shouldInterpolate: Bool, intent: CGColorRenderingIntent)
- bitsPerComponent 每个通道占用位数
- bitsPerPixel 每个像素占用位数,相当于所有通道加起来的位数,也就是色彩深度
- bytesPerRow 传入 0 即可,系统会自动计算
- space 色彩空间
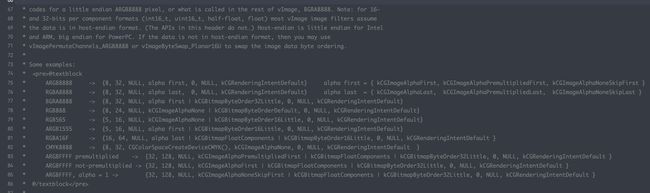
- bitmapInfo 这个是一个很重要的东西,其中常用的信息有 CGImageAlphaInfo,代表是否有透明通道,透明通道在前还是后面(ARGB 还是 RGBA),是否有浮点数(floatComponents),CGImageByteOrderInfo,代表字节顺序,采用大端还是小端,以及数据单位宽度,iOS 一般采用 32 位小端模式,一般用 orderDefault 就好。
那么对于常用的色彩深度,就可以用这些参数的组合来完成。同时笔者在查看更底层的 vImage 框架的 vImage_CGImageFormat 结构体时(CGImage 底层也是使用 vImage,具体可查看 Accelerate 框架 vImage 库的 vImage_Utilities 文件),发现了 Apple 的注释,里面也包含了常用的色彩深度用的参数。
这一块为了和 Android 保持一致,笔者封装了 Android 常用的色彩深度参数对应的枚举值。
public enum ColorConfig{
case alpha8
case rgb565
case argb8888
case rgbaF16
case unknown // 其余色彩配置
}
CGBitmapInfo 由于是 Optional Set,可以封装用到的属性的便捷方法。
extension CGBitmapInfo {
init(_ alphaInfo:CGImageAlphaInfo, _ isFloatComponents:Bool = false) {
var array = [
CGBitmapInfo(rawValue: alphaInfo.rawValue),
CGBitmapInfo(rawValue: CGImageByteOrderInfo.orderDefault.rawValue)
]
if isFloatComponents {
array.append(.floatComponents)
}
self.init(array)
}
}
那么 ColorConfig 对应的 CGImage 参数也可以对应起来了。
extension ColorConfig{
struct CGImageConfig{
let bitsPerComponent:Int
let bitsPerPixel:Int
let bitmapInfo: CGBitmapInfo
}
var imageConfig:CGImageConfig?{
switch self {
case .alpha8:
return CGImageConfig(bitsPerComponent: 8, bitsPerPixel: 8, bitmapInfo: CGBitmapInfo(.alphaOnly))
case .rgb565:
return CGImageConfig(bitsPerComponent: 5, bitsPerPixel: 16, bitmapInfo: CGBitmapInfo(.noneSkipFirst))
case .argb8888:
return CGImageConfig(bitsPerComponent: 8, bitsPerPixel: 32, bitmapInfo: CGBitmapInfo(.premultipliedFirst))
case .rgbaF16:
return CGImageConfig(bitsPerComponent: 16, bitsPerPixel: 64, bitmapInfo: CGBitmapInfo(.premultipliedLast, true))
case .unknown:
return nil
}
}
}
反过来,判断 CGImage 的 ColorConfig 的方法。
extension CGImage{
var colorConfig:ColorConfig{
if isColorConfig(.alpha8) {
return .alpha8
} else if isColorConfig(.rgb565) {
return .rgb565
} else if isColorConfig(.argb8888) {
return .argb8888
} else if isColorConfig(.rgbaF16) {
return .rgbaF16
} else {
return .unknown
}
}
func isColorConfig(_ colorConfig:ColorConfig) -> Bool{
guard let imageConfig = colorConfig.imageConfig else {
return false
}
if bitsPerComponent == imageConfig.bitsPerComponent &&
bitsPerPixel == imageConfig.bitsPerPixel &&
imageConfig.bitmapInfo.contains(CGBitmapInfo(alphaInfo)) &&
imageConfig.bitmapInfo.contains(.floatComponents) {
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
}
对外封装的 Api,也就是直接介绍的 ImageIO 的使用步骤,只是参数不一样。
/// 改变图片到指定的色彩配置
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - rawData: 原始图片数据
/// - config: 色彩配置
/// - Returns: 处理后数据
public static func changeColorWithImageData(_ rawData:Data, config:ColorConfig) -> Data?{
guard let imageConfig = config.imageConfig else {
return rawData
}
guard let imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithData(rawData as CFData, [kCGImageSourceShouldCache: false] as CFDictionary),
let writeData = CFDataCreateMutable(nil, 0),
let imageType = CGImageSourceGetType(imageSource),
let imageDestination = CGImageDestinationCreateWithData(writeData, imageType, 1, nil),
let rawDataProvider = CGDataProvider(data: rawData as CFData),
let imageFrame = CGImage(width: Int(rawData.imageSize.width),
height: Int(rawData.imageSize.height),
bitsPerComponent: imageConfig.bitsPerComponent,
bitsPerPixel: imageConfig.bitsPerPixel,
bytesPerRow: 0,
space: CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB(),
bitmapInfo: imageConfig.bitmapInfo,
provider: rawDataProvider,
decode: nil,
shouldInterpolate: true,
intent: .defaultIntent) else {
return nil
}
CGImageDestinationAddImage(imageDestination, imageFrame, nil)
guard CGImageDestinationFinalize(imageDestination) else {
return nil
}
return writeData as Data
}
/// 获取图片的色彩配置
///
/// - Parameter rawData: 原始图片数据
/// - Returns: 色彩配置
public static func getColorConfigWithImageData(_ rawData:Data) -> ColorConfig{
guard let imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithData(rawData as CFData, [kCGImageSourceShouldCache: false] as CFDictionary),
let imageFrame = CGImageSourceCreateImageAtIndex(imageSource, 0, nil) else {
return .unknown
}
return imageFrame.colorConfig
}
Android
对于 Android 来说,其原生的 Bitmap 库有相当方便的转换色彩深度的方法,只需要传入 Config 就好。
public Bitmap copy(Config config, boolean isMutable) {
checkRecycled("Can't copy a recycled bitmap");
if (config == Config.HARDWARE && isMutable) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hardware bitmaps are always immutable");
}
noteHardwareBitmapSlowCall();
Bitmap b = nativeCopy(mNativePtr, config.nativeInt, isMutable);
if (b != null) {
b.setPremultiplied(mRequestPremultiplied);
b.mDensity = mDensity;
}
return b;
}
iOS 的 CGImage 参数和 Android 的 Bitmap.Config 以及色彩深度对应关系如下表:
| 色彩深度 | iOS | Android |
|---|---|---|
| 8 位灰度(只有透明度) | bitsPerComponent: 8 bitsPerPixel: 8 bitmapInfo: CGImageAlphaInfo.alphaOnly | Bitmap.Config.ALPHA_8 |
| 16 位色(R5+G6+R5) | bitsPerComponent: 5 bitsPerPixel: 16 bitmapInfo: CGImageAlphaInfo.noneSkipFirst | Bitmap.Config.RGB_565 |
| 32 位色(A8+R8+G8+B8) | bitsPerComponent: 8 bitsPerPixel: 32 bitmapInfo: CGImageAlphaInfo.premultipliedFirst | Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888 |
| 64 位色(R16+G16+B16+A16 但使用半精度减少一半储存空间)用于宽色域或HDR | bitsPerComponent: 16 bitsPerPixel: 64 bitmapInfo: CGImageAlphaInfo.premultipliedLast + .floatComponents | Bitmap.Config.RGBA_F16 |
JPG 的压缩系数改变
JPG 的压缩算法相当复杂,以至于主流使用均是用 libjpeg 这个广泛的库进行编解码(在 Android 7.0 上开始使用性能更好的 libjpeg-turbo,iOS 则是用 Apple 自己开发未开源的 AppleJPEG)。而在 iOS 和 Android 上,都有 Api 输入压缩系数,来压缩 JPG。但具体压缩系数如何影响压缩大小,笔者并未深究。这里只能简单给出使用方法。
iOS
iOS 里面压缩系数为 0-1 之间的数值,据说 iOS 相册中采用的压缩系数是 0.9。同时,png 不支持有损压缩,所以 kCGImageDestinationLossyCompressionQuality 这个参数是无效。
static func compressImageData(_ rawData:Data, compression:Double) -> Data?{
guard let imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithData(rawData as CFData, [kCGImageSourceShouldCache: false] as CFDictionary),
let writeData = CFDataCreateMutable(nil, 0),
let imageType = CGImageSourceGetType(imageSource),
let imageDestination = CGImageDestinationCreateWithData(writeData, imageType, 1, nil) else {
return nil
}
let frameProperties = [kCGImageDestinationLossyCompressionQuality: compression] as CFDictionary
CGImageDestinationAddImageFromSource(imageDestination, imageSource, 0, frameProperties)
guard CGImageDestinationFinalize(imageDestination) else {
return nil
}
return writeData as Data
}
Andoid
Andoird 用 Bitmap 自带的接口,并输出到流中。压缩系数是 0-100 之间的数值。这里的参数虽然可以填 Bitmap.CompressFormat.PNG,但当然也是无效的。
val outputStream = ByteArrayOutputStream()
val image = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(rawData,0,rawData.count())
image.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, compression, outputStream)
resultData = outputStream.toByteArray()
GIF 的压缩
GIF 压缩上有很多种思路。参考开源项目 gifsicle 和 ImageMagick 中的做法,大概有以下几种。
由于 GIF 支持全局调色盘和局部调色盘,在没有局部调色盘的时候会用放在文件头中的全局调色盘。所以对于颜色变化不大的 GIF,可以将颜色放入全局调色盘中,去除局部调色盘。
-
对于颜色较少的 GIF,将调色盘大小减少,比如从 256 种减少到 128 种等。
-
对于背景一致,画面中有一部分元素在变化的 GIF,可以将多个元素和背景分开存储,然后加上如何还原的信息
-
对于背景一致,画面中有一部分元素在动的 GIF,可以和前面一帧比较,将不动的部分透明化
对于帧数很多的 GIF,可以抽取中间部分的帧,减少帧数
对于每帧分辨率很高的 GIF,将每帧的分辨率减小
对于动画的 GIF,3、4 是很实用的,因为背景一般是不变的,但对于拍摄的视频转成的 GIF,就没那么实用了,因为存在轻微抖动,很难做到背景不变。但在移动端,除非将 ImageMagick 或者 gifsicle 移植到 iOS&Android 上,要实现前面 4 个方法是比较困难的。笔者这里只实现了抽帧,和每帧分辨率压缩。
至于抽帧的间隔,参考了文章中的数值。
| 帧数 | 每 x 帧使用 1 帧 |
|---|---|
| <9 | x = 2 |
| 9 - 20 | x = 3 |
| 21 - 30 | x = 4 |
| 31 - 40 | x = 5 |
| >40 | x = 6 |
这里还有一个问题,抽帧的时候,原来的帧可能使用了 3、4 的方法进行压缩过,但还原的时候需要还原成完整的图像帧,再重新编码时,就没有办法再用 3、4 进行优化了。虽然帧减少了,但实际上会将帧还原成未做 3、4 优化的状态,一增一减,压缩的效果就没那么好了(所以这种压缩还是尽量在服务器做)。抽帧后记得将中间被抽取的帧的时间累加在剩下的帧的时间上,不然帧速度就变快了,而且不要用抽取数x帧时间偷懒来计算,因为不一定所有帧的时间是一样的。
iOS
iOS 上的实现比较简单,用 ImageIO 的函数即可实现,性能也比较好。
先定义从 ImageSource 获取每帧的时间的便捷扩展方法,帧时长会存在 kCGImagePropertyGIFUnclampedDelayTime 或者 kCGImagePropertyGIFDelayTime 中,两个 key 不同之处在于后者有最小值的限制,正确的获取方法参考苹果在 WebKit 中的使用方法。
extension CGImageSource {
func frameDurationAtIndex(_ index: Int) -> Double{
var frameDuration = Double(0.1)
guard let frameProperties = CGImageSourceCopyPropertiesAtIndex(self, index, nil) as? [AnyHashable:Any], let gifProperties = frameProperties[kCGImagePropertyGIFDictionary] as? [AnyHashable:Any] else {
return frameDuration
}
if let unclampedDuration = gifProperties[kCGImagePropertyGIFUnclampedDelayTime] as? NSNumber {
frameDuration = unclampedDuration.doubleValue
} else {
if let clampedDuration = gifProperties[kCGImagePropertyGIFDelayTime] as? NSNumber {
frameDuration = clampedDuration.doubleValue
}
}
if frameDuration < 0.011 {
frameDuration = 0.1
}
return frameDuration
}
var frameDurations:[Double]{
let frameCount = CGImageSourceGetCount(self)
return (0..先去掉不要的帧,合并帧的时间,再重新生成帧就完成了。注意帧不要被拖得太长,不然体验不好,我这里给的最大值是 200ms。
/// 同步压缩图片抽取帧数,仅支持 GIF
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - rawData: 原始图片数据
/// - sampleCount: 采样频率,比如 3 则每三张用第一张,然后延长时间
/// - Returns: 处理后数据
static func compressImageData(_ rawData:Data, sampleCount:Int) -> Data?{
guard let imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithData(rawData as CFData, [kCGImageSourceShouldCache: false] as CFDictionary),
let writeData = CFDataCreateMutable(nil, 0),
let imageType = CGImageSourceGetType(imageSource) else {
return nil
}
// 计算帧的间隔
let frameDurations = imageSource.frameDurations
// 合并帧的时间,最长不可高于 200ms
let mergeFrameDurations = (0..压缩分辨率也是类似的,每帧按分辨率压缩再重新编码就好。
Android
Android 原生对于 GIF 的支持就不怎么友好了,由于笔者 Android 研究不深,暂时先用 Glide 中的 GIF 编解码组件来完成。编码的性能比较一般,比不上 iOS,但除非换用更底层 C++ 库实现的编码库,Java 写的性能都很普通。先用 Gradle 导入 Glide,注意解码器是默认的,但编码器需要另外导入。
api 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:4.8.0'
api 'com.github.bumptech.glide:gifencoder-integration:4.8.0'
抽帧思路和 iOS 一样,只是 Glide 的这个 GIF 解码器没办法按指定的 index 取读取某一帧,只能一帧帧读取,调用 advance 方法往后读取。先从 GIF 读出头部信息,然后在读真正的帧信息。
/**
* 返回同步压缩 gif 图片 Byte 数据 [rawData] 的按 [sampleCount] 采样后的 Byte 数据
*/
private fun compressGifDataWithSampleCount(context: Context, rawData: ByteArray, sampleCount: Int): ByteArray? {
if (sampleCount <= 1) {
return rawData
}
val gifDecoder = StandardGifDecoder(GifBitmapProvider(Glide.get(context).bitmapPool))
val headerParser = GifHeaderParser()
headerParser.setData(rawData)
val header = headerParser.parseHeader()
gifDecoder.setData(header, rawData)
val frameCount = gifDecoder.frameCount
// 计算帧的间隔
val frameDurations = (0 until frameCount).map { gifDecoder.getDelay(it) }
// 合并帧的时间,最长不可高于 200ms
val mergeFrameDurations = (0 until frameCount).filter { it % sampleCount == 0 }.map {
min(
frameDurations.subList(
it,
min(it + sampleCount, frameCount)
).fold(0) { acc, duration -> acc + duration }, 200
)
}
// 抽取帧
val sampleImageFrames = (0 until frameCount).mapNotNull {
gifDecoder.advance()
var imageFrame: Bitmap? = null
if (it % sampleCount == 0) {
imageFrame = gifDecoder.nextFrame
}
imageFrame
}
val gifEncoder = AnimatedGifEncoder()
var resultData: ByteArray? = null
try {
val outputStream = ByteArrayOutputStream()
gifEncoder.start(outputStream)
gifEncoder.setRepeat(0)
// 每一帧图片都进行重新编码
sampleImageFrames.zip(mergeFrameDurations).forEach {
// 设置帧间隔
gifEncoder.setDelay(it.second)
gifEncoder.addFrame(it.first)
it.first.recycle()
}
gifEncoder.finish()
resultData = outputStream.toByteArray()
outputStream.close()
} catch (e: IOException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
return resultData
}
压缩分辨率的时候要注意,分辨率太大编码容易出现 Crash(应该是 OOM),这里设置为 512。
/**
* 返回同步压缩 gif 图片 Byte 数据 [rawData] 每一帧长边到 [limitLongWidth] 后的 Byte 数据
*/
private fun compressGifDataWithLongWidth(context: Context, rawData: ByteArray, limitLongWidth: Int): ByteArray? {
val gifDecoder = StandardGifDecoder(GifBitmapProvider(Glide.get(context).bitmapPool))
val headerParser = GifHeaderParser()
headerParser.setData(rawData)
val header = headerParser.parseHeader()
gifDecoder.setData(header, rawData)
val frameCount = gifDecoder.frameCount
// 计算帧的间隔
val frameDurations = (0..(frameCount - 1)).map { gifDecoder.getDelay(it) }
// 计算调整后大小
val longSideWidth = max(header.width, header.height)
val ratio = limitLongWidth.toFloat() / longSideWidth.toFloat()
val resizeWidth = (header.width.toFloat() * ratio).toInt()
val resizeHeight = (header.height.toFloat() * ratio).toInt()
// 每一帧进行缩放
val resizeImageFrames = (0 until frameCount).mapNotNull {
gifDecoder.advance()
var imageFrame = gifDecoder.nextFrame
if (imageFrame != null) {
imageFrame = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(imageFrame, resizeWidth, resizeHeight, true)
}
imageFrame
}
val gifEncoder = AnimatedGifEncoder()
var resultData: ByteArray? = null
try {
val outputStream = ByteArrayOutputStream()
gifEncoder.start(outputStream)
gifEncoder.setRepeat(0)
// 每一帧都进行重新编码
resizeImageFrames.zip(frameDurations).forEach {
// 设置帧间隔
gifEncoder.setDelay(it.second)
gifEncoder.addFrame(it.first)
it.first.recycle()
}
gifEncoder.finish()
resultData = outputStream.toByteArray()
outputStream.close()
return resultData
} catch (e: IOException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
return resultData
}
分辨率压缩
这个是最常用的,而且也比较简单。
iOS
iOS 的 ImageIO 提供了 CGImageSourceCreateThumbnailAtIndex 的 API 来创建缩放的缩略图。在 options 中添加需要缩放的长边参数即可。
/// 同步压缩图片数据长边到指定数值
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - rawData: 原始图片数据
/// - limitLongWidth: 长边限制
/// - Returns: 处理后数据
public static func compressImageData(_ rawData:Data, limitLongWidth:CGFloat) -> Data?{
guard max(rawData.imageSize.height, rawData.imageSize.width) > limitLongWidth else {
return rawData
}
guard let imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithData(rawData as CFData, [kCGImageSourceShouldCache: false] as CFDictionary),
let writeData = CFDataCreateMutable(nil, 0),
let imageType = CGImageSourceGetType(imageSource) else {
return nil
}
let frameCount = CGImageSourceGetCount(imageSource)
guard let imageDestination = CGImageDestinationCreateWithData(writeData, imageType, frameCount, nil) else{
return nil
}
// 设置缩略图参数,kCGImageSourceThumbnailMaxPixelSize 为生成缩略图的大小。当设置为 800,如果图片本身大于 800*600,则生成后图片大小为 800*600,如果源图片为 700*500,则生成图片为 800*500
let options = [kCGImageSourceThumbnailMaxPixelSize: limitLongWidth, kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailWithTransform:true, kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailFromImageIfAbsent:true] as CFDictionary
if frameCount > 1 {
// 计算帧的间隔
let frameDurations = imageSource.frameDurations
// 每一帧都进行缩放
let resizedImageFrames = (0..Android
Android 静态图用 Bitmap 里面的 createScaleBitmap API 就好了,GIF 上文已经讲了。
/**
* 返回同步压缩图片 Byte 数据 [rawData] 的长边到 [limitLongWidth] 后的 Byte 数据,Gif 目标长边最大压缩到 512,超过用 512
*/
fun compressImageDataWithLongWidth(context: Context, rawData: ByteArray, limitLongWidth: Int): ByteArray? {
val format = rawData.imageFormat()
if (format == ImageFormat.UNKNOWN) {
return null
}
val (imageWidth, imageHeight) = rawData.imageSize()
val longSideWidth = max(imageWidth, imageHeight)
if (longSideWidth <= limitLongWidth) {
return rawData
}
if (format == ImageFormat.GIF) {
// 压缩 Gif 分辨率太大编码时容易崩溃
return compressGifDataWithLongWidth(context, rawData, max(512, longSideWidth))
} else {
val image = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(rawData, 0, rawData.size)
val ratio = limitLongWidth.toDouble() / longSideWidth.toDouble()
val resizeImageFrame = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(
image,
(image.width.toDouble() * ratio).toInt(),
(image.height.toDouble() * ratio).toInt(),
true
)
image.recycle()
var resultData: ByteArray? = null
when (format) {
ImageFormat.PNG -> {
resultData = resizeImageFrame.toByteArray(Bitmap.CompressFormat.PNG)
}
ImageFormat.JPG -> {
resultData = resizeImageFrame.toByteArray(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG)
}
else -> {
}
}
resizeImageFrame.recycle()
return resultData
}
}
限制大小的压缩方式
也就是将前面讲的方法综合起来,笔者这边给出一种方案,没有对色彩进行改变,JPG 先用二分法减少最多 6 次的压缩系数,GIF 先抽帧,抽帧间隔参考前文,最后采用逼近目标大小缩小分辨率。
iOS
/// 同步压缩图片到指定文件大小
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - rawData: 原始图片数据
/// - limitDataSize: 限制文件大小,单位字节
/// - Returns: 处理后数据
public static func compressImageData(_ rawData:Data, limitDataSize:Int) -> Data?{
guard rawData.count > limitDataSize else {
return rawData
}
var resultData = rawData
// 若是 JPG,先用压缩系数压缩 6 次,二分法
if resultData.imageFormat == .jpg {
var compression: Double = 1
var maxCompression: Double = 1
var minCompression: Double = 0
for _ in 0..<6 {
compression = (maxCompression + minCompression) / 2
if let data = compressImageData(resultData, compression: compression){
resultData = data
} else {
return nil
}
if resultData.count < Int(CGFloat(limitDataSize) * 0.9) {
minCompression = compression
} else if resultData.count > limitDataSize {
maxCompression = compression
} else {
break
}
}
if resultData.count <= limitDataSize {
return resultData
}
}
// 若是 GIF,先用抽帧减少大小
if resultData.imageFormat == .gif {
let sampleCount = resultData.fitSampleCount
if let data = compressImageData(resultData, sampleCount: sampleCount){
resultData = data
} else {
return nil
}
if resultData.count <= limitDataSize {
return resultData
}
}
var longSideWidth = max(resultData.imageSize.height, resultData.imageSize.width)
// 图片尺寸按比率缩小,比率按字节比例逼近
while resultData.count > limitDataSize{
let ratio = sqrt(CGFloat(limitDataSize) / CGFloat(resultData.count))
longSideWidth *= ratio
if let data = compressImageData(resultData, limitLongWidth: longSideWidth) {
resultData = data
} else {
return nil
}
}
return resultData
}
Android
/**
* 返回同步压缩图片 Byte 数据 [rawData] 的数据大小到 [limitDataSize] 后的 Byte 数据
*/
fun compressImageDataWithSize(context: Context, rawData: ByteArray, limitDataSize: Int): ByteArray? {
if (rawData.size <= limitDataSize) {
return rawData
}
val format = rawData.imageFormat()
if (format == ImageFormat.UNKNOWN) {
return null
}
var resultData = rawData
// 若是 JPG,先用压缩系数压缩 6 次,二分法
if (format == ImageFormat.JPG) {
var compression = 100
var maxCompression = 100
var minCompression = 0
try {
val outputStream = ByteArrayOutputStream()
for (index in 0..6) {
compression = (maxCompression + minCompression) / 2
outputStream.reset()
val image = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(rawData, 0, rawData.size)
image.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, compression, outputStream)
image.recycle()
resultData = outputStream.toByteArray()
if (resultData.size < (limitDataSize.toDouble() * 0.9).toInt()) {
minCompression = compression
} else if (resultData.size > limitDataSize) {
maxCompression = compression
} else {
break
}
}
outputStream.close()
} catch (e: IOException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
if (resultData.size <= limitDataSize) {
return resultData
}
}
// 若是 GIF,先用抽帧减少大小
if (format == ImageFormat.GIF) {
val sampleCount = resultData.fitSampleCount()
val data = compressGifDataWithSampleCount(context, resultData, sampleCount)
if (data != null) {
resultData = data
} else {
return null
}
if (resultData.size <= limitDataSize) {
return resultData
}
}
val (imageWidth, imageHeight) = resultData.imageSize()
var longSideWidth = max(imageWidth, imageHeight)
// 图片尺寸按比率缩小,比率按字节比例逼近
while (resultData.size > limitDataSize) {
val ratio = Math.sqrt(limitDataSize.toDouble() / resultData.size.toDouble())
longSideWidth = (longSideWidth.toDouble() * ratio).toInt()
val data = compressImageDataWithLongWidth(context, resultData, longSideWidth)
if (data != null) {
resultData = data
} else {
return null
}
}
return resultData
}
注意在异步线程中使用,毕竟是耗时操作。
最后
所有代码均封装成文件在 iOS 和 Android 中了,如有错误和建议,欢迎指出。
Reference
无损压缩 vs 有损压缩 vs 损多少
图片格式 jpg、png、gif各有什么优缺点?什么情况下用什么格式的图片呢?
也谈图片压缩
移动端图片格式调研
浓缩的才是精华:浅析 GIF 格式图片的存储和压缩
压缩gif的正确姿势
谈谈 iOS 中图片的解压缩
iOS平台图片编解码入门教程(Image/IO篇)