在看Class的源码之前我们先来看看虚拟机的类加载机制。
什么是类加载机制:
就是将Class文件存入内存,并对数据校验,转换解析,初始化,最终形成能被虚拟机直接使用的模型 的过程
类加载 可以分为7个阶段
1 加载
- 加载过程中需要完成以下三件事:
- 通过类的全限定名类获取定义此类的二进制字节流
- 将这个字节流所代表的静态存储结构转换成方法区运行时数据结
- 在内存中生成一个代表这个类的java.lang.Class对象,作为数据访问的入口
2 验证
- 视为了确保Class文件的字节流中包含的信息符合当前虚拟机的要求,而且还不会危害虚拟机自身的安全。
- 验证阶段很重要,但也不是必要的,假如说一些代码被反复使用并验证过可靠性了,实施阶段就可以尝试用-Xverify:none参数来关闭大部分的类验证措施,以简短类加载时间。
连接 (可以细化为4-6阶段)
3 准备
准备阶段是正式为类变量分配内存并且设置类变量【静态变量】初始值的位置。这个设置初始值不是直接将赋值设置进去,而是数据类型的零值 。 比如 有代码public static int value=1 ,但是实际上其实只是设置了value=0; 但是有一种情况是例外,就是用了final关键字的时候,就是被初始化为1;
4 解析
5初始化
- new,getstatic,putstatic,invokestatic关键字(new 对象,读取/赋值静态字段(final除外),调用静态方法)
- 反射调用,如果之前类没有被初始化,那么这时候会初始化
- 初始化某个类 ,但是其父类还没有被初始化的时候,父类也会初始化 (该类如果是一个接口则不会初始化父类)
- 虚拟机启动 ,用户指定执行的类(如main方法调用的时候的那个类)
- 动态语言支持 java.lang.invoke.MethodHandle返回RET_getstatic,RET_putstatic
6 使用
7 卸载
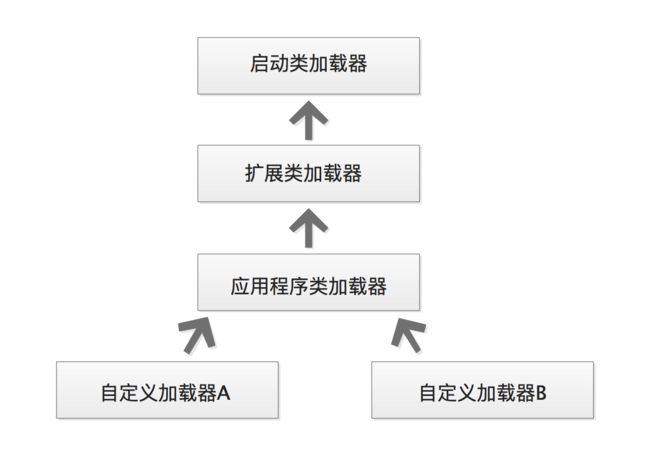
类加载器:
java中定义的类加载器可以细分为三种
1.启动类加载器
2.扩展类加载器
3.应用程序加载器
一般都是三种加载器互相配合加载。加载关系基本符合双亲委派模型。
什么是双亲委派模型:
工作过程:
比如我们要开始加载某个类了,这时候它不会自己马上就去加载,它会把这个请求委派给父类,然后不断往上委派,直到顶层。当父类说:哎呀,我加载不了哦【搜索范围找不到这个类】,子类就只有自己去加载了。
双亲委派模型被破坏:
1.兼容1.0的时候的LoadClass
2.SPI的加载:线程上下文加载器 父类去请求子类的加载器
OSGi(Open Service Gateway Initiative,直译为“开放服务网关”)实际上是一个由
OSGi 联盟(OSGi Alliance,如图 1-1 所示)发起的以 Java 为技术平台的动态模块化规范。
我们通过一道面试题来验证下
class T implements Cloneable{
public static int k = 0;
public static T t1 = new T("t1");
public static T t2 = new T("t2");
public static int i = print("i");
public static int n = 99;
public int j = print("j");
{
print("构造块");
}
static {
print("静态块");
}
public T(String str) {
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n);
++n; ++ i;
}
public static int print(String str){
System.out.println((++k) +":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n);
++n;
return ++ i;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
T t = new T("init");
}
}
好的,现在可以开始分析了。
按照我们之前说的7个阶段来说
首先 我们通过
加载->验证->链接【这时候将开始于我们的类内容正式相关】
我们知道链接可以细分为3个阶段
在第一个准备阶段:
准备阶段是正式为类变量分配内存并且设置类变量【静态变量】初始值的位置
在这里可以理解为 设置
k=0;
t1=null;
t=null;
i=0;
h=0;
然后开始第二个阶段解析:这里对执行代码没有直接影响
当来到第三个阶段初始化的时候,就会开始赋值,我们根据代码继续走着看看。从第一个开始赋值:
k=0;
t1=new T("t1");
这里是对T的实例化,所以会走到T的类变量赋值和构造方法和实际调用方法。先走到了
public int j = print("j");
然后调用print方法 输出:
1:j i=0 n=0
这时候再返回到执行完毕的j=1 n=1;
然后调用了初始化块:在执行print("构造快");
这时候输出
2:构造块 i=1 n=1
这时候就可以执行方法本身的构造方法了输出
3:t1 i=2 n=2
然后执行完了t1实例化的全部过程
继续执行t2实例化 ,
public static T t2 = new T("t2");
过程同t1
4:j j=3 n=3
5:构造块 j=4 n=4
6:t2 j=5 n=5
然后继续执行
public static int i = print("i");
7:i j=6 i=6
返回执行
public static int n = 99;
此时n=99
然后因为现在处于初始化不会执行变量赋值 以及初始化块和构造函数,因为其实我们还没有执行T t = new T("init");
所以直接跳到
static {
print("静态块");
}
8:静态块 j=7 n=99
然后 初始化完毕 。开始执行T t = new T("init");
这时候执行
public int j = print("j");
9:j j=8 n=100
执行
{
print("构造块");
}
10:构造块 j=9 n=101
执行构造方法
11:init j=10 n=102
所以答案是
1:j i=0 n=0
2:构造块 i=1 n=1
3:t1 i=2 n=2
4:j i=3 n=3
5:构造快 i=4 n=4
6:t2 i=5 n=5
7:i i=6 n=6
8:静态块 i=7 n=99
9:j i=8 n=100
10:构造快 i=9 n=101
11:init i=10 n=102
总结一下 我们可以知道 在实例化一个类的时候会进行类加载
1.过程中准备阶段进行静态变量以及静态块的的初始化,这时候是没有赋值的,为该类的‘零值’。
2.然后在类的初始化这个阶段进行赋值,赋值的时候只会对使用了static关键字的变量赋值,将代码里本来赋给他们的值,真正意义上的赋给他,并且执行静态语句块。【这个过程只会执行一次,因为一个class只会初始化加载一次】
1.2过程都是在虚拟机里run的时候。代码正式开始运行以前就执行了。
3.当进行实例化的时候只会进行对类变量,初始块,以及调用的构造方法进行真的实现。而静态相关方法只会进行一次。而且静态变量也不会被释放
那么实例化一个类有几种方法呢?
首先贴出实例化的类
package com.test;
public class ClassDTO implements Cloneable,Serializable{
private String name;
private Integer age;
public ClassDTO(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public ClassDTO() {
this.setName("momo");
this.setAge(12);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public Object clone(){
Object classDTO=null;
try {
classDTO= super.clone();
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("error");
}
return classDTO;
}
}
- new 关键字
ClassDTO classDTO=new ClassDTO();
- 反射,调用java.lang.Class类的newInstance()实例方法
ClassDTO classDTO =(ClassDTO)Class.forName("com.test.ClassDTO").newInstance();
这个方法和new关键字的区别:
这个生成对象只能调用无参的构造函数,new 没有这个限制
这个是创建通过反射创建了一个新的类,所以必须保证这个类已经被加载且链接,new使用的是类加载机制,没有要求
这个效率比较低,是弱类型,new关键字相反
- java.lang.reflect.Constructor类的newInstance()实例方法
Constructor constructor =
ClassDTO.class.getConstructor();
ClassDTO classDTO = constructor.newInstance();
- clone方法 这个需要重写cloneable接口
ClassDTO classDTO=new ClassDTO();
ClassDTO classDTO1=(ClassDTO)classDTO.clone();
- 反序列机制
ClassDTO classDTO=new ClassDTO();
//写
ObjectOutputStream output = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("classDTO.bin"));
output.writeObject(classDTO);
output.close();
//读
ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream( "classDTO.bin"));
ClassDTO classDTO1 = (ClassDTO) input.readObject();
然后我们就可以开始看java代码了
public final class Class implements java.io.Serializable,
GenericDeclaration,
Type,
AnnotatedElement {
private static final int ANNOTATION= 0x00002000; //注释类型
private static final int ENUM = 0x00004000;//枚举类型
private static final int SYNTHETIC = 0x00001000;//合成类型
//注册本地方法
private static native void registerNatives();
static {
registerNatives();
}
//私有方法 给jvm创造创造类的时候使用的
private Class(ClassLoader loader) {
// Initialize final field for classLoader. The initialization value of non-null
// prevents future JIT optimizations from assuming this final field is null.
classLoader = loader;
}
// 重写Object的toString
public String toString() {
//区别了接口和普通类的
return (isInterface() ? "interface " : (isPrimitive() ? "" : "class "))
+ getName();
}
//toString的详细版
public String toGenericString() {
if (isPrimitive()) {
return toString();
} else {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// Class modifiers are a superset of interface modifiers
int modifiers = getModifiers() & Modifier.classModifiers();
if (modifiers != 0) {
sb.append(Modifier.toString(modifiers));
sb.append(' ');
}
if (isAnnotation()) {
sb.append('@');
}
if (isInterface()) { // Note: all annotation types are interfaces
sb.append("interface");
} else {
if (isEnum())
sb.append("enum");
else
sb.append("class");
}
sb.append(' ');
sb.append(getName());
TypeVariable[] typeparms = getTypeParameters();
if (typeparms.length > 0) {
boolean first = true;
sb.append('<');
for(TypeVariable typeparm: typeparms) {
if (!first)
sb.append(',');
sb.append(typeparm.getTypeName());
first = false;
}
sb.append('>');
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
//通过类全限定名获得该类的类对象
@CallerSensitive //用来找到真正发起反射请求的类
public static Class forName(String className)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
return forName0(className, true, ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller), caller);
}
//方法返回与给定字符串名的类或接口的Class对象,使用给定的类加载器。使用指定的加载器加载
@CallerSensitive
public static Class forName(String name, boolean initialize,
ClassLoader loader)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
Class caller = null;
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
// Reflective call to get caller class is only needed if a security manager
// is present. Avoid the overhead of making this call otherwise.
caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
if (sun.misc.VM.isSystemDomainLoader(loader)) {
ClassLoader ccl = ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller);
if (!sun.misc.VM.isSystemDomainLoader(ccl)) {
sm.checkPermission(
SecurityConstants.GET_CLASSLOADER_PERMISSION);
}
}
}
return forName0(name, initialize, loader, caller);
}
private static native Class forName0(String name, boolean initialize,
ClassLoader loader,
Class caller)
throws ClassNotFoundException;
//通过newInstance 生成一个类的实例 默认调用无参构造方法
@CallerSensitive
public T newInstance()
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException
{
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), false);
}
// NOTE: the following code may not be strictly correct under
// the current Java memory model.
// Constructor lookup
if (cachedConstructor == null) {
if (this == Class.class) {
throw new IllegalAccessException(
"Can not call newInstance() on the Class for java.lang.Class"
);
}
try {
Class[] empty = {};
final Constructor c = getConstructor0(empty, Member.DECLARED);
// Disable accessibility checks on the constructor
// since we have to do the security check here anyway
// (the stack depth is wrong for the Constructor's
// security check to work)
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedAction() {
public Void run() {
c.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
cachedConstructor = c;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw (InstantiationException)
new InstantiationException(getName()).initCause(e);
}
}
Constructor tmpConstructor = cachedConstructor;
// Security check (same as in java.lang.reflect.Constructor)
int modifiers = tmpConstructor.getModifiers();
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(this, modifiers)) {
Class caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
if (newInstanceCallerCache != caller) {
Reflection.ensureMemberAccess(caller, this, null, modifiers);
newInstanceCallerCache = caller;
}
}
// Run constructor
try {
return tmpConstructor.newInstance((Object[])null);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Unsafe.getUnsafe().throwException(e.getTargetException());
// Not reached
return null;
}
}
//缓存已经调用的共有方法
private volatile transient Constructor cachedConstructor;
//缓存class 对象
private volatile transient Class newInstanceCallerCache;
//判断一个对象是否该class的实例
public native boolean isInstance(Object obj);
//判断一个该类和另一个类cls是否相同或是另一个类的子类或接口
public native boolean isAssignableFrom(Class cls);
//判断一个对象实例是否是一个 类/接口的/其子类子接口 的实例
public native boolean isInterface();
//判断是否出租
public native boolean isArray();
//判断该Class是否是基本类型+特殊类型,
/**
* @see java.lang.Boolean#TYPE
* @see java.lang.Character#TYPE
* @see java.lang.Byte#TYPE
* @see java.lang.Short#TYPE
* @see java.lang.Integer#TYPE
* @see java.lang.Long#TYPE
* @see java.lang.Float#TYPE
* @see java.lang.Double#TYPE
* @see java.lang.Void#TYPE 特殊类型
*/
public native boolean isPrimitive();
//判断该Class是否是注释类型
public boolean isAnnotation() {
return (getModifiers() & ANNOTATION) != 0;
}
//判断是否合成类型( 是由编译器引入的字段、方法、类或其他结构)
public boolean isSynthetic() {
return (getModifiers() & SYNTHETIC) != 0;
}
// 获取类名
public String getName() {
String name = this.name;
if (name == null)
this.name = name = getName0();
return name;
}
// cache the name to reduce the number of calls into the VM
private transient String name;
private native String getName0();
//返回类加载器
@CallerSensitive
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();
if (cl == null)
return null;
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
ClassLoader.checkClassLoaderPermission(cl, Reflection.getCallerClass());
}
return cl;
}
// Package-private to allow ClassLoader access
ClassLoader getClassLoader0() { return classLoader; }
// Initialized in JVM not by private constructor
// This field is filtered from reflection access, i.e. getDeclaredField
// will throw NoSuchFieldException
private final ClassLoader classLoader;
//返回该类中变量字段的类型变量数组
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public TypeVariable>[] getTypeParameters() {
ClassRepository info = getGenericInfo();
if (info != null)
return (TypeVariable>[])info.getTypeParameters();
else
return (TypeVariable>[])new TypeVariable[0];
}
//获得该类的直接父类的Class对象,如果该类是接口,则返回null
public native Class getSuperclass();
//返回详细版的父类class对象
public Type getGenericSuperclass() {
ClassRepository info = getGenericInfo();
if (info == null) {
return getSuperclass();
}
// Historical irregularity:
// Generic signature marks interfaces with superclass = Object
// but this API returns null for interfaces
if (isInterface()) {
return null;
}
return info.getSuperclass();
}
//获取类的包路径
public Package getPackage() {
return Package.getPackage(this);
}
//获取该类直接实现的所有接口的数组
public Class[] getInterfaces() {
ReflectionData rd = reflectionData();
if (rd == null) {
// no cloning required
return getInterfaces0();
} else {
Class[] interfaces = rd.interfaces;
if (interfaces == null) {
interfaces = getInterfaces0();
rd.interfaces = interfaces;
}
// defensively copy before handing over to user code
return interfaces.clone();
}
}
private native Class[] getInterfaces0();
//获取所有接口,同上面的不同之处在于,若超接口是参数化类型(泛型)则返回的是其实际类型
public Type[] getGenericInterfaces() {
ClassRepository info = getGenericInfo();
return (info == null) ? getInterfaces() : info.getSuperInterfaces();
}
//返回数组类型,若该类不是数组,返回null
public native Class getComponentType();
//返回修饰符对应的int值
public native int getModifiers();
/**
* Gets the signers of this class.
*
* @return the signers of this class, or null if there are no signers. In
* particular, this method returns null if this object represents
* a primitive type or void.
* @since JDK1.1
*/
public native Object[] getSigners();
/**
* Set the signers of this class.
*/
native void setSigners(Object[] signers);
//如果这个类是本地或匿名类,返回的底层类的立即封闭方法,否则返回null。
@CallerSensitive
public Method getEnclosingMethod() throws SecurityException {
EnclosingMethodInfo enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethodInfo();
if (enclosingInfo == null)
return null;
else {
if (!enclosingInfo.isMethod())
return null;
MethodRepository typeInfo = MethodRepository.make(enclosingInfo.getDescriptor(),
getFactory());
Class returnType = toClass(typeInfo.getReturnType());
Type [] parameterTypes = typeInfo.getParameterTypes();
Class[] parameterClasses = new Class[parameterTypes.length];
// Convert Types to Classes; returned types *should*
// be class objects since the methodDescriptor's used
// don't have generics information
for(int i = 0; i < parameterClasses.length; i++)
parameterClasses[i] = toClass(parameterTypes[i]);
// Perform access check
Class enclosingCandidate = enclosingInfo.getEnclosingClass();
enclosingCandidate.checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED,
Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
/*
* Loop over all declared methods; match method name,
* number of and type of parameters, *and* return
* type. Matching return type is also necessary
* because of covariant returns, etc.
*/
for(Method m: enclosingCandidate.getDeclaredMethods()) {
if (m.getName().equals(enclosingInfo.getName()) ) {
Class[] candidateParamClasses = m.getParameterTypes();
if (candidateParamClasses.length == parameterClasses.length) {
boolean matches = true;
for(int i = 0; i < candidateParamClasses.length; i++) {
if (!candidateParamClasses[i].equals(parameterClasses[i])) {
matches = false;
break;
}
}
if (matches) { // finally, check return type
if (m.getReturnType().equals(returnType) )
return m;
}
}
}
}
throw new InternalError("Enclosing method not found");
}
}
private native Object[] getEnclosingMethod0();
private EnclosingMethodInfo getEnclosingMethodInfo() {
Object[] enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethod0();
if (enclosingInfo == null)
return null;
else {
return new EnclosingMethodInfo(enclosingInfo);
}
}
private final static class EnclosingMethodInfo {
private Class enclosingClass;
private String name;
private String descriptor;
private EnclosingMethodInfo(Object[] enclosingInfo) {
if (enclosingInfo.length != 3)
throw new InternalError("Malformed enclosing method information");
try {
// The array is expected to have three elements:
// the immediately enclosing class
enclosingClass = (Class) enclosingInfo[0];
assert(enclosingClass != null);
// the immediately enclosing method or constructor's
// name (can be null).
name = (String) enclosingInfo[1];
// the immediately enclosing method or constructor's
// descriptor (null iff name is).
descriptor = (String) enclosingInfo[2];
assert((name != null && descriptor != null) || name == descriptor);
} catch (ClassCastException cce) {
throw new InternalError("Invalid type in enclosing method information", cce);
}
}
boolean isPartial() {
return enclosingClass == null || name == null || descriptor == null;
}
boolean isConstructor() { return !isPartial() && "".equals(name); }
boolean isMethod() { return !isPartial() && !isConstructor() && !"".equals(name); }
Class getEnclosingClass() { return enclosingClass; }
String getName() { return name; }
String getDescriptor() { return descriptor; }
}
private static Class toClass(Type o) {
if (o instanceof GenericArrayType)
return Array.newInstance(toClass(((GenericArrayType)o).getGenericComponentType()),
0)
.getClass();
return (Class)o;
}
//如果这个类是本地或匿名类,返回的底层类的立即封闭构造方法,否则返回null。
@CallerS @CallerSensitive
public Constructor getEnclosingConstructor() throws SecurityException {
EnclosingMethodInfo enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethodInfo();
if (enclosingInfo == null)
return null;
else {
if (!enclosingInfo.isConstructor())
return null;
ConstructorRepository typeInfo = ConstructorRepository.make(enclosingInfo.getDescriptor(),
getFactory());
Type [] parameterTypes = typeInfo.getParameterTypes();
Class[] parameterClasses = new Class[parameterTypes.length];
// Convert Types to Classes; returned types *should*
// be class objects since the methodDescriptor's used
// don't have generics information
for(int i = 0; i < parameterClasses.length; i++)
parameterClasses[i] = toClass(parameterTypes[i]);
// Perform access check
Class enclosingCandidate = enclosingInfo.getEnclosingClass();
enclosingCandidate.checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED,
Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
/*
* Loop over all declared constructors; match number
* of and type of parameters.
*/
for(Constructor c: enclosingCandidate.getDeclaredConstructors()) {
Class[] candidateParamClasses = c.getParameterTypes();
if (candidateParamClasses.length == parameterClasses.length) {
boolean matches = true;
for(int i = 0; i < candidateParamClasses.length; i++) {
if (!candidateParamClasses[i].equals(parameterClasses[i])) {
matches = false;
break;
}
}
if (matches)
return c;
}
}
throw new InternalError("Enclosing constructor not found");
}
}
//返回一个 Constructor 对象,该对象反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口的指定构造方法。
@CallerSensitive
public Class getDeclaringClass() throws SecurityException {
final Class candidate = getDeclaringClass0();
if (candidate != null)
candidate.checkPackageAccess(
ClassLoader.getClassLoader(Reflection.getCallerClass()), true);
return candidate;
}
private native Class getDeclaringClass0();
//如果这个类是本地或匿名类,返回底层类的立即封闭类。
@CallerSensitive
public Class getEnclosingClass() throws SecurityException {
// There are five kinds of classes (or interfaces):
// a) Top level classes
// b) Nested classes (static member classes)
// c) Inner classes (non-static member classes)
// d) Local classes (named classes declared within a method)
// e) Anonymous classes
// JVM Spec 4.8.6: A class must have an EnclosingMethod
// attribute if and only if it is a local class or an
// anonymous class.
EnclosingMethodInfo enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethodInfo();
Class enclosingCandidate;
if (enclosingInfo == null) {
// This is a top level or a nested class or an inner class (a, b, or c)
enclosingCandidate = getDeclaringClass();
} else {
Class enclosingClass = enclosingInfo.getEnclosingClass();
// This is a local class or an anonymous class (d or e)
if (enclosingClass == this || enclosingClass == null)
throw new InternalError("Malformed enclosing method information");
else
enclosingCandidate = enclosingClass;
}
if (enclosingCandidate != null)
enclosingCandidate.checkPackageAccess(
ClassLoader.getClassLoader(Reflection.getCallerClass()), true);
return enclosingCandidate;
}
//获取源代码中给出的“底层类”简称,木有包名,如果是个匿名函数则返回空空字符串。注意和getName区分
public String getSimpleName() {
if (isArray())
return getComponentType().getSimpleName()+"[]";
String simpleName = getSimpleBinaryName();
if (simpleName == null) { // top level class
simpleName = getName();
return simpleName.substring(simpleName.lastIndexOf(".")+1); // strip the package name
}
// According to JLS3 "Binary Compatibility" (13.1) the binary
// name of non-package classes (not top level) is the binary
// name of the immediately enclosing class followed by a '$' followed by:
// (for nested and inner classes): the simple name.
// (for local classes): 1 or more digits followed by the simple name.
// (for anonymous classes): 1 or more digits.
// Since getSimpleBinaryName() will strip the binary name of
// the immediatly enclosing class, we are now looking at a
// string that matches the regular expression "\$[0-9]*"
// followed by a simple name (considering the simple of an
// anonymous class to be the empty string).
// Remove leading "\$[0-9]*" from the name
int length = simpleName.length();
if (length < 1 || simpleName.charAt(0) != '$')
throw new InternalError("Malformed class name");
int index = 1;
while (index < length && isAsciiDigit(simpleName.charAt(index)))
index++;
// Eventually, this is the empty string iff this is an anonymous class
return simpleName.substring(index);
}
/**
* Return an informative string for the name of this type.
*
* @return an informative string for the name of this type
* @since 1.8
*/
public String getTypeName() {
if (isArray()) {
try {
Class cl = this;
int dimensions = 0;
while (cl.isArray()) {
dimensions++;
cl = cl.getComponentType();
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(cl.getName());
for (int i = 0; i < dimensions; i++) {
sb.append("[]");
}
return sb.toString();
} catch (Throwable e) { /*FALLTHRU*/ }
}
return getName();
}
////判断字符是否是ASCII码
private static boolean isAsciiDigit(char c) {
return '0' <= c && c <= '9';
}
public String getCanonicalName() {
if (isArray()) {
String canonicalName = getComponentType().getCanonicalName();
if (canonicalName != null)
return canonicalName + "[]";
else
return null;
}
if (isLocalOrAnonymousClass())
return null;
Class enclosingClass = getEnclosingClass();
if (enclosingClass == null) { // top level class
return getName();
} else {
String enclosingName = enclosingClass.getCanonicalName();
if (enclosingName == null)
return null;
return enclosingName + "." + getSimpleName();
}
}
//判断是否是注释类型
public boolean isAnonymousClass() {
return "".equals(getSimpleName());
}
//判断是否是局部类
public boolean isLocalClass() {
return isLocalOrAnonymousClass() && !isAnonymousClass();
}
//判断是否是成员类
public boolean isMemberClass() {
return getSimpleBinaryName() != null && !isLocalOrAnonymousClass();
}
/**
* Returns the "simple binary name" of the underlying class, i.e.,
* the binary name without the leading enclosing class name.
* Returns {@code null} if the underlying class is a top level
* class.
*/
private String getSimpleBinaryName() {
Class enclosingClass = getEnclosingClass();
if (enclosingClass == null) // top level class
return null;
// Otherwise, strip the enclosing class' name
try {
return getName().substring(enclosingClass.getName().length());
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new InternalError("Malformed class name", ex);
}
}
//局部类和匿名类返回true
private boolean isLocalOrAnonymousClass() {
// JVM Spec 4.8.6: A class must have an EnclosingMethod
// attribute if and only if it is a local class or an
// anonymous class.
return getEnclosingMethodInfo() != null;
}
//获取该类中所有公有的成员类
@CallerSensitive
public Class[] getClasses() {
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), false);
// Privileged so this implementation can look at DECLARED classes,
// something the caller might not have privilege to do. The code here
// is allowed to look at DECLARED classes because (1) it does not hand
// out anything other than public members and (2) public member access
// has already been ok'd by the SecurityManager.
return java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedAction[]>() {
public Class[] run() {
List> list = new ArrayList<>();
Class currentClass = Class.this;
while (currentClass != null) {
Class[] members = currentClass.getDeclaredClasses();
for (int i = 0; i < members.length; i++) {
if (Modifier.isPublic(members[i].getModifiers())) {
list.add(members[i]);
}
}
currentClass = currentClass.getSuperclass();
}
return list.toArray(new Class[0]);
}
});
}
//获取所有公有字段
@CallerSensitive
public Field[] getFields() throws SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return copyFields(privateGetPublicFields(null));
}
//获取所有公有方法
@CallerSensitive
public Method[] getMethods() throws SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return copyMethods(privateGetPublicMethods());
}
//获取所有公有构造器
@CallerSensitive
public Constructor[] getConstructors() throws SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return copyConstructors(privateGetDeclaredConstructors(true));
}
//根据名称获取字段
@CallerSensitive
public Field getField(String name)
throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
Field field = getField0(name);
if (field == null) {
throw new NoSuchFieldException(name);
}
return field;
}
//根据方法名称获取方法信息,后面的变长参数是该方法的每一个参数的对应的Class类型
@CallerSensitive
public Method getMethod(String name, Class... parameterTypes)
throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
Method method = getMethod0(name, parameterTypes, true);
if (method == null) {
throw new NoSuchMethodException(getName() + "." + name + argumentTypesToString(parameterTypes));
}
return method;
}
// 根据构造器名称获取构造器信息,后面的变长参数是该构造器的每一个参数的对应的Class类型
@CallerSensitive
public Constructor getConstructor(Class... parameterTypes)
throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return getConstructor0(parameterTypes, Member.PUBLIC);
}
//返回类中所有内部类,这里的类包括数组、接口等
@CallerSensitive
public Class[] getDeclaredClasses() throws SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), false);
return getDeclaredClasses0();
}
//返回类中成员字段
@CallerSensitive
public Field[] getDeclaredFields() throws SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return copyFields(privateGetDeclaredFields(false));
}
//返回类中成员字段
@CallerSensitive
public Method[] getDeclaredMethods() throws SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return copyMethods(privateGetDeclaredMethods(false));
}
//返回类中所有构造器
@CallerSensitive
public Constructor[] getDeclaredConstructors() throws SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return copyConstructors(privateGetDeclaredConstructors(false));
}
//返回对应的字段Field对象
@CallerSensitive
public Field getDeclaredField(String name)
throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
Field field = searchFields(privateGetDeclaredFields(false), name);
if (field == null) {
throw new NoSuchFieldException(name);
}
return field;
}
//返回对应的Method对象,name是方法名称,parameterTypes是对应形参
@CallerSensitive
public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class... parameterTypes)
throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
Method method = searchMethods(privateGetDeclaredMethods(false), name, parameterTypes);
if (method == null) {
throw new NoSuchMethodException(getName() + "." + name + argumentTypesToString(parameterTypes));
}
return method;
}
//getDeclaredMethod():对给出的name获取对应的类中的方法(Method对象)
* 若不存在,则抛出NoSuchMethodException异常
@CallerSensitive
public Constructor getDeclaredConstructor(Class... parameterTypes)
throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return getConstructor0(parameterTypes, Member.DECLARED);
}
//获取参数中指定的资源,以字节流返回
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
name = resolveName(name);
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();
if (cl==null) {
// A system class.
return ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(name);
}
return cl.getResourceAsStream(name);
}
//返回指定的资源 url格式
public java.net.URL getResource(String name) {
name = resolveName(name);
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();
if (cl==null) {
// A system class.
return ClassLoader.getSystemResource(name);
}
return cl.getResource(name);
}
}