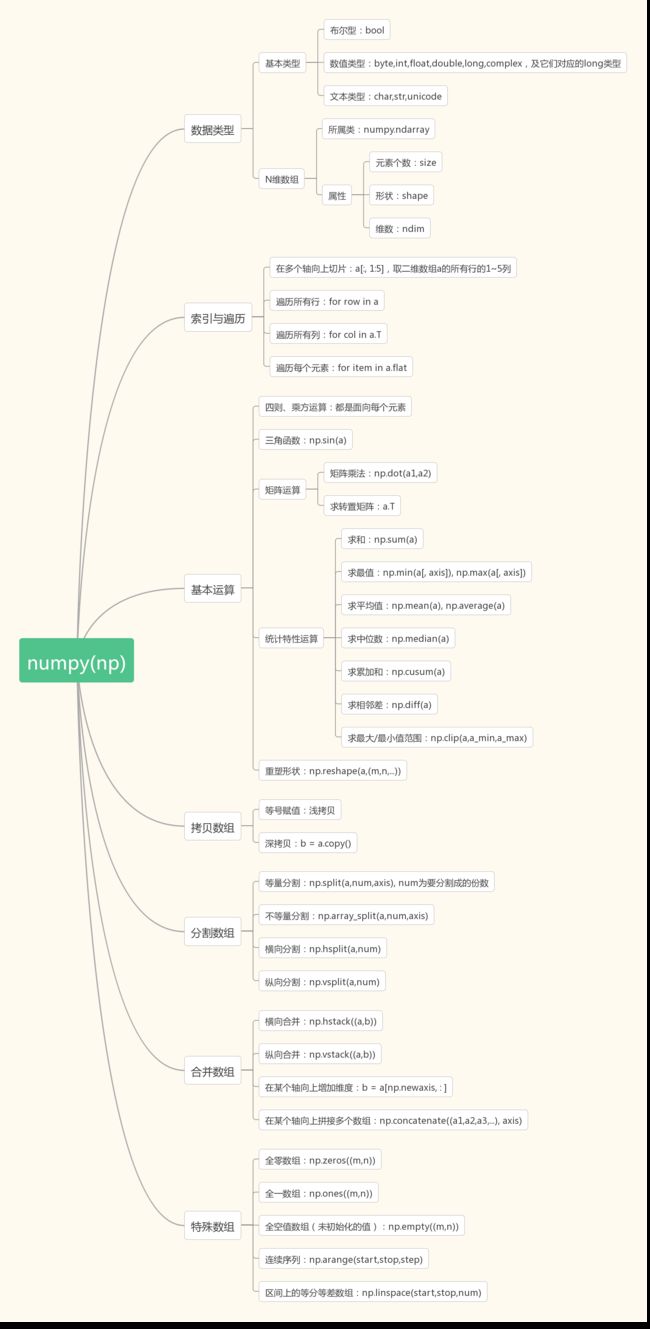
numpy库是python的一个著名的科学计算库,本文是一个quickstart。
引入:计算BMI
BMI = 体重(kg)/身高(m)^2
假如有如下几组体重和身高数据,让求每组数据的BMI值:
weight = [65.4,59.2,63.6,88.4,68.7]
height = [1.73,1.68,1.71,1.89,1.79]
print weight / height ** 2
执行上面代码,报错:TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for ** or pow(): 'list' and 'int'
这是因为普通的除法是元素级的而非向量级的,并不能应用到一组数据上。
解决方案:使用numpy.ndarray数据结构(N维数组),运算是面向矩阵的:
import numpy as np
np_weight = np.array(weight)
np_height = np.array(height)
print type(np_weight)
print type(np_height)
print np_weight
print np_height
[ 65.4 59.2 63.6 88.4 68.7]
[ 1.73 1.68 1.71 1.89 1.79]
注:和python的列表不同的是,numpy.ndarray数据结构的元素之间是没有逗号分隔的。
np_bmi = np_weight / np_height ** 2
print type(np_bmi)
print np_bmi
[ 21.85171573 20.97505669 21.75028214 24.7473475 21.44127836]
numpy数组:numpy.ndarray
numpy.ndarray是numpy最基本的数据结构,即N维数组,且数组中的元素需要是同一种类型,如果不是,则会自动转换成同一种类型,如:
print np.array([1.0,'hi',True])
['1.0' 'hi' 'True']
可以看到都被转成了字符串类型。
不同数据类型的不同行为
# 普通的python列表
py_list = [1,2,3]
# numpy数组
np_array = np.array(py_list)
print py_list + py_list # 这是列表的拼接
[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
print np_array + np_array # 这是每两个对应元素之间的运算
[2 4 6]
子集
print np_bmi[0]
21.8517157272
print np_bmi > 23
[False False False True False]
print np_bmi[np_bmi > 23]
[ 24.7473475]
二维numpy数组
二维numpy数组是以list作为元素的数组,比如:
np_2d = np.array([height,weight])
print type(np_2d)
print np_2d
[[ 1.73 1.68 1.71 1.89 1.79]
[ 65.4 59.2 63.6 88.4 68.7 ]]
print np_2d.shape
(2, 5)
通过shape属性值可以看出,np_2d是一个2行5列的二维数组。
single type原则
print np.array([[1,2],[3,'4']])
[['1' '2']
['3' '4']]
二维numpy数组的子集
np_2d = np.array([height,weight])
print np_2d
[[ 1.73 1.68 1.71 1.89 1.79]
[ 65.4 59.2 63.6 88.4 68.7 ]]
print np_2d[0][2]
1.71
print np_2d[0,2]
1.71
还可以在两个轴向上分别切片:
print np_2d[:,1:3]
[[ 1.68 1.71]
[ 59.2 63.6 ]]
选取第1行:
print np_2d[1,:]
[ 65.4 59.2 63.6 88.4 68.7]
求对应的BMI值:
print np_2d[1,:] / np_2d[0,:] ** 2
[ 21.85171573 20.97505669 21.75028214 24.7473475 21.44127836]
应用
用numpy生成呈正态分布的随机测试数据,并求各项基本的统计数据。
比如生成10000条数据集,记录的是某个镇上所有居民的身高(m)、体重(kg)数据,所用到的函数:
np.random.normal(均值,标准差,取样数)
height = np.random.normal(1.75,0.20,10000)
weight = np.random.normal(60.32,15,10000)
下面将若干个(这里是2个)一维数组拼成一个二维数组(有点像zip()函数的作用):
np_info = np.column_stack((height,weight))
print np_info
[[ 1.88474198 76.24957048]
[ 1.85353302 64.62674488]
[ 1.74999035 67.5831439 ]
...,
[ 1.78187257 50.11001273]
[ 1.90415778 50.65985964]
[ 1.51573081 41.00493358]]
求np_info身高平均值:
print np.mean(np_info[:,0])
1.75460102053
求身高的中位数:
print np.median(np_info[:,0])
1.75385473036
求身高和体重的相关系数:
print np.corrcoef(np_info[:,0],np_info[:,1])
[[ 1.00000000e+00 -1.50825116e-04]
[ -1.50825116e-04 1.00000000e+00]]
求身高的标准差:
print np.std(np_info[:,0])
0.201152169706
排序(不会影响源数组):
print np.sort(np_info[0:10,0])
[ 1.46053123 1.59268772 1.74939538 1.74999035 1.78229515 1.85353302
1.88474198 1.99755291 2.12384833 2.3727505 ]
求和:
print np.sum(np_info[0:10,0])
18.5673265584