本文已授权微信公众号:鸿洋(hongyangAndroid)原创首发。
一、简述
说到RecyclerView大家都很熟悉了,相比于ListView,它具有高度解耦、性能优化等优势,而且现在大多数安卓开发者都已经将RecyclerView用来完全替代ListView和GridView,因为它功能十分强大,但往往功能强大的东西,反而不太好控制,例如今天要说的这个ItemDecoration,ItemDecoration是条目装饰,下面来看看它的强大吧。
二、使用ItemDecoration绘制分割线
想想之前的ListView,要加条分割线,那是分分钟解决的小事,只需要在布局文件中对ListView控件设置其divier属性或者在动态中设置divider即可完成,但RecyclerView却没这么简单了,RecyclerView并没有提供任何直接设置分割线的方法,除了在条目布局中加入这种笨方法之外,也就只能通过ItemDecoration来实现了。
1、自定义ItemDecoration
要使用ItemDecoration,我们得必须先自定义,直接继承ItemDecoration即可。
public class MyDecorationOne extends RecyclerView.ItemDecoration {
}
2、重写getItemOffsets()和onDraw()
在实现自定义的装饰效果就必须重写getItemOffsets()和onDraw()。
public class MyDecorationOne extends RecyclerView.ItemDecoration {
/**
* 画线
*/
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.onDraw(c, parent, state);
}
/**
* 设置条目周边的偏移量
*/
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.getItemOffsets(outRect, view, parent, state);
}
}
3、解析getItemOffsets()和onDraw()
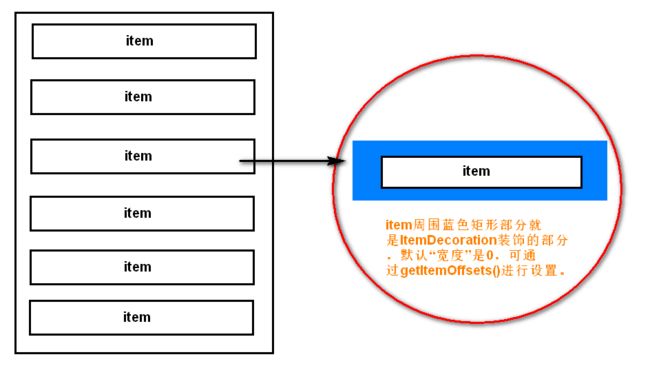
在理清这两个方法的作用之前,先理清下ItemDecoration的含义,直译:条目装饰,顾名思义,ItemDecoration是对Item起到了装饰作用,更准确的说是对item的周边起到了装饰的作用,通过下面的图应该能帮助你理解这话的含义。
上图中已经说到了,getItemOffsets()就是设置item周边的偏移量(也就是装饰区域的“宽度”)。而onDraw()才是真正实现装饰的回调方法,通过该方法可以在装饰区域任意画画,这里我们来画条分割线。
4、“实现”getItemOffsets()和onDraw()
本例中实现的是线性列表的分割线(即使用LinearLayoutManager)。
1)当线性列表是水平方向时,分割线竖直的;当线性列表是竖直方向时,分割线是水平的。
2)当画竖直分割线时,需要在item的右边偏移出一条线的宽度;当画水平分割线时,需要在item的下边偏移出一条线的高度。
/**
* 画线
*/
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.onDraw(c, parent, state);
if (orientation == RecyclerView.HORIZONTAL) {
drawVertical(c, parent, state);
} else if (orientation == RecyclerView.VERTICAL) {
drawHorizontal(c, parent, state);
}
}
/**
* 设置条目周边的偏移量
*/
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.getItemOffsets(outRect, view, parent, state);
if (orientation == RecyclerView.HORIZONTAL) {
//画垂直线
outRect.set(0, 0, mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth(), 0);
} else if (orientation == RecyclerView.VERTICAL) {
//画水平线
outRect.set(0, 0, 0, mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight());
}
}
5、画出一条华丽的分割线
因为getItemOffsets()是相对每个item而言的,即每个item都会偏移出相同的装饰区域。而onDraw()则不同,它是相对Canvas来说的,通俗的说就是要自己找到要画的线的位置,这是自定义ItemDecoration中唯一比较难的地方了。
/**
* 在构造方法中加载系统自带的分割线(就是ListView用的那个分割线)
*/
public MyDecorationOne(Context context, int orientation) {
this.orientation = orientation;
int[] attrs = new int[]{android.R.attr.listDivider};
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs);
mDivider = a.getDrawable(0);
a.recycle();
}
/**
* 画竖直分割线
*/
private void drawVertical(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int left = child.getRight() + params.rightMargin;
int top = child.getTop() - params.topMargin;
int right = left + mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth();
int bottom = child.getBottom() + params.bottomMargin;
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
/**
* 画水平分割线
*/
private void drawHorizontal(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int left = child.getLeft() - params.leftMargin;
int top = child.getBottom() + params.bottomMargin;
int right = child.getRight() + params.rightMargin;
int bottom = top + mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight();
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
下图仅对水平分割线的左、上坐标进行图解,其他坐标的计算以此类推。
6、效果
看了下面的效果,你可能会吐槽说,不就是加条分割线吗?要不要这么大费周章?是的,一开始我也是这么想,确实只是为了画条分割线的话,这也太麻烦了,而且项目开发中很少对分割线有多高的定制要求,一般就是ListView那样的,最多就是改改颜色这些。所以本人在之前有对RecyclerView进行过一次封装,可以轻松实现分割线,有兴趣的可以戳我看看!!。好了,下面继续。
三、使用ItemDecoration绘制表格
经过上面的学习,相信心中已经对ItemDecoration有个大概的底了,下面再来实现个其他的效果吧——绘制表格。
1、分析
我们知道ItemDecoration就是装饰item周边用的,画条分割线只需要2步,1是在item的下方偏移出一定的宽度,2是在偏移出来的位置上画线。画表格线其实也一样,除了画item下方的线,还画item右边的线就好了(当然换成左边也行)。
2、实现
为了完成表格的样式,本例中使用的是网格列表(即使用GridLayoutManager)。
1)自定义分割线
为了效果更加明显,这里自定义分割线样式。
2)自定义ItemDecoration
实现上跟画分割线没多大差别,瞄一下就明白了。
public class MyDecorationTwo extends RecyclerView.ItemDecoration {
private final Drawable mDivider;
public MyDecorationTwo(Context context) {
mDivider = context.getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.divider);
}
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.onDraw(c, parent, state);
drawVertical(c, parent);
drawHorizontal(c, parent);
}
private void drawVertical(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent) {
int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int left = child.getRight() + params.rightMargin;
int top = child.getTop() - params.topMargin;
int right = left + mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth();
int bottom = child.getBottom() + params.bottomMargin;
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
private void drawHorizontal(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent) {
int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int left = child.getLeft() - params.leftMargin;
int top = child.getBottom() + params.bottomMargin;
int right = child.getRight() + params.rightMargin;
int bottom = top + mDivider.getMinimumHeight();
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.getItemOffsets(outRect, view, parent, state);
outRect.set(0, 0, mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth(), mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight());
}
}
3、效果(有瑕疵)
可以看出下面的效果是有问题的,表格的最后一列和最后一行不应该出现边边。
4、修复
既然知道表格的最后一列和最后一行不应该出现边边,那就让最后一列和最后一行的边边消失就好了。有以下几个思路。
- 在onDraw()方法中,判断当前列是否为最后一列和判断当前行是否为最后一行来决定是否绘制边边。
- 在getItemOffsets()方法中对行列进行判断,来决定是否设置条目偏移量(当偏移量为0时,自然就看不出边边了)。
这里我选用第二种方式。这里要说明一下,getItemOffsets()有两个,一个是getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state),另一个是getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, int itemPosition, RecyclerView parent),第二个已经过时,但是该方法中有回传当前item的position,所以我选用了过时的getItemOffsets()。
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, int itemPosition, RecyclerView parent) {
super.getItemOffsets(outRect, itemPosition, parent);
int right = mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth();
int bottom = mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight();
if (isLastSpan(itemPosition, parent)) {
right = 0;
}
if (isLastRow(itemPosition, parent)) {
bottom = 0;
}
outRect.set(0, 0, right, bottom);
}
public boolean isLastRow(int itemPosition, RecyclerView parent) {
RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager = parent.getLayoutManager();
if (layoutManager instanceof GridLayoutManager) {
int spanCount = ((GridLayoutManager) layoutManager).getSpanCount();
int itemCount = parent.getAdapter().getItemCount();
if ((itemCount - itemPosition - 1) < spanCount)
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean isLastSpan(int itemPosition, RecyclerView parent) {
RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager = parent.getLayoutManager();
if (layoutManager instanceof GridLayoutManager) {
int spanCount = ((GridLayoutManager) layoutManager).getSpanCount();
if ((itemPosition + 1) % spanCount == 0)
return true;
}
return false;
}
代码理解上并不难,这里不做多余的解释。
5、效果(几乎没有瑕疵)
四、使用ItemDecoration实现侧边字母提示
上面的两个例子仅仅只是画线,下面的这个例子就来画字吧。先看下效果。
1、分析
说到底也就是在item左边偏移出来的空间区域中心画个字母而已。下面是大体思路:
- 在item的左边偏移出一定的空间(本例偏移量是40dp)。
- 在onDraw()时,使用Pinyin工具类获取item中名字拼音的第一个字母。
- 判断如果当前是第一个item,就画出字母。
- 若不是第一个item则判断当前item的名字字母与上一个字母是否一致,不一致则画出当前字母。
2、实现
1)自定义文字拼音工具类
****该工具类需要用到pinyin4j-2.5.0.jar***
public class PinyinUtils {
public static String getPinyin(String str) {
HanyuPinyinOutputFormat format = new HanyuPinyinOutputFormat();
format.setCaseType(HanyuPinyinCaseType.UPPERCASE);
format.setToneType(HanyuPinyinToneType.WITHOUT_TONE);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
char[] charArray = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {
char c = charArray[i];
// 如果是空格, 跳过
if (Character.isWhitespace(c)) {
continue;
}
if (c >= -127 && c < 128 || !(c >= 0x4E00 && c <= 0x9FA5)) {
// 肯定不是汉字
sb.append(c);
} else {
String s = "";
try {
// 通过char得到拼音集合. 单 -> dan, shan
s = PinyinHelper.toHanyuPinyinStringArray(c, format)[0];
sb.append(s);
} catch (BadHanyuPinyinOutputFormatCombination e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sb.append(s);
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
2)自定义ItemDecoration
public class MyDecorationThree extends RecyclerView.ItemDecoration {
Context mContext;
List mData;
Paint paint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
public MyDecorationThree(Context context, List data) {
mContext = context;
mData = data;
paint.setTextSize(sp2px(16));
paint.setColor(Color.RED);
}
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.onDraw(c, parent, state);
drawLetterToItemLeft(c, parent);
}
private void drawLetterToItemLeft(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent) {
RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager = parent.getLayoutManager();
if (!(layoutManager instanceof LinearLayoutManager))
return;
int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
int position = ((LinearLayoutManager) layoutManager).findFirstVisibleItemPosition() + i;
View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
float left = 0;
float top = child.getTop() - params.topMargin;
float right = child.getLeft() - params.leftMargin;
float bottom = child.getBottom() + params.bottomMargin;
float width = right - left;
float height = bottom - (bottom - top) / 2;
//当前名字拼音的第一个字母
String letter = PinyinUtils.getPinyin(mData.get(position)).charAt(0) + "";
if (position == 0) {
drawLetter(letter, width, height, c, parent);
} else {
String preLetter = PinyinUtils.getPinyin(mData.get(position - 1)).charAt(0) + "";
if (!letter.equalsIgnoreCase(preLetter)) {
drawLetter(letter, width, height, c, parent);
}
}
}
}
private void drawLetter(String letter, float width, float height, Canvas c, RecyclerView parent) {
float fontLength = getFontLength(paint, letter);
float fontHeight = getFontHeight(paint);
float tx = (width - fontLength) / 2;
float ty = height - fontHeight / 2 + getFontLeading(paint);
c.drawText(letter, tx, ty, paint);
}
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.getItemOffsets(outRect, view, parent, state);
outRect.set(dip2px(40), 0, 0, 0);
}
private int dip2px(int dip) {
float density = mContext.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
int px = (int) (dip * density + 0.5f);
return px;
}
public int sp2px(int sp) {
return (int) (TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_SP, sp, mContext.getResources().getDisplayMetrics()) + 0.5f);
}
/**
* 返回指定笔和指定字符串的长度
*/
private float getFontLength(Paint paint, String str) {
return paint.measureText(str);
}
/**
* 返回指定笔的文字高度
*/
private float getFontHeight(Paint paint) {
Paint.FontMetrics fm = paint.getFontMetrics();
return fm.descent - fm.ascent;
}
/**
* 返回指定笔离文字顶部的基准距离
*/
private float getFontLeading(Paint paint) {
Paint.FontMetrics fm = paint.getFontMetrics();
return fm.leading - fm.ascent;
}
}
最后附上Demo链接
https://github.com/GitLqr/MaterialDesignDemo