Nuttx相关的历史文章:
- Nuttx Task Schedule
- Nuttx信号机制
- Nuttx编译系统
介绍
广义来说,消息队列提供了一种从一个进程向另一个进程发送数据块的方法,也就是说它是一种进程间的通信方法。
Nuttx支持POSIX命名消息队列机制,用于内部的task之间的通信。任何task都可以发送和接收消息。中断处理函数中也可以通过消息队列来发送消息。
API接口
在使用API进行开发的时候,需要包含头文件#include
- 打开函数
mqd_t mq_open(const char *mqName, int oflags, ...)
该接口会在调用Task中打开/创建一个消息队列,消息队列与调用Task建立联系,调用Task可以使用返回值来引用消息队列。
其中oflags代表了不同的含义,可以将这些位进行组合:
- O_RDONLY:只读
- O_WRONLY:只写
- O_RDWR:可读可写
- O_CREAT:如果消息队列不存在,则创建
- O_EXCL:打开的时候名字必须不能存在
- O_NONBLOCK:非阻塞等数据
- 关闭函数
int mq_close(mqd_t mqdes)
调用Task负责将打开的消息队列进行关闭。
- unlink函数
int mq_unlink(const char *mqName)
该接口会删除名字为mqName的消息队列。当有一个或多个Task打开一个消息队列,此时调用mq_unlink,需要等到所有引用该消息队列的Task都执行关闭操作后,才会删除消息队列。
- 消息发送函数
int mq_send(mqd_t mqdes, const void *msg, size_t msglen, int prio)
该接口将msg消息添加到mqdes消息队列中,msglen指定了消息的字节长度,这个长度不能超过mq_getattr()接口中获取的最大长度。如果消息队列未满,mq_send()会将msg放置到prio指定的消息队列中。高优先级的消息会插在低优先级消息之前。prio的值不能超过MQ_PRIO_MAX。
如果消息队列已满,并且O_NONBLOCK没有设置,mq_send()会一直阻塞,直到消息队列有空间去存放消息。如果NON_BLOCK设置了,那么消息将不会入列,并且会返回错误码。
int mq_timedsend(mqd_t mqdes, const char *msg, size_t msglen, int prio,
const struct timespec *abstime);
该接口实现的功能与mq_send一致,唯一不同之处在于,如果消息队列已满,并且O_NONBLOCK没有设置,mq_timedsend不会一直阻塞,而会在设置的时间到期后被唤醒并接着往下执行。参数abstime指的是绝对时间。
- 消息接收函数
ssize_t mq_receive(mqd_t mqdes, void *msg, size_t msglen, int *prio);
该接口从mqdes消息队列中接收最高优先级中停留时间最久的消息。如果msglen的长度与mq_msgsize的长度不一致,mq_receive将会返回错误值。接收到的消息将会从消息队列中移除,并把内容拷贝至msg中。
如果消息队列是空的,并且O_NONBLOCK没有设置,mq_receive会一直阻塞。如果有多个task等待在一个消息队列上,当消息产生时,只有优先级最高并且等待时间最长的task将会被唤醒。
ssize_t mq_timedreceive(mqd_t mqdes, void *msg, size_t msglen,
int *prio, const struct timespec *abstime);
该接口实现的功能与mq_receive是一样的,唯一的区别在于,如果消息队列是空的,并且O_NONBLOCK没有设置,mq_timedreceive不会一直阻塞,而会在设置的时间到期后被唤醒并接着往下执行。参数abstime指的是绝对时间。
- 消息队列通知函数
int mq_notify(mqd_t mqdes, const struct sigevent *notification);
当输入参数notification为非NULL时,mq_notify会在task和消息队列中建立连接,当消息队列从空队列到非空队列转换时,会发送一个特定的信号给建立连接的task。一个notification能和一个消息队列建立连接。当参数notification为NULL时,建立的连接会被断开,这样就能建立另一个新的连接。
当notification发送给注册连接的task之后,这个注册连接关系就会移除掉,消息队列也就可以接受新的注册连接了。
- 消息队列属性设置函数
int mq_setattr(mqd_t mqdes, const struct mq_attr *mqStat,
struct mq_attr *oldMqStat);
该接口用于设置消息队列mqdes的属性。当oldMqStat为非空时,它将保存设置之前的属性值。
- 消息队列属性获取函数
int mq_getattr(mqd_t mqdes, struct mq_attr *mqStat);
该接口可以用于获取mqdes消息队列的状态信息。包括消息队列的最大容量、消息的最大长度、Flags以及当前队列中消息的数量等。
数据结构
消息队列的数据结构分为两类:一类用于描述消息定义;一类用于描述消息队列以及对应的属性。
- 消息相关数据结构
enum mqalloc_e
{
MQ_ALLOC_FIXED = 0, /* pre-allocated; never freed */
MQ_ALLOC_DYN, /* dynamically allocated; free when unused */
MQ_ALLOC_IRQ /* Preallocated, reserved for interrupt handling */
};
/* This structure describes one buffered POSIX message. */
struct mqueue_msg_s
{
FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *next; /* Forward link to next message */
uint8_t type; /* (Used to manage allocations) */
uint8_t priority; /* priority of message */
#if MQ_MAX_BYTES < 256
uint8_t msglen; /* Message data length */
#else
uint16_t msglen; /* Message data length */
#endif
char mail[MQ_MAX_BYTES]; /* Message data */
};
该结构主要描述消息的分配类型、优先级、消息的长度,以及消息的内容。
- 消息队列相关数据结构
/* This structure defines a message queue */
struct mq_des; /* forward reference */
struct mqueue_inode_s
{
FAR struct inode *inode; /* Containing inode */
sq_queue_t msglist; /* Prioritized message list */
int16_t maxmsgs; /* Maximum number of messages in the queue */
int16_t nmsgs; /* Number of message in the queue */
int16_t nwaitnotfull; /* Number tasks waiting for not full */
int16_t nwaitnotempty; /* Number tasks waiting for not empty */
#if CONFIG_MQ_MAXMSGSIZE < 256
uint8_t maxmsgsize; /* Max size of message in message queue */
#else
uint16_t maxmsgsize; /* Max size of message in message queue */
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_DISABLE_SIGNALS
FAR struct mq_des *ntmqdes; /* Notification: Owning mqdes (NULL if none) */
pid_t ntpid; /* Notification: Receiving Task's PID */
struct sigevent ntevent; /* Notification description */
#endif
};
/* This describes the message queue descriptor that is held in the
* task's TCB
*/
struct mq_des
{
FAR struct mq_des *flink; /* Forward link to next message descriptor */
FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *msgq; /* Pointer to associated message queue */
int oflags; /* Flags set when message queue was opened */
};
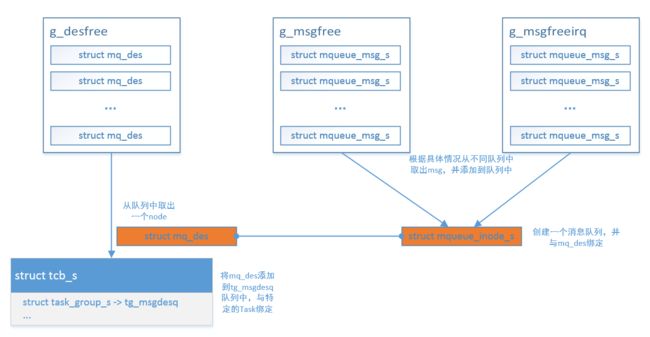
其中struct mq_des结构用于描述在一个Task中的消息队列,保存在struct task_group_s结构中,该成员结构为sq_queue_t队列,是因为线程组可以拥有多个消息队列,可以用一个队列来存储这些消息队列描述符。如下:
struct task_group_s
{
...
#ifndef CONFIG_DISABLE_MQUEUE
/* POSIX Named Message Queue Fields *******************************************/
sq_queue_t tg_msgdesq; /* List of opened message queues */
#endif
...
}
此外,还有三个全局的队列,其中g_msgfree和g_msgfreeirq队列用于存放message,区别是是否在中断处理函数中去使用。message会从这两个队列中进行申请,加入到消息队列中,当最终完成了消息的传递后,会将message再添加到这两个队列中。g_desfree队列用于存放消息队列描述符,每一个消息队列都对应一个描述符,当消息队列销毁的时候,需要将消息队列描述符添加到g_desfree队列中。
/* The g_msgfree is a list of messages that are available for general use.
* The number of messages in this list is a system configuration item.
*/
EXTERN sq_queue_t g_msgfree;
/* The g_msgfreeInt is a list of messages that are reserved for use by
* interrupt handlers.
*/
EXTERN sq_queue_t g_msgfreeirq;
/* The g_desfree data structure is a list of message descriptors available
* to the operating system for general use. The number of messages in the
* pool is a constant.
*/
EXTERN sq_queue_t g_desfree;
在上述三个队列,会在mq_initialize()接口中进行初始化,主要完成message的预分配,以及消息队列描述符的预分配。而mq_initialize()会在os_start()函数中进行调用。
实现原理
先来一个大体的介绍图吧
我们知道,每一个struct tcb_s结构体中,都保存了group->tg_msgdesq成员,用于存放打开的不同消息队列。当一个任务调用mq_open接口来打开一个消息队列时(假设此时消息队列不存在,需要新建),首先会从g_desfree这个全局队列中,获取一个消息队列描述符,并且会创建一个struct mqueue_inode_s消息队列,将创建的消息队列和消息队列描述符绑定在一起,并且添加到任务的结构体中,这样,每个任务就知道本身所创建的消息队列了。由于消息队列需要创建设备节点,因此在mq_open这个函数中,还需要添加创建inode相关的接口,用于文件系统相关操作,比如,如果该消息队列存在,也就是inode存在,那就不需要再额外创建了。
消息的发送与接收过程也比较简单,图中的struct mqueue_msg_s就相当于一个集装箱,实际的数据传递都会用这个集装箱进行搬运。因此,在发送的时候,如果不在中断上下文中,则从g_msgfree中申请一个节点,把需要发送的数据拷贝至该节点,并将该节点添加到消息队列中。接收的过程,则是从消息队列中拿出节点,使用完消息数据后,将该节点再返回给g_msgfree队列中。在中断上下文中,也同样的道理。,当然在这个过程中,涉及到阻塞睡眠的问题,以及队列信号通知的情况,下边会继续深入。
mq_close执行,会将所有的资源进行释放,返回给全局队列中,同时创建的inode如果引用值变成了0,则需要进行释放。
下边将分别从几个函数来分析:
mq_open()
mq_open函数会完成以下任务:
- 调用
inode_find()接口去查询是否已经存在一个消息队列对应的inode了,由于消息队列都会对应到一个文件节点,比如"/var/mqueue/my_mq",需要为消息队列创建inode。如果mq_open()打开的是已有的消息队列,那么inode_find()就能找到对应的节点,否则就需要调用inode_reserve()去创建。 - 如果消息队列不存在,除了创建
inode之外,还需要调用mq_descreate()接口创建消息队列描述符,mq_descreate()接口中调用mq_desalloc(),从全局队列中挪取描述符节点,并加入到struct tcb_s结构中,这个在上图中也能看出来。 - 调用
mq_msgqalloc()接口,创建一个消息队列,并将消息队列与mq_descreate()获取的消息队列描述符进行绑定。最终更新更新inode的信息。
关键代码如下:
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_open
*
* Description:
* This function establish a connection between a named message queue and
* the calling task. After a successful call of mq_open(), the task can
* reference the message queue using the address returned by the call. The
* message queue remains usable until it is closed by a successful call to
* mq_close().
*
* Parameters:
* mq_name - Name of the queue to open
* oflags - open flags
* Optional parameters. When the O_CREAT flag is specified, two optional
* parameters are expected:
*
* 1. mode_t mode (ignored), and
* 2. struct mq_attr *attr. The mq_maxmsg attribute
* is used at the time that the message queue is
* created to determine the maximum number of
* messages that may be placed in the message queue.
*
* Return Value:
* A message queue descriptor or (mqd_t)-1 (ERROR)
*
* Assumptions:
*
****************************************************************************/
mqd_t mq_open(FAR const char *mq_name, int oflags, ...)
{
...
sched_lock();
/* Get the inode for this mqueue. This should succeed if the message
* queue has already been created. In this case, inode_find() will
* have incremented the reference count on the inode.
*/
SETUP_SEARCH(&desc, fullpath, false);
ret = inode_find(&desc);
if (ret >= 0)
{
/* Something exists at this path. Get the search results */
inode = desc.node;
DEBUGASSERT(inode != NULL);
/* Verify that the inode is a message queue */
if (!INODE_IS_MQUEUE(inode))
{
errcode = ENXIO;
goto errout_with_inode;
}
/* It exists and is a message queue. Check if the caller wanted to
* create a new mqueue with this name.
*/
if ((oflags & (O_CREAT | O_EXCL)) == (O_CREAT | O_EXCL))
{
errcode = EEXIST;
goto errout_with_inode;
}
/* Create a message queue descriptor for the current thread */
msgq = inode->u.i_mqueue;
mqdes = mq_descreate(NULL, msgq, oflags);
if (!mqdes)
{
errcode = ENOMEM;
goto errout_with_inode;
}
}
else
{
/* The mqueue does not exists. Were we asked to create it? */
if ((oflags & O_CREAT) == 0)
{
/* The mqueue does not exist and O_CREAT is not set */
errcode = ENOENT;
goto errout_with_lock;
}
/* Create the mqueue. First we have to extract the additional
* parameters from the variable argument list.
*/
va_start(ap, oflags);
mode = va_arg(ap, mode_t);
attr = va_arg(ap, FAR struct mq_attr *);
va_end(ap);
/* Create an inode in the pseudo-filesystem at this path */
inode_semtake();
ret = inode_reserve(fullpath, &inode);
inode_semgive();
if (ret < 0)
{
errcode = -ret;
goto errout_with_lock;
}
/* Allocate memory for the new message queue. The new inode will
* be created with a reference count of zero.
*/
msgq = (FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *)mq_msgqalloc(mode, attr);
if (!msgq)
{
errcode = ENOSPC;
goto errout_with_inode;
}
/* Create a message queue descriptor for the TCB */
mqdes = mq_descreate(NULL, msgq, oflags);
if (!mqdes)
{
errcode = ENOMEM;
goto errout_with_msgq;
}
/* Bind the message queue and the inode structure */
INODE_SET_MQUEUE(inode);
inode->u.i_mqueue = msgq;
msgq->inode = inode;
/* Set the initial reference count on this inode to one */
inode->i_crefs = 1;
}
RELEASE_SEARCH(&desc);
sched_unlock();
...
}
罗列一下struct inode的定义吧:
/* Named OS resources are also maintained by the VFS. This includes:
*
* - Named semaphores: sem_open(), sem_close(), and sem_unlink()
* - POSIX Message Queues: mq_open() and mq_close()
* - Shared memory: shm_open() and shm_unlink();
*
* These are a special case in that they do not follow quite the same
* pattern as the other file system types in that they have operations.
*/
/* These are the various kinds of operations that can be associated with
* an inode.
*/
union inode_ops_u
{
FAR const struct file_operations *i_ops; /* Driver operations for inode */
#ifndef CONFIG_DISABLE_MOUNTPOINT
FAR const struct block_operations *i_bops; /* Block driver operations */
FAR const struct mountpt_operations *i_mops; /* Operations on a mountpoint */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FS_NAMED_SEMAPHORES
FAR struct nsem_inode_s *i_nsem; /* Named semaphore */
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_DISABLE_MQUEUE
FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *i_mqueue; /* POSIX message queue */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PSEUDOFS_SOFTLINKS
FAR char *i_link; /* Full path to link target */
#endif
};
/* This structure represents one inode in the Nuttx pseudo-file system */
struct inode
{
FAR struct inode *i_peer; /* Link to same level inode */
FAR struct inode *i_child; /* Link to lower level inode */
int16_t i_crefs; /* References to inode */
uint16_t i_flags; /* Flags for inode */
union inode_ops_u u; /* Inode operations */
#ifdef CONFIG_FILE_MODE
mode_t i_mode; /* Access mode flags */
#endif
FAR void *i_private; /* Per inode driver private data */
char i_name[1]; /* Name of inode (variable) */
};
mq_send()
mq_send()函数主要完成以下任务:
- 调用
mq_verifysend()对传入参数进行合法性验证,比如消息的长度、优先级等的设置,出错则设置errono并返回。 - 如果存在以下三种情况中的任意一种:1)
mq_send()是在中断环境中调用;2)消息队列非满;3)调用mq_waitsend()等到了消息队列非满的信号;则调用mq_msgalloc()分配消息,并通过mq_dosend()完成实际的发送。否则就是发送失败。 -
mq_waitsend()函数会被mq_send()/mq_timesend()调用,如果消息队列已经满了的话,这个函数会进行阻塞等待,在本函数中会去判断O_NONBLOCK标志是否被置上了。函数阻塞,也就是将自身让出CPU,并且调度其他Task运行,mq_wairtsend()是通过调用up_block_task(struct tcb_s *tcb, tstate_t task_state)接口实现,该接口会将tcb从任务队列中移除,并添加到task_state对应的队列中。 -
mq_dosend()完成真正的消息发送,在该函数中,会将用户的消息内容拷贝至struct mqueue_msg_s描述的集装箱中,然后再把消息按优先级的顺序插入到消息队列中。此外,还会调用sig_mqnotempty()/sig_notification()接口发送队列非空的信号。最后,查询g_waitingformqnotempty队列,是否有任务在等待这个队列变成非空,如果有的话,就将该任务unblock掉。
关键代码如下:
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_send
*
* Description:
* This function adds the specified message (msg) to the message queue
* (mqdes). The "msglen" parameter specifies the length of the message
* in bytes pointed to by "msg." This length must not exceed the maximum
* message length from the mq_getattr().
*
* If the message queue is not full, mq_send() place the message in the
* message queue at the position indicated by the "prio" argument.
* Messages with higher priority will be inserted before lower priority
* messages. The value of "prio" must not exceed MQ_PRIO_MAX.
*
* If the specified message queue is full and O_NONBLOCK is not set in the
* message queue, then mq_send() will block until space becomes available
* to the queue the message.
*
* If the message queue is full and O_NONBLOCK is set, the message is not
* queued and ERROR is returned.
*
* Parameters:
* mqdes - Message queue descriptor
* msg - Message to send
* msglen - The length of the message in bytes
* prio - The priority of the message
*
* Return Value:
* On success, mq_send() returns 0 (OK); on error, -1 (ERROR)
* is returned, with errno set to indicate the error:
*
* EAGAIN The queue was full and the O_NONBLOCK flag was set for the
* message queue description referred to by mqdes.
* EINVAL Either msg or mqdes is NULL or the value of prio is invalid.
* EPERM Message queue opened not opened for writing.
* EMSGSIZE 'msglen' was greater than the maxmsgsize attribute of the
* message queue.
* EINTR The call was interrupted by a signal handler.
*
* Assumptions/restrictions:
*
****************************************************************************/
int mq_send(mqd_t mqdes, FAR const char *msg, size_t msglen, int prio)
{
...
/* mq_send() is a cancellation point */
(void)enter_cancellation_point();
/* Verify the input parameters -- setting errno appropriately
* on any failures to verify.
*/
if (mq_verifysend(mqdes, msg, msglen, prio) != OK)
{
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
/* Get a pointer to the message queue */
sched_lock();
msgq = mqdes->msgq;
/* Allocate a message structure:
* - Immediately if we are called from an interrupt handler.
* - Immediately if the message queue is not full, or
* - After successfully waiting for the message queue to become
* non-FULL. This would fail with EAGAIN, EINTR, or ETIMEOUT.
*/
flags = enter_critical_section();
if (up_interrupt_context() || /* In an interrupt handler */
msgq->nmsgs < msgq->maxmsgs || /* OR Message queue not full */
mq_waitsend(mqdes) == OK) /* OR Successfully waited for mq not full */
{
/* Allocate the message */
leave_critical_section(flags);
mqmsg = mq_msgalloc();
/* Check if the message was sucessfully allocated */
if (mqmsg == NULL)
{
/* No... mq_msgalloc() does not set the errno value */
set_errno(ENOMEM);
}
}
else
{
/* We cannot send the message (and didn't even try to allocate it)
* because:
* - We are not in an interrupt handler AND
* - The message queue is full AND
* - When we tried waiting, the wait was unsuccessful.
*
* In this case mq_waitsend() has already set the errno value.
*/
leave_critical_section(flags);
}
/* Check if we were able to get a message structure -- this can fail
* either because we cannot send the message (and didn't bother trying
* to allocate it) or because the allocation failed.
*/
if (mqmsg != NULL)
{
/* The allocation was successful (implying that we can also send the
* message). Perform the message send.
*
* NOTE: There is a race condition here: What if a message is added by
* interrupt related logic so that queue again becomes non-empty.
* That is handled because mq_dosend() will permit the maxmsgs limit
* to be exceeded in that case.
*/
ret = mq_dosend(mqdes, mqmsg, msg, msglen, prio);
}
...
}
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_waitsend
*
* Description:
* This is internal, common logic shared by both mq_send and mq_timesend.
* This function waits until the message queue is not full.
*
* Parameters:
* mqdes - Message queue descriptor
*
* Return Value:
* On success, mq_send() returns 0 (OK); on error, -1 (ERROR) is
* returned, with errno set to indicate the error:
*
* EAGAIN The queue was full and the O_NONBLOCK flag was set for the
* message queue description referred to by mqdes.
* EINTR The call was interrupted by a signal handler.
* ETIMEOUT A timeout expired before the message queue became non-full
* (mq_timedsend only).
*
* Assumptions/restrictions:
* - The caller has verified the input parameters using mq_verifysend().
* - Executes within a critical section established by the caller.
*
****************************************************************************/
int mq_waitsend(mqd_t mqdes)
{
FAR struct tcb_s *rtcb;
FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *msgq;
/* mq_waitsend() is not a cancellation point, but it is always called from
* a cancellation point.
*/
if (enter_cancellation_point())
{
#ifdef CONFIG_CANCELLATION_POINTS
/* If there is a pending cancellation, then do not perform
* the wait. Exit now with ECANCELED.
*/
set_errno(ECANCELED);
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
#endif
}
/* Get a pointer to the message queue */
msgq = mqdes->msgq;
/* Verify that the queue is indeed full as the caller thinks */
if (msgq->nmsgs >= msgq->maxmsgs)
{
/* Should we block until there is sufficient space in the
* message queue?
*/
if ((mqdes->oflags & O_NONBLOCK) != 0)
{
/* No... We will return an error to the caller. */
set_errno(EAGAIN);
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
/* Yes... We will not return control until the message queue is
* available or we receive a signal or at timout occurs.
*/
else
{
/* Loop until there are fewer than max allowable messages in the
* receiving message queue
*/
while (msgq->nmsgs >= msgq->maxmsgs)
{
/* Block until the message queue is no longer full.
* When we are unblocked, we will try again
*/
rtcb = this_task();
rtcb->msgwaitq = msgq;
msgq->nwaitnotfull++;
set_errno(OK);
up_block_task(rtcb, TSTATE_WAIT_MQNOTFULL);
/* When we resume at this point, either (1) the message queue
* is no longer empty, or (2) the wait has been interrupted by
* a signal. We can detect the latter case be examining the
* errno value (should be EINTR or ETIMEOUT).
*/
if (get_errno() != OK)
{
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
}
}
}
leave_cancellation_point();
return OK;
}
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_dosend
*
* Description:
* This is internal, common logic shared by both mq_send and mq_timesend.
* This function adds the specified message (msg) to the message queue
* (mqdes). Then it notifies any tasks that were waiting for message
* queue notifications setup by mq_notify. And, finally, it awakens any
* tasks that were waiting for the message not empty event.
*
* Parameters:
* mqdes - Message queue descriptor
* msg - Message to send
* msglen - The length of the message in bytes
* prio - The priority of the message
*
* Return Value:
* This function always returns OK.
*
* Assumptions/restrictions:
*
****************************************************************************/
int mq_dosend(mqd_t mqdes, FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *mqmsg, FAR const char *msg,
size_t msglen, int prio)
{
FAR struct tcb_s *btcb;
FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *msgq;
FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *next;
FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *prev;
irqstate_t flags;
/* Get a pointer to the message queue */
sched_lock();
msgq = mqdes->msgq;
/* Construct the message header info */
mqmsg->priority = prio;
mqmsg->msglen = msglen;
/* Copy the message data into the message */
memcpy((FAR void *)mqmsg->mail, (FAR const void *)msg, msglen);
/* Insert the new message in the message queue */
flags = enter_critical_section();
/* Search the message list to find the location to insert the new
* message. Each is list is maintained in ascending priority order.
*/
for (prev = NULL, next = (FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *)msgq->msglist.head;
next && prio <= next->priority;
prev = next, next = next->next);
/* Add the message at the right place */
if (prev)
{
sq_addafter((FAR sq_entry_t *)prev, (FAR sq_entry_t *)mqmsg,
&msgq->msglist);
}
else
{
sq_addfirst((FAR sq_entry_t *)mqmsg, &msgq->msglist);
}
/* Increment the count of messages in the queue */
msgq->nmsgs++;
leave_critical_section(flags);
/* Check if we need to notify any tasks that are attached to the
* message queue
*/
#ifndef CONFIG_DISABLE_SIGNALS
if (msgq->ntmqdes)
{
struct sigevent event;
pid_t pid;
/* Remove the message notification data from the message queue. */
memcpy(&event, &msgq->ntevent, sizeof(struct sigevent));
pid = msgq->ntpid;
/* Detach the notification */
memset(&msgq->ntevent, 0, sizeof(struct sigevent));
msgq->ntpid = INVALID_PROCESS_ID;
msgq->ntmqdes = NULL;
/* Notification the client via signal? */
if (event.sigev_notify == SIGEV_SIGNAL)
{
/* Yes... Queue the signal -- What if this returns an error? */
#ifdef CONFIG_CAN_PASS_STRUCTS
DEBUGVERIFY(sig_mqnotempty(pid, event.sigev_signo,
event.sigev_value));
#else
DEBUGVERIFY(sig_mqnotempty(pid, event.sigev_signo,
event.sigev_value.sival_ptr));
#endif
}
#ifdef CONFIG_SIG_EVTHREAD
/* Notify the client via a function call */
else if (event.sigev_notify == SIGEV_THREAD)
{
DEBUGVERIFY(sig_notification(pid, &event));
}
#endif
}
#endif
/* Check if any tasks are waiting for the MQ not empty event. */
flags = enter_critical_section();
if (msgq->nwaitnotempty > 0)
{
/* Find the highest priority task that is waiting for
* this queue to be non-empty in g_waitingformqnotempty
* list. sched_lock() should give us sufficent protection since
* interrupts should never cause a change in this list
*/
for (btcb = (FAR struct tcb_s *)g_waitingformqnotempty.head;
btcb && btcb->msgwaitq != msgq;
btcb = btcb->flink);
/* If one was found, unblock it */
ASSERT(btcb);
btcb->msgwaitq = NULL;
msgq->nwaitnotempty--;
up_unblock_task(btcb);
}
leave_critical_section(flags);
sched_unlock();
return OK;
}
mq_receive
mq_receive()接口,与mq_send()类似,主要完成以下几个任务:
- 调用
mq_verifyreceive()对参数进行验证 - 调用
mq_waitreceive()进行等待消息操作,如果消息队列为空并且没有设置O_NONBLOCK,则睡眠等待,让出CPU,设置了O_NONBLOCK的话就直接报错返回。如果消息队列不为空,则直接从队列头部挪取一个消息节点。 - 调用
mq_doreceive()来完成实际的接收处理。 - 在
do_mqreceive()接口中,将``struct mqueue_msg_s中的内容拷贝至用户提供的ubuffer地址中。调用mq_msgree()释放struct mqueue_msg_s内容,也就是返回g_msgfree全局队列中。查询g_waitingformqnotfull队列中的任务,是否有任务在等待该队列变成非满,如果有的话,则调用up_unblock_task()把该任务unblock`。
关键代码如下:
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_receive
*
* Description:
* This function receives the oldest of the highest priority messages
* from the message queue specified by "mqdes." If the size of the
* buffer in bytes (msglen) is less than the "mq_msgsize" attribute of
* the message queue, mq_receive will return an error. Otherwise, the
* selected message is removed from the queue and copied to "msg."
*
* If the message queue is empty and O_NONBLOCK was not set,
* mq_receive() will block until a message is added to the message
* queue. If more than one task is waiting to receive a message, only
* the task with the highest priority that has waited the longest will
* be unblocked.
*
* If the queue is empty and O_NONBLOCK is set, ERROR will be returned.
*
* Parameters:
* mqdes - Message Queue Descriptor
* msg - Buffer to receive the message
* msglen - Size of the buffer in bytes
* prio - If not NULL, the location to store message priority.
*
* Return Value:
* One success, the length of the selected message in bytes is returned.
* On failure, -1 (ERROR) is returned and the errno is set appropriately:
*
* EAGAIN The queue was empty, and the O_NONBLOCK flag was set
* for the message queue description referred to by 'mqdes'.
* EPERM Message queue opened not opened for reading.
* EMSGSIZE 'msglen' was less than the maxmsgsize attribute of the
* message queue.
* EINTR The call was interrupted by a signal handler.
* EINVAL Invalid 'msg' or 'mqdes'
*
* Assumptions:
*
****************************************************************************/
ssize_t mq_receive(mqd_t mqdes, FAR char *msg, size_t msglen,
FAR int *prio)
{
FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *mqmsg;
irqstate_t flags;
ssize_t ret = ERROR;
DEBUGASSERT(up_interrupt_context() == false);
/* mq_receive() is a cancellation point */
(void)enter_cancellation_point();
/* Verify the input parameters and, in case of an error, set
* errno appropriately.
*/
if (mq_verifyreceive(mqdes, msg, msglen) != OK)
{
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
/* Get the next message from the message queue. We will disable
* pre-emption until we have completed the message received. This
* is not too bad because if the receipt takes a long time, it will
* be because we are blocked waiting for a message and pre-emption
* will be re-enabled while we are blocked
*/
sched_lock();
/* Furthermore, mq_waitreceive() expects to have interrupts disabled
* because messages can be sent from interrupt level.
*/
flags = enter_critical_section();
/* Get the message from the message queue */
mqmsg = mq_waitreceive(mqdes);
leave_critical_section(flags);
/* Check if we got a message from the message queue. We might
* not have a message if:
*
* - The message queue is empty and O_NONBLOCK is set in the mqdes
* - The wait was interrupted by a signal
*/
if (mqmsg)
{
ret = mq_doreceive(mqdes, mqmsg, msg, prio);
}
sched_unlock();
leave_cancellation_point();
return ret;
}
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_waitreceive
*
* Description:
* This is internal, common logic shared by both mq_receive and
* mq_timedreceive. This function waits for a message to be received on
* the specified message queue, removes the message from the queue, and
* returns it.
*
* Parameters:
* mqdes - Message queue descriptor
*
* Return Value:
* On success, a reference to the received message. If the wait was
* interrupted by a signal or a timeout, then the errno will be set
* appropriately and NULL will be returned.
*
* Assumptions:
* - The caller has provided all validity checking of the input parameters
* using mq_verifyreceive.
* - Interrupts should be disabled throughout this call. This is necessary
* because messages can be sent from interrupt level processing.
* - For mq_timedreceive, setting of the timer and this wait must be atomic.
*
****************************************************************************/
FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *mq_waitreceive(mqd_t mqdes)
{
FAR struct tcb_s *rtcb;
FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *msgq;
FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *rcvmsg;
/* mq_waitreceive() is not a cancellation point, but it is always called
* from a cancellation point.
*/
if (enter_cancellation_point())
{
#ifdef CONFIG_CANCELLATION_POINTS
/* If there is a pending cancellation, then do not perform
* the wait. Exit now with ECANCELED.
*/
set_errno(ECANCELED);
leave_cancellation_point();
return NULL;
#endif
}
/* Get a pointer to the message queue */
msgq = mqdes->msgq;
/* Get the message from the head of the queue */
while ((rcvmsg = (FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *)sq_remfirst(&msgq->msglist)) == NULL)
{
/* The queue is empty! Should we block until there the above condition
* has been satisfied?
*/
if ((mqdes->oflags & O_NONBLOCK) == 0)
{
/* Yes.. Block and try again */
rtcb = this_task();
rtcb->msgwaitq = msgq;
msgq->nwaitnotempty++;
set_errno(OK);
up_block_task(rtcb, TSTATE_WAIT_MQNOTEMPTY);
/* When we resume at this point, either (1) the message queue
* is no longer empty, or (2) the wait has been interrupted by
* a signal. We can detect the latter case be examining the
* errno value (should be either EINTR or ETIMEDOUT).
*/
if (get_errno() != OK)
{
break;
}
}
else
{
/* The queue was empty, and the O_NONBLOCK flag was set for the
* message queue description referred to by 'mqdes'.
*/
set_errno(EAGAIN);
break;
}
}
/* If we got message, then decrement the number of messages in
* the queue while we are still in the critical section
*/
if (rcvmsg)
{
msgq->nmsgs--;
}
leave_cancellation_point();
return rcvmsg;
}
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_doreceive
*
* Description:
* This is internal, common logic shared by both mq_receive and
* mq_timedreceive. This function accepts the message obtained by
* mq_waitmsg, provides the message content to the user, notifies any
* threads that were waiting for the message queue to become non-full,
* and disposes of the message structure
*
* Parameters:
* mqdes - Message queue descriptor
* mqmsg - The message obtained by mq_waitmsg()
* ubuffer - The address of the user provided buffer to receive the message
* prio - The user-provided location to return the message priority.
*
* Return Value:
* Returns the length of the received message. This function does not fail.
*
* Assumptions:
* - The caller has provided all validity checking of the input parameters
* using mq_verifyreceive.
* - The user buffer, ubuffer, is known to be large enough to accept the
* largest message that an be sent on this message queue
* - Pre-emption should be disabled throughout this call.
*
****************************************************************************/
ssize_t mq_doreceive(mqd_t mqdes, FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *mqmsg,
FAR char *ubuffer, int *prio)
{
FAR struct tcb_s *btcb;
irqstate_t flags;
FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *msgq;
ssize_t rcvmsglen;
/* Get the length of the message (also the return value) */
rcvmsglen = mqmsg->msglen;
/* Copy the message into the caller's buffer */
memcpy(ubuffer, (FAR const void *)mqmsg->mail, rcvmsglen);
/* Copy the message priority as well (if a buffer is provided) */
if (prio)
{
*prio = mqmsg->priority;
}
/* We are done with the message. Deallocate it now. */
mq_msgfree(mqmsg);
/* Check if any tasks are waiting for the MQ not full event. */
msgq = mqdes->msgq;
if (msgq->nwaitnotfull > 0)
{
/* Find the highest priority task that is waiting for
* this queue to be not-full in g_waitingformqnotfull list.
* This must be performed in a critical section because
* messages can be sent from interrupt handlers.
*/
flags = enter_critical_section();
for (btcb = (FAR struct tcb_s *)g_waitingformqnotfull.head;
btcb && btcb->msgwaitq != msgq;
btcb = btcb->flink);
/* If one was found, unblock it. NOTE: There is a race
* condition here: the queue might be full again by the
* time the task is unblocked
*/
ASSERT(btcb);
btcb->msgwaitq = NULL;
msgq->nwaitnotfull--;
up_unblock_task(btcb);
leave_critical_section(flags);
}
/* Return the length of the message transferred to the user buffer */
return rcvmsglen;
}
mq_close
mq_close()完成的工作主要是回收mq_open()中申请的资源,主要在mq_close_group()接口中实现:
- 调用
mq_desclose_group()接口来从调用任务对应的struct tcb_s结构中移除消息队列描述符,并调用mq_desfree()来释放消息队列描述符,也就是将其添加回g_desfree全局队列中。 - 调用
mq_inode_release()接口来将inode资源释放,在该函数中会判断inode->i_crefs和inode->i_flags两个成员,如果引用值变成了0或者状态值变成了FSNODEFLAG_DELETED,则将消息队列释放,并且最终将inode释放。消息队列释放的过程中,会把队列中剩余的未被读走的消息全部都释放掉。之前我曾经怀疑这个地方是否会存在内存泄漏,看来还是我的认知浅薄了。FSNODEFLAG_DELETED状态会在mq_unlink()接口中进行设置,mq_unlink(FAR const char *mq_name)会将mq_name对应的消息队列移除,如果有多个Task打开该消息队列的话,这个移除工作就会推迟到引用值为0.
主要代码如下:
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_close
*
* Description:
* This function is used to indicate that the calling task is finished
* with the specified message queue mqdes. The mq_close() deallocates
* any system resources allocated by the system for use by this task for
* its message queue.
*
* If the calling task has attached a notification to the message queue
* via this mqdes, this attachment will be removed and the message queue
* is available for another process to attach a notification.
*
* Parameters:
* mqdes - Message queue descriptor.
*
* Return Value:
* 0 (OK) if the message queue is closed successfully,
* otherwise, -1 (ERROR).
*
* Assumptions:
* - The behavior of a task that is blocked on either a mq_send() or
* mq_receive() is undefined when mq_close() is called.
* - The results of using this message queue descriptor after a successful
* return from mq_close() is undefined.
*
****************************************************************************/
int mq_close(mqd_t mqdes)
{
FAR struct tcb_s *rtcb = (FAR struct tcb_s *)sched_self();
int ret;
/* Lock the scheduler to prevent any asynchrounous task delete operation
* (unlikely).
*/
sched_lock();
rtcb = (FAR struct tcb_s *)sched_self();
DEBUGASSERT(mqdes != NULL && rtcb != NULL && rtcb->group != NULL);
ret = mq_close_group(mqdes, rtcb->group);
sched_unlock();
return ret;
}
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_close_group
*
* Description:
* This function is used to indicate that all threads in the group are
* finished with the specified message queue mqdes. The mq_close_group()
* deallocates any system resources allocated by the system for use by
* this task for its message queue.
*
* Parameters:
* mqdes - Message queue descriptor.
* group - Group that has the open descriptor.
*
* Return Value:
* 0 (OK) if the message queue is closed successfully,
* otherwise, -1 (ERROR).
*
****************************************************************************/
int mq_close_group(mqd_t mqdes, FAR struct task_group_s *group)
{
FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *msgq;
FAR struct inode *inode;
DEBUGASSERT(mqdes != NULL && group != NULL);
/* Verify the inputs */
if (mqdes)
{
sched_lock();
/* Find the message queue associated with the message descriptor */
msgq = mqdes->msgq;
DEBUGASSERT(msgq && msgq->inode);
/* Close/free the message descriptor */
mq_desclose_group(mqdes, group);
/* Get the inode from the message queue structure */
inode = msgq->inode;
DEBUGASSERT(inode->u.i_mqueue == msgq);
/* Decrement the reference count on the inode, possibly freeing it */
mq_inode_release(inode);
sched_unlock();
}
return OK;
}
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_inode_release
*
* Description:
* Release a reference count on a message queue inode.
*
* Parameters:
* inode - The message queue inode
*
* Return Value:
* None
*
****************************************************************************/
void mq_inode_release(FAR struct inode *inode)
{
/* Decrement the reference count on the inode */
inode_semtake();
if (inode->i_crefs > 0)
{
inode->i_crefs--;
}
/* If the message queue was previously unlinked and the reference count
* has decremented to zero, then release the message queue and delete
* the inode now.
*/
if (inode->i_crefs <= 0 && (inode->i_flags & FSNODEFLAG_DELETED) != 0)
{
FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *msgq = inode->u.i_mqueue;
DEBUGASSERT(msgq);
/* Free the message queue (and any messages left in it) */
mq_msgqfree(msgq);
inode->u.i_mqueue = NULL;
/* Release and free the inode container. If it has been properly
* unlinked, then the peer pointer should be NULL.
*/
inode_semgive();
DEBUGASSERT(inode->i_peer == NULL);
inode_free(inode);
return;
}
inode_semgive();
}
mq_timedsend()/mq_timedreceive()
mq_timedsend()/mq_timedreceive()接口实现跟mq_send()/mq_receive()基本类似,唯一不同的是增加了一个定时的功能,而这个定时的功能是通过watchdog来实现的。
在Nuttx中,看门狗以linked list全局队列的形式来维护,创建一个看门狗后,会添加进全局队列中,然后会在Timer中断处理中去调用wd_timer()接口,以判断看门狗的时间是否到期,如果到期了就去执行注册进看门狗中的回调函数。
mq_rcvtimeout()/mq_sndtimeout()接口就是用来被注册到看门狗的回调函数。当设定的时间到期了后,在中断上下文中回调这两个函数,而这两个函数都会调用到mq_waitirq(),在mq_waitirq()接口中,会去清空struct tcb_s结构中的msgwaitq队列,并将该消息队列中等待的数值减1,并设置错误状态,然后恢复该任务的执行。(Task在调用mq_timedsend()/mq_timedreceive()时,在时间未到期时会先睡眠等待,当时间到期后,在看门狗的回调函数中去恢复该任务继续执行)
关键代码如下:
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_timedsend
*
* Description:
* This function adds the specificied message (msg) to the message queue
* (mqdes). The "msglen" parameter specifies the length of the message
* in bytes pointed to by "msg." This length must not exceed the maximum
* message length from the mq_getattr().
*
* If the message queue is not full, mq_timedsend() place the message in the
* message queue at the position indicated by the "prio" argrument.
* Messages with higher priority will be inserted before lower priority
* messages. The value of "prio" must not exceed MQ_PRIO_MAX.
*
* If the specified message queue is full and O_NONBLOCK is not set in the
* message queue, then mq_timedsend() will block until space becomes available
* to the queue the message or a timeout occurs.
*
* mq_timedsend() behaves just like mq_send(), except that if the queue
* is full and the O_NONBLOCK flag is not enabled for the message queue
* description, then abstime points to a structure which specifies a
* ceiling on the time for which the call will block. This ceiling is an
* absolute timeout in seconds and nanoseconds since the Epoch (midnight
* on the morning of 1 January 1970).
*
* If the message queue is full, and the timeout has already expired by
* the time of the call, mq_timedsend() returns immediately.
*
* Parameters:
* mqdes - Message queue descriptor
* msg - Message to send
* msglen - The length of the message in bytes
* prio - The priority of the message
* abstime - the absolute time to wait until a timeout is decleared
*
* Return Value:
* On success, mq_send() returns 0 (OK); on error, -1 (ERROR)
* is returned, with errno set to indicate the error:
*
* EAGAIN The queue was empty, and the O_NONBLOCK flag was set for the
* message queue description referred to by mqdes.
* EINVAL Either msg or mqdes is NULL or the value of prio is invalid.
* EPERM Message queue opened not opened for writing.
* EMSGSIZE 'msglen' was greater than the maxmsgsize attribute of the
* message queue.
* EINTR The call was interrupted by a signal handler.
*
* Assumptions/restrictions:
*
****************************************************************************/
int mq_timedsend(mqd_t mqdes, FAR const char *msg, size_t msglen, int prio,
FAR const struct timespec *abstime)
{
FAR struct tcb_s *rtcb = this_task();
FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *msgq;
FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *mqmsg = NULL;
irqstate_t flags;
int ticks;
int result;
int ret = ERROR;
DEBUGASSERT(up_interrupt_context() == false && rtcb->waitdog == NULL);
/* mq_timedsend() is a cancellation point */
(void)enter_cancellation_point();
/* Verify the input parameters -- setting errno appropriately
* on any failures to verify.
*/
if (mq_verifysend(mqdes, msg, msglen, prio) != OK)
{
/* mq_verifysend() will set the errno appropriately */
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
/* Pre-allocate a message structure */
mqmsg = mq_msgalloc();
if (mqmsg == NULL)
{
/* Failed to allocate the message. mq_msgalloc() does not set the
* errno value.
*/
set_errno(ENOMEM);
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
/* Get a pointer to the message queue */
sched_lock();
msgq = mqdes->msgq;
/* OpenGroup.org: "Under no circumstance shall the operation fail with a
* timeout if there is sufficient room in the queue to add the message
* immediately. The validity of the abstime parameter need not be checked
* when there is sufficient room in the queue."
*
* Also ignore the time value if for some crazy reason we were called from
* an interrupt handler. This probably really should be an assertion.
*
* NOTE: There is a race condition here: What if a message is added by
* interrupt related logic so that queue again becomes non-empty. That
* is handled because mq_dosend() will permit the maxmsgs limit to be
* exceeded in that case.
*/
if (msgq->nmsgs < msgq->maxmsgs || up_interrupt_context())
{
/* Do the send with no further checks (possibly exceeding maxmsgs)
* Currently mq_dosend() always returns OK.
*/
ret = mq_dosend(mqdes, mqmsg, msg, msglen, prio);
sched_unlock();
leave_cancellation_point();
return ret;
}
/* The message queue is full... We are going to wait. Now we must have a
* valid time value.
*/
if (!abstime || abstime->tv_nsec < 0 || abstime->tv_nsec >= 1000000000)
{
result = EINVAL;
goto errout_with_mqmsg;
}
/* Create a watchdog. We will not actually need this watchdog
* unless the queue is full, but we will reserve it up front
* before we enter the following critical section.
*/
rtcb->waitdog = wd_create();
if (!rtcb->waitdog)
{
result = EINVAL;
goto errout_with_mqmsg;
}
/* We are not in an interrupt handler and the message queue is full.
* Set up a timed wait for the message queue to become non-full.
*
* Convert the timespec to clock ticks. We must have interrupts
* disabled here so that this time stays valid until the wait begins.
*/
flags = enter_critical_section();
result = clock_abstime2ticks(CLOCK_REALTIME, abstime, &ticks);
/* If the time has already expired and the message queue is empty,
* return immediately.
*/
if (result == OK && ticks <= 0)
{
result = ETIMEDOUT;
}
/* Handle any time-related errors */
if (result != OK)
{
goto errout_in_critical_section;
}
/* Start the watchdog and begin the wait for MQ not full */
wd_start(rtcb->waitdog, ticks, (wdentry_t)mq_sndtimeout, 1, getpid());
/* And wait for the message queue to be non-empty */
ret = mq_waitsend(mqdes);
/* This may return with an error and errno set to either EINTR
* or ETIMEOUT. Cancel the watchdog timer in any event.
*/
wd_cancel(rtcb->waitdog);
/* Check if mq_waitsend() failed */
if (ret < 0)
{
/* mq_waitsend() will set the errno, but the error exit will reset it */
result = get_errno();
goto errout_in_critical_section;
}
/* That is the end of the atomic operations */
leave_critical_section(flags);
/* If any of the above failed, set the errno. Otherwise, there should
* be space for another message in the message queue. NOW we can allocate
* the message structure.
*
* Currently mq_dosend() always returns OK.
*/
ret = mq_dosend(mqdes, mqmsg, msg, msglen, prio);
sched_unlock();
wd_delete(rtcb->waitdog);
rtcb->waitdog = NULL;
leave_cancellation_point();
return ret;
/* Exit here with (1) the scheduler locked, (2) a message allocated, (3) a
* wdog allocated, and (4) interrupts disabled. The error code is in
* 'result'
*/
errout_in_critical_section:
leave_critical_section(flags);
wd_delete(rtcb->waitdog);
rtcb->waitdog = NULL;
/* Exit here with (1) the scheduler locked and 2) a message allocated. The
* error code is in 'result'
*/
errout_with_mqmsg:
mq_msgfree(mqmsg);
sched_unlock();
set_errno(result);
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_timedreceive
*
* Description:
* This function receives the oldest of the highest priority messages from
* the message queue specified by "mqdes." If the size of the buffer in
* bytes (msglen) is less than the "mq_msgsize" attribute of the message
* queue, mq_timedreceive will return an error. Otherwise, the selected
* message is removed from the queue and copied to "msg."
*
* If the message queue is empty and O_NONBLOCK was not set,
* mq_timedreceive() will block until a message is added to the message
* queue (or until a timeout occurs). If more than one task is waiting
* to receive a message, only the task with the highest priority that has
* waited the longest will be unblocked.
*
* mq_timedreceive() behaves just like mq_receive(), except that if the
* queue is empty and the O_NONBLOCK flag is not enabled for the message
* queue description, then abstime points to a structure which specifies a
* ceiling on the time for which the call will block. This ceiling is an
* absolute timeout in seconds and nanoseconds since the Epoch (midnight
* on the morning of 1 January 1970).
*
* If no message is available, and the timeout has already expired by the
* time of the call, mq_timedreceive() returns immediately.
*
* Parameters:
* mqdes - Message Queue Descriptor
* msg - Buffer to receive the message
* msglen - Size of the buffer in bytes
* prio - If not NULL, the location to store message priority.
* abstime - the absolute time to wait until a timeout is declared.
*
* Return Value:
* One success, the length of the selected message in bytes is returned.
* On failure, -1 (ERROR) is returned and the errno is set appropriately:
*
* EAGAIN The queue was empty, and the O_NONBLOCK flag was set
* for the message queue description referred to by 'mqdes'.
* EPERM Message queue opened not opened for reading.
* EMSGSIZE 'msglen' was less than the maxmsgsize attribute of the
* message queue.
* EINTR The call was interrupted by a signal handler.
* EINVAL Invalid 'msg' or 'mqdes' or 'abstime'
* ETIMEDOUT The call timed out before a message could be transferred.
*
* Assumptions:
*
****************************************************************************/
ssize_t mq_timedreceive(mqd_t mqdes, FAR char *msg, size_t msglen,
FAR int *prio, FAR const struct timespec *abstime)
{
FAR struct tcb_s *rtcb = this_task();
FAR struct mqueue_msg_s *mqmsg;
irqstate_t flags;
int ret = ERROR;
DEBUGASSERT(up_interrupt_context() == false && rtcb->waitdog == NULL);
/* mq_timedreceive() is a cancellation point */
(void)enter_cancellation_point();
/* Verify the input parameters and, in case of an error, set
* errno appropriately.
*/
if (mq_verifyreceive(mqdes, msg, msglen) != OK)
{
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
if (!abstime || abstime->tv_nsec < 0 || abstime->tv_nsec >= 1000000000)
{
set_errno(EINVAL);
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
/* Create a watchdog. We will not actually need this watchdog
* unless the queue is not empty, but we will reserve it up front
* before we enter the following critical section.
*/
rtcb->waitdog = wd_create();
if (!rtcb->waitdog)
{
set_errno(EINVAL);
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
/* Get the next message from the message queue. We will disable
* pre-emption until we have completed the message received. This
* is not too bad because if the receipt takes a long time, it will
* be because we are blocked waiting for a message and pre-emption
* will be re-enabled while we are blocked
*/
sched_lock();
/* Furthermore, mq_waitreceive() expects to have interrupts disabled
* because messages can be sent from interrupt level.
*/
flags = enter_critical_section();
/* Check if the message queue is empty. If it is NOT empty, then we
* will not need to start timer.
*/
if (mqdes->msgq->msglist.head == NULL)
{
int ticks;
/* Convert the timespec to clock ticks. We must have interrupts
* disabled here so that this time stays valid until the wait begins.
*/
int result = clock_abstime2ticks(CLOCK_REALTIME, abstime, &ticks);
/* If the time has already expired and the message queue is empty,
* return immediately.
*/
if (result == OK && ticks <= 0)
{
result = ETIMEDOUT;
}
/* Handle any time-related errors */
if (result != OK)
{
leave_critical_section(flags);
sched_unlock();
wd_delete(rtcb->waitdog);
rtcb->waitdog = NULL;
set_errno(result);
leave_cancellation_point();
return ERROR;
}
/* Start the watchdog */
wd_start(rtcb->waitdog, ticks, (wdentry_t)mq_rcvtimeout, 1, getpid());
}
/* Get the message from the message queue */
mqmsg = mq_waitreceive(mqdes);
/* Stop the watchdog timer (this is not harmful in the case where
* it was never started)
*/
wd_cancel(rtcb->waitdog);
/* We can now restore interrupts */
leave_critical_section(flags);
/* Check if we got a message from the message queue. We might
* not have a message if:
*
* - The message queue is empty and O_NONBLOCK is set in the mqdes
* - The wait was interrupted by a signal
* - The watchdog timeout expired
*/
if (mqmsg)
{
ret = mq_doreceive(mqdes, mqmsg, msg, prio);
}
sched_unlock();
wd_delete(rtcb->waitdog);
rtcb->waitdog = NULL;
leave_cancellation_point();
return ret;
}
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_sndtimeout
*
* Description:
* This function is called if the timeout elapses before the message queue
* becomes non-full.
*
* Parameters:
* argc - the number of arguments (should be 1)
* pid - the task ID of the task to wakeup
*
* Return Value:
* None
*
* Assumptions:
*
****************************************************************************/
static void mq_sndtimeout(int argc, wdparm_t pid)
{
FAR struct tcb_s *wtcb;
irqstate_t flags;
/* Disable interrupts. This is necessary because an interrupt handler may
* attempt to send a message while we are doing this.
*/
flags = enter_critical_section();
/* Get the TCB associated with this pid. It is possible that task may no
* longer be active when this watchdog goes off.
*/
wtcb = sched_gettcb((pid_t)pid);
/* It is also possible that an interrupt/context switch beat us to the
* punch and already changed the task's state.
*/
if (wtcb && wtcb->task_state == TSTATE_WAIT_MQNOTFULL)
{
/* Restart with task with a timeout error */
mq_waitirq(wtcb, ETIMEDOUT);
}
/* Interrupts may now be re-enabled. */
leave_critical_section(flags);
}
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_rcvtimeout
*
* Description:
* This function is called if the timeout elapses before the message queue
* becomes non-empty.
*
* Parameters:
* argc - the number of arguments (should be 1)
* pid - the task ID of the task to wakeup
*
* Return Value:
* None
*
* Assumptions:
*
****************************************************************************/
static void mq_rcvtimeout(int argc, wdparm_t pid)
{
FAR struct tcb_s *wtcb;
irqstate_t flags;
/* Disable interrupts. This is necessary because an interrupt handler may
* attempt to send a message while we are doing this.
*/
flags = enter_critical_section();
/* Get the TCB associated with this pid. It is possible that task may no
* longer be active when this watchdog goes off.
*/
wtcb = sched_gettcb((pid_t)pid);
/* It is also possible that an interrupt/context switch beat us to the
* punch and already changed the task's state.
*/
if (wtcb && wtcb->task_state == TSTATE_WAIT_MQNOTEMPTY)
{
/* Restart with task with a timeout error */
mq_waitirq(wtcb, ETIMEDOUT);
}
/* Interrupts may now be re-enabled. */
leave_critical_section(flags);
}
/****************************************************************************
* Name: mq_waitirq
*
* Description:
* This function is called when a signal or a timeout is received by a
* task that is waiting on a message queue -- either for a queue to
* becoming not full (on mq_send) or not empty (on mq_receive).
*
* Parameters:
* wtcb - A pointer to the TCB of the task that is waiting on a message
* queue, but has received a signal instead.
*
* Return Value:
* None
*
* Assumptions:
*
****************************************************************************/
void mq_waitirq(FAR struct tcb_s *wtcb, int errcode)
{
FAR struct mqueue_inode_s *msgq;
irqstate_t flags;
/* Disable interrupts. This is necessary because an interrupt handler may
* attempt to send a message while we are doing this.
*/
flags = enter_critical_section();
/* It is possible that an interrupt/context switch beat us to the punch and
* already changed the task's state. NOTE: The operations within the if
* are safe because interrupts are always disabled with the msgwaitq,
* nwaitnotempty, and nwaitnotfull fields are modified.
*/
if (wtcb->task_state == TSTATE_WAIT_MQNOTEMPTY ||
wtcb->task_state == TSTATE_WAIT_MQNOTFULL)
{
/* Get the message queue associated with the waiter from the TCB */
msgq = wtcb->msgwaitq;
DEBUGASSERT(msgq);
wtcb->msgwaitq = NULL;
/* Decrement the count of waiters and cancel the wait */
if (wtcb->task_state == TSTATE_WAIT_MQNOTEMPTY)
{
DEBUGASSERT(msgq->nwaitnotempty > 0);
msgq->nwaitnotempty--;
}
else
{
DEBUGASSERT(msgq->nwaitnotfull > 0);
msgq->nwaitnotfull--;
}
/* Mark the errno value for the thread. */
wtcb->pterrno = errcode;
/* Restart the task. */
up_unblock_task(wtcb);
}
/* Interrupts may now be enabled. */
leave_critical_section(flags);
}
补充
在消息队列的代码中,经常会看到以下代码:
-
sched_lock()/sched_unlock(): 这两个函数需要配对使用,用于禁止context切换,也就是禁止抢占。 -
enter_critical_section()/leave_critical_section():这两个函数表明进入了临界区,需要对临界区进行保护。 -
enter_cancellation_point()/leave_cancellation_point():用于在某些函数中创建线程取掉点。