Android View 相关源码分析之一 从setContentView说起
Android View 相关源码分析之二 继LayoutInflater来说
现在开始分析View的绘制机制
View的测量 布局 绘制过程
测量之前的事情
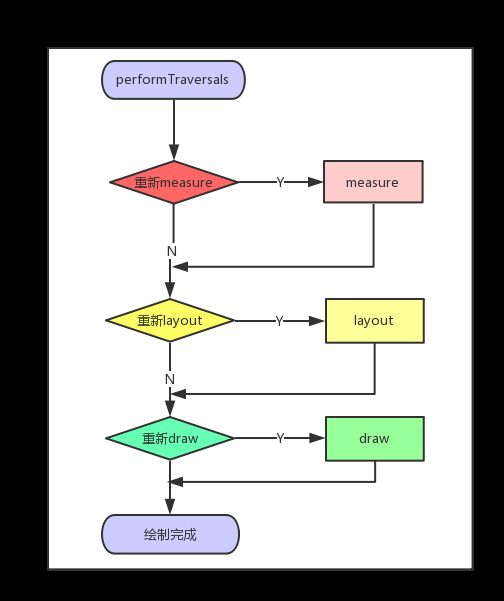
View的整个绘制流程是开始于ViewRootImpl类的performTraversals方法(1k行) 根据相关设置来觉得十分要重新执行相关功能
private void performTraversals() {
// cache mView since it is used so much below...
final View host = mView;
...
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
...
//measure
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
...
//layout
mView.layout(0, 0, mView.getMeasuredWidth(), mView.getMeasuredHeight());
...
//draw
mView.draw(canvas);
...
}
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
...
}
return measureSpec;
}
View 绘制流程图如下
measure源码分析
结论:
measure的过程就是父View向子View递归调用view.measure方法 (measure中回调onMeasure方法)的过程
measure方法是 final的 只能重载onMeasure方法
最顶层的DocerView的MeasureSpec由ViewRootImpl的getRootMeasureSpec方法提供 LayoutParams的参数为MATCH_PARENT specMode是EXACTLY,specSize为物理屏幕大小
只要是ViewGroup的子类就必须要求LayoutParams继承子MarginLayoutParams 否则无法使用layout_margin参数
View的getMeasuredWidth()和getMeasuredHeight()方法来获取View测量的宽高,要必须保证这两个方法在onMeasure流程之后被调用才能返回有效值。
/**
*
* This is called to find out how big a view should be. The parent supplies constraint information in the width and height parameters.
*
*
*
* The actual measurement work of a view is performed in
* {@link #onMeasure(int, int)}, called by this method. Therefore, only
* {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} can and must be overridden by subclasses.
*
*
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec Horizontal space requirements as imposed by the
* parent
* @param heightMeasureSpec Vertical space requirements as imposed by the
* parent
*
* @see #onMeasure(int, int)
*/
//没舍得删这些注释 感觉重要的事情都说了 为了计算整个View树的实际大小 设置实际的高和宽 每个子View都是根据父视图和自身决定实际宽高的 在onMeasure()方法中进行实际测量.传入widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec参数来表示了父View的规格 不但传入了模式 还传入了size 而对于DecorView来说 传入的模式一般为EXACTLY模式 size对应屏幕的宽高. 所以说子View的大小是父子View共同决定的
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
MeasureSpec内部类
MeasureSpec是View的内部类 int型,由高2位规格模式specMode和低30位具体尺寸specSize组成 其中specMode只有三种
- MeasureSpec.EXACTLY //确定模式,父View希望子View的大小是确定的,由specSize决定;
- MeasureSpec.AT_MOST //最多模式,父View希望子View的大小最多是specSize指定的值;
- MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED //未指定模式,父View完全依据子View的设计值来决定;
onMeasure()方法
/**
*
* Measure the view and its content to determine the measured width and the
* measured height. This method is invoked by {@link #measure(int, int)} and
* should be overridden by subclasses to provide accurate and efficient
* measurement of their contents.
*
*
*
* CONTRACT: When overriding this method, you
* must call {@link #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)} to store the
* measured width and height of this view. Failure to do so will trigger an
* IllegalStateException, thrown by
* {@link #measure(int, int)}. Calling the superclass'
* {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} is a valid use.
*
*
*
* The base class implementation of measure defaults to the background size,
* unless a larger size is allowed by the MeasureSpec. Subclasses should
* override {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} to provide better measurements of
* their content.
*
*
*
* If this method is overridden, it is the subclass's responsibility to make
* sure the measured height and width are at least the view's minimum height
* and width ({@link #getSuggestedMinimumHeight()} and
* {@link #getSuggestedMinimumWidth()}).
*
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec horizontal space requirements as imposed by the parent.
* The requirements are encoded with
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec}.
* @param heightMeasureSpec vertical space requirements as imposed by the parent.
* The requirements are encoded with
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec}.
*
* @see #getMeasuredWidth()
* @see #getMeasuredHeight()
* @see #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)
* @see #getSuggestedMinimumHeight()
* @see #getSuggestedMinimumWidth()
* @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getMode(int)
* @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getSize(int)
*/
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
getDefaultSize方法相关
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
//通过measureSpec得到mode和size
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
//最小宽度和高度由View的Background尺寸和View的minXXX共同决定
protected int getSuggestedMinimumHeight() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinHeight : max(mMinHeight, mBackground.getMinimumHeight());
}
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
setMeasuredDimension方法 对View的成员变量measuredWidth和measuredHeight变量赋值 也就是说该方法最终决定了View的大小
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
public boolean isLayoutRequested() {
return (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
}
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}
至此一次最基础的View的measure过程就完成了 但是由于View可以嵌套 所以measure是递归传递的所以ViewGroup中需要对其子类进行measure过程 measureChildren方法实质为循环调用measureChild方法
而measureChild和measureChildWithMargins的区别是后者将margin和padding也作为了子视图的大小
一下分析measureChildWithMargins方法
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
//获取当前子视图的LayoutParams
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//设定子View的测量规格
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
//子view的继续调用
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
//在getChildMeasureSpec中通过父View和本身的模式共同决定当前View的size
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
//获取当前父View的mode和size
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
//获取父View的的剩余大小
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
//定义结果变量
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
//根据对应的mode做处理
//通过父View和本身的模式共同决定当前View的size
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//将size和mode整合为MeasureSpec模式后返回
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
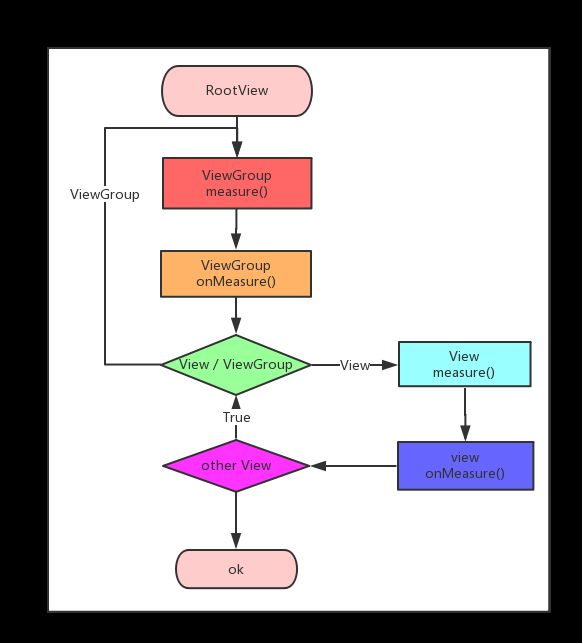
layout源码分析
View layout整体流程与measure过程基本一样
结论:
- 需要根据ViewGroup本身的情况讨论 LinearLayout下会更看重子View的height和width 来安排对应位置 而RelativeLayout则更加关注子View的left right top bottom值 并且优先级高于width和height 甚至在部分自定义ViewGroup中 measure可能是无用的 直接使用layout方法来设置子View的位置也可以
- ViewGroup需要实现自己的layout逻辑
- layout_XXX中的各个熟悉都是针对子View的父ViewGroup的
- 同样使用View的getWidth()和getHeight()方法来获取View测量的宽高 必须保证这两个方法在onLayout流程之后被调用才能返回有效值
/**
* Assign a size and position to a view and all of its
* descendants
*
* This is the second phase of the layout mechanism.
* (The first is measuring). In this phase, each parent calls
* layout on all of its children to position them.
* This is typically done using the child measurements
* that were stored in the measure pass().
*
* Derived classes should not override this method.
* Derived classes with children should override
* onLayout. In that method, they should
* call layout on each of their children.
*
* @param l Left position, relative to parent
* @param t Top position, relative to parent
* @param r Right position, relative to parent
* @param b Bottom position, relative to parent
*/
//同样注解写的很好了 分派给他和他的所有的子视图大小和位置
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"})
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) {
onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
//调用setFrame方法把参数分别赋值于
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
//判断view的位置是否发生过变化 , 确定是否对当前view重新layout
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
//调用onLayout
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {
ArrayList listenersCopy =
(ArrayList)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();
int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);
}
}
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_IS_LAID_OUT;
}
onLyayout方法
View中
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
}
ViewGroup中
protected abstract void onLayout(boolean changed,
int l, int t, int r, int b);
均是空方法 后面会就LinearLayout和RelativeLayout源码进行分析
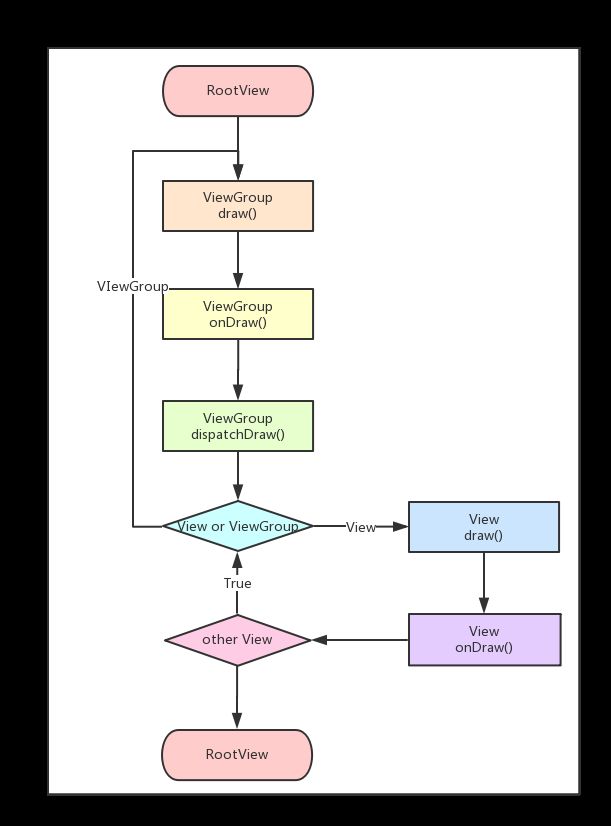
draw源码分析
View的draw流程图如下
结论:
- View需要在子类中实现onDraw的过程
- 在ViewGroup中 会调用其子View的方法 顺序与子view的添加顺序一致
draw的源码也很长 但是官方也给出给出了draw的过程
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
...
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
...
if (!dirtyOpaque) {
drawBackground(canvas);
}
// skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
...
// Step 2, save the canvas' layers
...
if (drawTop) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, top, right, top + length, null, flags);
}
...
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers
...
if (drawTop) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * topFadeStrength);
matrix.postTranslate(left, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
p.setShader(fade);
canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, top + length, p);
}
...
// Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
onDrawScrollBars(canvas);
...
}
Step 1, draw the background, if needed
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
//如果需要的话绘制背景
if (!dirtyOpaque) {
drawBackground(canvas);
}
private void drawBackground(Canvas canvas) {
//通过xml中属性background或者代码中setBackGroundColor\setBackgroundResource等方法赋值的背景drawable
final Drawable background = mBackground;
if (background == null) {
return;
}
//根据layout中确定的view位置来设置背景的绘制区域
setBackgroundBounds();
// 如果需要的话使用显示列表
//canvas.isHardwareAccelerated() 硬件加速判定
//硬件加速时会将图层缓存到GPU上 而不是重绘View的每一层
if (canvas.isHardwareAccelerated() && mAttachInfo != null
&& mAttachInfo.mHardwareRenderer != null) {
mBackgroundRenderNode = getDrawableRenderNode(background, mBackgroundRenderNode);
final RenderNode renderNode = mBackgroundRenderNode;
if (renderNode != null && renderNode.isValid()) {
setBackgroundRenderNodeProperties(renderNode);
((DisplayListCanvas) canvas).drawRenderNode(renderNode);
return;
}
}
final int scrollX = mScrollX;
final int scrollY = mScrollY;
//调用Drawable的draw方法来完成背景的绘制工作
if ((scrollX | scrollY) == 0) {
background.draw(canvas);
} else {
canvas.translate(scrollX, scrollY);
background.draw(canvas);
canvas.translate(-scrollX, -scrollY);
}
}
void setBackgroundBounds() {
if (mBackgroundSizeChanged && mBackground != null) {
mBackground.setBounds(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop);
mBackgroundSizeChanged = false;
rebuildOutline();
}
}
Step 2, save the canvas' layers
// Step 2, save the canvas' layers
//保存绘制图层
if (drawTop) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, top, right, top + length, null, flags);
}
Step 3, draw the content
// Step 3, draw the content
//对View的内容进行绘制
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
/**
* Implement this to do your drawing.
*
* @param canvas the canvas on which the background will be drawn
*/
//onDraw也是空方法需要子类根据自身去实现相应的
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
}
Step 4, draw the children
// Step 4, draw the children
//绘制其子View
dispatchDraw(canvas);
/**
* Called by draw to draw the child views. This may be overridden
* by derived classes to gain control just before its children are drawn
* (but after its own view has been drawn).
* @param canvas the canvas on which to draw the view
*/
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//dispatchDraw同样空方法 与onDraw不同的是dispatchDraw在ViewGroup中被重写
}
ViewGroup
//dispatchDraw方法中根据子View的不同情况 包括但不只包括该View是否显示 是否有进入或消失动画等进行了部分的调整
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
...
more |= drawChild(canvas, transientChild, drawingTime);
...
}
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) {
return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime);
}
Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers
// Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers
//绘制过度效果和恢复图层
if (drawTop) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * topFadeStrength);
matrix.postTranslate(left, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
p.setShader(fade);
canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, top + length, p);
}
Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
// Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
//对滚动条进行绘制
onDrawScrollBars(canvas);
至此 View的绘制过程全部分析完了