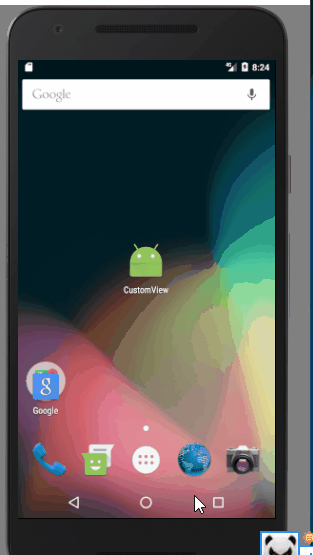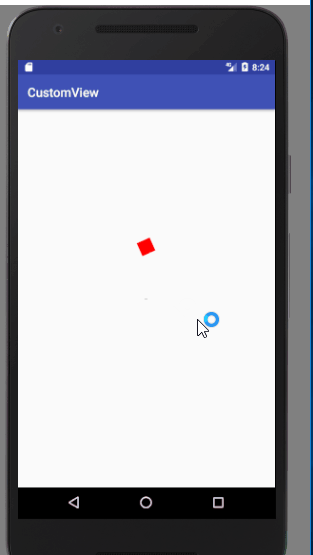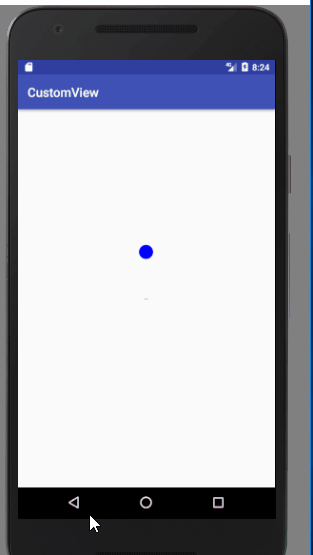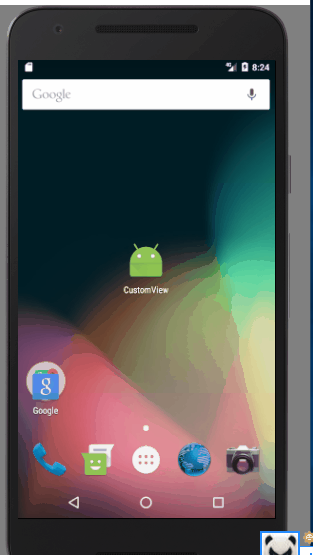
先上图
思考步骤还是和上一篇讲的一样,相同的套路:
自定义View(1)--QQ运动计步器
构造器不说了,正常情况一般三个都会写,这篇我没从attr里面写东西,所以这一步跳过了,我们直接来要真正思考的地方:首先我们这里实现的话有很多种方式,可以用图片,可以自己绘制,这里我们选择自己绘制,但是绘制的话,我们又要考虑这个动画是需要我们自己算坐标然后重绘?还是写成单独的一个view然后通过动画实现,这里我选择了后者,原因有三个:第一个是如果在 view内部写相关的移动旋转逻辑的话,计算量不用说增加了,这个是很费时间的,而且很容易出错;第二个是因为你不停的调用invalidate,看了源码的都知道,调用这个函数的会做很多工作,造成不必要的gpu耗费,这样不好;第三个是实用性,如果以后我们需要这样一个图像,我们可以直接把这个形状的view复制过去就可以使用,所以我们理清思路。
首先,上面跳动的view作为一个单独的view,下面的弧形阴影也做为一个单独的view,然后在外层通过一个viewGroup把他们组装起来并且控制相关的代码和其性能的优化。
我们先绘制图形的 view,也就是上下跳动的哪个view。我们 需要组装,所以我们肯定要重写onMeasure设置其宽高,这里我打算指定他的高度和宽度为圆的半径的两倍:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec),
measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec));
}
/**
* Determines the width of this view
*
* @param measureSpec A measureSpec packed into an int
* @return The width of the view, honoring constraints from measureSpec
*/
private int measureWidth(int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = mRadio * 2;
}
return result;
}
/**
* Determines the height of this view
*
* @param measureSpec A measureSpec packed into an int
* @return The height of the view, honoring constraints from measureSpec
*/
private int measureHeight(int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = 2 * mRadio;
}
return result;
}
接下来我们绘制图形,考略到我们需要变换不同形状的view,所以我写的时候分别写了三个绘制不同图案的函数,然后添加一个flag判断绘谁即可
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
initCenterPoint();
if (mFlog == 0)
drawCircle(canvas);
else if (mFlog == 1)
drawRect(canvas);
else
drawTriangle(canvas);
}
private void initCenterPoint() {
if (mCenterX == -1 || mCenterY == -1) {
mCenterX = getMeasuredWidth() / 2;
mCenterY = getMeasuredHeight() / 2;
// setPivotX(mCenterX);
// setPivotY(mCenterY);
}
}
/**
* 画圆
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawCircle(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.drawCircle(mCenterX, mCenterY, mRadio, mCirclePaint);
}
/**
* 画正方形
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawRect(Canvas canvas) {
Rect rect = new Rect(mCenterX - mRadio,
mCenterY - mRadio,
mCenterX + mRadio,
mCenterY + mRadio);
canvas.drawRect(rect, mRectPaint);
}
public void setFlog(int mFlog) {
this.mFlog = mFlog;
invalidate();
}
/**
* 绘制三角形
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawTriangle(Canvas canvas) {
Path path = new Path();
path.moveTo(mCenterX, mCenterY - mRadio);
path.lineTo(mCenterX - mRadio, mCenterY + mRadio);
path.lineTo(mCenterX + mRadio, mCenterY + mRadio);
canvas.drawPath(path, mTrianglePaint);
}
测试一下这个图案已经绘制完成了,接下来我们绘制下面的阴影,同样的我们需要先测量,我这里设置宽高为半径值的2/3,宽为两倍的半径:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec),
measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec));
}
/**
* Determines the width of this view
*
* @param measureSpec A measureSpec packed into an int
* @return The width of the view, honoring constraints from measureSpec
*/
private int measureWidth(int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = mRadio * 2;
}
return result;
}
/**
* Determines the height of this view
*
* @param measureSpec A measureSpec packed into an int
* @return The height of the view, honoring constraints from measureSpec
*/
private int measureHeight(int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = 2 * mRadio / 3;
}
return result;
}
接下来我们绘制图案,我在绘制这个图案的时候是采用drawArc的方式,所以我们需要计算一下它的范围,我这采用的方案如下:
因为我们要上面的那块横线挨着物块view掉下的位置,所以rect的中心点就是这个,然后计算如下:
int left = getWidth() / 2 - mRadio;
int top = -getHeight() / 2;
int right = getWidth() / 2 + mRadio;
int bottom = getHeight() / 2;
mRectF = new RectF(left, top, right, bottom);
其实getHeight就是2/3的半径
我们绘制的时候,绘制180°即可,:
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
if (mRectF == null) {
int left = getWidth() / 2 - mRadio;
int top = -getHeight() / 2;
int right = getWidth() / 2 + mRadio;
int bottom = getHeight() / 2;
mRectF = new RectF(left, top, right, bottom);
}
canvas.drawArc(mRectF, 0, 180, false, mArcPaint);
}
最后我们将这两个图案组装起来,加上动画即可:
public void startAnim() {
if (mAnimatorSet == null) {
mAnimatorSet = new AnimatorSet();
//up
ObjectAnimator rotationAnim = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mShapeView, "rotation", 0.0f, 360.0f);
rotationAnim.setDuration(JUMP_UP_TIME);
rotationAnim.setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator());//先快后慢
ObjectAnimator translationAnimUp = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mShapeView, "translationY", 0, -JUMP_MAX_HEIGHT);
translationAnimUp.setDuration(JUMP_UP_TIME);
translationAnimUp.setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator());//先快后慢
ObjectAnimator scaleXAnimUp = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mArcView, "scaleX", 1.0f, 0.2f);
scaleXAnimUp.setDuration(JUMP_UP_TIME);
scaleXAnimUp.setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator());//先快后慢
ObjectAnimator scaleYAnimUp = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mArcView, "scaleY", 1.0f, 0.2f);
scaleYAnimUp.setDuration(JUMP_UP_TIME);
scaleYAnimUp.setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator());//先快后慢
//down
ObjectAnimator translationAnimDown = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mShapeView, "translationY", -JUMP_MAX_HEIGHT, 0);
translationAnimDown.setDuration(JUMP_UP_TIME);
translationAnimDown.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());//先慢后快
ObjectAnimator scaleXAnimXDown = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mArcView, "scaleX", 0.2f, 1.0f);
scaleXAnimXDown.setDuration(JUMP_UP_TIME);
scaleXAnimXDown.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());//先慢后快
ObjectAnimator scaleYAnimDown = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mArcView, "scaleY", 0.2f, 1.0f);
scaleYAnimDown.setDuration(JUMP_UP_TIME);
scaleYAnimDown.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());//先慢后快
mAnimatorSet.play(translationAnimUp)
.with(rotationAnim)
.with(scaleXAnimUp)
.with(scaleYAnimUp)
.before(translationAnimDown)
.before(scaleXAnimXDown)
.before(scaleYAnimDown);
mAnimatorSet.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
super.onAnimationEnd(animation);
mFlog++;//圆形 0-->1方形 -->2 三角形 -->3->0---->
if (mFlog > 2) {
mFlog = 0;
}
mShapeView.setFlog(mFlog);
startAnim();
}
});
}
mAnimatorSet.start();
}
这样的话效果实现了,感觉没什么问题了。但是不要忘记了优化
优化
在这里我们主要优化这个动画对应Activity的生命周期 ,让其可见的时候加载动画,不可见的时候停止动画。主要使用Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks这个接口实现,具体实现的代码如下:
@Override
protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
mActivity.getApplication().registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(animLifecyleCallback);
super.onAttachedToWindow();
}
@Override
protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
mActivity.getApplication().unregisterActivityLifecycleCallbacks(animLifecyleCallback);
super.onDetachedFromWindow();
}
private SimpleActivityLifecycleCallbacks animLifecyleCallback = new SimpleActivityLifecycleCallbacks() {
@Override
public void onActivityResumed(Activity activity) { // 页面第一次启动的时候不会执行
if (activity == mActivity)
startAnim();
super.onActivityResumed(activity);
}
@Override
public void onActivityPaused(Activity activity) {
if (activity == mActivity)
stopAnim();
super.onActivityPaused(activity);
}
};
这样就更加优雅了。
源码github下载地址:
https://github.com/ChinaZeng/CustomView