首先我们先写好文章中的Java写的server端http://xiva.iteye.com/blog/993336
下面我们可以访问一下下面的地址:http://code.google.com/p/cocoaasyncsocket/
为了开发的便捷,我使用了AsyncSocket这个类,这样可以异步通信。
建立一个基于视图的应用程序,按照http://code.google.com/p/cocoaasyncsocket/wiki/Reference_AsyncSocket
我们AsyncSocket.h和AsyncSocket.m到我们的项目中,并且导入CFNetwork.framework。这样基本准备工作就做好了。
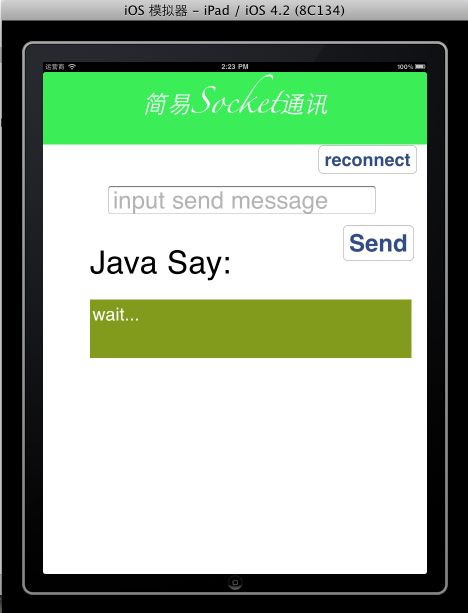
下面提供应用中的代码以及界面图:
Socketdemoviewcontroller.h代码
#import
#import "AsyncSocket.h"
#define SRV_CONNECTED 0
#define SRV_CONNECT_SUC 1
#define SRV_CONNECT_FAIL 2
#define HOST_IP @"192.168.110.1"
#define HOST_PORT 8080
@interface SocketDemoViewController : UIViewController {
UITextField *inputMsg;
UILabel *outputMsg;
AsyncSocket *client;
}
@property (nonatomic, retain) AsyncSocket *client;
@property (nonatomic, retain) IBOutlet UITextField *inputMsg;
@property (nonatomic, retain) IBOutlet UILabel *outputMsg;
- (int) connectServer: (NSString *) hostIP port:(int) hostPort;
- (void) showMessage:(NSString *) msg;
- (IBAction) sendMsg;
- (IBAction) reConnect;
- (IBAction) textFieldDoneEditing:(id)sender;
- (IBAction) backgroundTouch:(id)sender;
@end
socketdemoviewcontroller.m代码
#import "SocketDemoViewController.h"
@implementation SocketDemoViewController
@synthesize inputMsg, outputMsg;
@synthesize client;
// Implement viewDidLoad to do additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
- (void)viewDidLoad {
//[super viewDidLoad];
[self connectServer:HOST_IP port:HOST_PORT];
//监听读取
}
// Override to allow orientations other than the default portrait orientation.
- (BOOL)shouldAutorotateToInterfaceOrientation:(UIInterfaceOrientation)interfaceOrientation {
return YES;
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
// Releases the view if it doesn't have a superview.
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Release any cached data, images, etc that aren't in use.
}
- (void)viewDidUnload {
self.client = nil;
// Release any retained subviews of the main view.
// e.g. self.myOutlet = nil;
}
- (int) connectServer: (NSString *) hostIP port:(int) hostPort{
if (client == nil) {
client = [[AsyncSocket alloc] initWithDelegate:self];
NSError *err = nil;
//192.168.110.128
if (![client connectToHost:hostIP onPort:hostPort error:&err]) {
NSLog(@"%@ %@", [err code], [err localizedDescription]);
UIAlertView *alert = [[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:[@"Connection failed to host "
stringByAppendingString:hostIP]
message:[[[NSString alloc]initWithFormat:@"%@",[err code]] stringByAppendingString:[err localizedDescription]]
delegate:self
cancelButtonTitle:@"OK"
otherButtonTitles:nil];
[alert show];
[alert release];
//client = nil;
return SRV_CONNECT_FAIL;
} else {
NSLog(@"Conectou!");
return SRV_CONNECT_SUC;
}
}
else {
[client readDataWithTimeout:-1 tag:0];
return SRV_CONNECTED;
}
}
- (IBAction) reConnect{
int stat = [self connectServer:HOST_IP port:HOST_PORT];
switch (stat) {
case SRV_CONNECT_SUC:
[self showMessage:@"connect success"];
break;
case SRV_CONNECTED:
[self showMessage:@"It's connected,don't agian"];
break;
default:
break;
}
}
- (IBAction) sendMsg{
NSString *inputMsgStr = self.inputMsg.text;
NSString * content = [inputMsgStr stringByAppendingString:@"\r\n"];
NSLog(@"%a",content);
NSData *data = [content dataUsingEncoding:NSISOLatin1StringEncoding];
[client writeData:data withTimeout:-1 tag:0];
//[data release];
//[content release];
//[inputMsgStr release];
//继续监听读取
//[client readDataWithTimeout:-1 tag:0];
}
#pragma mark -
#pragma mark close Keyboard
- (IBAction) textFieldDoneEditing:(id)sender{
[sender resignFirstResponder];
}
- (IBAction) backgroundTouch:(id)sender{
[inputMsg resignFirstResponder];
}
#pragma mark socket uitl
- (void) showMessage:(NSString *) msg{
UIAlertView * alert = [[UIAlertView alloc]initWithTitle:@"Alert!"
message:msg
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:@"OK"
otherButtonTitles:nil];
[alert show];
[alert release];
}
#pragma mark socket delegate
- (void)onSocket:(AsyncSocket *)sock didConnectToHost:(NSString *)host port:(UInt16)port{
[client readDataWithTimeout:-1 tag:0];
}
- (void)onSocket:(AsyncSocket *)sock willDisconnectWithError:(NSError *)err
{
NSLog(@"Error");
}
- (void)onSocketDidDisconnect:(AsyncSocket *)sock
{
NSString *msg = @"Sorry this connect is failure";
[self showMessage:msg];
[msg release];
client = nil;
}
- (void)onSocketDidSecure:(AsyncSocket *)sock{
}
- (void)onSocket:(AsyncSocket *)sock didReadData:(NSData *)data withTag:(long)tag{
NSString* aStr = [[NSString alloc] initWithData:data encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSLog(@"Hava received datas is :%@",aStr);
self.outputMsg.text = aStr;
[aStr release];
[client readDataWithTimeout:-1 tag:0];
}
#pragma mark dealloc
- (void)dealloc {
[client release];
[inputMsg release];
[outputMsg release];
[super dealloc];
}
@end
运行界面
首先从头文件开始看吧,
1,导入头文件#import "AsyncSocket.h",然后是一些宏
2,声明一个AsyncSocket对象,其他就是一些IBoutlet
再次我们看看视图加载
- (void)viewDidLoad {
//[super viewDidLoad];
[self connectServer:HOST_IP port:HOST_PORT];
//监听读取
}
显然我们调用了connectServer::这个方法。
在这个方法中,首先初始化我们的对象,使用代理的方式。对象显示是self。然后我们便需在我们的类中实现它的各种方法,来得到各种我们想得到的。
client = [[AsyncSocket alloc] initWithDelegate:self];
下面就是连接服务器了,
[client connectToHost:hostIP onPort:hostPort error:&err]
并且当client不为空时,我们就读取服务器的信息
[client readDataWithTimeout:-1 tag:0];
- (void)onSocket:(AsyncSocket *)sock didReadData:(NSData *)data withTag:(long)tag{
NSString* aStr = [[NSString alloc] initWithData:data encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSLog(@"Hava received datas is :%@",aStr);
self.outputMsg.text = aStr;
[aStr release];
[client readDataWithTimeout:-1 tag:0];
}
- (IBAction) sendMsg{
NSString *inputMsgStr = self.inputMsg.text;
NSString * content = [inputMsgStr stringByAppendingString:@"\r\n"];
NSLog(@"%a",content);
NSData *data = [content dataUsingEncoding:NSISOLatin1StringEncoding];
[client writeData:data withTimeout:-1 tag:0];
}
我们在看看上面发送消息的代码,中的在于"\r\n"的拼接,否则在java端的程序,无法知道你发过来的信息是否结束,当然你也可以使用其他的方式来读取客户端,比如定时;但是我在java端写的server是readLine来判断的,所以需要拼接这个\r\n.