这篇文章,我将仿写第一篇文章中提到的ScrollingActivity,并且说明Behavior的其他回调方法。
1)使用Behavior布局
第一篇文章中,我提到了CoordinatorLayout的三种布局方式,当时留了一个坑,现在来说明如何使用Behavior布局,即如何使ScrollingActivity的NestedScrollView放置在Header之下。
在Behavior的代码中,我们会看到两个非常熟悉的回调
/**
* Called when the parent CoordinatorLayout is about to measure the given child view.
*
* This method can be used to perform custom or modified measurement of a child view
* in place of the default child measurement behavior. The Behavior's implementation
* can delegate to the standard CoordinatorLayout measurement behavior by calling
* {@link CoordinatorLayout#onMeasureChild(android.view.View, int, int, int, int)
* parent.onMeasureChild}.
*
* @param parent the parent CoordinatorLayout
* @param child the child to measure
* @param parentWidthMeasureSpec the width requirements for this view
* @param widthUsed extra space that has been used up by the parent
* horizontally (possibly by other children of the parent)
* @param parentHeightMeasureSpec the height requirements for this view
* @param heightUsed extra space that has been used up by the parent
* vertically (possibly by other children of the parent)
* @return true if the Behavior measured the child view, false if the CoordinatorLayout
* should perform its default measurement
*/
public boolean onMeasureChild(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
return false;
}
还有
/**
* Called when the parent CoordinatorLayout is about the lay out the given child view.
*
* This method can be used to perform custom or modified layout of a child view
* in place of the default child layout behavior. The Behavior's implementation can
* delegate to the standard CoordinatorLayout measurement behavior by calling
* {@link CoordinatorLayout#onLayoutChild(android.view.View, int)
* parent.onLayoutChild}.
*
* If a Behavior implements
* {@link #onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout, android.view.View, android.view.View)}
* to change the position of a view in response to a dependent view changing, it
* should also implement onLayoutChild in such a way that respects those
* dependent views. onLayoutChild will always be called for a dependent view
* after its dependency has been laid out.
*
* @param parent the parent CoordinatorLayout
* @param child child view to lay out
* @param layoutDirection the resolved layout direction for the CoordinatorLayout, such as
* {@link ViewCompat#LAYOUT_DIRECTION_LTR} or
* {@link ViewCompat#LAYOUT_DIRECTION_RTL}.
* @return true if the Behavior performed layout of the child view, false to request
* default layout behavior
*/
public boolean onLayoutChild(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child, int layoutDirection) {
return false;
}
这两个方法会在渲染被动View时被依次调用,那么要使ScrollingView的NestedScrollView置于Header之下,只需覆写onLayoutChild方法即可。
@Override
public boolean onLayoutChild(CoordinatorLayout parent, TextView child, int layoutDirection) {
NestedScrollView dependency = (NestedScrollView) parent.getDependencies(child).get(0);
dependency.layout(0, child.getMeasuredHeight(), parent.getWidth(), child.getMeasuredHeight() + dependency.getMeasuredHeight());
return false;
}
这里,让child置于dependency之下,并且让child的大小为一个屏幕。
我们可以使用CoordinatorLayout #getDependencies来获得child对应的被动View列表
,同样也可以使用CoordinatorLayout #getDependents来获得child对应的主动View列表,由于在这里NestedScrollView只有一个被动View,所以简单粗暴的get(0)即可。
对child进行布局,需要调用child#layout方法对他进行布局。
注意,如果在onLayoutChild方法中我们对child做了布局时,则这个函数应该返回true,否则,当默认使用CoordinatorLayout对其进行布局时,应该返回false。一旦该函数返回true,就必须调用child.layout方法为child进行布局,否则child将不会显示。这个方法只针对child,其他View则不受函数返回值的影响
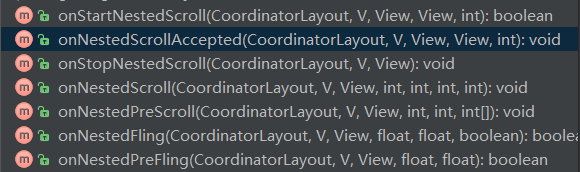
2)Behavior的NestedScrolling 回调
上图中的七个回调,会在发生NestedScrolling的不同时机分别被调用,这点看名字就可以了。
1. onStartNestedScroll
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout,
V child, View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes)
为了使其他的回调生效必须覆写onStartNestedScroll,并在合适情景的时候返回true。
当CoordinatorLayout下有多个Behavior时,每一个onStartNestedScroll方法返回true的Behavior都能接收到NestedScrolling事件。
onStartNestedScroll方法有一个新的参数directTargetChild,它表示产生这次NestedScroll事件的View,*能产生NestedScroll事件的View有NestedScrollView、RecyclerView、以及实现了NestedScrollingChild接口的View。(NestedScrollView、RecyclerView都实现了这个接口)
2. onNestedPreScroll
现在,让onStartNestedScroll直接返回true
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, TextView child, View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
return true;
}
这样代码就能走到onNestedPreScroll这个回调了(默认onStartNestedScroll返回false,则onNestedPreScroll不会被调用)。回想ScrollingActivity的Demo,在Toolbar缩小到最小前,NestedScrollView整体向上平移,但NestedScrollView的内容没有发生滑动;在Toolbar缩小到最小时,NestedScrollView不发生平移,且NestedScrollView的内容开始滚动。这个逻辑就是在onNestedPreScroll这个回调中做的。
/**
* Called when a nested scroll in progress is about to update, before the target has
* consumed any of the scrolled distance.
*
* Any Behavior associated with the direct child of the CoordinatorLayout may elect
* to accept the nested scroll as part of {@link #onStartNestedScroll}. Each Behavior
* that returned true will receive subsequent nested scroll events for that nested scroll.
*
*
* onNestedPreScroll is called each time the nested scroll is updated
* by the nested scrolling child, before the nested scrolling child has consumed the scroll
* distance itself. Each Behavior responding to the nested scroll will receive the
* same values. The CoordinatorLayout will report as consumed the maximum number
* of pixels in either direction that any Behavior responding to the nested scroll reported
* as consumed.
*
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout performing the nested scroll
* @param dx the raw horizontal number of pixels that the user attempted to scroll
* @param dy the raw vertical number of pixels that the user attempted to scroll
* @param consumed out parameter. consumed[0] should be set to the distance of dx that
* was consumed, consumed[1] should be set to the distance of dy that
* was consumed
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedPreScroll(View, int, int, int[])
*/
public void onNestedPreScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
int dx, int dy, int[] consumed) {
// Do nothing
}
对于ScrollingActivity,当NestedScrollView开始滑动时,就产生了NestedScrolling事件(即一个dy,也可以理解为一组dy)。在嵌套滑动的体系下,NestedScrollView在开始让自身滑动dy前,如果其他的View需要从中消耗dy',那么NestedScrollView最终只能让自身的内容滑动dy - dy'
参数中,dy和dx表示的是NestedScrollingChild所产生的原始事件的距离 。target是产生NestedScrolling事件的View,这个例子中指的是NestedScrollView。consumed是一个二维数组,consumed[0]表示child在x方向要消耗的距离,consumed[1]则表示y方向。如果需要消耗一段距离则赋值 consumed[1] = d; 即可。
在我们的ScrollingActivity中的onNestedPreScroll方法,直接让NestedScrollView向上平移
@Override
public void onNestedPreScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, TextView child, View target, int dx, int dy, int[] consumed) {
NestedScrollView dependency = (NestedScrollView) parent.getDependencies(child).get(0);
ViewCompat.offsetTopAndBottom(dependency , -dy);
}
效果如下:
可以看到,在不设置consumed时,不仅NestedScrollView向上平移了,并且它的内容也发生了滚动。
现在让这个Behavior消耗掉所有的dy:
@Override
public void onNestedPreScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, NestedScrollView child, View target, int dx, int dy, int[] consumed) {
NestedScrollView dependency = (NestedScrollView) parent.getDependencies(child).get(0);
ViewCompat.offsetTopAndBottom(dependency , -dy);
consumed[1] = dy;
}
运行的效果符合预期:
继续完善逻辑:
@Override
public void onNestedPreScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, TextView child, View target, int dx, int dy, int[] consumed) {
int topViewMinHeight = DisplayUtilsLite.dp2px(mContext, StaticConfig.TOP_VIEW_MIN_HEIGHT_DP);
int topViewMaxHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
boolean notOnTop;//NestedScrollView没滑动到顶部时
boolean overScrollDownAtTop;//NestedScrollView在顶部,向下滑到底,继续向下滑
boolean overScrollUpAtBottom;//NestedScrollView在底部,向上滑到顶,继续向上滑
NestedScrollView dependency = (NestedScrollView) coordinatorLayout.getDependencies(child).get(0);
notOnTop = (dependency.getTop() > topViewMinHeight);
overScrollDownAtTop = (dependency.getTop() == topViewMinHeight) && (dy < 0) && (dependency.getScrollY() == 0);
overScrollUpAtBottom = (dependency.getTop() == topViewMaxHeight) && (dy > 0) && (dependency.getScrollY() == 0);
if (notOnTop || overScrollDownAtTop || overScrollUpAtBottom){//平移NestedScrollView
if ((dependency.getTop() - dy) < topViewMinHeight){
ViewCompat.offsetTopAndBottom(dependency, -(dependency.getTop() - topViewMinHeight));
}else if((dependency.getTop() - dy) > topViewMaxHeight){
ViewCompat.offsetTopAndBottom(dependency, (topViewMaxHeight - dependency.getTop()));
}else{
ViewCompat.offsetTopAndBottom(dependency, -dy);
}
consumed[1] = dy;
}
}
现在的效果是这样的:
3)onDependentViewChanged,让TextView跟随滑动发生改变
@Override
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, TextView child, View dependency) {
child.setTranslationY(dependency.getTop() - topViewMaxHeight);
return super.onDependentViewChanged(parent, child, dependency);
}
这里就简单的让TextView平移了一下,最终的效果就是这样的了
4)onTouchEvent
在ScrollingActivity Demo中,滑动上面的AppBar和滑动下面的NestedScrollView效果是一样的。这部分的逻辑就是在onTouchEvent里面做的。这个回调就很熟悉了,需要注意的一点是,只有child View上产生的事件才会进入这个方法。
简单写一下相关的代码:
float y;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(CoordinatorLayout parent, TextView child, MotionEvent ev) {
NestedScrollView dependency = (NestedScrollView) parent.getDependencies(child).get(0);
switch (ev.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
y = ev.getRawY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
ViewCompat.offsetTopAndBottom(dependency, (int) (ev.getRawY() - y));
y = ev.getRawY();
break;
}
return true;
}
大概就是这样了,还有一些逻辑就和自定义View时没有任何区别,就没有必要再赘述了。
5)
至此ScrollingActivity就仿完了,倒是不难,就是有点繁琐。