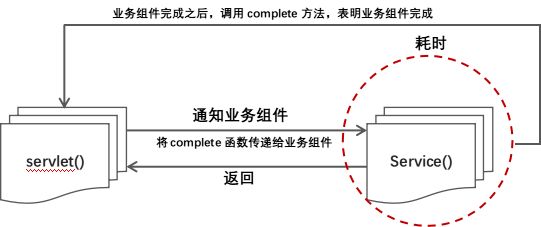
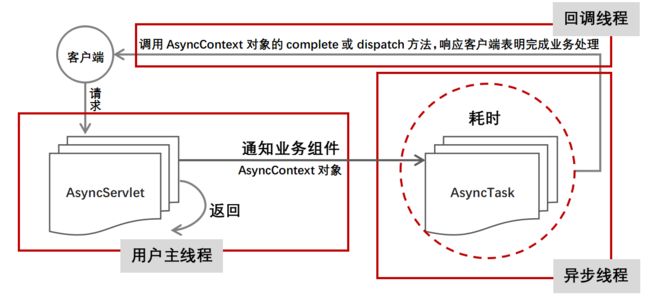
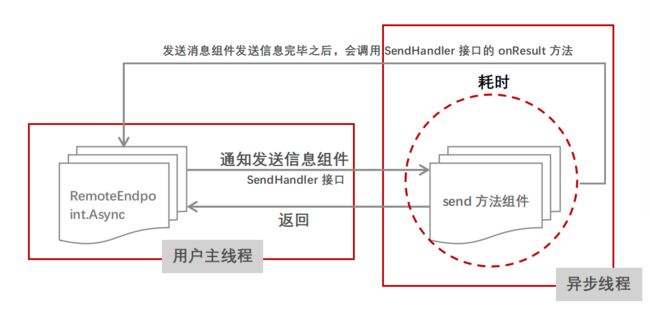
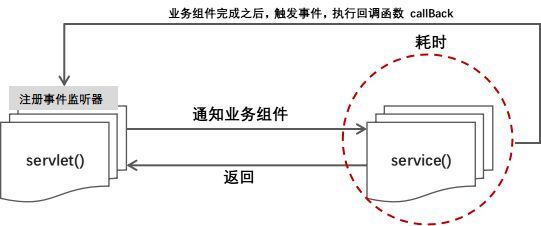
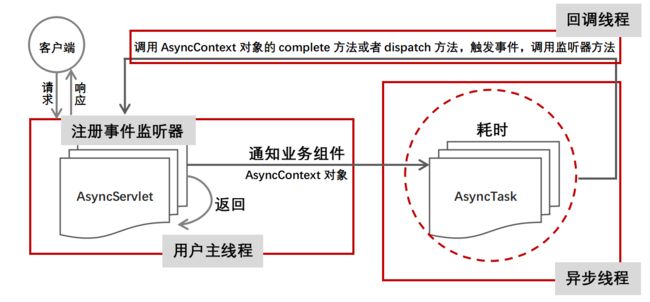
传递回调函数
1、使用Javascript编写
function complete(information){
console.log(information);
}
function servlet(command){
console.log("调用业务组件")
service(command,complete);
}
function service(command,callBack){
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(command);
callBack("业务组件完成调用");
},1000);
}
//用户调用业务处理
servlet("select * from user_table where username = wangbinghua");
Servlet() 作为用户调用的方法,其通知业务组件service(),并不知道业务组件何时调用完毕,因此将complete()回调函数作为参数,调用业务组件。等待业务组件处理完毕业务之后,再次调用complete()函数,表明已经完成业务调用。
2、使用Java编写
在java中无法传递函数,因此将接口作为参数进行传递,从而达到传递函数的目的。
interface CallBack{
//回调函数
public void callBack(String result);
}
用户主线程,调用业务组件。而业务主线程驱动ServletProcess类的invokeService方法,在调用业务组件的同时,开启一条线程来处理业务逻辑。因主线程驱动的ServletProcess类无法得知异步线程何时才能完成业务逻辑处理。所以,将回调函数所在的接口作为参数传递给业务逻辑所处的异步线程。在异步线程完成之后,再次调用callBack方法,表明业务逻辑完成处理。
class ServletProcess implements CallBack{
private ServiceProcess serviceProcess;
public ServletProcess(ServiceProcess serviceProcess){
this.serviceProcess = serviceProcess;
}
public void dealOtherRequest(){
System.out.println("接受其他用户的请求");
}
public void invokeService(final String information){
System.out.println("用户线程开始:" + new Date());
//开启异步线程调用业务处理组件(耗时)
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("异步线程开始");
//调用业务组件
serviceProcess.dealService(information,ServletProcess.this);
}
}).start();
//接受其他用户的请求
this.dealOtherRequest();
System.out.println("用户线程结束:" + new Date());
}
//业务组件完成后,调用该方法
public void callBack(String result) {
System.out.println(result);
}
}
异步线程驱动的业务组件:
class ServiceProcess{
public void dealService(String information,ServletProcess servletProcess){
//处理业务
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("处理业务:" + information);
System.out.println("异步线程结束");
//处理完毕之后,通知ServletProcess组件
servletProcess.callBack("处理数据,渲染页面");
}
}
3、类比Servlet异步处理
如果使用同步处理,那么用户每次请求一次,就需要从线程池中获取一个线程进行处理用户的请求。那么在同步的条件下,都是由这一个线程同时进行请求处理和业务处理。如果业务处理比较耗时,那么线程就会进行阻塞。此时,有更多的用户进行请求,线程池中的线程在极端情况下全部阻塞,那么就无法处理用户的请求。用户必须等待之前的业务处理的完成,很大程度上影响系统的吞吐量。因此提倡采用servlet的异步处理。
servlet通知完耗时业务组件处理业务之后,马上返回到线程池中,而不进行等待。后续的操作由回调函数或者事件监听器完成。这样,接下来更多的用户请求,就会充分利用线程池中的线程。
AsyncServlet异步调用业务组件处理业务逻辑,则其通知AsyncTask异步线程调用业务组件,然后立即返回。与此同时,Web容器线程将AsyncContext对象传递给AsyncTask异步线程。当异步线程处理业务完毕之后,将调用AsyncContext对象的complete方法或者dispach方法,表明业务处理完毕。
@WebServlet(name = "Servlet",urlPatterns = {"/us"},asyncSupported = true)
public class AsyncServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
AsyncContext asyncContext = request.startAsync();
asyncContext.start(new AsyncTask(asyncContext));
}
}
class AsyncTask implements Runnable{
private AsyncContext asyncContext;
public AsyncTask(AsyncContext asyncContext){
this.asyncContext = asyncContext;
}
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("deal some things!");
this.asyncContext.dispatch("/async.jsp");
// this.asyncContext.complete();
}
}
3、类比WebSocket异步处理
**
WebSocket的java服务器端要向客户端发送消息,可能发送这个消息非常耗时,那么此时会造成服务器端程序阻塞,使得服务器端的处理性能急剧下降。因此,可以对消息的发送进行异步处理。即WebSocket对应的Java API中的Async对象向服务器端发送消息时,调用send方法,其只是通知send方法,立即返回。异步线程(使用Future接口)来负责向客户端发送消息,此时容器主线程并不知道什么时候异步线程可以发送消息完毕。因此,在使用异步线程调用send方法的同时,将SendHandler接口传递给异步线程。当异步线程发送消息完毕时,则调用SendHandler接口的onResult方法,表明异步线程已经发送消息完毕,从而让容器主线程感知到。
**
@OnMessage
public void receiveMessage(Session session,String message,@PathParam("loginName") String loginName)
throws IOException {
System.out.println("服务器收到的信息为:" + message);
session.getAsyncRemote().sendText(SendInformationAsync.sendInfo(), new SendHandler() {
//服务器向客户端发送数据完毕之后,则调用SendHandler接口的onResult方法
public void onResult(SendResult result) {
if(result.isOK()){
System.out.println("信息发送完毕");
}
}
});
}
使用监听器
1、使用Javascript编写
用户主线程调用servlet方法,而servlet方法调用业务组件service。此时用注册一个事件的监听器,即事件发生之后,调用callBack方法。用户在servlet方法中调用service方法,立即返回,并不知道service方法中的业务何时处理完成。利用事件监听器,在service方法中的业务处理完成之后,出发刚才注册的事件,即可调用callBack方法。
function servlet(command){
//调用业务组件
console.log("调用业务组件");
service(command);
}
function callBack(){
console.log("渲染页面");
}
function service(command){
//业务组件
setTimeout(function(){
//处理业务
console.log("开始处理业务");
console.log(command);
console.log("处理业务完毕")
//触发事件
$("#event").trigger("click");
},1000);
}
$("#event").on("click",callBack);
servlet("select * from user_table where username = wangbinghua");
2、类比servlet异步处理
在Web容器主线程中,调用业务组件,注册一个异步线程的监听器。该监听器主要监听四个事件,success,timeout,error,startAsync。Web容器的主线程调用业务组件,则开启一个异步线程,立即返回。主线程并不知道异步线程是否已经完成了业务处理。因此,异步线程在完成了业务处理之后,AsyncContext对象调用complete或者dispatch方法,即触发了success事件。触发该事件之后,立即调用监听器的onSuccess方法,表明异步线程已经完成业务处理。
@WebServlet(name = "Servlet",urlPatterns = {"/us"},asyncSupported = true)
public class AsyncServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
final AsyncContext asyncContext = request.startAsync();
//注册事件监听器
asyncContext.addListener(new AsyncListener() {
//异步线程业务处理完成之后,调用该方法
public void onComplete(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException {
try {
asyncContext.getRequest().getRequestDispatcher("/async.jsp").
forward(asyncContext.getRequest(),asyncContext.getResponse());
} catch (ServletException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("异步线程完成");
}
public void onTimeout(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException {
System.out.println("onTimeout");
}
public void onError(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException {
System.out.println("onError");
}
public void onStartAsync(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException {
System.out.println("onStartAsync");
}
});
asyncContext.start(new AsyncTask(asyncContext));
}
}
class AsyncTask implements Runnable{
private AsyncContext asyncContext;
public AsyncTask(AsyncContext asyncContext){
this.asyncContext = asyncContext;
}
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("deal some things!");
// this.asyncContext.dispatch("/async.jsp");
this.asyncContext.complete();
}
}