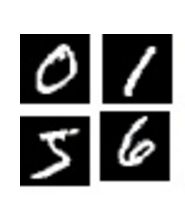转载请注明出处 http://www.jianshu.com/p/75a8eb564de7
在学习了通过构建CNN来识别MNIST之后,我们都大概理解了tensorflow的构建过程,那么怎么才用CNN来识别自己的数据呢?
想想都有意思,那就请认真的看下面的文章
说明:
- 图片数据是通过代码自己生成的不用下载,下面先讲的就是怎么生成图片,生成的时候需要用到 字体文件和cv2库 我在下文中都给出了地址和安装方式。
- 生成了图片之后,训练的时候是image是从文件夹读的,label是从文本读的,如果想改,完全可以按照规则改成自己的数据,不过记得再完成卷积之后的全连接层的时候一定要改按照图片的大小改输入。
- 有什么问题欢迎留言。
解释基本都在代码中,基本都有注释,欢迎留言
完整代码和image样本:如果把data下面的训练图片和测试图片都下载了的话,可以不同再生成图片,可直接训练,再研究如何调用图片即可
https://coding.net/u/centaur/p/Share/git/tree/master/custom_image_tutorials
生成数据
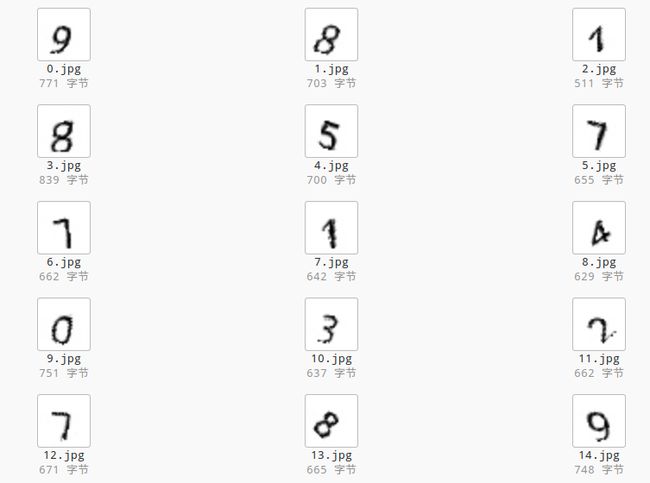
先看一下生成的数据如下图
这里的数据类似于MNSIT的形式,只含有十个数字。
MNIST是手写的数字,这里为了模仿这个效果对图片做了一定的扭曲和旋转
下面做一个对比
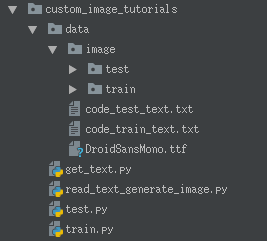
因为文件中多个地方都用到了相对于代码存储位置,这里大家先看一下我的目录结构
- data下面的image分别是测试和训练的样本 路径是
"data/image/train/"和"data/image/train/" - 下面是两个文本 分别是训练和测试的label,文本中
9#8#1#8#5#7#7#1#4#0#3#2#7#8#9#8#5#3#1#8#4#1#1#5#2#7#9#5#2#7#0#1#7......每两个标签之间通过#连接,图片是按照0,1,2...的顺序命名的,这样正好把image和label对应了起来,在训练的时候容易取。 - DroidSansMono.ttf是生成图片中字的字体,可做更改,代码中也要记着更改。
- get_text.py是生成两个label文本的代码,其中可指定生成训练和测试样本的数量
- read_text_generate_image.py是通过读label文本然后生成对应的图片。再生成图片的时候一定要记着把字体放在data/目录下面下载地址
- train.py是训练的代码
生成测试样本和训练样本的label。
生成label的代码比较简单就不做赘述
import random
import os
number = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9']
path_dir = "data/"
# 不存在直接创建
if not os.path.exists(path_dir):
os.makedirs(path_dir)
# 随机的返回一个字符,这里不只限于生成一个字符(后期扩展性)
def random_number_text(char_set=number, code_size=1):
code_text = []
for each in range(code_size):
c = random.choice(char_set)
code_text.append(c)
return code_text
def write_labels(size, name):
code_list = []
for each in range(size):
number_list = random_number_text()
code = ''.join(number_list) # 用引号中的东西去连接list的两个条目
code_list.append(code)
code_text = '#'.join(code_list)
print(code_text)
f = open(path_dir + name, 'w')
f.write(code_text)
f.close()
def main():
# 可指定大小
trian_size = 5000
test_size = 1000
train_label_name = "code_train_text.txt"
test_label_name = "code_test_text.txt"
write_labels(trian_size, train_label_name)
write_labels(test_size, test_label_name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
根据样本生成image
再生成图片的时候一定要记着把字体放在data/目录下面下载地址
有人安装opencv 请用pip install opencv-python这个指令
如果你的电脑是Windows还可能报下面这个错误:
import cv2
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
ImportError: DLL load failed: 找不到指定的模块。
不要惊慌,这是因为opencv需要依赖MSVCP140.dll 这个C++类库,而python 3.5 以上的版本不包括这个类库,你的系统正好是windows 家庭版啥的,也没有这个类库,因此去下载
不要惊慌 解决方案
生成图片需要用到cv2 这个库 记着安装pip install opencv-python
read_text_generate_image.py
import os
import random
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
import numpy as np
import cv2
# 超参数 需要的文件先创建
image_path_train = "data/image/train/"
if not os.path.exists(image_path_train):
os.makedirs(image_path_train)
image_path_test = "data/image/test/"
if not os.path.exists(image_path_test):
os.makedirs(image_path_test)
# 指定字体
DEFAULT_FONTS = "data/DroidSansMono.ttf"
# 生成图片的大小
WIDHT = 28
HEIGHT = 28
# 把label中的内容返回list调用
def get_content_from_file(label_name):
content = open("data/" + label_name, "r", encoding="utf-8")
code_text = content.read()
return code_text.split("#")
# 用opencv 转为灰度 这里需要用到cv2
def convert2gray(img):
if len(img.shape) > 2:
gray = np.mean(img, -1)
# 上面的转法较快,正规转法如下
# r, g, b = img[:,:,0], img[:,:,1], img[:,:,2]
# gray = 0.2989 * r + 0.5870 * g + 0.1140 * b
return gray
else:
return img
# 再目录dir_path下生成 名字为i.jpg 内容为c的图片
def generate_image(i, c, dir_path):
path = dir_path + str(i) + ".jpg"
print(path)
color = (0, 0, 0) # 字体颜色
background = (255, 255, 255) # 背景颜色
print(str(i) + "要存的字符是" + c)
# 创建函数
image = create_image_one_char(c, color, background)
image = convert2gray(np.array(image)) # 转为灰度
cv2.imwrite(path, image)# 用cv2存起来
# 更加内容c 生成扭曲和旋转的image
def create_image_one_char(c, color, background):
# 自定义字体
font = ImageFont.truetype(DEFAULT_FONTS, 30)
im = Image.new('RGBA', (WIDHT, HEIGHT), background)
drawAvatar = ImageDraw.Draw(im)
w, h = im.size
drawAvatar.text((4, -3), c, fill=color, font=font) # 在图片上写下内容
del drawAvatar # 释放对象
# 旋转 整个图片旋转
im = im.crop(im.getbbox())
im = im.rotate(random.uniform(-30, 30), Image.BILINEAR, expand=1)
# 扭曲
# 随机生成 几个坐标 为了得到相对扭曲的四个角的坐标
dx = w * random.uniform(0.1, 0.4)
dy = h * random.uniform(0.2, 0.5)
x1 = int(random.uniform(-dx, dx))
y1 = int(random.uniform(-dy, dy))
x2 = int(random.uniform(-dx, dx))
y2 = int(random.uniform(-dy, dy))
w2 = w + abs(x1) + abs(x2)
h2 = h + abs(y1) + abs(y2)
data = (
x1, y1,
-x1, h2 - y2,
w2 + x2, h2 + y2,
w2 - x2, -y1,
)
im = im.resize((w2, h2))
# 变量data是一个8元组(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3),它包括源四边形的左
# 上,左下,右下和右上四个角。 通过四个角去拉扯一张图片
im = im.transform((WIDHT, HEIGHT), Image.QUAD, data)
image = Image.new('RGB', (WIDHT, HEIGHT), background)
# 把旋转乱了的图片贴在一个正规的图片上
image.paste(im, (0, 0), im)
return image
# 超参数
train_label_name = "code_train_text.txt"
test_label_name = "code_test_text.txt"
# 根据label名和文件夹位置生成图片
def write_image(label_name, dir_path):
code_list = get_content_from_file(label_name)
for each in range(len(code_list)):
generate_image(each, code_list[each], dir_path)
def main():
# 分别处理 训练样本和测试样本
write_image(train_label_name, image_path_train)
write_image(test_label_name, image_path_test)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
CNN训练
转载请注明出处http://www.jianshu.com/p/75a8eb564de7
网络模型
网络模型是一个两层的卷积和池化 加上两个全连接层
def code_cnn():
# 第一个卷积层
W_conv1 = weigth_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = weigth_variable([32])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1) # 28*28*32
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) # 14*14*32
# 第二个卷积层
W_conv2 = weigth_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = weigth_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2) # 14*14*64
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) # 7*7*64
h_pool2 = tf.nn.dropout(h_pool2, keep_prob)
# 三层全连接层
W_fc1 = weigth_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_varibale([1024])
# [n_samples, 7, 7, 64] ->> [n_samples, 7*7*64]
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob) # 防止过度拟合
# 第四层全连接层
W_fc2 = weigth_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_varibale([10])
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
return prediction
取数据训练
既然把数据存成了图片那么就需要把图片读出来转成tensor
1. 把image和label从文件总读出来,都成相应的list方便操作。
# 根据路径得到文本的内容
def getStrContent(path):
return open(path, 'r', encoding="utf-8").read()
# 返回 训练样本路径的list 和 对应的标签用来以后训练
def get_image_path_labels(IMAGE_PATH=IMAGE_PATH, LABEL_PATH=LABEL_PATH, IMAGE_MUMBER=IMAGE_MUMBER):
image_path = IMAGE_PATH
label_path = LABEL_PATH
image_paths = []
for each in range(IMAGE_MUMBER):
image_paths.append(image_path + str(each) + ".jpg")
string = getStrContent(label_path)
labels = string.split("#")
return image_paths, labels
def main():
# 得到训练样本路径list和标签的list
image_paths, labels = get_image_path_labels()
train_code_cnn(image_paths, labels)
2. 数据被放在了对应的list中那么就可对应的取数据,训练数据
我们训练样本生成了5000个测试样本生成了1000个
下面代码中的batch设置为了100 每次把100张图片存成一个tensor.
所以我们需要对5000个数据进行迭代读取。
生成一个batch
# 生成一个训练batch 把batch个image和lebel拼成两个tensor
# 这里的each是一个迭代器 因为有5000个图片每次100个,所以是循环传入的0到49
def get_next_batch(batch_size, each, images, labels):
# image的tensor
batch_x = np.zeros([batch_size, IMAGE_HEIGHT * IMAGE_WIDTH])
# label的tensor
batch_y = np.zeros([batch_size, 10])
def get_text_and_image(i, each):
image_num = each * batch_size + i
label = labels[image_num]
image_path = images[image_num]
captcha_image = Image.open(image_path) #按照路径打开图片
captcha_image = np.array(captcha_image)
return label, captcha_image
# 按照 batch_size迭代
for i in range(batch_size):
text, image = get_text_and_image(i, each)
image = convert2gray(image)#转为灰度
batch_x[i, :] = image.flatten() / 255 # (image.flatten()-128)/128 mean为0
batch_y[i, :] = text2vec(text)
return batch_x, batch_y
训练数据
在训练的时候会进行测试,分别用测试数据集和训练数据集合进行测试
一般来说训练数据要比测试数据好很多,不过我训练了一会发现两个差不多
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
# 每个epoch
for each in range(int(IMAGE_MUMBER / BATCH_SIZE)):
batch_x, batch_y = get_next_batch(BATCH_SIZE, each, image_paths, labels)
_, loss_ = sess.run([train_step, cross_entropy]
, feed_dict={xs: batch_x, ys: batch_y, keep_prob: 0.5})
print("epoch: %d iter: %d/%d loss: %f"
% (epoch + 1, BATCH_SIZE * each, IMAGE_MUMBER, loss_))
# 测试样本计算准确率
# 这里还是按照训练的时候的方法,把image好label分别都成list
# 然后统一转为tensor再通过测试函数进行测试。
test_iamge_path = "data/image/test/"
test_labels_path = "data/code_test_text.txt"
test_image_paths, test_labels = \
get_image_path_labels(test_iamge_path, test_labels_path, 200)
batch_x_test, batch_y_test = \
get_random_batch(BATCH_SIZE, test_image_paths, test_labels,200)
accuracy_test = compute_accuracy(batch_x_test, batch_y_test, sess)
print("测试样本测试 epoch: %d acc: %f" % (epoch + 1, accuracy_test))
# 训练样本计算准确率
batch_x_test, batch_y_test = get_random_batch(BATCH_SIZE, image_paths, labels)
accuracy = compute_accuracy(batch_x_test, batch_y_test, sess)
print("训练样本测试 epoch: %d acc: %f" % (epoch + 1, accuracy))
因为图片比较小,训练起来很快 再28个epoch的时候训练数据能达到100%,训练数据能达到99%
epoch: 28 iter: 4300/5000 loss: 0.070238
epoch: 28 iter: 4400/5000 loss: 0.039228
epoch: 28 iter: 4500/5000 loss: 0.039181
epoch: 28 iter: 4600/5000 loss: 0.048799
epoch: 28 iter: 4700/5000 loss: 0.165373
epoch: 28 iter: 4800/5000 loss: 0.040288
epoch: 28 iter: 4900/5000 loss: 0.061203
测试样本 epoch: 28 acc: 0.990000
训练样本 epoch: 28 acc: 1.000000
转载请注明出处http://www.jianshu.com/p/75a8eb564de7
到这里算是介绍完了,我把完整的代码贴在下面
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import random
IMAGE_MUMBER = 5000
EPOCH = 200
BATCH_SIZE = 100
IMAGE_PATH = "data/image/train/"
LABEL_PATH = "data/code_train_text.txt"
# 计算weight
def weigth_variable(shape):
# stddev : 正态分布的标准差
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) # 截断正态分布
return tf.Variable(initial)
# 计算biases
def bias_varibale(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
# 计算卷积
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# 定义池化
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
IMAGE_HEIGHT = 28
IMAGE_WIDTH = 28
CHAR_SET_LEN = 10
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, IMAGE_HEIGHT * IMAGE_WIDTH])
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # 防止过拟合
x_image = tf.reshape(xs, [-1, IMAGE_HEIGHT, IMAGE_WIDTH, 1])
# 训练网络
def code_cnn():
# 第一个卷积层
W_conv1 = weigth_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = weigth_variable([32])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1) # 28*28*32
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) # 14*14*32
# 第二个卷积层
W_conv2 = weigth_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = weigth_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2) # 14*14*64
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) # 7*7*64
h_pool2 = tf.nn.dropout(h_pool2, keep_prob)
# 三层全连接层
W_fc1 = weigth_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_varibale([1024])
# [n_samples, 7, 7, 64] ->> [n_samples, 7*7*64]
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob) # 防止过度拟合
# 第四层全连接层
W_fc2 = weigth_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_varibale([10])
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
return prediction
def convert2gray(img):
if len(img.shape) > 2:
gray = np.mean(img, -1)
# 上面的转法较快,正规转法如下
# r, g, b = img[:,:,0], img[:,:,1], img[:,:,2]
# gray = 0.2989 * r + 0.5870 * g + 0.1140 * b
return gray
else:
return img
# 文本转向量
def text2vec(text):
text_len = len(text)
vector = np.zeros(1 * CHAR_SET_LEN)
def char2pos(c):
if c == '_':
k = 62
return k
k = ord(c) - 48
if k > 9:
k = ord(c) - 55
if k > 35:
k = ord(c) - 61
if k > 61:
raise ValueError('No Map')
return k
for i, c in enumerate(text):
idx = i * CHAR_SET_LEN + char2pos(c)
vector[idx] = 1
return vector
# 向量转回文本
def vec2text(vec):
char_pos = vec.nonzero()[0]
text = []
for i, c in enumerate(char_pos):
char_at_pos = i # c/63
char_idx = c % CHAR_SET_LEN
if char_idx < 10:
char_code = char_idx + ord('0')
elif char_idx < 36:
char_code = char_idx - 10 + ord('A')
elif char_idx < 62:
char_code = char_idx - 36 + ord('a')
elif char_idx == 62:
char_code = ord('_')
else:
raise ValueError('error')
text.append(chr(char_code))
return "".join(text)
# 生成一个训练batch
def get_next_batch(batch_size, each, images, labels):
batch_x = np.zeros([batch_size, IMAGE_HEIGHT * IMAGE_WIDTH])
batch_y = np.zeros([batch_size, 10])
def get_text_and_image(i, each):
image_num = each * batch_size + i
label = labels[image_num]
image_path = images[image_num]
captcha_image = Image.open(image_path)
captcha_image = np.array(captcha_image)
return label, captcha_image
for i in range(batch_size):
text, image = get_text_and_image(i, each)
image = convert2gray(image)
batch_x[i, :] = image.flatten() / 255 # (image.flatten()-128)/128 mean为0
batch_y[i, :] = text2vec(text)
return batch_x, batch_y
# 随机生成一个训练batch
def get_random_batch(batch_size, images, labels,IMAGE_MUMBER = IMAGE_MUMBER):
batch_x = np.zeros([batch_size, IMAGE_HEIGHT * IMAGE_WIDTH])
batch_y = np.zeros([batch_size, 1 * CHAR_SET_LEN])
def get_captcha_text_and_image(i):
image_num = i
label = labels[image_num]
image_path = images[image_num]
captcha_image = Image.open(image_path)
captcha_image = np.array(captcha_image)
return label, captcha_image
for i in range(batch_size):
text, image = get_captcha_text_and_image(random.randint(0, IMAGE_MUMBER - 1))
image = convert2gray(image)
batch_x[i, :] = image.flatten() / 255 # (image.flatten()-128)/128 mean为0
batch_y[i, :] = text2vec(text)
return batch_x, batch_y
# 计算准确率
def compute_accuracy(v_xs, v_ys, sess): # 传入测试样本和对应的label
global prediction
y_pre = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: v_xs, keep_prob: 1})
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_pre, 1), tf.argmax(v_ys, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
result = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={xs: v_xs, ys: v_ys, keep_prob: 1})
return result
prediction = code_cnn()
def train_code_cnn(image_paths, labels):
# 定义网络
global prediction
# 计算loss cross_entropy
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(ys * tf.log(prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
sess = tf.Session()
# 初始化variable
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
# 每个epoch
for each in range(int(IMAGE_MUMBER / BATCH_SIZE)):
batch_x, batch_y = get_next_batch(BATCH_SIZE, each, image_paths, labels)
_, loss_ = sess.run([train_step, cross_entropy]
, feed_dict={xs: batch_x, ys: batch_y, keep_prob: 0.5})
print("epoch: %d iter: %d/%d loss: %f"
% (epoch + 1, BATCH_SIZE * each, IMAGE_MUMBER, loss_))
# 训练样本测试准确率
test_iamge_path = "data/image/test/"
test_labels_path = "data/code_test_text.txt"
test_image_paths, test_labels = \
get_image_path_labels(test_iamge_path, test_labels_path, 200)
batch_x_test, batch_y_test = \
get_random_batch(BATCH_SIZE, test_image_paths, test_labels,200)
accuracy_test = compute_accuracy(batch_x_test, batch_y_test, sess)
print("测试样本测试 epoch: %d acc: %f" % (epoch + 1, accuracy_test))
batch_x_test, batch_y_test = get_random_batch(BATCH_SIZE, image_paths, labels)
accuracy = compute_accuracy(batch_x_test, batch_y_test, sess)
print("训练样本测试 epoch: %d acc: %f" % (epoch + 1, accuracy))
# 根据路径得到文本的内容
def getStrContent(path):
return open(path, 'r', encoding="utf-8").read()
# 返回 训练样本路径的list 和 对应的标签用来以后训练
def get_image_path_labels(IMAGE_PATH=IMAGE_PATH, LABEL_PATH=LABEL_PATH, IMAGE_MUMBER=IMAGE_MUMBER):
image_path = IMAGE_PATH
label_path = LABEL_PATH
image_paths = []
for each in range(IMAGE_MUMBER):
image_paths.append(image_path + str(each) + ".jpg")
string = getStrContent(label_path)
labels = string.split("#")
return image_paths, labels
def main():
# 得到训练样本路径list和标签的list
image_paths, labels = get_image_path_labels()
train_code_cnn(image_paths, labels)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()